NSG 5003 quiz 1
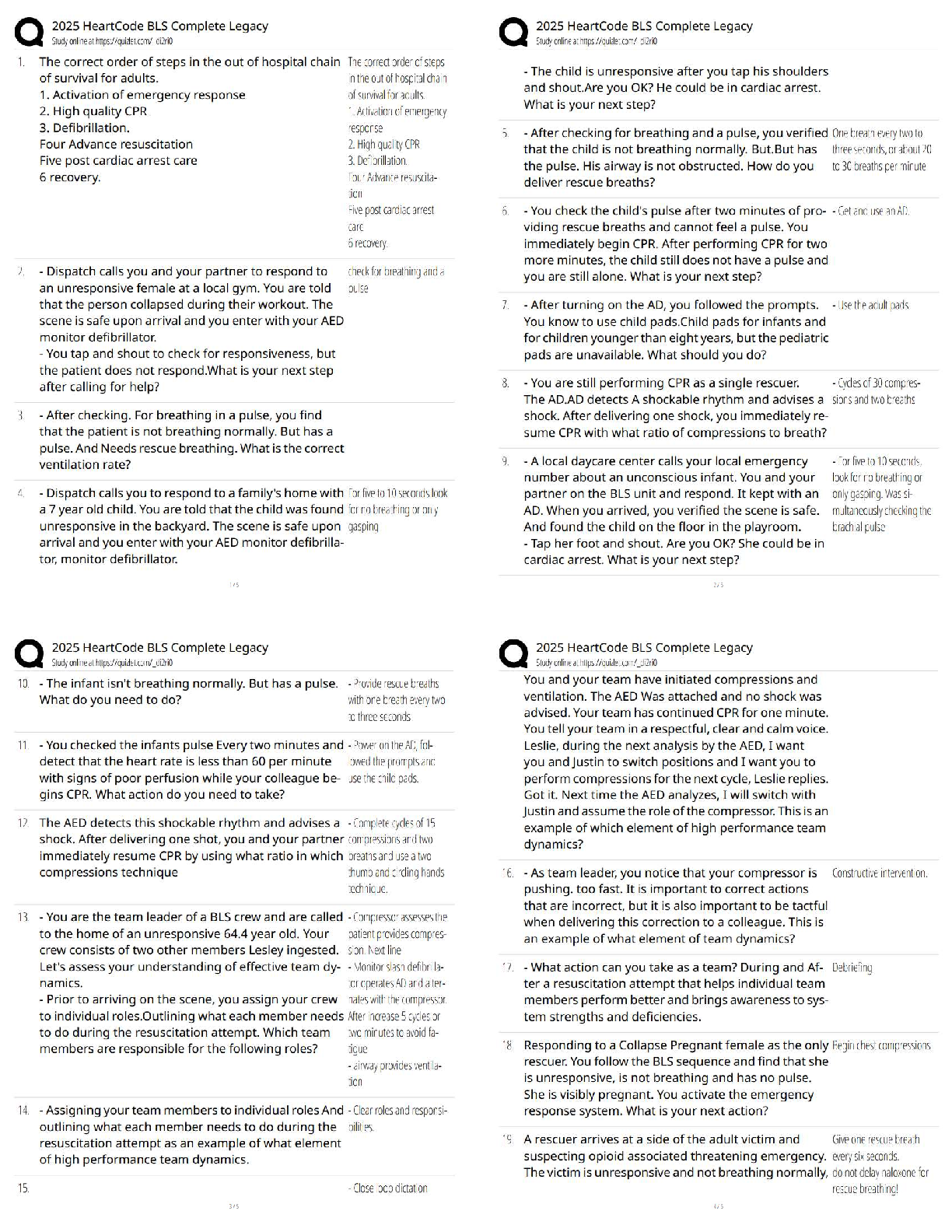
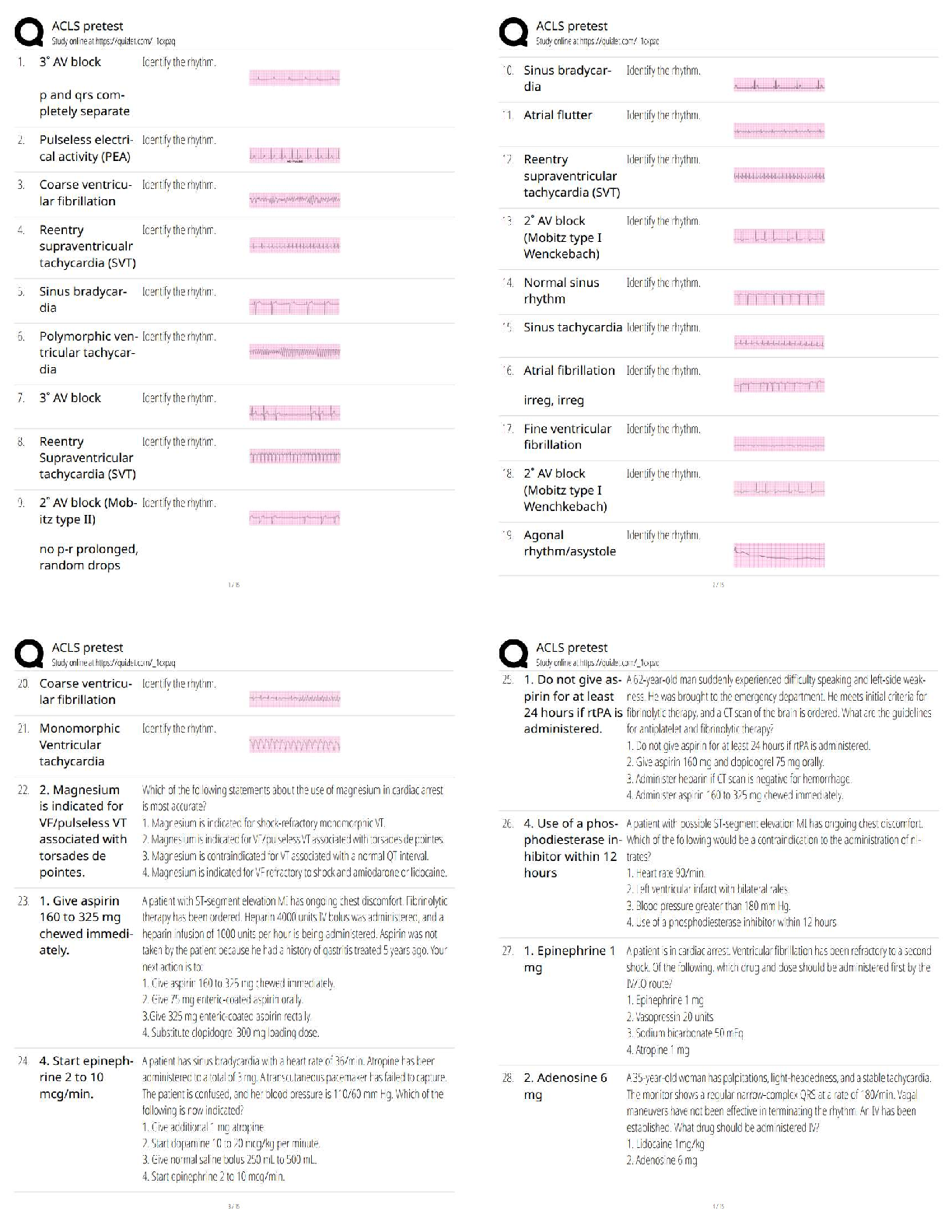
Quiz 1
Question : Why is it possible for potassium to diffuse easily into and out of cells?
Student Answer: Potassium has a greater con
...
NSG 5003 quiz 1
Quiz 1
Question : Why is it possible for potassium to diffuse easily into and out of cells?
Student Answer: Potassium has a greater concentration in the ICF.
Sodium has a greater concentration in the ECF.
The resting plasma membrane is more permeable to potassium.
An excess of anions is inside the cell.
Instructor Explanation: Because the resting plasma membrane is more permeable to K+ than to Na+, K+ can easily diffuse from its area of higher concentration in the ICF to its area of lower concentration in the ECF. Because Na+ and K+ are both cations, the net result is an excess of anions inside the cell, resulting in the resting membrane potential. The remaining options do not correctly identify the process that most easily diffuses K+.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 3. Question : A major determinant of the resting membrane potential necessary for the transmission of nerve impulses is the ratio between:
Student Answer: Intracellular and extracellular Na+
Intracellular and extracellular K+
Intracellular Na+ and extracellular K+
Intracellular K+ and extracellular Na+
Instructor Explanation: The ratio of K+ in the ICF to K+ in the ECF is the major determinant of the resting membrane potential, which is necessary for the transmission and conduction of nerve impulses, for the maintenance of normal cardiac rhythms, and for the skeletal and smooth muscle contraction. This is not true of the other options.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 5. Question : What is a consequence of plasma membrane damage to the mitochondria?
