AAPD - Sedation Quiz
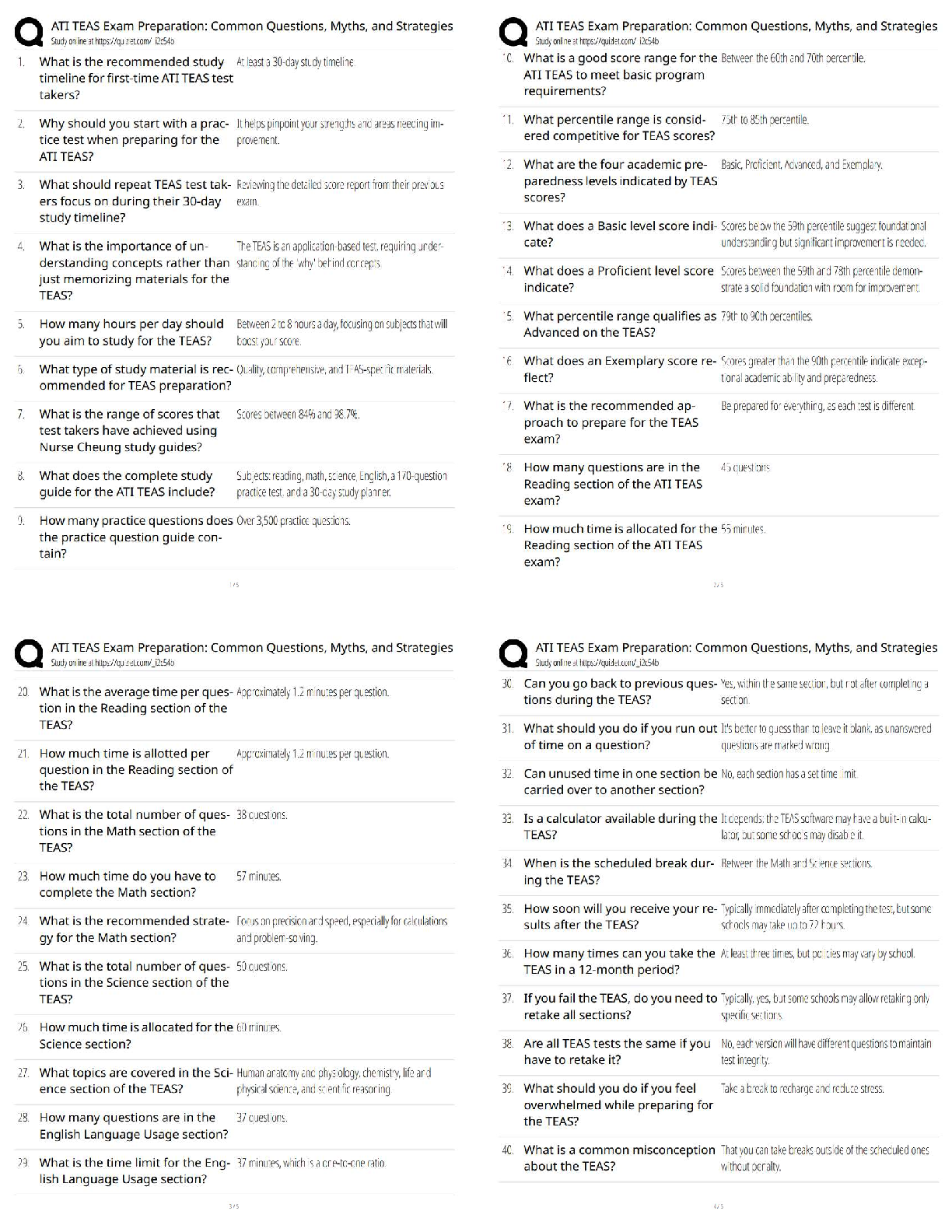
What level of sedation is anxiolysis? - ✔✔Minimal Sedation
What level of sedation is conscious sedation? - ✔✔Moderate Sedation
What level of sedation is analgesia? - ✔✔Moderate to Deep
How much o
...
