BIOL 261 Quizzes 1-5 - 45 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Document Content and Description Below
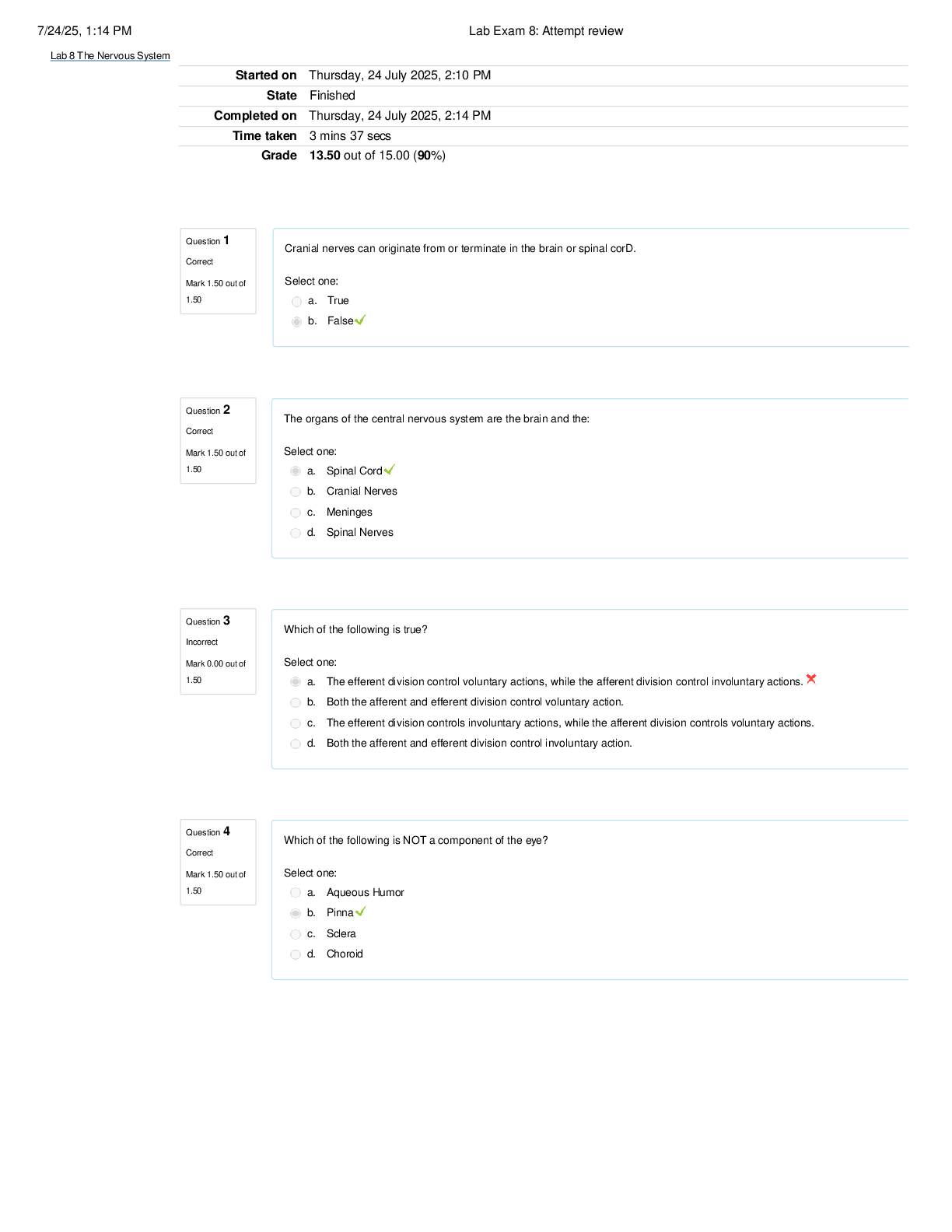
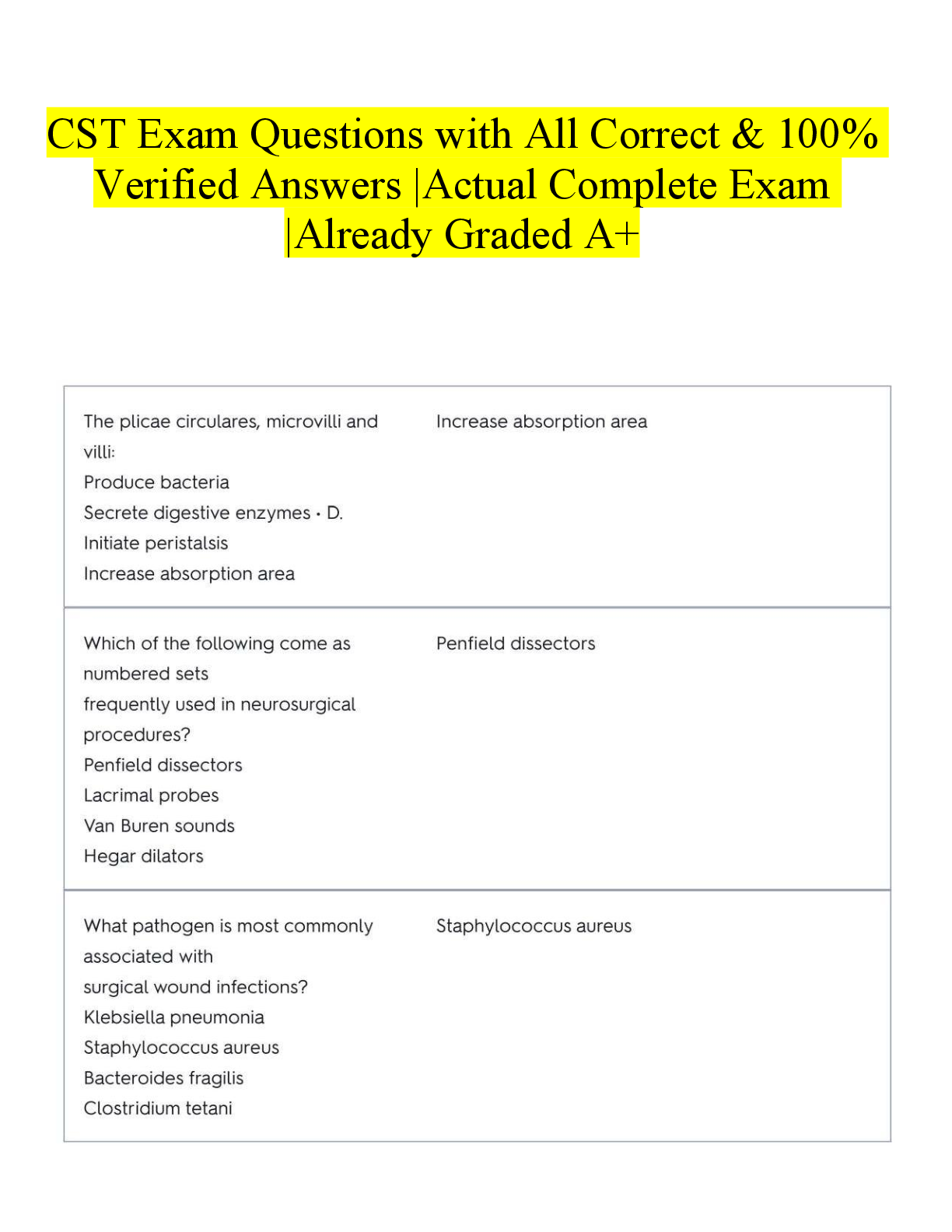
BIOL 261 Quizzes 1-5 - 45 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Question 1 A coefficient of coincidence of 0.25 means that: a. the frequency of double crossovers is 1/4. b. the frequency of double crossovers is 1/4 ... of the number expected if there were no interference. c. there were four times as many single crossovers as double crossovers. d. there were four times as many single crossovers in one region as there were in an adjacent region. Question 2 A monohybrid test cross analyzes a. The genotype of the strain being assessed b. The phenotype of the strain being assessed c. Both the genotype and the phenotype of the strain being assessed d. The phenotype of both strains in the cross Question 3 If a cross is made between two parental strains that breed true for two genes, what is the expected F2 ratio in a test cross in the absence of epistasis? a. 3:1 b. 9:3:3:1 c. 9:7 d. 9:4:3 Question 4 To transform Step. pneumoniae, Griffiths a. purified DNA from virulent bacteria b. treated heat-killed avirulent bacteria with living, virulent cells c. heat killed bacteria and injected them into avirulent bacteria d. heat killed bacteria and mixed them with avirulent bacteria e. None of the above Question 5 What blood type is the universal recipient? a. O b. A c. B d. AB Question 6 Two unlinked genes in mice are involved in hair colour. The homozygous recessive version of either gene prevents pigment formation and leads to white hair, while the homozygous dominant allele of one gene causes brown hair, and the homozygous dominant allele of the other gene causes orange hair. Mice with the dominant orange and dominant brown arrangement