Mathematics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Edexcel AS Level Maths Statistics Questions and Answers Already Passed (All)
Edexcel AS Level Maths Statistics Questions and Answers Already Passed
Document Content and Description Below
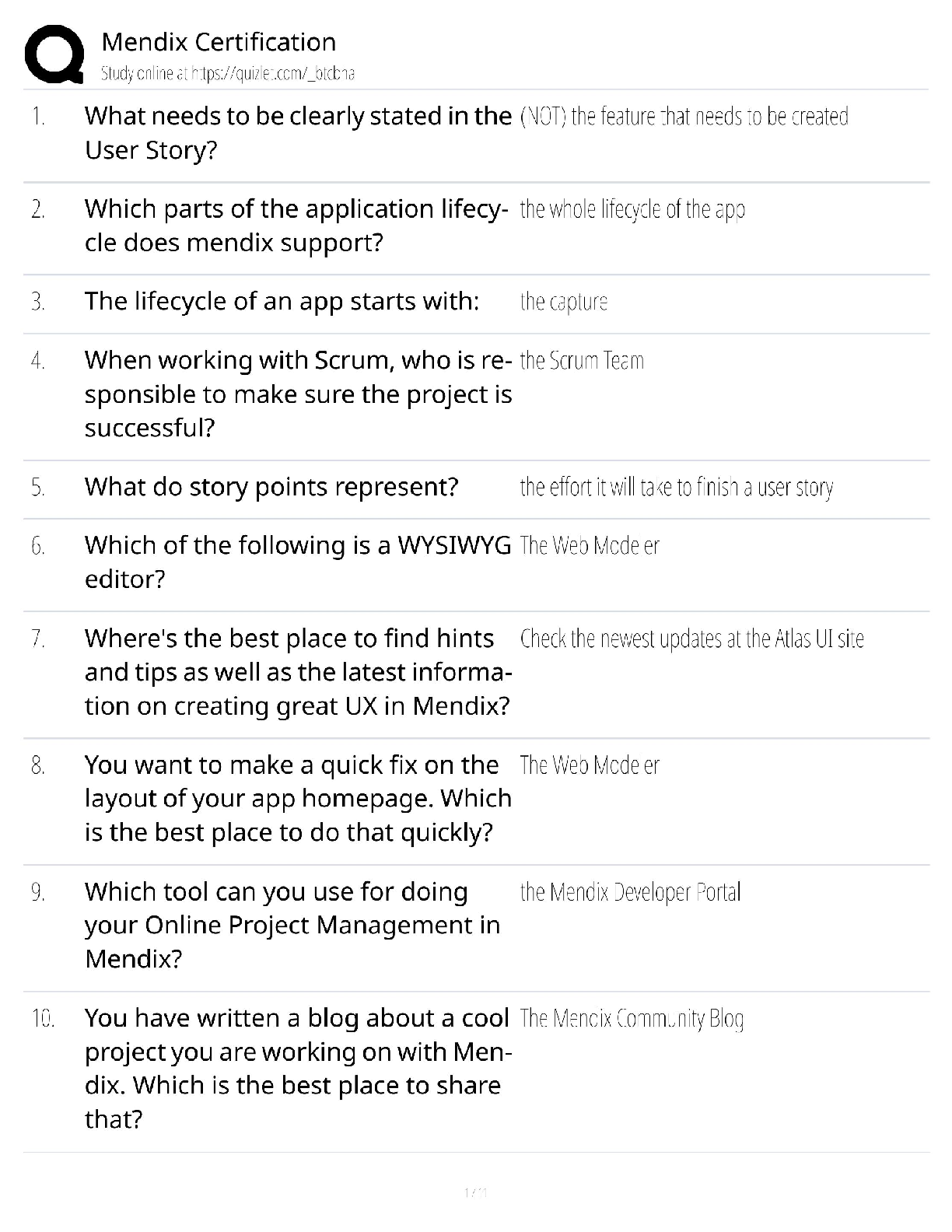
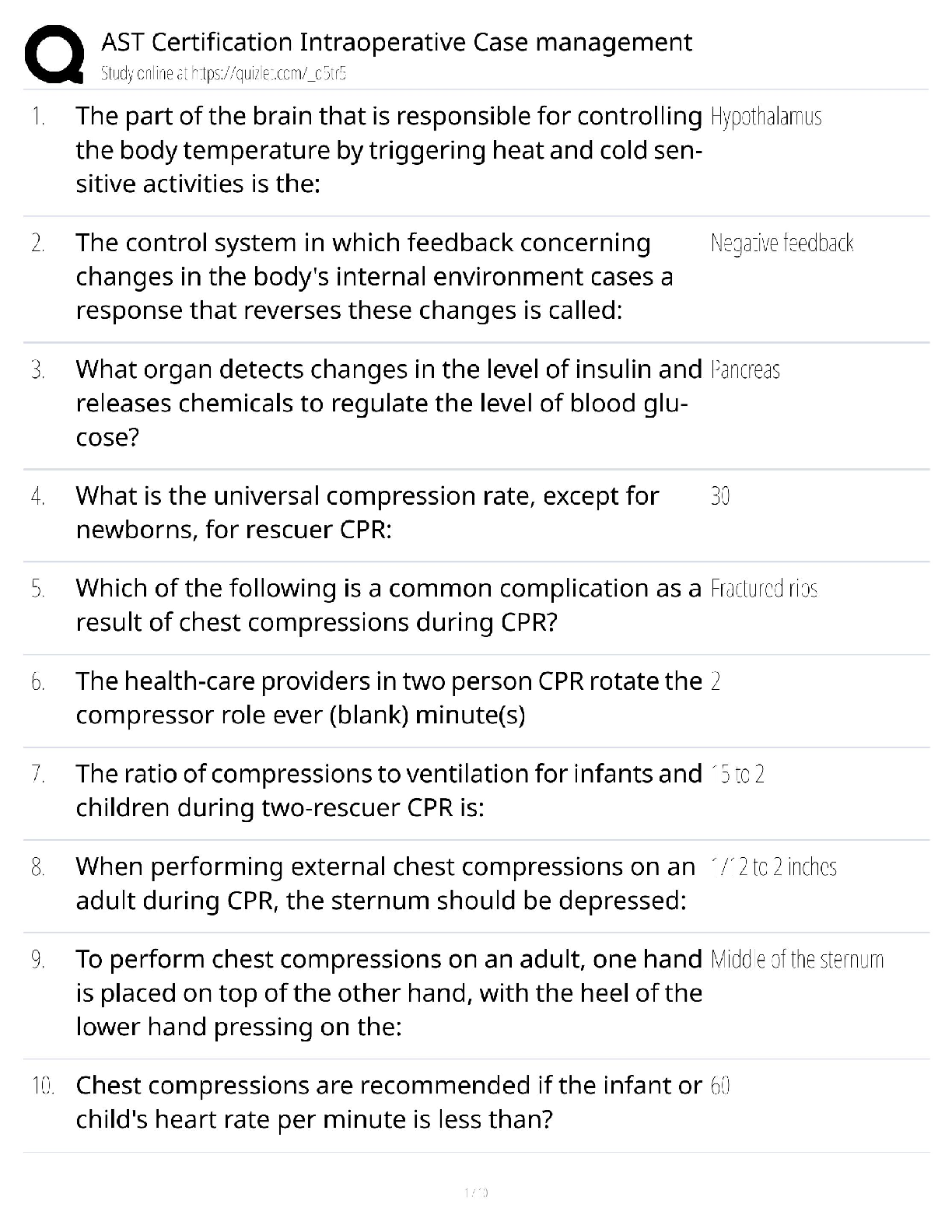
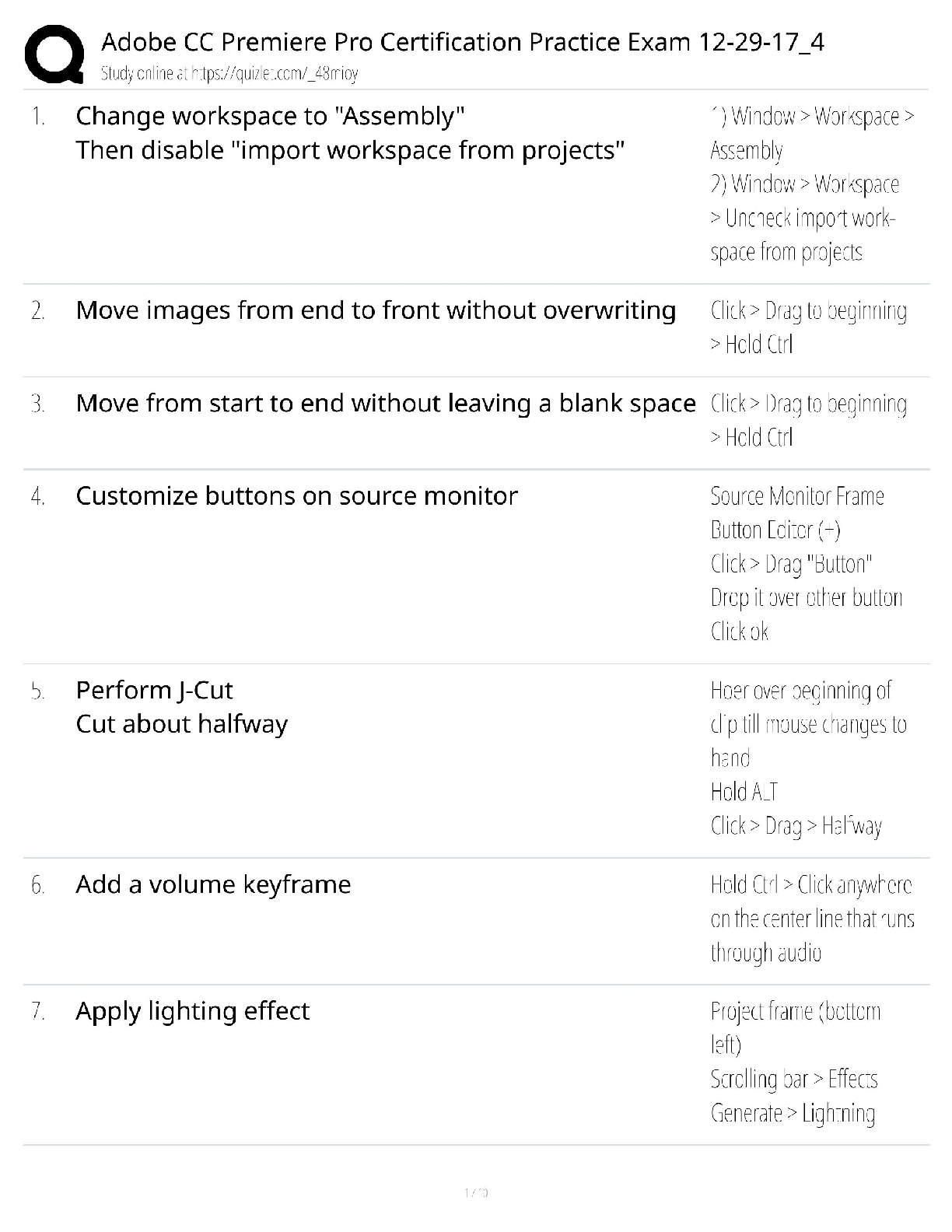
Edexcel AS Level Maths Statistics Questions and Answers Already Passed Population ✔✔The whole set of items that are of interest Census ✔✔Observes or measures every member of a population A ... dvantages of a census ✔✔It should give a completely accurate result Disadvantage of a census ✔✔Time consuming and expensive Hard to process large quantity of data Sample ✔✔A selection of observations taken from a subset of the population which is used to find out information about the population as a whole Advantages of a sample ✔✔Less time consuming Fewer people have to respond Less data than a census Disadvantage of a sample ✔✔The data may not be as accurate The data may not be large enough toggle information about the population Sampling Units ✔✔Individual units of a population Sampling Frame ✔✔A list of individually named or numbered sampling units Simple Random Sample ✔✔A sample where every sampling unit has an equal chance of being chosen Advantages of Simple Random Sample ✔✔Free of bias Easy and cheap to implement Each sampling unit has equal