RNC-NIC Exam Review
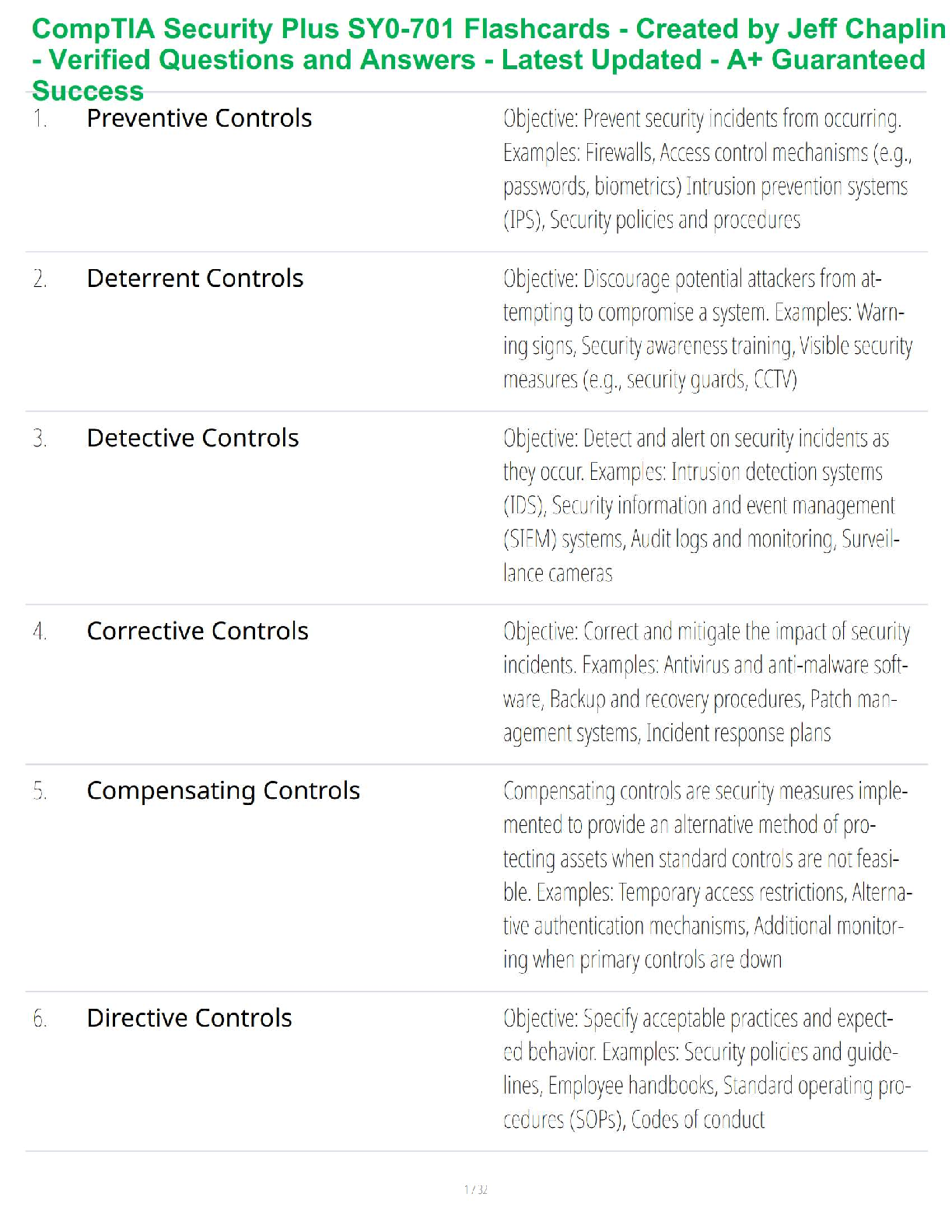
Neonates born to mothers with uncontrolled asthma are at increased risk for
a. acidosis
b. apnea
c. low birth weight - ✔✔C-Neonates born to women with asthma that is not under control are at
incr
...
RNC-NIC Exam Review
Neonates born to mothers with uncontrolled asthma are at increased risk for
a. acidosis
b. apnea
c. low birth weight - ✔✔C-Neonates born to women with asthma that is not under control are at
increased risk for prematurity and low birth weight. If asthma is controlled, neonatal outcomes
are similar to those neonates born to mothers WITHOU asthma.
