Medicine > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NASM CPT -7th Edition Questions and Answers 100% Pass (All)
NASM CPT -7th Edition Questions and Answers 100% Pass
Document Content and Description Below
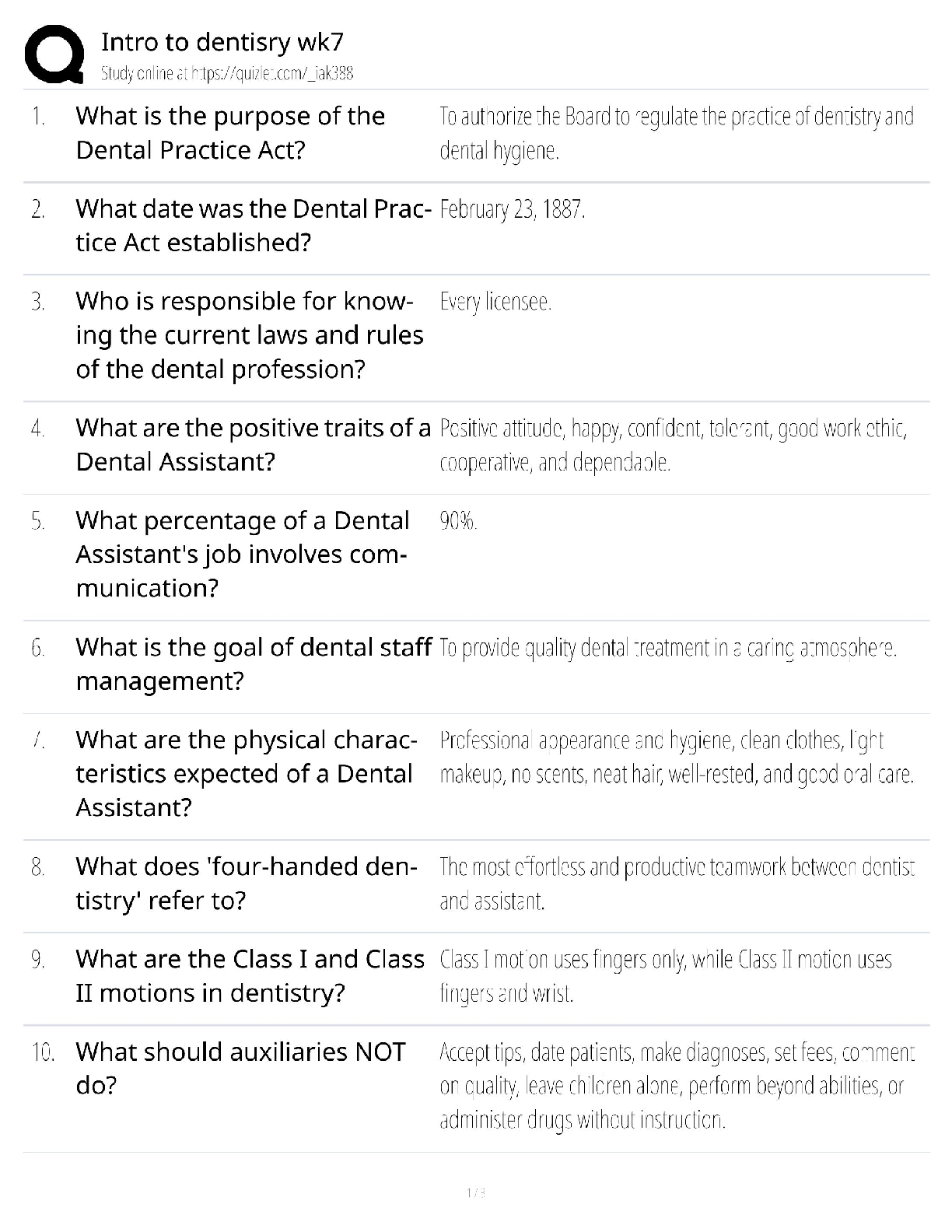
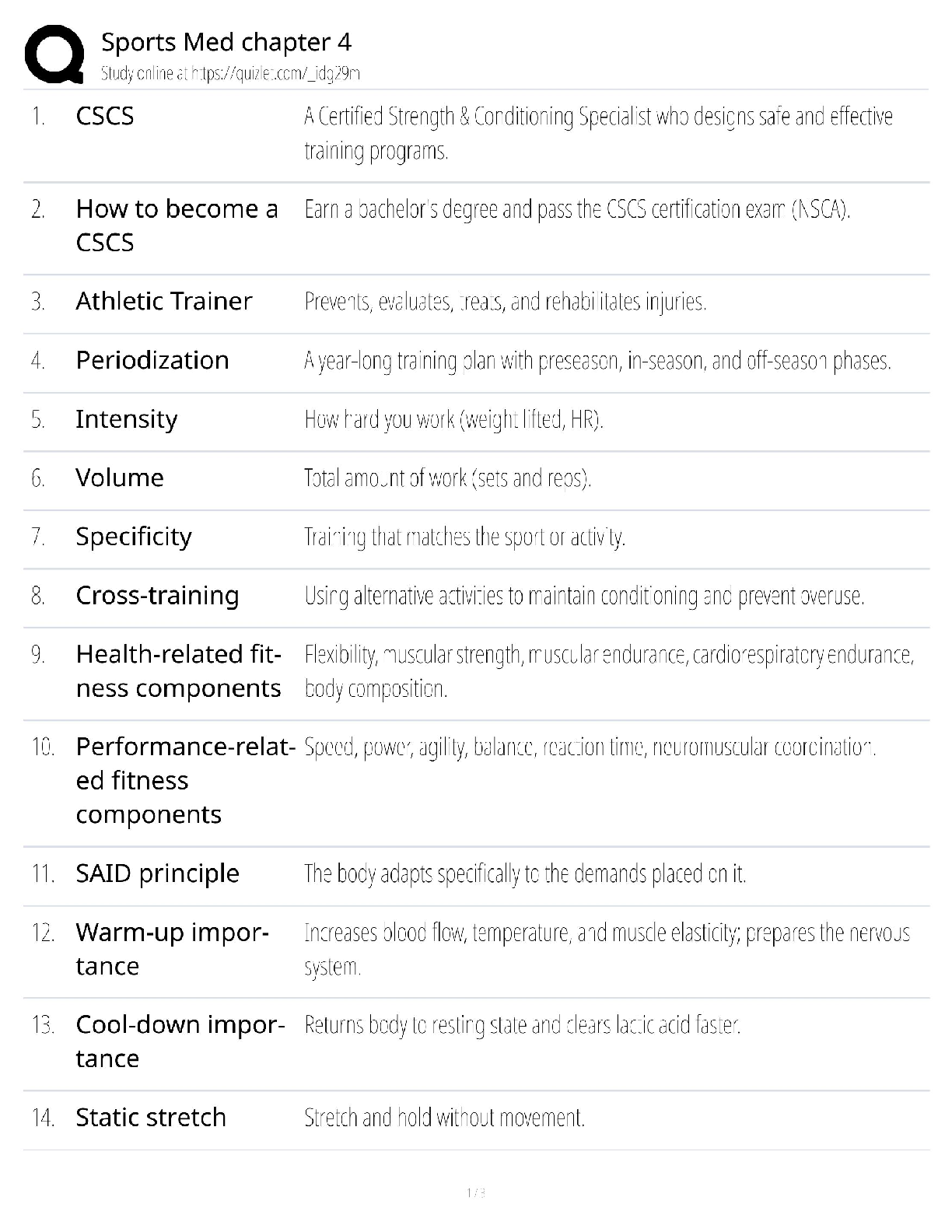
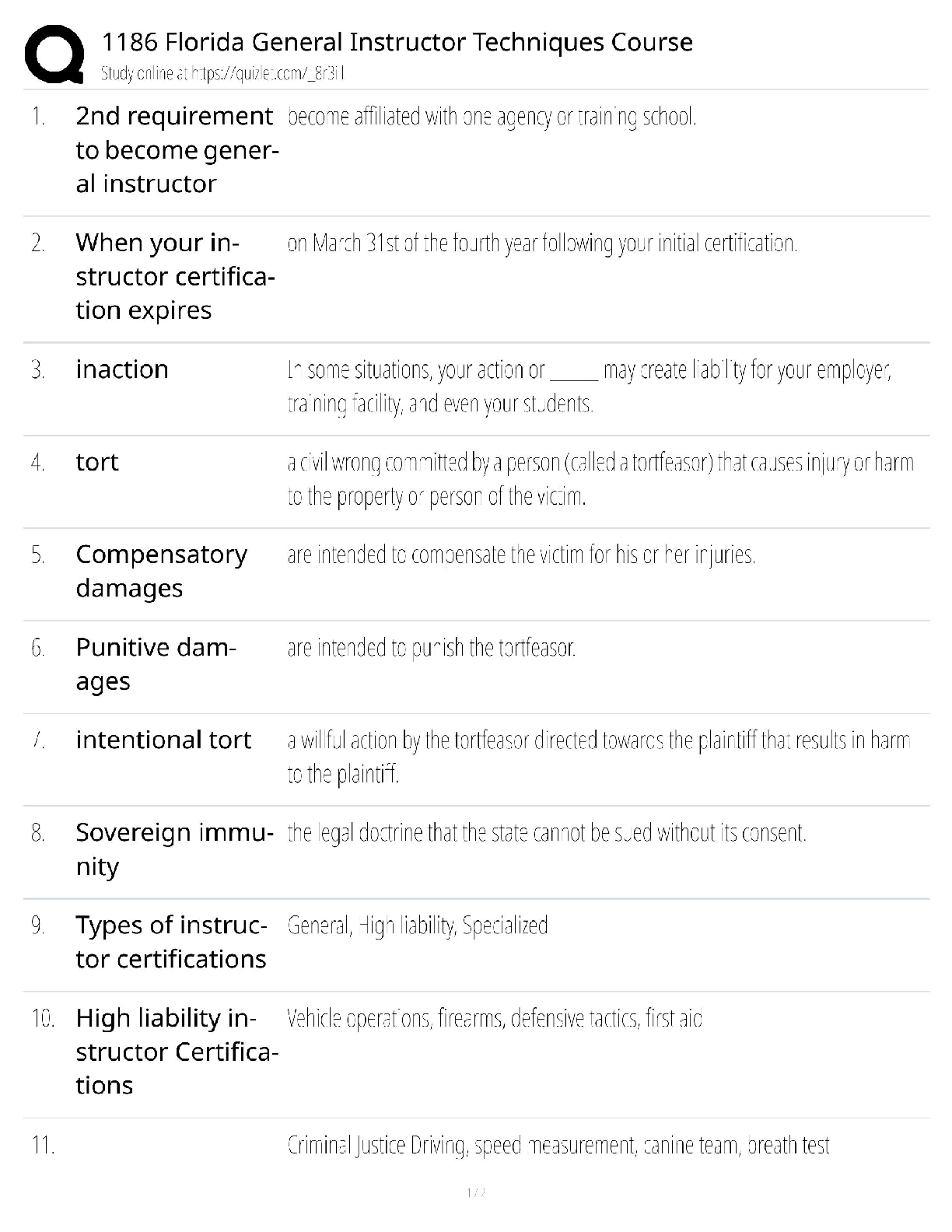
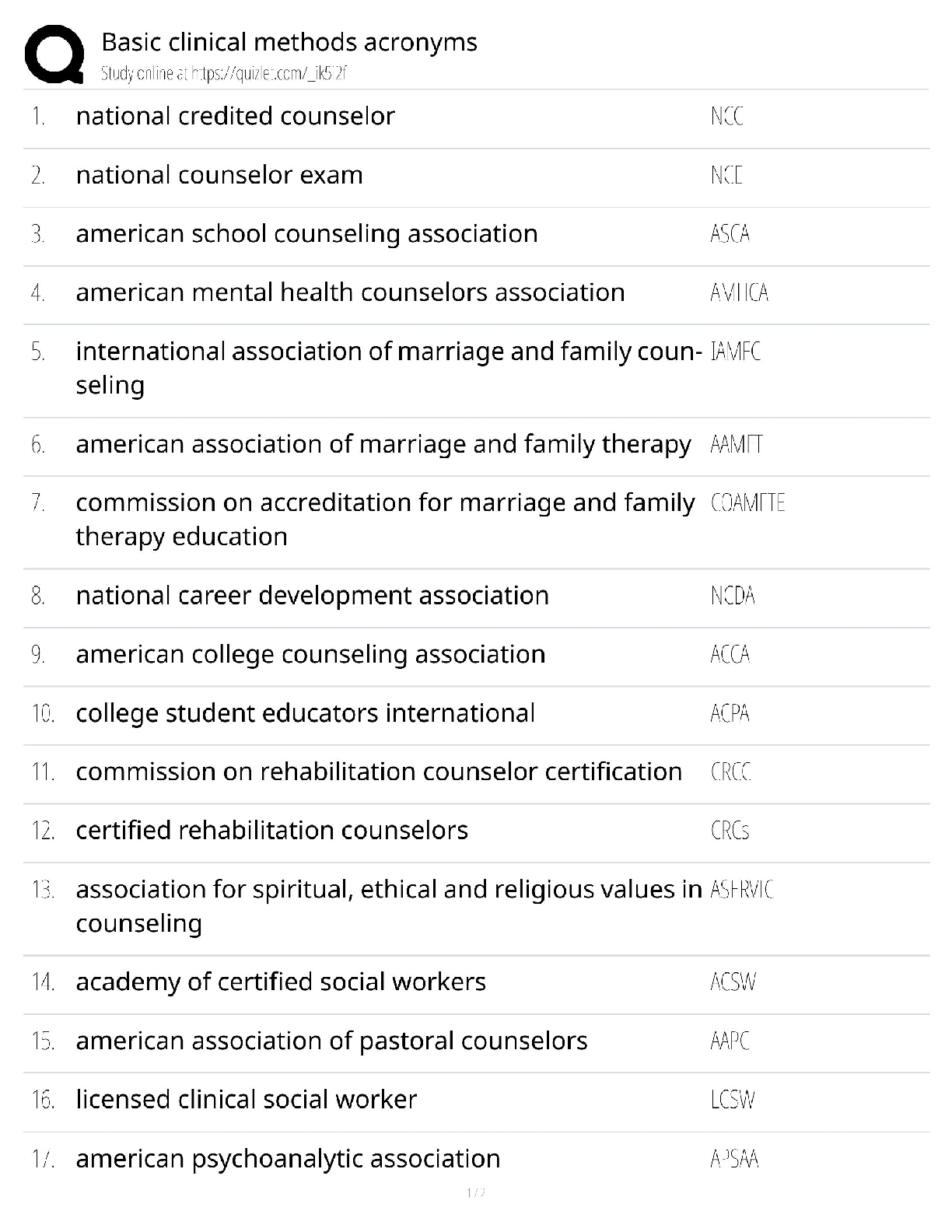
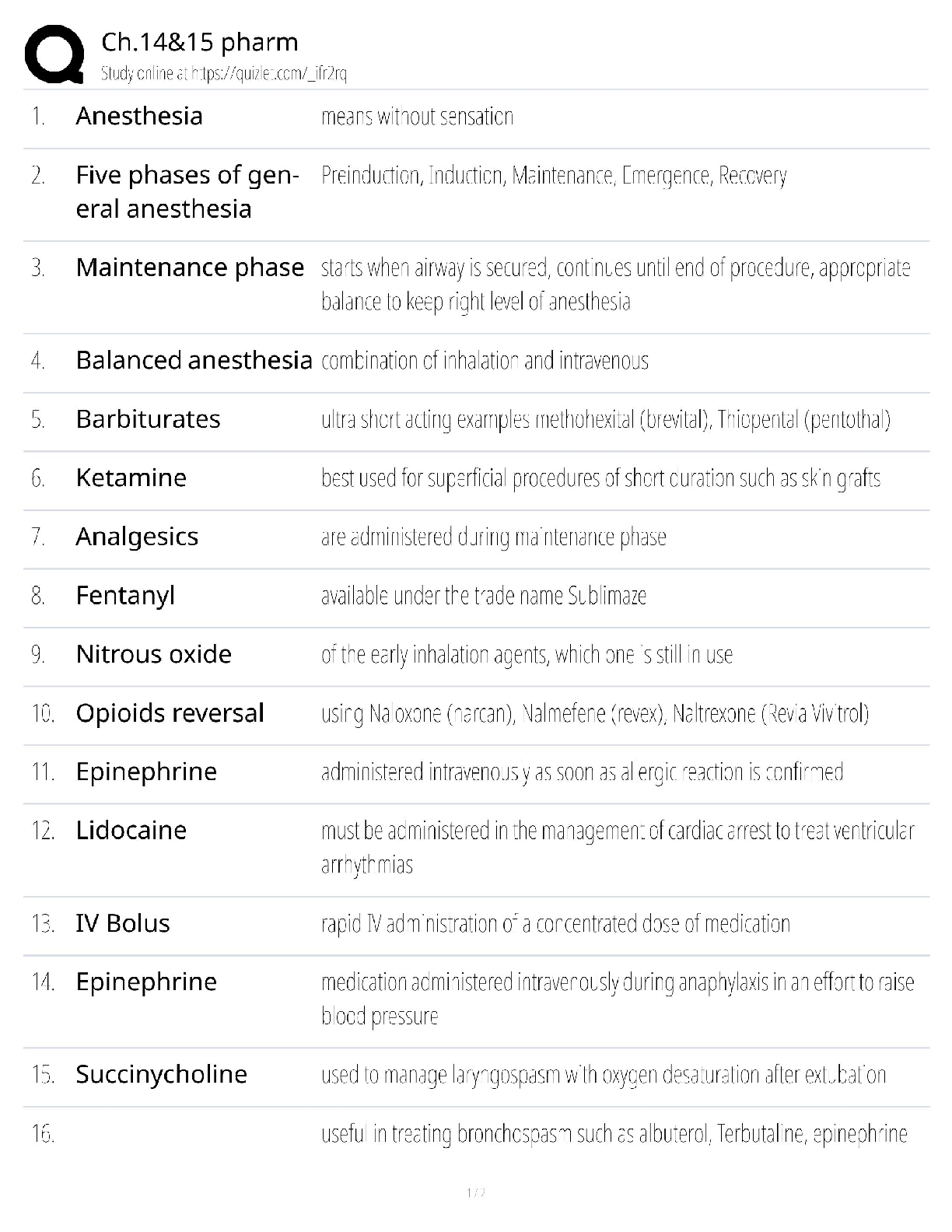
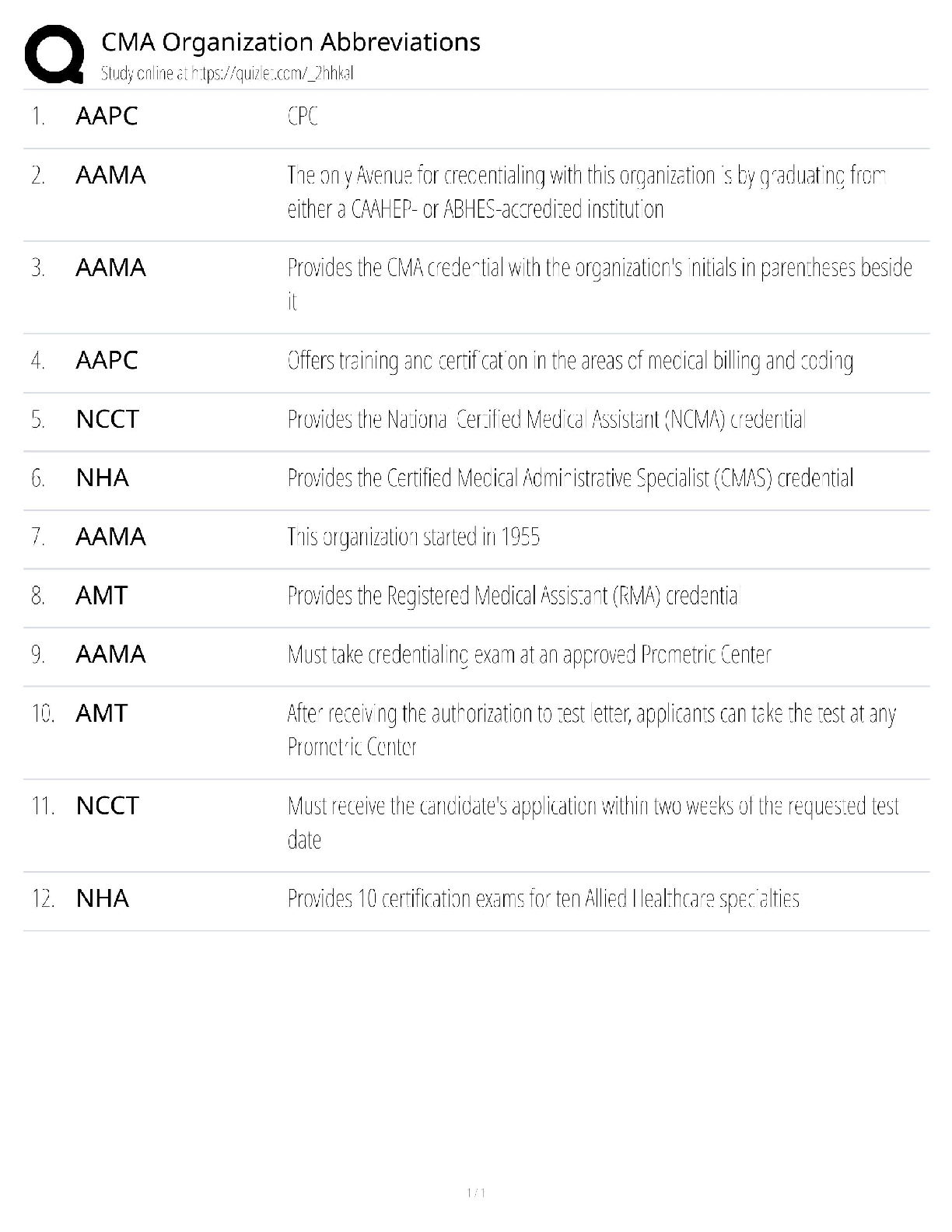
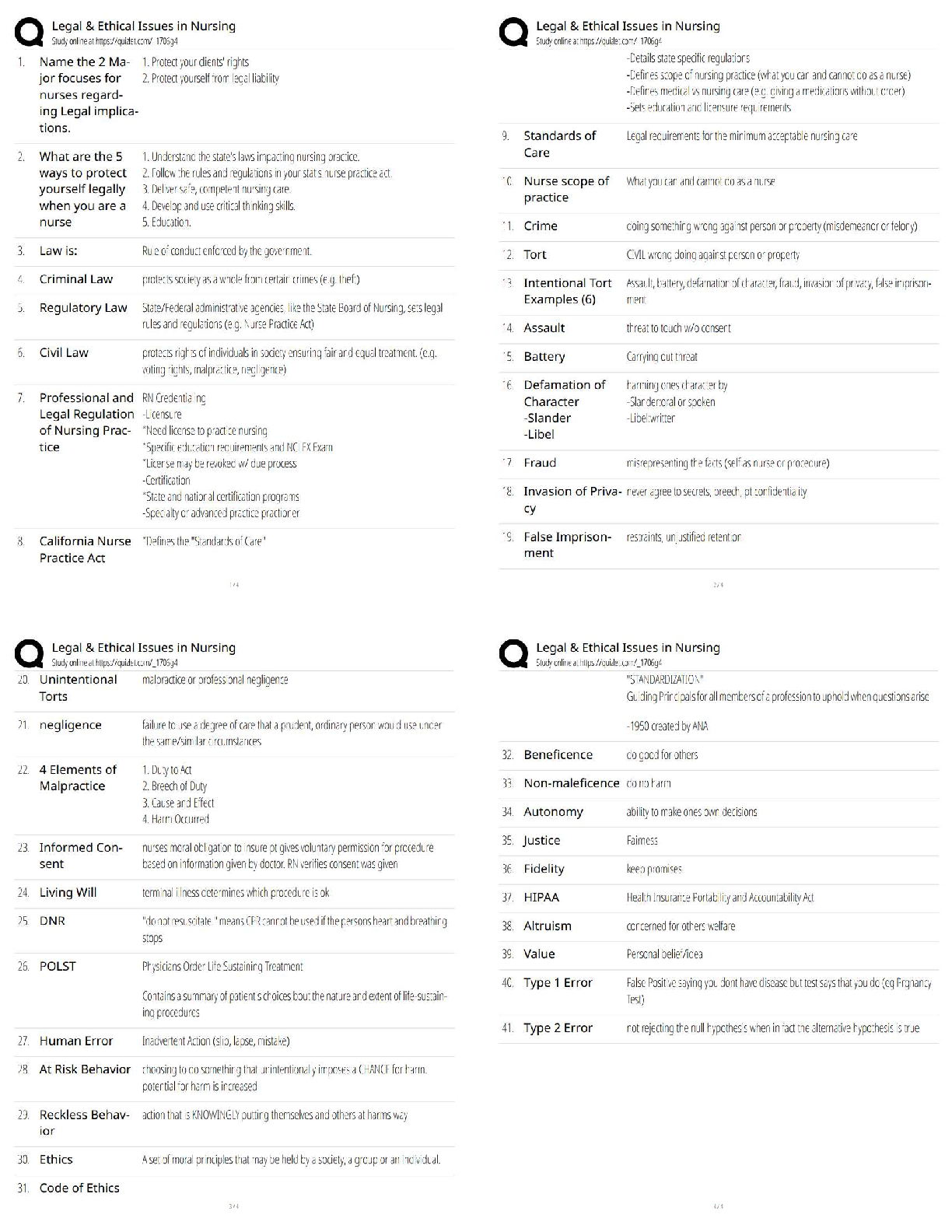
NASM CPT -7th Edition Questions and Answers 100% Pass Obesity ✔✔BMI of 30 or higher Overweight ✔✔BMI over 25 OPT Model ✔✔stabilization-strength endurance-muscular development-max stren ... gth-power Acute Disease ✔✔symptoms develop rapidly Chronic Disease ✔✔persists for long duration, cannot be cured altogether LDL cholesterol ✔✔Bad- Should be less than 100 HDL cholesterol ✔✔Good- Should be kept around 60 Type 1 Diabetes ✔✔Genetic- cannot prevented Type 2 