Psychology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > AQA A-level Psychology: Memory Latest 2023 Graded A+ (All)
AQA A-level Psychology: Memory Latest 2023 Graded A+
Document Content and Description Below
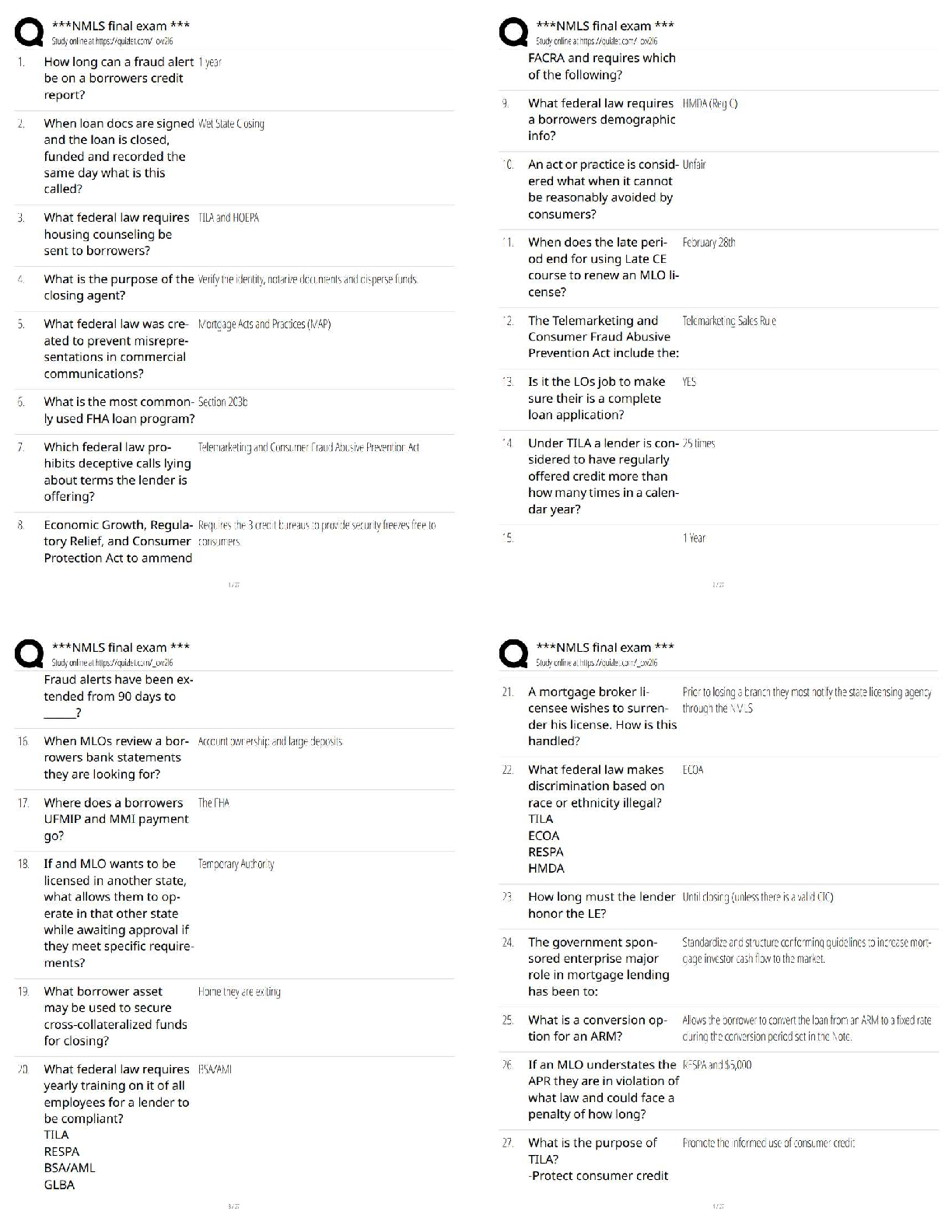
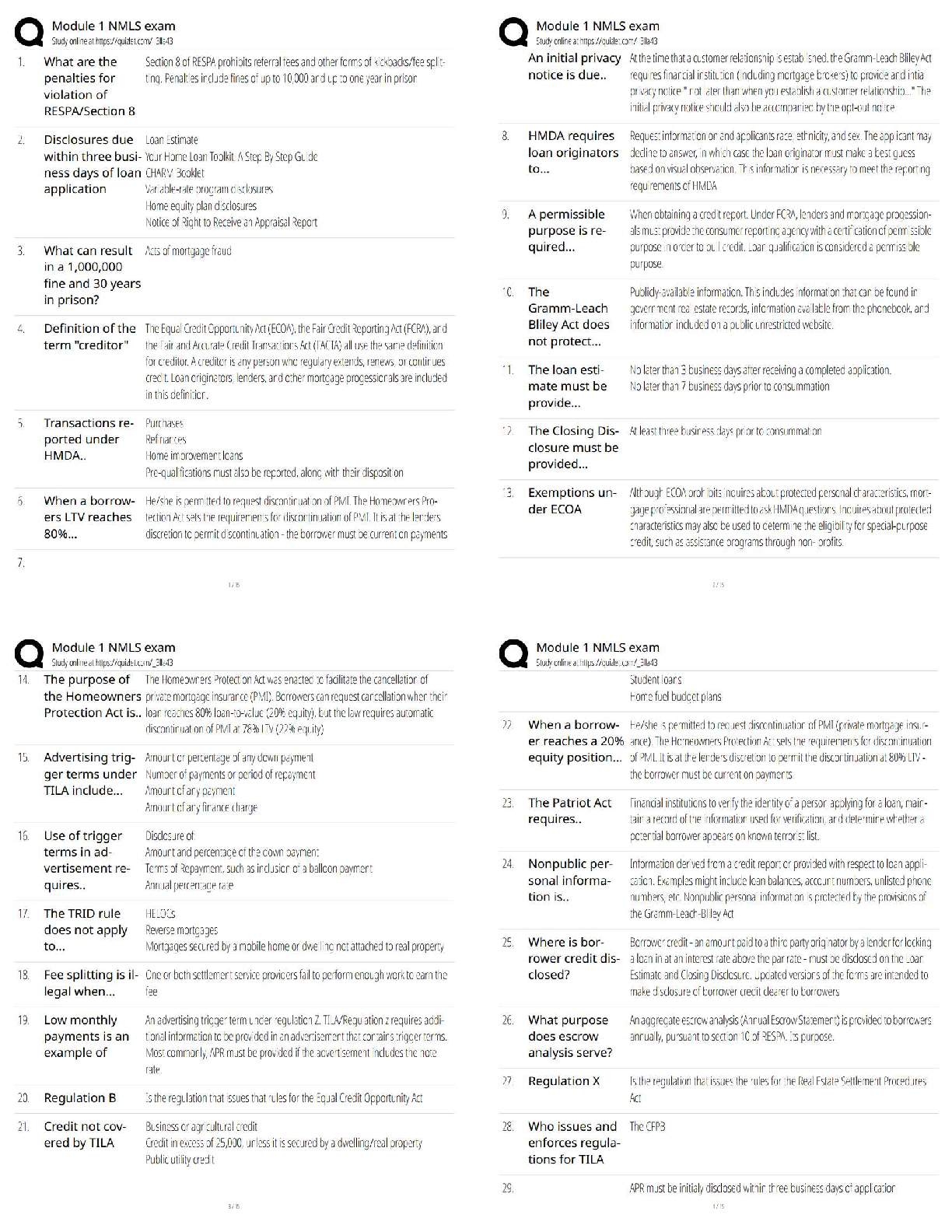
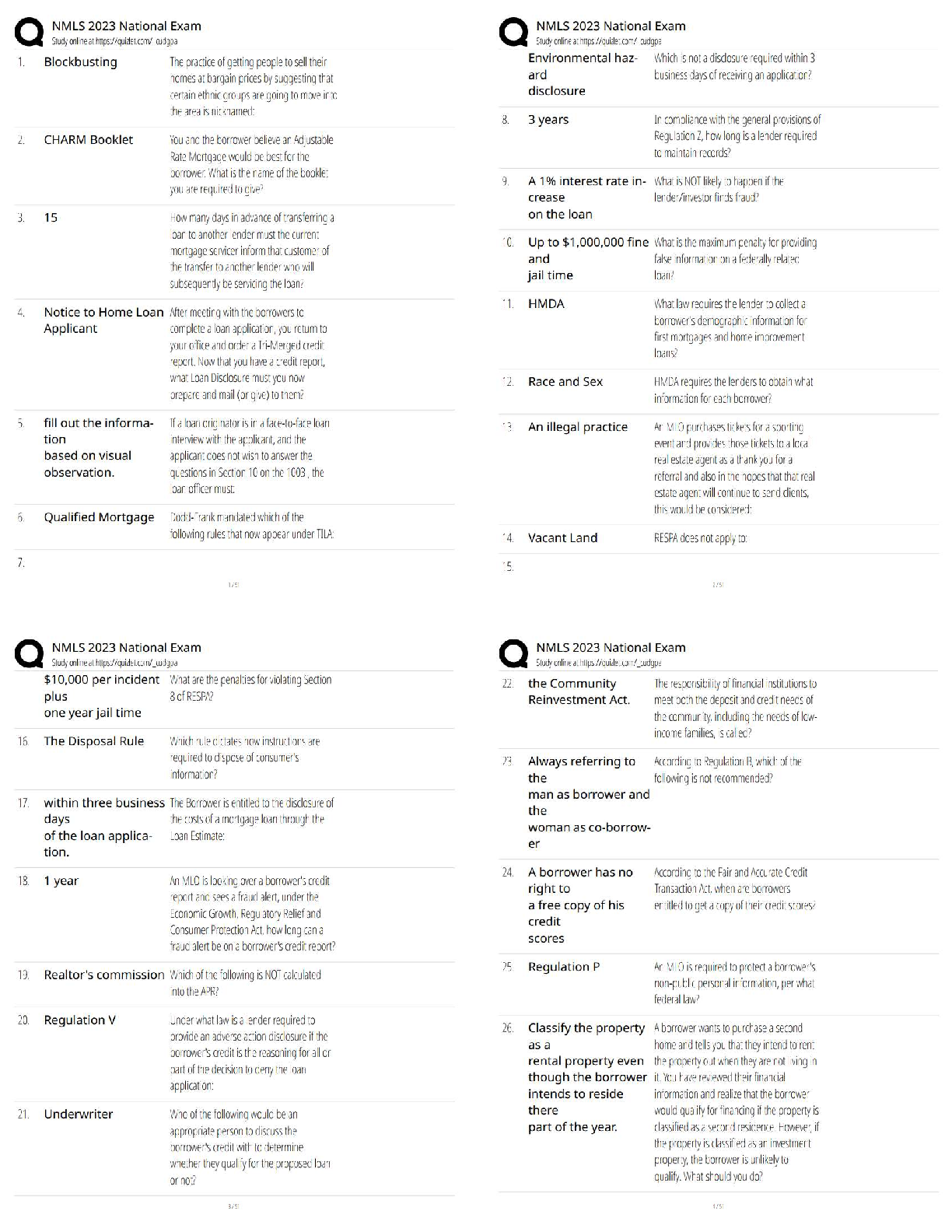
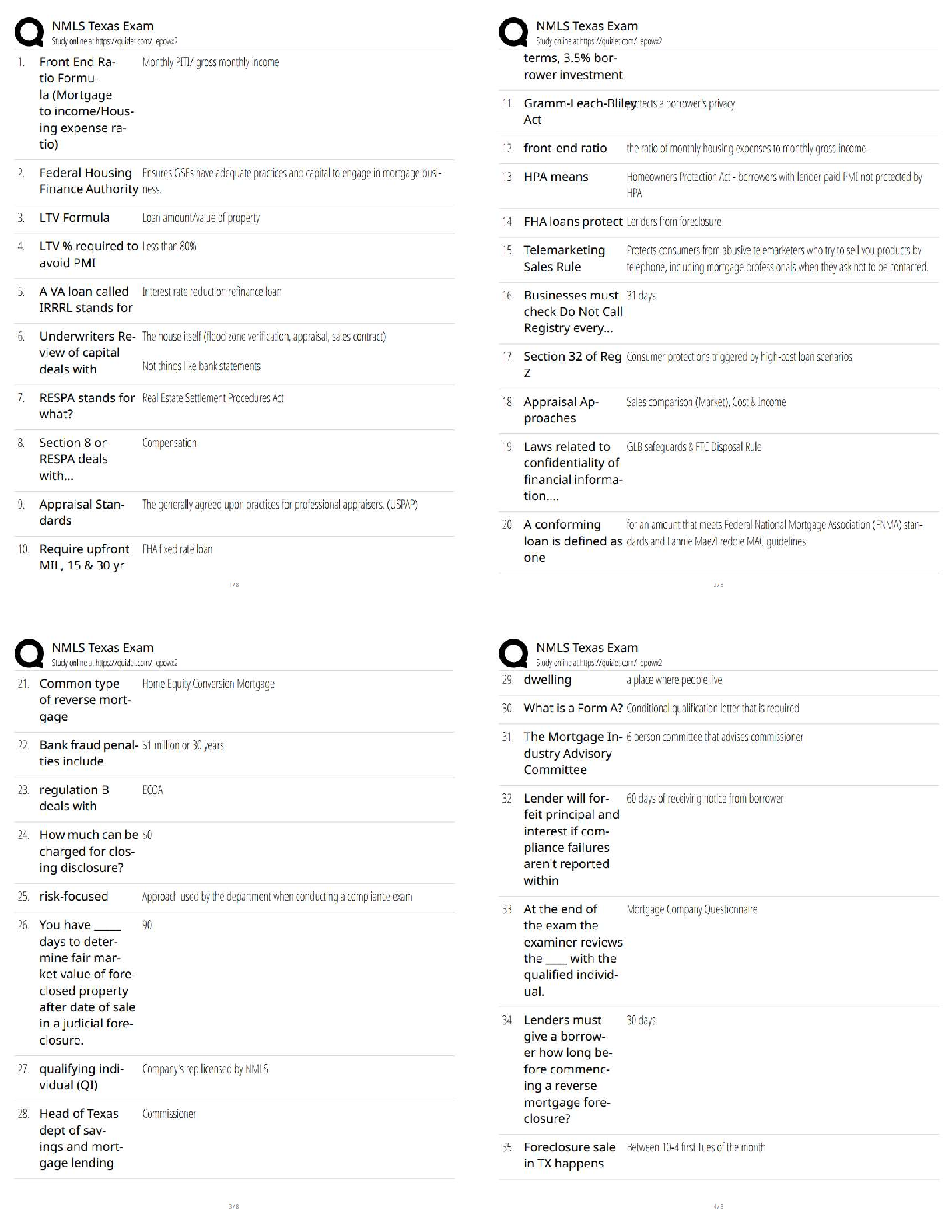
AQA A-level Psychology: Memory Latest 2023 Graded A+ Capacity The amount of information that can be stored. Coding The format in which information is stored. Duration The amount of time informa ... tion can be stored. Episodic memory A type of LTM. Store of personal events such as the last time you went to the beach. Semantic memory A type of LTM store. Stores general information, knowledge that's shared by everyone for example that Paris is the capital of France. Procedural memory A type of LTM store. Responsible for how to do things, also known as motor skills. For example how to ride a bike. Declarative memory It refers to memories which can be consciously recalled such as facts and events. Sensory register duration Holds information for fractions of a second, after the physical stimulus is no longer available. Varies depending on the sense. Short-term