at the same time have orange-brown hair. Two white haired mice are bred, and the F1 mice are all yellow haired. What do you predict will happen in the F2 generation of a. most of the mice will have white hair b. none of the mice will have yellow hair c. ¼ of the mice will have yellow hair d. the mice will fit the classic 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio for unlinked genes Question 7 Assuming equal sex ratios, if a mating has already produced three girls, what is the probability that the next child will be a girl? a. 0 b. 1 c. 1/2 d. (1/2)3 Question 8 A woman with keratosis, a skin condition caused by a rare dominant allele, marries a normal man, and they have two children. What is the probability that both children are normal? a. 0 b. 0.5 c. 0.25 d. 1 Question 9 Two plants show incomplete dominance for flower colour; the homozygous WT flowers are red, the homozygous mutant flowers are white, and the heterozygotes are pink. Two red plants are crossed, and the F1 plants are self-crossed. a. the F2 will show red, white and pink flowers b. all the F2 plants will be pink c. the plants will breed true for the red phenotype d. because of incomplete dominance, all the F1 plants will be pink Question 10 In the Hersey Chase experiment [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 11 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

BIOL 261 GENETICS QUIZZES, MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW AND FINAL EXAM REVIEW BUNDLE
BIOL 261 GENETICS | BIOL 261 Quizzes 1-5, BIOL 261 Final Exam Review. BIOL 261 Midterm 1 Review, BIOL 261 Genetics Review Questions for Final Exam
By Nurse Henny 2 years ago
$30
4
Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 22, 2023
Number of pages
11
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 22, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
87