Student Answer: Enzymatic digestion halts DNA synthesis.
Influx of calcium ions halts ATP production.
Edema from an influx in sodium causes a reduction in ATP production.
Potassium shifts out of the mitochondria, which destroys the infrastructure.
Instructor Explanation: The most serious consequence of plasma membrane damage is, as in hypoxic injury, to the mitochondria. An influx of calcium ions from the extracellular compartment activates multiple enzyme systems, resulting in cytoskeleton disruption, membrane damage, activation of inflammation, and eventually DNA degradation. Calcium ion accumulation in the mitochondria causes the mitochondria to swell, which is an occurrence that is associated with irreversible cellular injury. The injured mitochondria can no longer generate ATP, but they do continue to accumulate calcium ions. The remaining options do not accurately describe the consequence of plasma membrane damage to the mitochondria.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 6. Question : Current research supports the belief that after heart muscle injury, the damage:
Student Answer: Remains indefinitely because cardiac cells do not reproduce
Is repaired by newly matured cardiomyocytes
Gradually decreases in size as mitotic cell division occurs
Is replaced by hypertrophy of remaining cells
Instructor Explanation: The recent discovery that cardiac stem cells exist in the heart and differentiate into various cardiac cell lineages has profoundly changed the understanding of myocardial biology; it is now believed that bone marrow–derived cardiac stem cells or progenitor cells that have the ability to mature into cardiomyocytes may populate the heart after injury. The other options do not accurately describe the process that is believed to occur to address cardiac muscle damage.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 9. Question : Free radicals cause cell damage by:
Student Answer: Stealing the cell’s oxygen to stabilize the electron, thus causing hypoxia
Stimulating the release of lysosomal enzymes that digest the cell membrane
Transferring one of their charged, stabilized atoms to the cell membrane, which causes lysis
Giving up an electron, which causes injury to the chemical bonds of the cell membrane
Instructor Explanation: A free radical is an electrically uncharged atom or group of atoms having an unpaired electron. Having one unpaired electron makes the molecule unstable; thus to stabilize, the molecule gives up an electron to another molecule or steals one. Therefore it is capable of forming injurious chemical bonds with proteins, lipids, or carbohydrates—key molecules in membranes and nucleic acids. The remaining options do not accurately describe the role played by free radicals in cell damage.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 12. Question : The loss of the ATP during ischemia causes cells to:
Student Answer: Shrink because of the influx of calcium (Ca)
Shrink because of the influx of potassium chloride (KCl)
Swell because of the influx of sodium chloride (NaCl)
Swell because of the influx of nitric oxide (NO)
Instructor Explanation: A reduction in ATP levels causes the plasma membrane’s sodium-potassium (Na+–K+) pump and sodium-calcium exchange to fail, which leads to an intracellular accumulation of sodium and calcium and diffusion of potassium out of the cell. (The Na+–K+ pump is discussed in Chapter 1.) Sodium and water can then freely enter the cell, and cellular swelling results. The other options do not accurately describe the result of ATP at the cellular level.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 14. Question : Which statement is true about eukaryotic cells?
Student Answer: They lack a distinct nucleus.
They contain compartments called organelles.
They lack an encasing nuclear membrane.
They are smaller than the typical prokaryote cell.
Instructor Explanation: Eukaryotic cells have a characteristic set of membrane-bound intracellular compartments called organelles that include a well-defined nucleus and are larger than prokaryotes. The remaining statements are not true regarding eukaryotic cells.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 15. Question : Which mode of chemical signaling uses local chemical mediators that are quickly taken up, destroyed, or immobilized?
Student Answer: Paracrine
Autocrine
Neurotransmitter
Hormone
Instructor Explanation: In paracrine signaling, cells secrete local chemical mediators that are quickly taken up, destroyed, or immobilized. The other options do not correctly describe this process.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 19. Question : During cell injury caused by hypoxia, an increase in the osmotic pressure occurs within the cell because:
Student Answer: Plasma proteins enter the cell.
The adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase-driven pump is stronger during hypoxia.
Sodium chloride enters the cell.
An influx of glucose occurs through the injured cell membrane.
