Crossfit Level 2 Latest Updated 2023
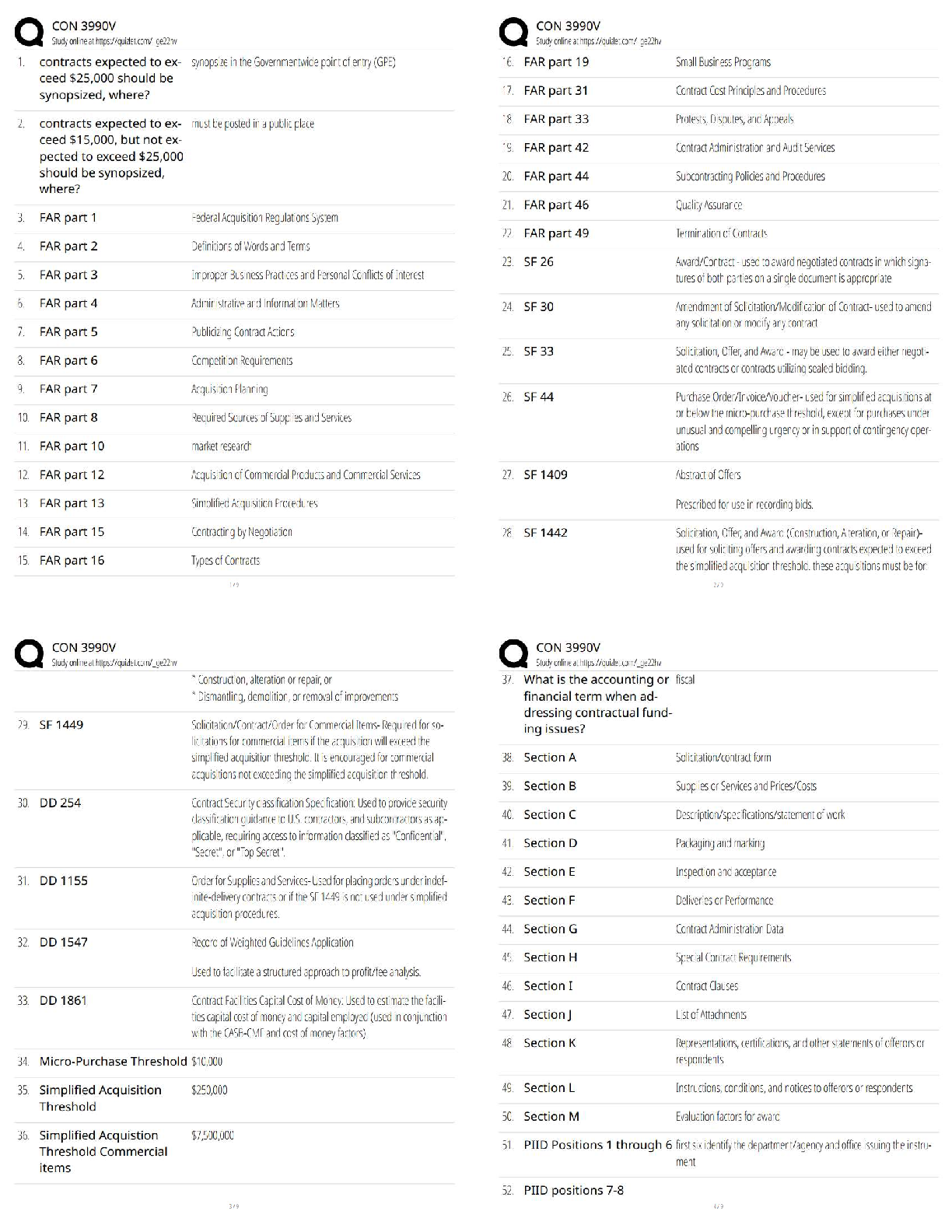
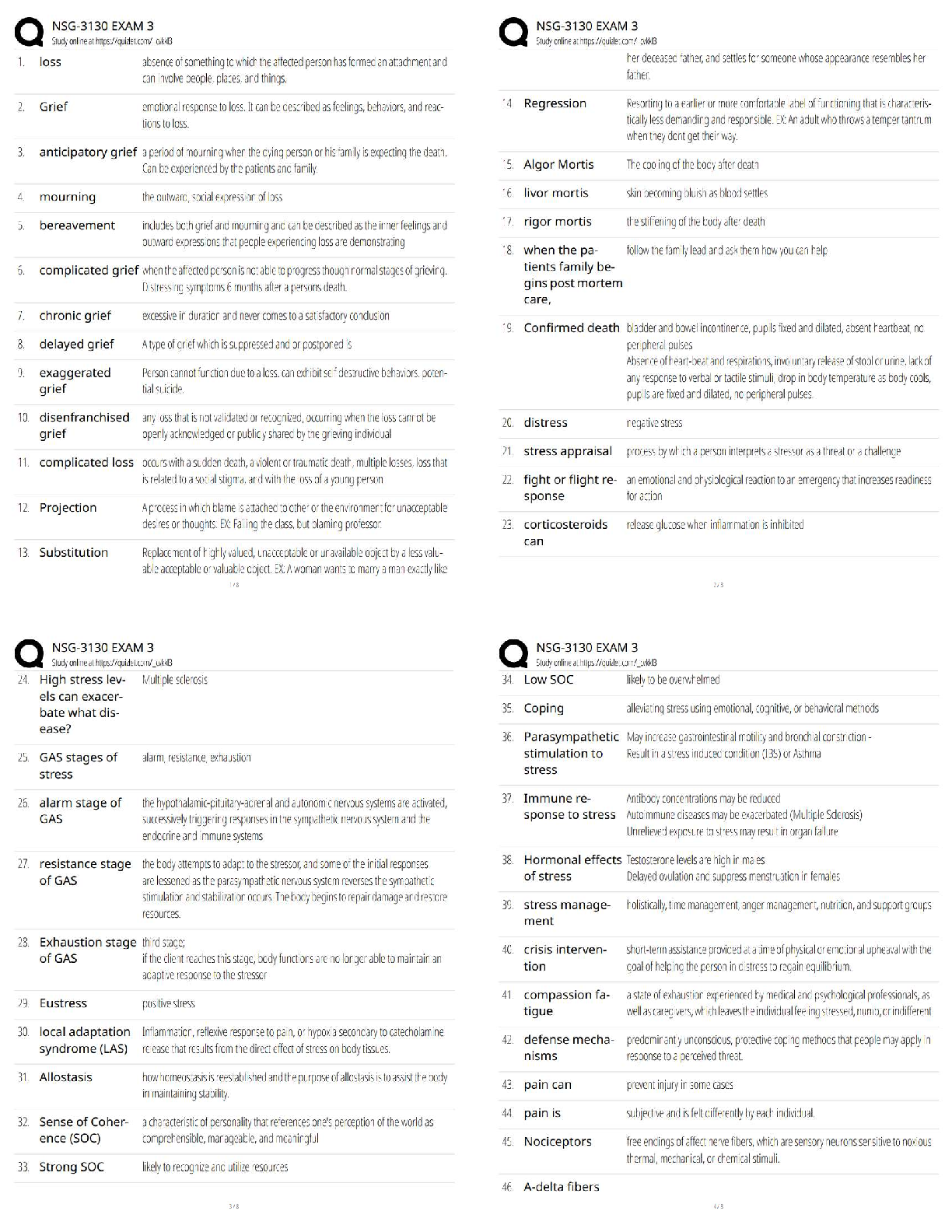
Already Graded A
Push Press Progressions ✔✔dip & hold, dip & drive slow, dip & drive fast, push press
Push Jerk Progressions ✔✔jump & land (hands at sides), jump & land (hands at s
...