Diabetes ✔✔obesity is a primary indicator, insulin resistant COPD ✔✔Chronic respiratory dysfunctions. Brisk walk can be one of the best forms of exercise for them. LPHC ✔✔lumbo-pelvic-hip complex 4 P's of Marketing ✔✔Product, Price, Place, Promotion SWOT Analysis ✔✔strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats Extrinsic Motivation ✔✔External- for others or reward Intrinsic Motivation ✔✔Internal-- comes from within BCT ✔✔Behavior Change Techniques- client interventions that are used to change some determinant of behavior Stages of Change Model ✔✔precontemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, maintenance SMART goals ✔✔Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, Timely Troponin ✔✔protein structure that is important for muscular contractions by providing a binding state Neurotransmitters ✔✔chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons motor function ✔✔The neuromuscular response to the sensory information (like when a person walks differently from sidewalk to sand) somatic nervous system ✔✔largely responsible for voluntary control of movement autonomic nervous system ✔✔the part of the PNS that supplies input to organs (involuntary processes). sympathetic nervous system ✔✔"fight or flight"- more excited state parasympathetic nervous system ✔✔"rest & digest"- more relaxed state 3 primary nervous system functions ✔✔sensory, integrative, motor functions sensory nervous system function ✔✔ability to sense changes integrative nervous system function ✔✔interprets sensory info Proprioception ✔✔our internal sense of body position or orientation axial skeleton ✔✔skull, rib cage, and vertebral column- aprox 80 bones appendicular skeleton ✔✔arms, legs, pelvic girdle- aprox 126 bones Skeletal Depressions ✔✔flattened or indented portions of bone Skeletal Processes ✔✔Projections from bone where tendons & ligaments can attach Neuron ✔✔specialized cell; the functional unit