memory duration Up to 30 seconds. Long- term memory duration A few minutes to a lifetime. Long-term memory capacity Potentially unlimited. Short-term memory capacity 7+-2 Sensory register capacity The visual information/sound that are being experienced at a given moment. Long-term memory coding Mainly semantic. Short-term memory coding Mainly acoustic. Sensory register coding In its original form- so there a register for each sense( iconic-visual, haptic-touch, echoic-sound, olfactory-smell, gustatory-taste). Limitations of the multi-store model • it's too simple •rehearsal isn't always necessary in transferring material from STM to LTM. • there's more than one type of rehearsal • there's more than one type of STM The multi-store model of memory Proposed by Atkinson and Shiffrin in 1968 to visualise memory as a flow we f information through an information processing sysytem. Attention Information is transferred from one store to another. You pay attention to pass information from the sensory register store to the STM. Rehearsal Is needed to pass information from the STM to LTM. Forgetting Memory traces in STM are fragile and can be lost within 30 seconds. Through displacement or decay, unless repeated (rehearsed). Memory in the LTM is lost through decay, retrieval failure or interference. Retrieval Being able to get information out of our memory. Decay Information that's lost over time if not used. Displacement information is lost by new information. Displacing the old, due to the limited capacity of STM. The Central Executive Oversees and coordinates the other components (slave systems). It has a limited capacity (so it can't attend to too many things at once). Responsible for a range of important control processes e.g. switching between tasks. Decides what information to attend to. Phonological loop Has a limited-capacity and is a temporary storage system for holding verbal information. Divided into the phonological store (inner ear) and the articulating loop (inner voice). Phonological store (inner ear) Where we passively hold information. Articulating loop (inner voice) Where we actively repeat information. Visuo-spatial sketchpad Where we store visual information can be thought of as our inner eye. Has a limited capacity. Divided into the visual cache and inner scribe. Visual cache A passive store for information about visual form and colour. Inner scribe An active rehearsal mechanism processing spatial and movement information. Episodic