*NURSING > EXAM > AGNP BOARD EXAM QUESTIONS and ANSWERS ; Prescription (82 Questions and Answers) (All)
AGNP BOARD EXAM QUESTIONS and ANSWERS ; Prescription (82 Questions and Answers)
Document Content and Description Below
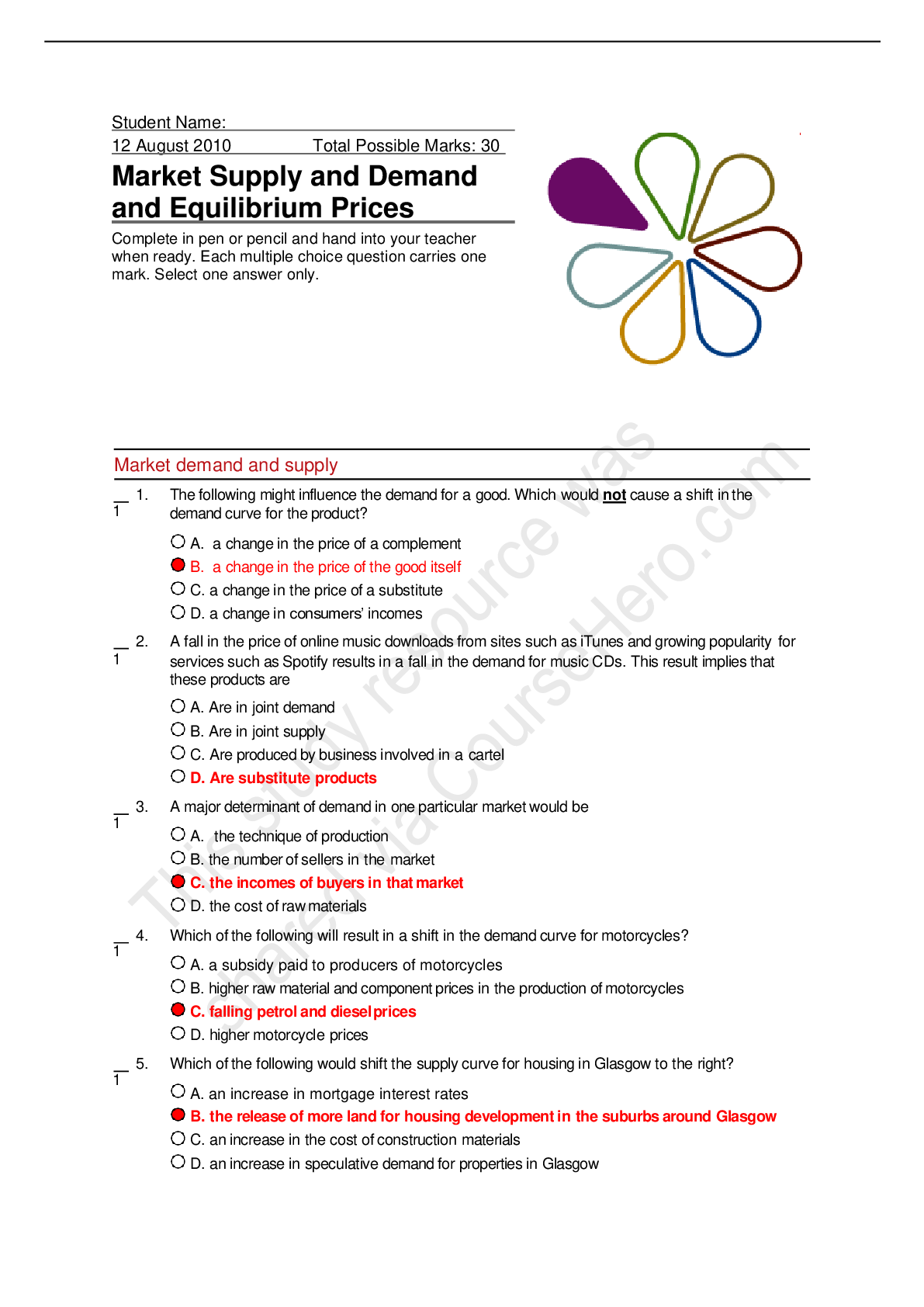
AGNP BOARD EXAM QUESTIONS and ANSWERS ; Prescription (82 Questions and Answers) Question: Which of the following is NOT recommended as an alternative treatment for bacterial vaginosis? Intramusc ... ular ceftriaxone (Rocephin) Correct Clindamycin (Cleocin) vaginal cream Metronidazole (Flagyl) vaginal cream Tinidazole (Tindamax) orally Explanation: Intramuscular ceftriaxone (Rocephin) is not indicated in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Metronidazole (Flagyl) vaginal cream may be used if metronidazole oral is ineffective or not well tolerated. Alternative regimens include several tinidazole regimens or clindamycin (oral or intravaginal). Question: The recommended empiric treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease is: penicillin G benzathine (Bicillin) intramuscularly plus ceftriaxone (Rocephin) intramuscularly. azithromycin (Zithromax) orally plus ceftriaxone (Rocephin) intramuscularly. ceftriaxone (Rocephin) intramuscularly plus doxycycline (Vibramycin). Correct metronidazole (Flagyl) plus ofloxacin (Floxin). Explanation: The recommended empiric treatment for mild to moderate symptoms of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is ceftriaxone (Rocephin) 250 mg intramuscularly plus doxycycline (Vibramycin) 100 mg twice daily x 14 days with or without metronidazole (Flagyl) 500 mg PO twice daily x 14 days. All regimens used to treat PID should also be effective against Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis because negative endocervical screening for these organisms does not rule out upper-reproductive tract infection. Question: For the treatment of chlamydia, azithromycin (Zithromax) should be given: as one-time dose. Correct daily for 3 days. daily for 5 days. daily for 7 days. Explanation: For the treatment of chlamydia, azithromycin (Zithromax) should be given as a single dose, 1 gram orally. Azithromycin (Zithromax) is classified as a macrolide. It is active against most isolates of Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Question: Clindamycin (Cleocin) to treat bacterial vaginosis should NOT be used in combination with: atorvastatin. prednisone. estradiol. Correct ibuprofen. Explanation: Clindamycin (Cleocin) may decrease hormonal contraceptive efficacy and should not be coadministered with estradiol. The other choices are not known to cause drug-drug interactions when administered with clindamycin. Question: When treating latent syphilis, treatment outcomes do NOT include the prevention of: asymptomatic progression of the disease. neurosyphilis. sexual transmission. Correct transfer to a fetus in pregnancy. Explanation: Because latent syphilis is not transmitted sexually, the objective of treating patients in this stage of disease is to prevent complications (neurosyphilis and progression of disease) and transmission from a pregnant woman to her fetus. Question: The most commonly reported side effects of azithromycin (Zithromax) for treatment of chlamydia are: alopecia and headache. blurred vision and tinnitus. diarrhea and nausea. Correct dry mouth and tachycardia. Explanation: The most common treatment-related side effects of azithromycin (Zithromax) are related to the gastrointestinal system with diarrhea/loose stools, nausea, and abdominal