AAPD - Sedation Quiz
What level of sedation is anxiolysis? - ✔✔Minimal Sedation
What level of sedation is conscious sedation? - ✔✔Moderate Sedation
What level of sedation is analgesia? - ✔✔Moderate to Deep
How much of delay is the pulse oximeter? - ✔✔6-12 seconds
Is reflex withdrawal a purposeful response? - ✔✔No, must be acommanied by another response
(pushing away)
Duration is long or short? Choral Hydrate - ✔✔Long
Duration is long or short? Pentobarbital - ✔✔Long
Duration is long or short? Phenothiazine - ✔✔Long
Level of sedation for anatomic airway abnormalities or extreme tonsillar hypertrophy -
✔✔Consult recommended
Level of sedation for extreme tonsillar hypertrophy - ✔✔Consult recommended
When is it preferatble to have 2 or more adults accompany children for sedation? - ✔✔Child is
still in car safety seats
Complications facilities most be prepared for - ✔✔Airway obstruction, hypoventilation,
hypoxemia, apnea
Consequence of unmanaged airway - ✔✔CV: hypotension, cardiopulmonary arrest
Documentation before sedation - ✔✔1. Informed consent, 2, Instructions and Information
NPO before elective surrgery: Clear liquids - ✔✔2 hours Minimum
NPO before elective surrgery: Breast Milk - ✔✔4 hours Minimum
NPO before elective surrgery: Infant Formula - ✔✔6 hours Minimum
NPO before elective surrgery: Nonhuman Milk - ✔✔6 hours Minimum
NPO before elective surrgery: Light Meal - ✔✔6 hours Minimum
Immobilization device requirements - ✔✔No airway obstruction, chest restriction, exposed hand
or foot, monitoring, monitoring
Example of medications that may inhibit cytochrome P450 - ✔✔St. John's wort
Example of medications that may inhibit cytochrome P450 - ✔✔Echinacea
What may Kava do to sedatives? - ✔✔Increase the effects
What does Kava effect? - ✔✔Potentiates GABA inhibitory neurotranmission
How does Valerian produce sedations? - ✔✔Modulates GABA neurotransmission and receptor
funtion
Example of medications that may inhibit cytochrome P450 - ✔✔Erythromycin