Instructor Explanation: In hypoxic injury, movement of fluid and ions into the cell is associated with acute failure of metabolism and a loss of ATP production. Normally, the pump that transports sodium ions out of the cell is maintained by the presence of ATP and ATPase, the active-transport enzyme. In metabolic failure caused by hypoxia, reduced ATP and ATPase levels permit sodium to accumulate in the cell, whereas potassium diffuses outward. The increase of intracellular sodium increases osmotic pressure, which draws more water into the cell. The remaining options do not accurately describe the cell injury that results in increased osmotic pressure caused by hypoxia.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 20. Question : When a mucous gland cell creates a new substance from previously absorbed material, this process is known as which specialized cellular function?
Student Answer: Excretion
Metabolic absorption
Reproduction
Secretion
Instructor Explanation: Certain cells, such as mucous gland cells, can synthesize new substances from substances they absorb and then secrete the new substances to serve elsewhere as needed. The other options are not used to describe the function described in the stem.
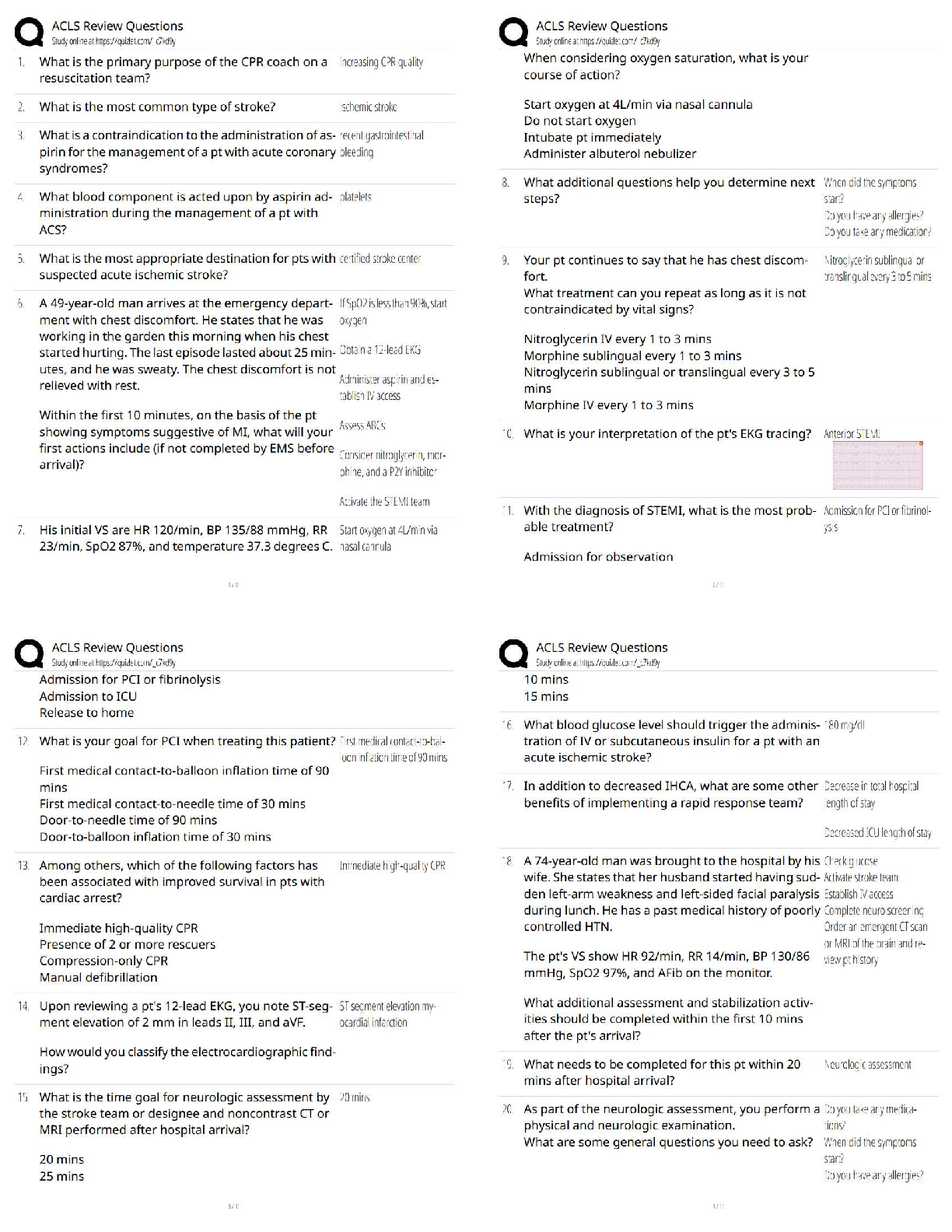
Quiz 2
Question 4. Question : A reduction in an individual’s number of NK cells appears to correlate with an increased risk for the development of:
Student Answer: Depression
Type 1 diabetes
Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD)
Gastroesophageal reflux disorder (GERD)
Instructor Explanation: A meta-analysis of studies shows a relationship between depression and the reduction in lymphocyte proliferation and natural killer cell activity. Currently, no research supports the other options.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 6. Question : Which statement concerning exotoxins is true?