Crossfit Level 2 Latest Updated 2023
Already Graded A
Push Press Progressions ✔✔dip & hold, dip & drive slow, dip & drive fast, push press
Push Jerk Progressions ✔✔jump & land (hands at sides), jump & land (hands at shoulders),
jump & extend arms after hips extend, push jerk
Sumo DL High Pull Progressions ✔✔Sumo DL, Sumo DL shrug slow, sumo DL shrug fast,
SDHP
Med Ball Clean Progressions ✔✔DL, DL shrug fast, FS, Pull Under, med ball clean
Trainer's ability to coach others (based on 6 areas) ✔✔teaching, seeing, correcting, group
management, presence & attitude, demonstration
Teaching ✔✔the ability to effectively articulate & instruct the mechanics of each movement
Seeing ✔✔The ability to discern good from poor movement mechanics and identify both gross
and subtle faults whether athlete is in motion or static
Static Faults ✔✔faults that occur near end ranges of motion- starting, receiving, or finishingDynamic Faults ✔✔athlete moving btw the static positions- ex. not reaching full hip extension in
drive of the clean, push early in push press, initiating squat with knees
Profile view ✔✔most useful view to watch an athlete
Correcting ✔✔the ability to facilitate better mechanics using visual, verbal, and/or tactile cues
Ability to correct depends on (4 things) ✔✔use successful cues, know multiple corrections for
each fault, triage faulty movement, balance critique w/ praise
Function of a cue ✔✔to help athlete execute perfect mechanics, NOT to perfectly describe the
mechanics of the movement
Qualities of a good cue ✔✔short, specific, actionable
3 steps to developing a good cue ✔✔1. identify fault 2. identify what is out of place 3. give
direction to that body part
Verbal cue ✔✔tell specific instruction
Visual cue ✔✔create contrasting images btw current & desired positioning
Tactile cure ✔✔use physical targets to achieve proper mechanics
Triaging faults ✔✔assigning urgency to faults, ordering based on severity of deviation from
ideal & athlete's capacity relative to the task
Group management ✔✔ability to organize and manage both at a micro level (class) and macro
level (gym); managing time well, organization of space, equipment and participants, adhere to
schedule etc.
Presence & attitude ✔✔ability to create a positive and engaging learning environment
Demonstration ✔✔the ability to provide athletes w/ an accurate visual example
Common movement themes for functional movements ✔✔midline stabilization, core to
extremity movement, balance about the frontal plane, posterior chain engagement, sound hip
function, active shoulders, full ROM about a joint, effective stance or grip
Midline ✔✔relationship of the spine and pelvis during functional movement
midline stabilization ✔✔athlete's capacity to prevent movement from this neutral spinal position;
synonymous w/ core strength
Creates midline stabilization ✔✔engagement of abs, internal & external obliques, and spinal
errectors
Deviations from neutral spine ✔✔Flexion, extension
Most risky deviation from neutral/ midline stabilization ✔✔loss of neutral spine during
movement
Core to Extremity movements ✔✔a sequence of muscular contraction beginning w/ large force
producing, low velocity muscles of the core and hips and ends w/ small force producing, high
velocity muscles of the extremities
Muscles more likely of injury ✔✔smaller muscle groups and tendons/ligaments
Balance about the frontal plane ✔✔athletes movements accommodate the object and may or may
not be characterized by straight lines; frontal plane divides athlete into anterior/posterior halves
(bisects athlete at mid foot
Posterior chain ✔✔hamstrings, glutes, spinal errectors
Posterior chain engagement ✔✔balance of pressure btw balls of feet and heels; creates increased
power generation, helps keep knees in line w/ toes, promoted midline stabilization and balance
about frontal plane
Sound hip function ✔✔athletes ability to flex & extend hip to maximize contribution to
movement
Major safety issues w/ slow or incomplete hip extension ✔✔none
Poor hip function ✔✔muted hip, lack of hip extension, slow hip extension
muted hip ✔✔never closes/flexes; permanently open hip
Active shoulders ✔✔scapular position & stabilization, applying force in direction opposite the
load
Full ROM about a joint ✔✔allows greater compliment of musculature to be used, preserves joint
health, flexibility and strength
Effective stance/ grip ✔✔hand & foot position during a movement
When to use narrow stance ✔✔DL, presses, & oly lifts
When to use wider stance ✔✔squatting
major safety concerns from lack of effective stance/grip ✔✔none
Assessing safety & performance/ risk ✔✔athletic capacity, loading, positioning, assigned tasks
Variance ✔✔intended variation of functional movement, loads, rep schemes, and time durations
methods of scaling ✔✔movement functions, loading paramenters, time frame, rep volume
Populations in need of scaling ✔✔beginners, intermediate, advanced, injured athletes
Common programming pitfalls ✔✔lack of regular assessment, incorrectly applied variance, lack
of higher skill development, excessive volume, thinking CF Games is standard
Examples of variance not applied correctly ✔✔hopper, biasing, never repeating workouts, too
much accessory work
Components of class ✔✔warm-up, workout, cool down
General Warm up ✔✔increase core temp and blood flow to muscles
Specific Warm-up ✔✔build and refine proper mechanics, prep mentally & physically
Heavy days ✔✔necessary, should be programmed once a week or once every 2 cycles
Working reps of heavy sets ✔✔> 80% 1rm; 7-25 working reps
[Show More]
.png)

.png)