Example of medications that may inhibit cytochrome P450 - ✔✔Cimetidine
Sedation medication that processed through cytochrom P450 - ✔✔Midazolam
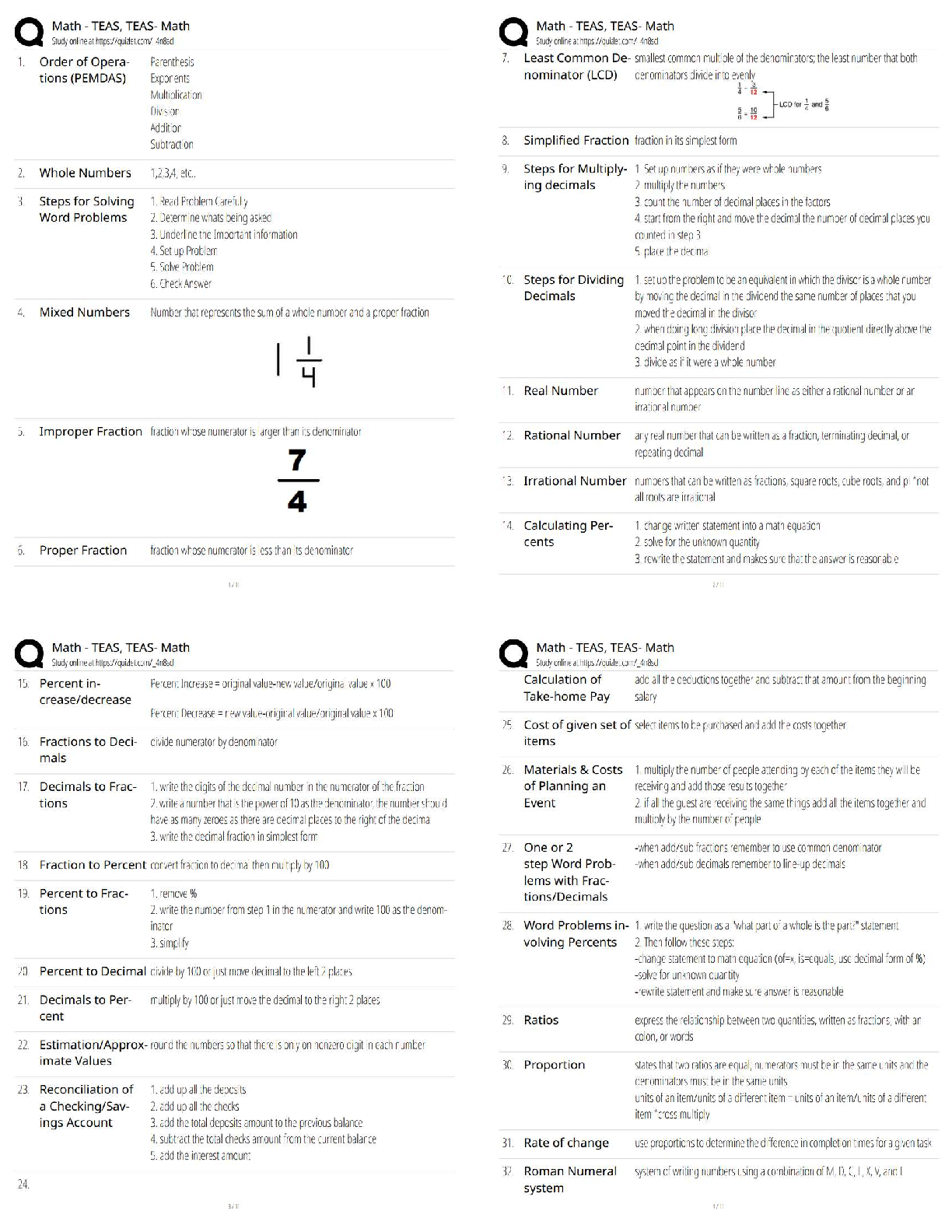
Components of Health Evaluations: 1 - ✔✔Age and Weight
Components of Health Evaluations: 2 - ✔✔Health History
Components of Health Evaluations: 3 - ✔✔Review of Systems: Caridac, Pulmonary, Hepatitic
funcion
Components of Health Evaluations: 4 - ✔✔Vital Signs: HR, BP, Respiratory Rate, Temp
Components of Health Evaluations: 5 - ✔✔Physical examination: airway evaluation
Components of Health Evaluations: 6 - ✔✔Physical status: ASA classification
Components of Health Evaluations: 7 - ✔✔Medical home contact information
Components of Health History: 1 - ✔✔Allegies, adverse drug reaction
Components of Health History: 2 - ✔✔Medication/drug hisootroy (OTC, herbal, illicit)
Components of Health History: 3 - ✔✔Relevants diseases, phyical abnormalities, neurologic
impairment, airway (apnea, snoring)
Components of Health History: 4 - ✔✔Pregnancy Status
Components of Health History: 5 - ✔✔Summary of previous relavent hospitilizations
Components of Health History: 6 - ✔✔History of sedation/GA and complications
Components of Health History: 7 - ✔✔Relevant family hx (esp. anethesia)
Components of Health History: 8 - ✔✔Prescriptions- copy if RX written, not to be administered
withoue benefit of direct supervision by medical personnel
Normal Pulse Rates: <1 y.o. - ✔✔100-160 bpm
Normal Pulse Rates: 1 - 10 yr - ✔✔60-140 bpm
Normal Pulse Rates: 10+ yr - ✔✔60-100 bpm
Normal Pulse Rates: Well conditioned athleted - ✔✔40-60 bpm
Time of Documentation: Health Evaluation - ✔✔At time of sedation (before sedation
Time of Documentation: Instructions and care instruction - ✔✔Before sedation
Time of Documentation: Informed consent - ✔✔Before sedation
Time of Documentation: Prescription - ✔✔At time of sedation
Time of Documentation: Sedation Record - ✔✔During treatment
Documnation during treatment:1 - ✔✔Time out