of the nervous system Nucleus ✔✔Control center of the cell- contains majority of genetic material Organelles ✔✔A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell Mitochondria ✔✔Powerhouse of the cell- uses nutrients to create energy Electrolytes ✔✔minerals that have an electrical charge (sodium potassium, magnesium, water) CNS ✔✔central nervous system PNS ✔✔peripheral nervous system Afferent Pathway ✔✔pathway that relays information to the CNS from the PNS muscle spindles ✔✔receptors sensitive to change in length of the muscle and the rate of that change Golgi tendon organs ✔✔Receptors sensitive to change in tension of the muscle and the rate of that change Neuroplasticity ✔✔the ability within the brain to constantly change or grow Neurocircuitry ✔✔Interconnection of neurons in brain & spinal cord Levers ✔✔Rigid rods where muscles attach Remodeling ✔✔process that bone is constantly renewed Osteoclasts ✔✔cells that break down & remove bone tissue Osteoblasts ✔✔form & lay down new bone tissue vertebral column ✔✔cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, coccyx Cervical Spine ✔✔c1-c7 (7) Thoracic Spine ✔✔t1-t12 (12) Lumbar Spine ✔✔l1-l5 (5) Sacrum ✔✔5 fused vertebrae Coccyx ✔✔3-5 small fused bones (tailbone) Osteokinematics ✔✔bone movement (movement of limb) Athrokinematics ✔✔joint movement (roll, slide, spin) synovial joints ✔✔joints with fluid filled capsule nonaxial joints ✔✔only one movement- either back & forth or side to side uniaxial joint ✔✔hinge joint (elbow, toe, ankle) saddle joint ✔✔thumb joint- only carpometacarpal pivot joint ✔✔base of skull, elbow ball & socket joints ✔✔most mobile, movement in all three directions (hip, shoulder) Nonsynovial joints ✔✔little to no movement (sutures of skull) Ligaments ✔✔Connect bone to bone (torn or stretched =sprain) Tendons ✔✔Connect muscle to bone (torn or stretched = strain) 3 types of muscles ✔✔skeletal, cardiac, smooth skeletal