pain. Most of the adverse reactions leading to discontinuation were related to the gastrointestinal tract. Potentially serious adverse reactions of angioedema and cholestatic jaundice have been reported. Question: The most common reason for persistent gonococcal infections is: inappropriate prescribing of the correct treatment regimen. treatment failure due to high resistance rates. failure of the patient to abstain from unprotected sexual intercourse. Correct lack of test-of-cure and follow-up after treatment. Explanation: A high prevalence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection has been observed among men and women previously treated for gonorrhea. Rather than signaling treatment failure, most of these infections result from reinfection caused by failure of sex partners to receive treatment or the initiation of sexual activity with a new infected partner. This indicates a need for improved patient education and treatment of sex partners. If the patient’s last potential sexual exposure was >60 days before onset of symptoms or diagnosis, the most recent sex partner should be treated. To avoid reinfection, sex partners should be instructed to abstain from unprotected sexual intercourse for 7 days after they and their sexual partner(s) have completed treatment and after resolution of symptoms. Question: The recommended treatment for chlamydia infection when azithromycin (Zithromax) or doxycycline (Doryx) is contraindicated is: clindamycin (Cleocin). erythromycin (Ery-Tab). Correct metronidazole (Flagyl). tetracycline (Sumycin). Explanation: First-line therapies for the treatment of chlamydia infection include azithromycin (Zithromax) or doxycycline (Doryx). Alternative therapies include levofloxacin (Levaquin), erythromycin base, erythromycin ethylsuccinate, or ofloxacin (Floxin). Question: An alternative intramuscular medication for ceftriaxone (Rocephin) in the treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease is: cefoxitin. Correct penicillin G benzathine (Bicillin). gentamicin. streptomycin. Explanation: Cefoxitin, a second-generation cephalosporin, has better anaerobic coverage than ceftriaxone (Rocephin), and in combination with probenecid and doxycycline is effective in achieving short-term clinical response in women with pelvic inflammatory disease. Ceftriaxone has better coverage against Neisseria gonorrhoeae. The addition of metronidazole (Flagyl) will also effectively treat bacterial vaginosis, which is frequently associated with PID. Question: The generic name for Flagyl is: fluconazole. methazolamide. metronidazole. Correct tinidazole. Explanation: The generic name for Flagyl is metronidazole. Flagyl is classified as a nitroimidazole. In addition to the treatment of bacterial vaginosis, it is used in the treatment of parasite infections, Clostridium difficile, and Helicobacter pylori. The brand name for fluconazole is Diflucan (an antifungal); methazolamide is Neptazane (a diuretic); tinidazole is Tindamax (an antiparasitic, antibacterial). ............continued [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 25 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

AGNP BOARD EXAMS (23 Different Versions) ; Questions and Answers
AGNP BOARD EXAMS (23 Different Versions) ; Questions and Answers
By YourTutor 4 years ago
$95.5
23
Reviews( 0 )
$18.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 01, 2021
Number of pages
25
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 01, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
102