Documnation during treatment:2 - ✔✔Drugs administeried (name, route/site, dosage, effect),
oxygen & inhalation medications (%, duration)
Documnation during treatment:3 - ✔✔Level of consciouness/responsiveness + Vitals (BP, HR,
RR, O2)
Documnation during treatment:4 - ✔✔Adverse
Documnation after treatment: - ✔✔Level of consciouness/responsiveness + Vitals (BP, HR, RR,
O2at room air)
Simple evaluation tool to use after discharge - ✔✔Ability to remain awak for >20min in quiet
environment
Acronym for sedation perparation/set up - ✔✔SOAPME
SOAPME: S - ✔✔Suction (size appropriate, functioning
SOAPME: O - ✔✔Oxygen (adequate supply, flow)
SOAPME: A - ✔✔Airway management tools (size appropriate)
SOAPME: P - ✔✔Pharmacy (antagonist ans basic drugs of emergency life support)
SOAPME: M - ✔✔Monitors (functioning - e.g. oximeter, BP)
SOAPME: E - ✔✔Equipment or durgs (special for a particular case, e.g. defibrilator)
Yankuer type suction - ✔✔Yankuer.jpg
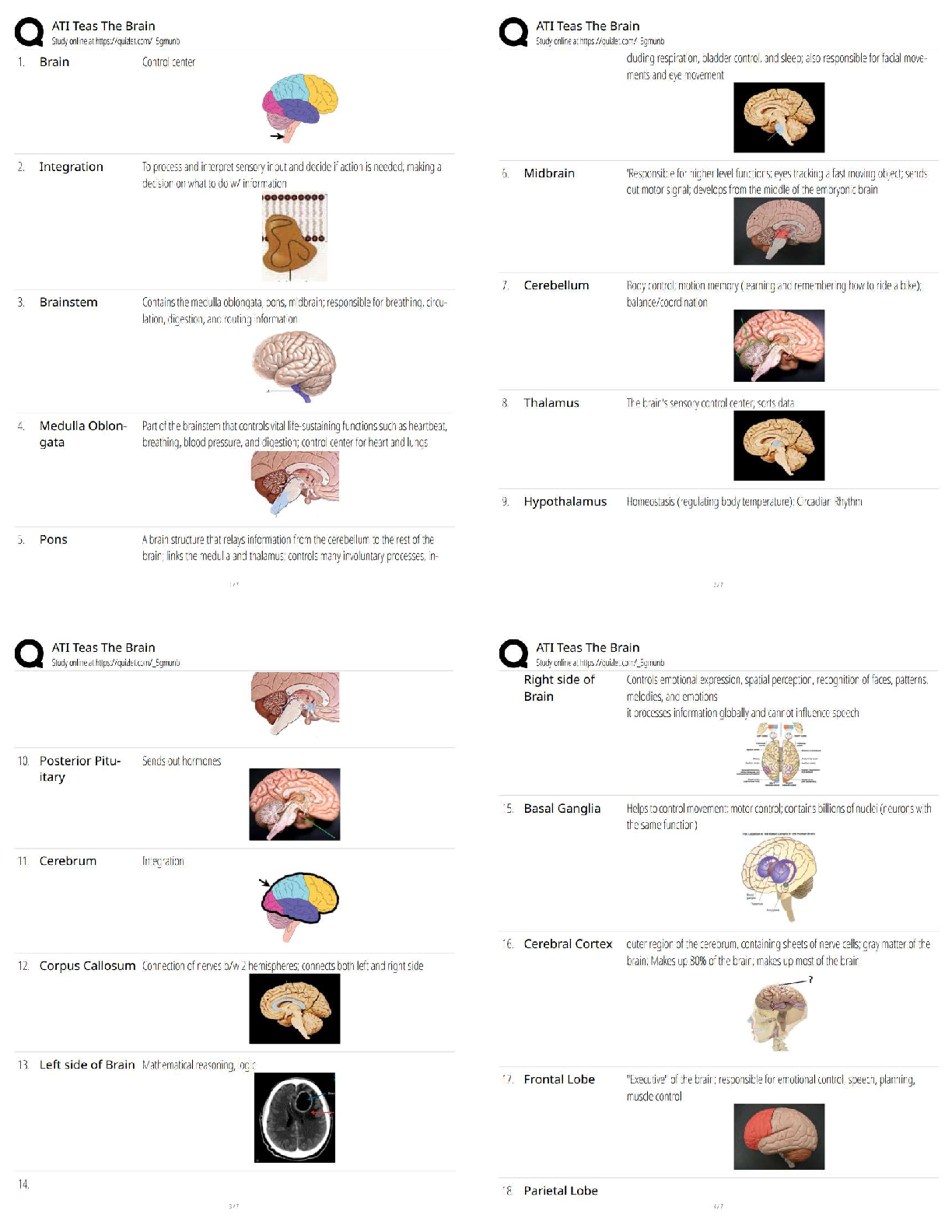
Practiioner qualifications for moderate sedation: 1 - ✔✔Competent to proivde monitoring and
manage complications to deep sedation
Practiioner qualifications for moderate sedation: 2 - ✔✔Bag-vavle mask ventilation
Practiioner qualifications for moderate sedation: 3 - ✔✔PALS training (required)
Practiioner qualifications for moderate sedation: 4 - ✔✔Regular skill reinforcement (strongly
encouraged)
Is PALS Training Required for Moderate Sedation? - ✔✔Yes
Minimum ariway skill required for Moderate Sedation - ✔✔Bag-vavle mask ventilation, PALS
Is PALS Training Required for Moderate Sedation? - ✔✔Yes
Is skill reinforcement required for Moderate Sedation? - ✔✔No but strongly encourgaed
Support personnel qualifications for moderate sedation: 1 - ✔✔Pediatric basic life support
Support personnel qualifications for moderate sedation: 2 - ✔✔Specific assignments in event of
emergency
Support personnel qualifications for moderate sedation: 3 - ✔✔Current knowledge of emergency
