Chemistry > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > AQA A-Level Organic Synthesis Latest 2023 Already Passed (All)
AQA A-Level Organic Synthesis Latest 2023 Already Passed
Document Content and Description Below
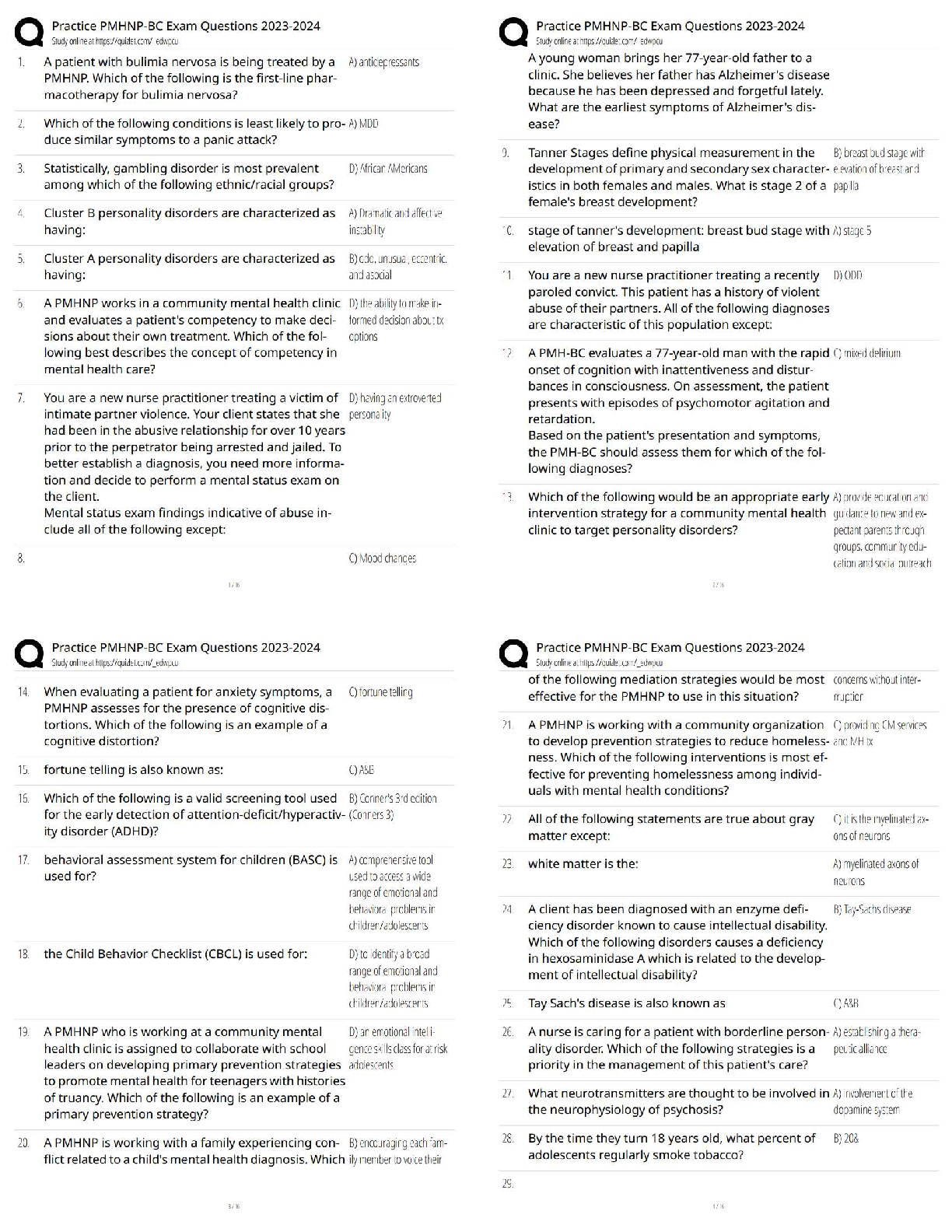
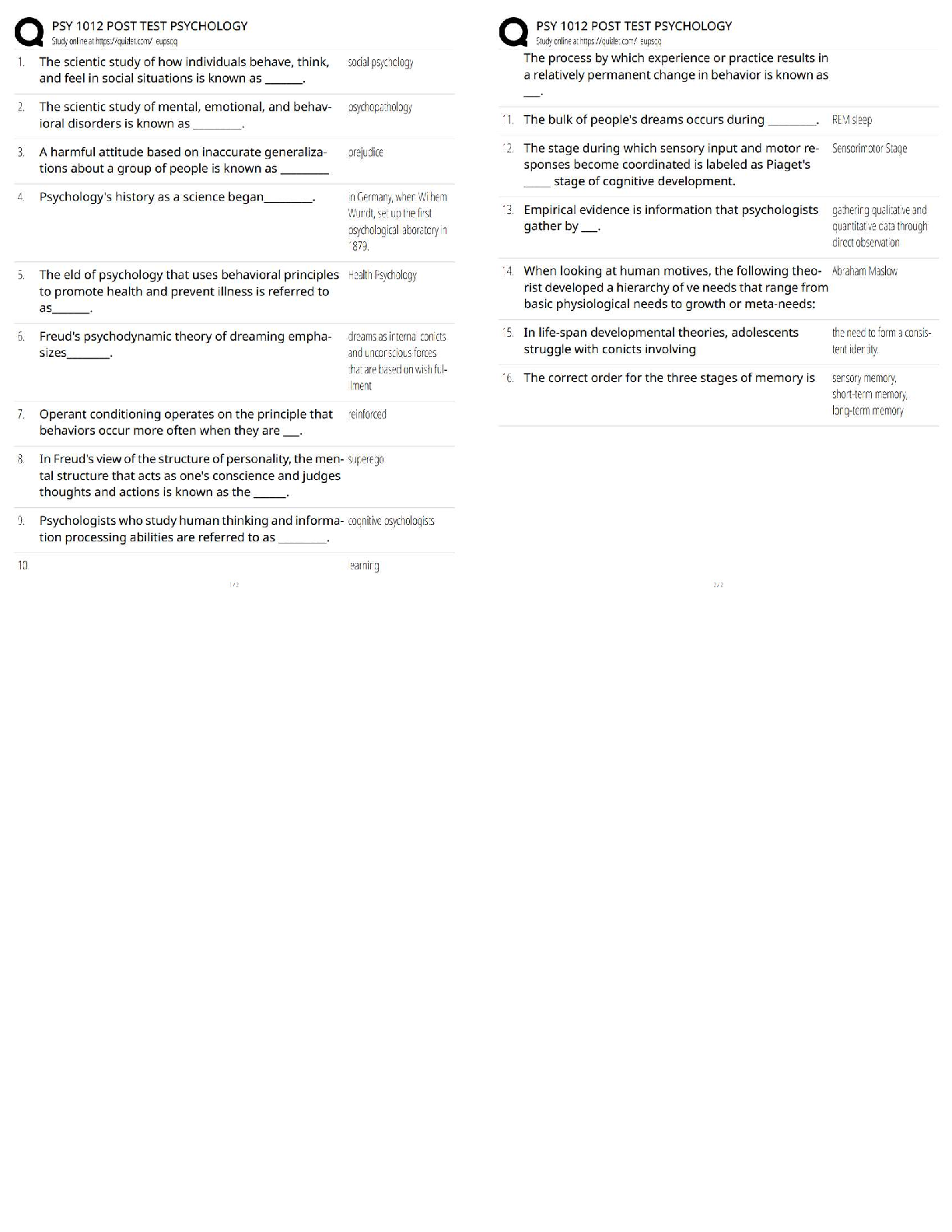
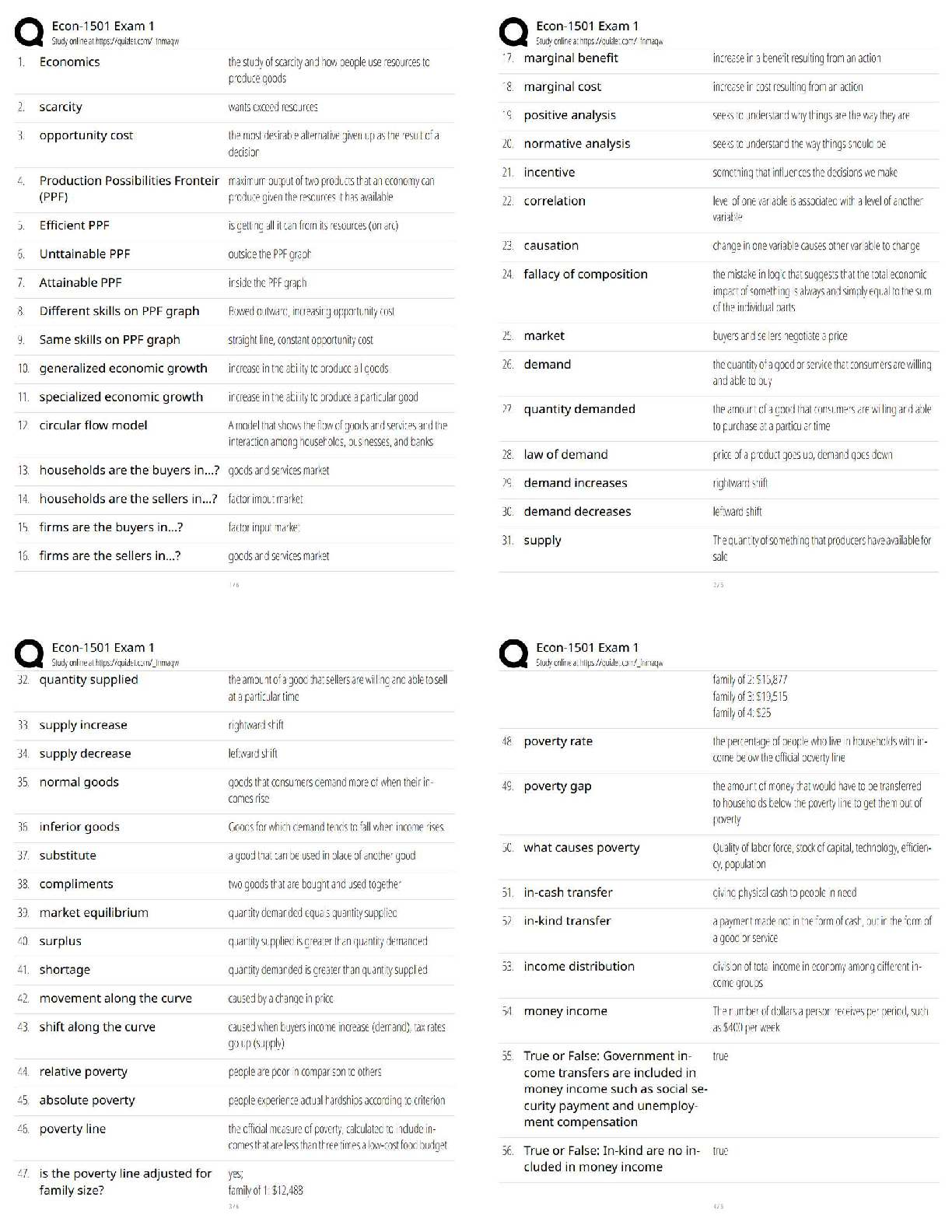
AQA A-Level Organic Synthesis Latest 2023 Already Passed Alkane to Halogenoalkane ✔✔X2, UV light Mechanism = free radical substitution Halogenoalkane to Alkene ✔✔KOH, dissolved in ethanol ... and heated under reflux Mechanism = Elimination Alkene to Halogenoalkane ✔✔HX at room temperature Mechanism = Electropholic Addition Halogenoalkane to Alcohol ✔✔Warm NaOH/KOH, heated under reflux Mechanism = Nucleophilic Substitution Halogenoalkane to Nitrile ✔✔KCN, dissolved in ethanol and heated under reflux Mechanism = Nucleophilic Substitution Halogenoalkane to Primary Amine ✔✔Use a primary Halogenoalkane, excess ammonia and heat Mechanism = Nucleophilic Substitutuon Halogenoalkane to Secondary/Tertiary