buffer Added in 2000. General storage facility holding and combining information from the central executive, Visio-spatial sketchpad and the phonological loop. Contains visual and acoustic properties, cannot be stored in any other systems. Stores information from the LTM for brief periods. Has a limited capacity. The working memory model Designed by Baddeley and Hitch (1974) as an alternative to the multi-store model of memory. Because they thought it underestimated the complexity of the STM. Proactive Interference (PI) When old information interferes with new information. Retroactive Interference (RI) When new information interferes with old information. Limitations with interference studies The majority of research on interference is carried out in controlled laboratory settings meaning they lack ecological validity. Encoding specificity principle The idea that cues and contexts specific to a particular memory will be most effective in helping us recall. Retrieval failure The inability to recall long-term memories because of inadequate or missing retrieval cues. Eye witness testimony (EWT) Any firsthand account given by an individual of an event they have seen. Misleading questions Question that suggests what answer is desired or leads to the desired answer. Post-event discussion A conversation between co-witnesses or an interviewer and an eyewitness after a crime has taken place which may contaminate a witness' memory for the event. Anxiety The condition of feeling uneasy or worried about what may happen. The role of anxiety Some evidence states that people might be better at remembering things if you are anxious, whereas other evidence suggests you may be less reliable when you're anxious, as you are focused on yourself. cognitive interview -Change of order -Change of perspective -Mental reinstatement -Report everything Who created the cognitive interview and why? designed by Geiselman et al (1985) and designed to be used by police investigators. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 7 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

AQA A Level Psychology Memory Bundled Exams Questions and Answers 100% Pass
AQA A Level Psychology Memory Bundled Exams Questions and Answers 100% Pass
By Nutmegs 2 years ago
$19
7
Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 07, 2023
Number of pages
7
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 07, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
127










.png)