cart invintory
Is support personnel required for moderate sedation - ✔✔Yes
Duties of support personnel in moderate sedation - ✔✔Monitor phyiologic parameters, assis in
supporitiave or resuscitation measure
May support personnel assist in moderate sedation? - ✔✔Yes - in interriptible patient-related
tasks of shor duraction
Pracitioners should/must/or encourages to review or practice emergency drills? - ✔✔Should
Monitoring/Documentation for Moderate sedation Requirements: 1 - ✔✔Baseline Vitals or
documentation why can't get
Monitoring/Documentation for Moderate sedation Requirements: 2 - ✔✔Drugs used (details),
vitals (time based)
Monitoring/Documentation for Moderate sedation Requirements: 3 - ✔✔Vitals: Oxygen and
heart rate (shall be monitored continuously)
Monitoring/Documentation for Moderate sedation Requirements: 4 - ✔✔BP and RR (shall be
monitored intermittently)
Monitoring/Documentation Moderate sedation: Restraint Recommendations - ✔✔No airway
obstruction, chest restriction, exposed hand or foot, monitoring, monitoring
Monitoring/Documentation Moderate sedation: After procedure requirements 1 -
✔✔Functioning Sunction Apparatus
Monitoring/Documentation Moderate sedation: After procedure requirements 2 - ✔✔>90%
oxygen delivery, positive pressure ventilation
What % of oxygen delivery is required for pt receiving moderate sedation? - ✔✔>90%
Is a bag vale mask considerted positive-pressure ventilation? - ✔✔Yes
How long must a patient stay awake before discharge? - ✔✔20 min in quiet environment
True or False? The state abd risks of deep sedation is less than general anestheisa - ✔✔False -
they are indistinguishable
Personnel qualifications for deep sedation: 1 - ✔✔At least one trained in Pediatric Advanced
Life Support (Required)
Personnel qualifications for deep sedation: 2 - ✔✔Skilled in airway management and
cardiopulomonary resuscitation
Personnel qualifications for deep sedation: 3 - ✔✔One person whose only responsibility is to