muscle ✔✔connects bones, produces movement cardiac muscle ✔✔makes up the heart smooth muscle ✔✔makes up tissue of internal organs fascia ✔✔surrounds muscles, connects them to other muscles Epimysium ✔✔"deep fascia" Type 1 muscle fibers ✔✔"slow twitch" resistant to fatigue Type 2 muscle fibers ✔✔"fast twitch" faster to fatigue Myofibrils ✔✔contractile components of a muscle cell Perimysium ✔✔connective tissue that surrounds a fascicle Endomysium ✔✔wraps around individual fibers within a fascicle Fascicle ✔✔bundle of fibers within a muscle sliding filament theory ✔✔series of steps in muscle contraction atrium (atria) ✔✔each of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood INTO the heart Ventricles ✔✔the two lower chambers of the heart, and they pump blood OUT to the lungs and body. Pulmonic side of heart ✔✔Right side; receives deoxygenated blood from body Systemic side of heart ✔✔Left side; pumps freshly oxygenated blood to body RHR- Resting Heart Rate ✔✔the number of times your heart beats per minute when at rest (avg is 60-100 bmp) Bradycardia ✔✔slow heart rate (below 60 bpm) Tachycardia ✔✔fast heart rate (above 100 bpm) 3 blood cell types ✔✔red, white, platelets 3 types of blood vessels ✔✔arteries, capillaries, veins Arteries ✔✔carry blood away from the heart Capillaries ✔✔The smallest blood vessels, and the site o exchange elements between the blood and the tissues. Veins ✔✔carry blood back to the heart Arterioles ✔✔small arteries Venules ✔✔small vessels that gather blood from the capillaries into the veins venous pooling ✔✔accumulation of the blood into the extremities due to low blood flow systolic pressure ✔✔the upper number in the fraction that measures blood pressure, the pressure when the heart contracts diastolic pressure ✔✔the lower number in BP reading, the pressure when heart relaxes ( fills with blood between beats) Breathing: inspiration and expiration ✔✔inspiration is inhale, expiration is exhale Valsalva maneuver ✔✔holding breath during an intense muscle contraction, which can reduce blood flow to the brain and cause dizziness or fainting (not for people with high BP) Diffusion ✔✔getting oxygen from environment into the tissues of the body Tachypnea ✔✔fast breathing, more than 24 breaths per minute Bradypnea ✔✔slow breathing, fewer than 8 breaths per minute Dyspnea ✔✔shortness of breath, or labored breathing intercalated discs ✔✔help hold cardiac muscles together [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 13 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)
.png)
NASM CPT BUNDLED EXAMS (2022/2023) (VERIFIED SOLUTIONS)
NASM CPT BUNDLED EXAMS (2022/2023) (VERIFIED SOLUTIONS)
By Nutmegs 2 years ago
$25
23
Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 19, 2023
Number of pages
13
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 19, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
129








.png)