Amines, their Salts and Quaternary Ammonium Salts ✔✔Use a non primary Halogenoalkane and excess ammonia and heat Mechanism = Nucleophilic Substitution Nitrile to Primary Amine ✔✔LiAlH4 with a dilute acid OR H2 gas with a nickel catalyst at a high temperature Reaction type = Reduction Alkene to Dibromoalkane ✔✔This is the test for an Alkene. Add bromine water at room temperature Solution will decolourise if Alkene is present. Alkene to Alcohol ✔✔H3PO4 catalyst, steam at 300 deg at 60 atm Reaction type = Hydration OR H2O with a cold H2SO4 catalyst Mechanism = electrophilic Addition Alcohol to Alkene ✔✔Concentrated H2SO4 heated under reflux Mechanism = Elimination Alcohol to Aldehyde ✔✔Primary Alcohol, acidified potassium dichromate and heated under distillation Reaction type = Oxidation Alcohol to Ketone ✔✔Secondary Alcohol, acidified potassium dichromate and heated under reflux Reaction type = Oxidation Aldehyde/Ketone to Alcohol ✔✔NaBH4, in Water with Methanol Mechanism = Nucleophilic Addition Aldehyde to Carboxylic Acid ✔✔Acidified potassium dichromate heated under reflux Reaction type = Oxidation Aldehyde/Ketone to Hydroxynitrile ✔✔KCN, H2SO4 at room temperature Mechanism = nucleophilic Addition Alcohol to Carboxylic Acid ✔✔Primary alcohol acidified potassium dichromate heated under reflux Reaction type = Oxidation Ester to Carboxylic Acid ✔✔Dilute H2SO4 catalyst, H2O, heated under reflux Reaction type = Acid Hydrolysis OR Dilute NaOH, heated under reflux Reaction type = Base Hydrolysis Carboxylic Acid to Ester ✔✔Alcohol, concentrated H2SO4 catalyst and heat Reaction type = Esterification Acyl Chloride / Acid Anhydride to Carboxylic Acid ✔✔H20 at room temperature Mechanism = Nucleophilic Addition Elimination Acyl Chloride / Acid Anhydride to Ester ✔✔Alcohol at room temperature Mechanism = Nucleophilic Addition Elimination Acyl Chloride / Acid Anhydride to Primary Amine ✔✔NH3 at room temperature Mechanism = Nucleophilic Addition Elimination Acyl Chloride / Acid Anhydride to N-substituted Amide ✔✔Amine at room temperature Mechanism = Nuclephilic Addition Elimination Benzene to Nitrobenzene ✔✔Concentrated H2SO4, Concentrated HNO3 (to make the NO2+) below 50 deg Mechanism = Electrophilic Substitution (when attaching to benzene) Benzene to Phenylketone ✔✔RCOCL, ALCL3 catalyst, heated under reflux and in a nonaqueous environment Reaction type = Friedel-Crafts Acylation Nitrobenzene to Aromatic Amine ✔✔Tin, Concentrated HCl, heated under reflux then add NaOH Reaction type = Reduction Aromatic Amine to N-Phenylethanamide ✔✔CH3COCl, r.t.p The test to distinguish between aldehyde and ketones ✔✔Tollen's reagent. If aldehyde is present then a silver mirror will form on the test tube (silver precipitate) [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

AQA A LEVEL Chemistry Bundled Exams Questions and Answers 100% Pass
AQA A LEVEL Chemistry Bundled Exams Questions and Answers 100% Pass
By Nutmegs 2 years ago
$22
13
Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 07, 2023
Number of pages
6
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 07, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
149










.png)