observe vitals, airway patency, ventilation and administer or direct drug administration
May support personnel also assist in deep sedation? - ✔✔At least one person whose only
responsibility is to observe vitals, airway patency, ventilation and administer or direct drug
administration
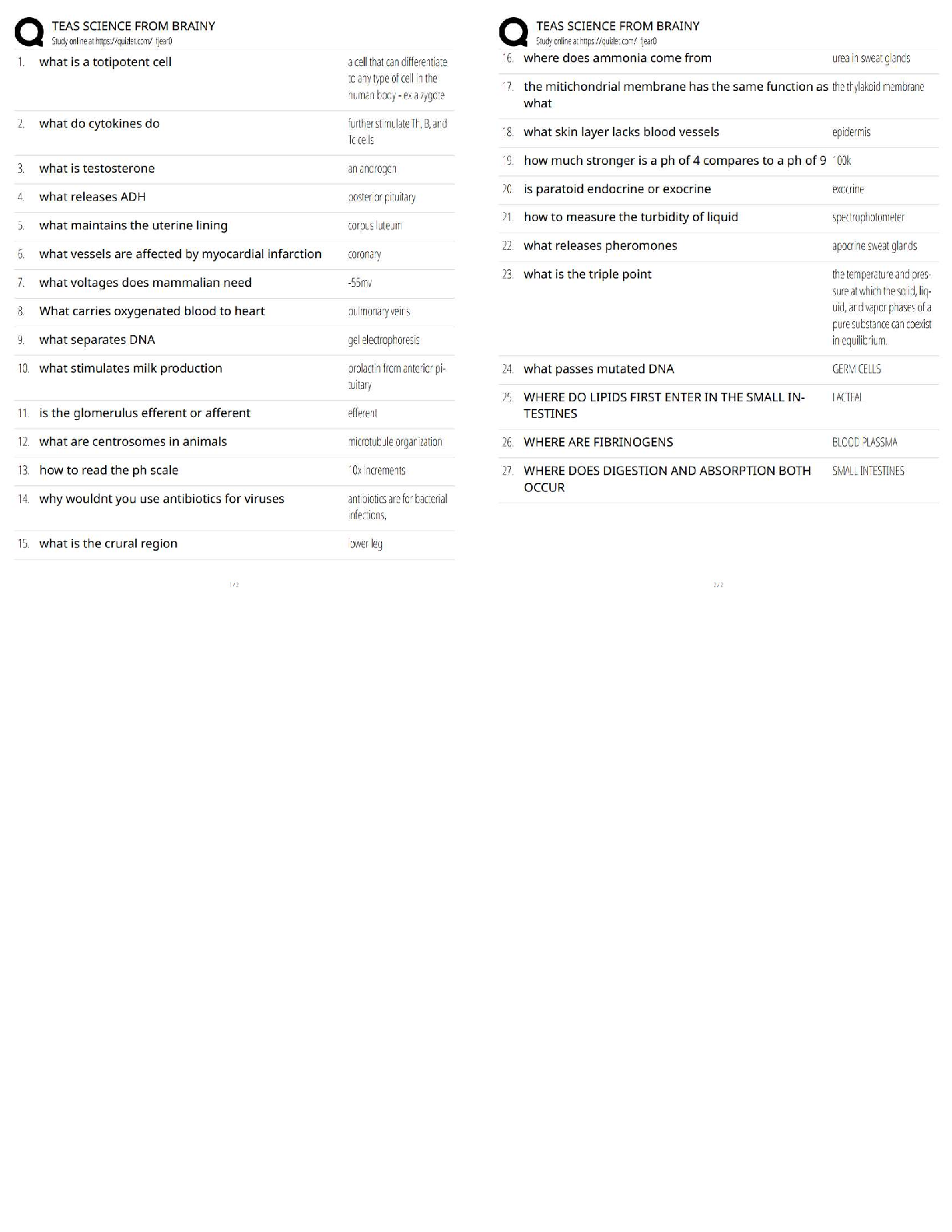
What does intranasal drug administration considered equivalent to? Oral, Transdermal, or IV -
✔✔IV - bypasses the liver
Does a conscious sedation permit allow for intranasal delivery? - ✔✔No - intranasal is
considered paraental
Monitoring/Documentation for Moderate sedation: Equipment - ✔✔Moderate sedation
recommendations + Readily Available: ECG monitor, AED
Monitoring/Documentation for Moderate sedation Requirements: 1 - ✔✔Vascular Access - IV
line shold be in place or someone readiy able to palce one
Monitoring/Documentation for Moderate sedation Requirements: 2 - ✔✔Same as moderate but
O2 and HR should be documented every 5 min
Monitoring/Documentation for Moderate sedation Requirements: 3 - ✔✔Precordial or
capnograph encouraged
Monitoring/Documentation for Moderate sedation Requirements: 4 - ✔✔Drugs administeried
(name, route/site, dosage, effect), oxygen & inhalation medications (%, duration)
Monitoring/Documentation Deep sedation: After procedure requirements - ✔✔Same as
moderate
Capnography - ✔✔Expired CO2 monitoring
Is capnography required? - ✔✔No - it is encouraged, particurly if other means of monitoring is
limited
True/False: Capnography are prone to false positive so cannot be used to detect complete airway
obstruction/apnea - ✔✔False - True for fals positive but accurate in detecting obstruction
Tru/False: Use of patient stimulators is not recommended - ✔✔False - It is encouraged to better
train medical professional to respond more appropriately and effectively to rare events
What are risk do conventional monitoring devices (ECG, pulse ox) pose during MRI? -
✔✔Thermal injury - if wires coild