Student Answer: Exotoxins are contained in cell walls of gram-negative bacteria.
Exotoxins are released during the lysis of bacteria.
Exotoxins are able to initiate the complement and coagulation cascades.
Exotoxins are released during bacterial growth.
Instructor Explanation: Exotoxins are proteins released during bacterial growth. The other options are not true of exotoxins.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 7. Question : Which statements are true regarding viruses? (Select all that apply.)
Student Answer: Viruses are very complex microorganisms.
Viruses are referred to as eukaryotes.
Viruses are capable of producing messenger ribonucleic acid RNA (mRNA).
Viruses penetrate the plasma membrane via endocytosis.
Viruses are capable of uncoating cytoplasmic nucleocapsids.
Instructor Explanation: Viruses are extremely simple microorganisms and do not possess any of the metabolic organelles found in prokaryotes (e.g., bacteria) or eukaryotes (e.g., human cells). Once bound, the virus can penetrate the plasma membrane by receptor-mediated endocytosis. Within the cytoplasm, the virus uncoats the protective nucleocapsid and releases viral genetic information. Most RNA viruses directly produce mRNA, which is translated into viral proteins, and genomic RNA, which is eventually packaged into new viruses.
Points Received: 0.3 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 12. Question : Cytokines are thought to cause fevers by stimulating the synthesis of which chemical mediator?
Student Answer: Leukotriene
Histamine
Prostaglandin
Bradykinin
Instructor Explanation: Cytokines seem to raise the thermoregulatory set point through stimulation of prostaglandin synthesis and turnover in thermoregulatory (brain) and nonthermoregulatory (peripheral) tissues. The other options do not accurately identify the appropriate chemical mediator.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 14. Question : Fusion is the step in phagocytosis during which:
Student Answer: Microorganisms are killed and digested.
An intracellular phagocytic vacuole is formed.
Lysosomal granules enter the phagocytes.
Microorganisms are ingested.
Instructor Explanation: Fusion occurs with lysosomal granules entering the phagocyte (phagolysosome). The remaining options do not accurately describe fusion as a step in phagocytosis.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 15. Question : The main functions of NK cells include: (Select all that apply.)
Student Answer: Recognizing virus-infected cells
Eliminating virus-infected cells
Recognizing bacteria-infected cells
Eliminating bacteria-infected cells
Eliminating previously identified cancer cells
Instructor Explanation: The main functions of NK cells are recognizing and eliminating cells infected with viruses, not bacteria. They are also somewhat effective at eliminating other abnormal host cells, specifically cancer cells.
Points Received: 0.3 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 19. Question : Which cytokine is needed for the maturation of a functional Th cell?
Student Answer: IL-1
IL-2
IL-4
IL-12
Instructor Explanation: Of the options provided, IL-2 production is critical for the Th cell to mature efficiently into a functional helper cell.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 20. Question : Which disease is an example of a rickettsial infection?
Student Answer: Cholera
Candida
Sleeping sickness
Rocky Mountain spotted fever
Instructor Explanation: Rocky Mountain spotted fever is a result of a rickettsiae. Cholera is a bacterial infection, candida is a fungal infection, and sleeping sickness is a protozoal infection.
Quiz 3
Question : Which characteristic among women correlates with a high morbidity of cancer of the colon, uterus, and kidney?
Student Answer: Women older than 45 years of age
Women who have never had children
Women who have a high body mass index (BMI)
Woman who have smoked for more than ten years
Instructor Explanation: A recent hypothesis states that the observed increased incidence of such cancers as breast, endometrium, colon, liver, kidney, and adenomas of the esophagus may be associated with obesity. No current research supports the remaining options.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
Question 2. Question : A carcinoma refers to abnormal cell proliferation originating from which tissue?
Student Answer: Blood vessels
Epithelial cells
Connective tissue
Glandular tissue
Instructor Explanation: Only cancers arising from epithelial cells are called carcinomas.
Points Received: 0 of 0.5
Comments:
[Show More]
.png)












.png)