chance of selection Disadvantage of Simple Random Sample ✔✔A sampling frame is needed Not suitable when the population size is very big Systematic Sampling ✔✔A method of sampling where the required elements are chosen at regular intervals from an ordered list Advantages of Systematic Sampling ✔✔Simple and quick to use Suitable for large samples Disadvantages of Systematic Sampling ✔✔A sampling frame is needed It can introduce bias if sampling frame is not random Disadvantages of Stratified Sampling ✔✔Sample accuracy reflects the population structure guarantees proportional representation of groups within a population Advantages of Stratified Sampling ✔✔Population must clearly classified into distinct strata Stratified Sampling ✔✔A method of sampling where the population is divided into mutually exclusive strata and a random sample is taken from each Stratum equation ✔✔(Number in stratum/number in population)* overall sample size Quota Sampling ✔✔A method of sampling where a researcher selects a sample that reflects the characteristics of the whole population Advantages of Quota Sampling ✔✔Allows a small sample to still represent the whole population No sampling frame required Quick, easy and inexpensive Allows for easy comparison between different groups in the population Disadvantages of Quota Sampling ✔✔Not random sampling can produce bias Population must be divided into groups which can be costly or inaccurate Non-responces are recorded as such Opportunity Sampling ✔✔A method of sampling where the people sampled are those who are available at the time the study is carried out and who fit the criteria you are looking for Advantages of Opportunity Sampling ✔✔Easy to carry out Inexpensive Disadvantages of Opportunity Sampling ✔✔Unlikely to provide a representative sample Highly dependent on individual researcher Quantitative Variables/Data ✔✔Variables or data associated with numerical observations Qualitative Variables/Data ✔✔Variables or data associated with non-numerical observations Continuous Variable ✔✔A variable that can take any value in a given range Discrete Variable ✔✔A variable that can take only specific values in a given range Class Boundaries ✔✔The maximum and minimum values that belong in each class Midpoint ✔✔The average of the class boundaries Class Width ✔✔The difference between the upper and lower class boundaries Interpercentile range ✔✔The difference between the values for 2 given percentiles. Cleaning the data ✔✔The process of removing anomalies from a data set. bivariate data ✔✔Data which has pairs of values for two variables Correlation ✔✔A measure of the linear relationship between two variables regression line ✔✔a line of best fit, y = a+bx mutually exclusive events ✔✔events that have no sample points in common , P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) independent events ✔✔The outcome of one event does not affect the outcome of the second event , P(A and B) = P(A) x P(B) tree diagram ✔✔A diagram used to show the total number of possible outcomes probability distribution ✔✔Describes the probability of any outcome in the sample space. binomial distribution ✔✔When there are a fixed number of trials There are 2 possible outcomes (success or failure) There is a fixed probability of success The trials are independent of each other the null hypothesis ✔✔The hypothesis you assume to be correct alternative hypothesis ✔✔Tells us about the parameter if your assumption is wrong critical region ✔✔the area in the tails of the comparison distribution in which the null hypothesis can be rejected mutually exclusive ✔✔Events have no outcomes in common, they can't happen at the same time independent ✔✔When one event has no effect on another [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 7 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

EXCEL BUNDLED EXAMS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS (2022/2023) WITH VERIFIED SOLUTIONS
EXCEL BUNDLED EXAMS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS (2022/2023) WITH VERIFIED SOLUTIONS
By Nutmegs 2 years ago
$30
29
Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 13, 2023
Number of pages
7
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 13, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
224




.png)