What alternative montiroing methods are there for MRI? - ✔✔Capnography
What is minimum oxgene flow rate during nitrous oxide delivery? - ✔✔25%
True/False: Nitrous oxide delivery must cover the mouth and nose. - ✔✔TRUE
True/False: Nitrous oxide delivery must be used in conjunction with a calibrated and functional
O2 analyzer. - ✔✔TRUE
What is the maximum of nitrous oxide to be considered minimal sedation? - ✔✔50% - when
used alone.
Tru/False: Local anesthetics do not considered sedatives when used only with nitrous oxide. -
✔✔True - even though they have sedative properties.
Nitrous oxide to be used to achieve moderate or deep sedation? - ✔✔Yes - riske occurs at > 50%
or when used in combination with other medications
Procaine: Ester or Amide - ✔✔Ester
Chloroprocaine: Ester or Amide - ✔✔Ester
Tetracaine: Ester or Amide - ✔✔Ester
Lidocaine:Ester or Amide - ✔✔Amide
Mepivaciane: Ester or Amide - ✔✔Amide
Bupiacaine: Ester or Amide - ✔✔Amide
Levobupicaine: Ester or Amide - ✔✔Amide
Ropivacine: Ester or Amide - ✔✔Amide
Articaine: Ester or Amide - ✔✔Amide
Procaine: Max dose with Epi (mg/kg) - ✔✔6 (Dental)/ 10 (medical)
Chloroprocaine: Max dose with Epi (mg/kg) - ✔✔12 (Dental)/ 20(medical)
Tetracaine: Max dose with Epi (mg/kg) - ✔✔1 (Dental)/ 1.4 (medical)
Lidocaine:Max dose with Epi (mg/kg) - ✔✔4.4 (Dental)/ 7.0 (medical)/ 3-5 for IV regional
anestheis
Mepivaciane: Max dose with Epi (mg/kg) - ✔✔4.4 (Dental)/ 3.0 (medical)
Bupiacaine: Max dose with Epi (mg/kg) - ✔✔1.3 (Dental)/ 3.0 (medical)
Levobupicaine: Max dose with Epi (mg/kg) - ✔✔2 (Dental)/ 3.0 (medical)
Ropivacine: Max dose with Epi (mg/kg) - ✔✔2 (Dental)/ 3.0 (medical)
Articaine: Max dose with Epi (mg/kg) - ✔✔7 (Dental)
When epinephrine is not used, local anesthetic doses should be increased or decreased? -
✔✔Decreased
In infants <6 months, doses of amides should be decreased by what % - ✔✔30%
A 2% concentration solution contains how many mg/mL? - ✔✔20.0mg/mL
[Show More]




















.png)