Metabolic Engineering: Homework 8
1. (2 points) Short answer
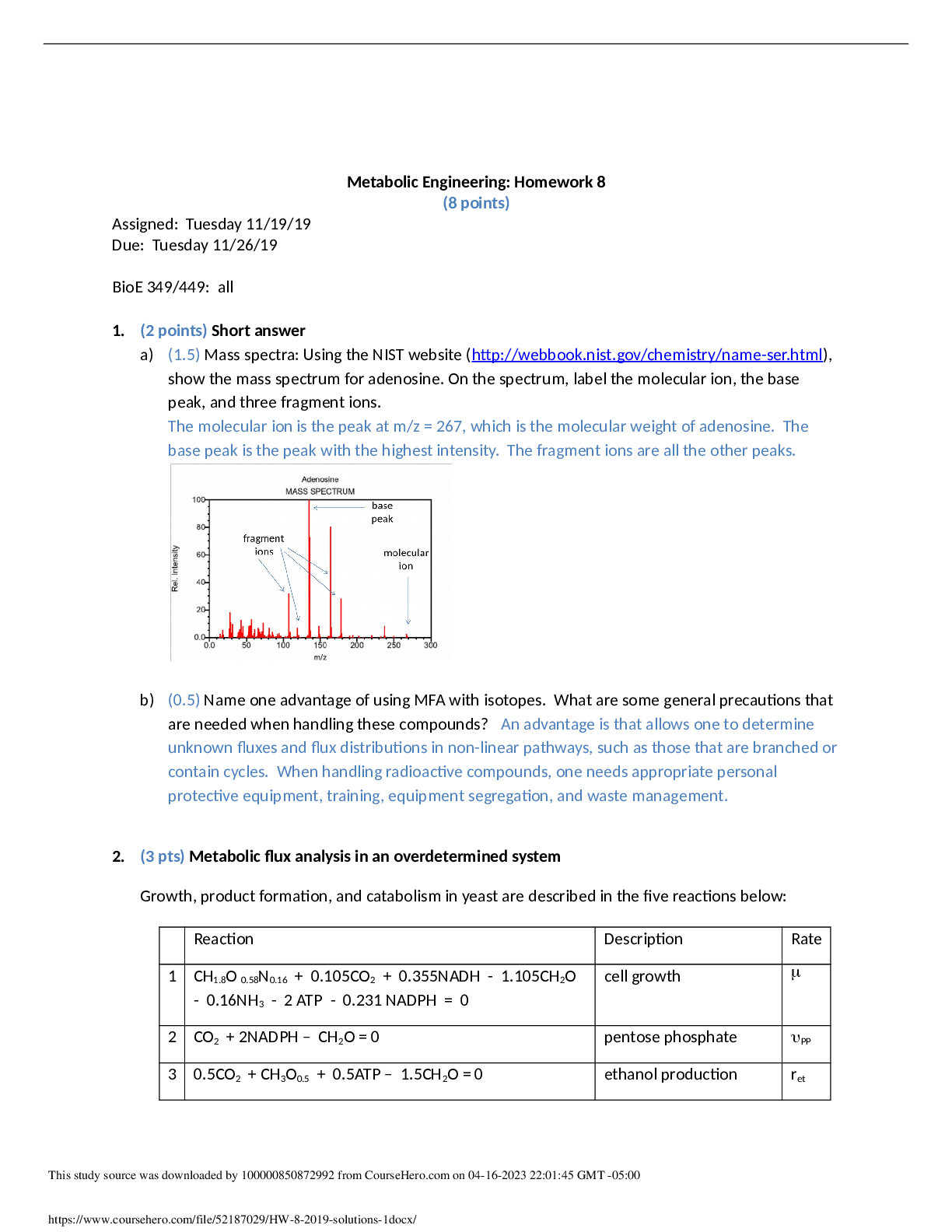
a) (1.5) Mass spectra: Using the NIST website (http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/name-ser.html),
show the mass spectrum for adenosine. On the spectrum, la
...
Metabolic Engineering: Homework 8
1. (2 points) Short answer
a) (1.5) Mass spectra: Using the NIST website (http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/name-ser.html),
show the mass spectrum for adenosine. On the spectrum, label the molecular ion, the base
peak, and three fragment ions.
b) (0.5) Name one advantage of using MFA with isotopes. What are some general precautions that
are needed when handling these compounds
2. (3 pts) Metabolic flux analysis in an overdetermined system
Growth, product formation, and catabolism in yeast are described in the five reactions below:
Reaction Description Rate
1 CH1.8O 0.58N0.16 + 0.105CO2 + 0.355NADH - 1.105CH2O
- 0.16NH3 - 2 ATP - 0.231 NADPH = 0
cell growth
4 CH8/3O - 0.333NADH - 0.333ATP - CH2O = 0 glycerol production rgly
5 -ATP = 0 ATP consumption for
maintenance
mATP
Notes: glucose = CH2O; ethanol = CH3O0.5; glycerol= CH8/3O. The intracellular products are ATP,
NADH, and NADPH.
a) (1pt)The rates of biomass formation, ethanol production, and glycerol production are measured.
The results for the measured rates are: =0.07 h-1, reth=0.03 C-mol eth/(C-mol X - h), and rgly=0.07
C-mol gly/(C-mol X - h). Determine:
1. PP and mATP
b) (1pt)Express the system using Stephanopoulos Equation (8.13). Again, the rates of biomass,
ethanol, and glycerol are measured and are the same as they are in Part (a). Partition T into T11,
T12, T21, T22. Partition v into v1 and v2.
c) (1pt)Using your result from Part (b), what are the best estimates of v1 and v2? What are the best
estimates of the rate of ethanol formation and the ATP maintenance rate?
3. (3 pts) Sensitivity analysis
Using the same metabolic pathway shown in Problem 2:
a) (1pt)Calculate the norm of GT using the eigenvalue method (text, Eqn 2, Box 8.1) and by using
the “norm” function in MATLAB. Compare your results.
b) (1pt)Calculate the condition number of GT using Eqn 8.28 and the “cond” function in MATLAB.
Compare your results. Is GT well conditioned or poorly conditioned?
c) (1pt)Now the rates of biomass and ethanol are measured. Calculate vc/vm . Is the rate of
glycerol formation more sensitive to changes in the biomass rate or to changes in the ethanol
rate?
[Show More]