Pregnancy outcomes of women with renal disease most relates to
a. etiology of renal disease
b. degree of renal insufficiency
c. length of time since onset of the disease - ✔✔B-regardless of etiology of the renal disease in
pregnancy, the two factors that most influence pregnancy outcomes is the degree of renal
insufficiency and the presence of hypertension.
Untreated maternal thyrotoxicosis can lead to
a. congenital anomalies
b. neonatal hypothyroidism
c. preterm delivery - ✔✔C-If a woman with hypothyroidism or thyrotoxicosis is not treated
during pregnancy, there is a high incidence of preterm delivery, low birth weight and still births.
Congenital anomalies are not common. Hypothyroidism may result in the neonate due to the
thyroid medications not the maternal disease.
Unregulated glucose control in a woman with diabetes early in pregnancy can predispose the
fetus to
a. chromosomal damage
b. embryonic growth delays
c. teratogenic effects - ✔✔C-Preconception counseling and early prenatal care are essential for
women with diabetes when contemplating childbirth. Uncontrolled glucose levels early in
pregnancy can lead to organogenesis and the development of congenital anomalies.
Infants with fetal alchohol syndrome demonstrate tremors, irritability and hypertonus due to
a. central nervous system injury
b. interferance with protein synthesis
c. withdrawal from alcohol - ✔✔C-Infants born with fetal alcohol syndrome usually presents
with tremors, irritability, and hypertonus. These symptoms are primarily due to alcohol
withdrawal.
Common manifestations of neonates who were exposed to cocaine in utero include
a. apnea and lethargy
b. neonatal abstinence syndrome
c. touch aversion and overstimulation - ✔✔C-Exposure to cocaine in utero leaves infants with a
wide variety of problems. Teratogenicity has had some association with cocaine exposure but its
direct link has not not been confirmed. Neonates are hypertonic, irritable and easily
overstimulated by sensory input or direct contact. To avoid any stimulation, the neonate may
totally shut down going into a deep sleep or alternatively the infant may cry incessantly. There is
no specific pattern of withdrawal as there is with neonatal abstinence syndrome and heroin
exposure.
The primary route of the transmission of neonatal systemic lupus erythematosus is
a. familial tendency
b. multifactorial inheritance
c. placental transfer of antibodies - ✔✔C-Neonates born to mothers with systemic lupus
erythematosus can demonstrate various symptoms, known as neonatal systemic lupus
erythematosus. These include rash, thrombocytopenia and cardiac abnormalities, specificallly
congenital heart block. The attributed antecedent for neonatal disease is placental transfer of antibodies from mother to fetus.
In a 34 week gestational age neonate, the expected muscle development would indicate a
a. complete Moro reflex
b. poor grasp reflex
c. weak sucking reflex - ✔✔A-At 34 weeks of gestation, the examination of muscle tone
development would include: strong synchronized sucking reflex, a strong grasp reflex, complete
Moro reflex and good extension with no tendency to adduction.
A physical finding consistent with prematurity is
a. abundant lanuga
b. accelerated plantar creasing
c. stippled areola with raised edges - ✔✔A-External criteria of determination of gestational age
involve a wide variety of physical parameters including: presence of edema, skin texture, color
and opacity, presence of lanugo, plantar creases, nipple formation and amount of breast tissue,
ear form and firmness and appearance of genitalia. Based on the options provided in the
question, the abundant lanugo is consistent with prematurity. As the infant achieves a greater
gestational age, lanugo diminishes. Plantar creases are not prominent in the premature infant and
becomes more pronounced with increasing gestational age. The nipples of premature infants are
usually flat with no definition.
Three neonates are plotted on a growth curve shown. Because of weight and gestational age, they
are at increased risk for
a. Congenital anomalies
b. hypoglycemia
c. respiratory distress syndrome - ✔✔A-Of the choices given, the only risk all these babies share
is increased of congenital anomalies. Hypoglycemia no RDS is increased for Baby B who is
term, AGA. Baby C, who is post-term, is not at risk for RDS.
When performing a gestational age assessment, the nurse should recognize that a finding that
correlates with advancing gestational age is increased
a. degree of arm flexion with arm recoil maneuver
b. resistance with scarf sign maneuver
c. square window angle - ✔✔B-In gestational age assessment, the degress of arm flexion or arm
recoil decreases with advancing gestational age as does the square window angle. With scarf sign
maneuver, increased resistance correlates with advancing gestational age.
A neonate can be assumed to be at and an advanced gestational age if neuromuscular
development demonstrates increased
a. hip flexion and adduction
b. popliteal angle
c. square window angle measurement - ✔✔A-Neuromuscular criteria can be a good indicator of
gestational age. Those findings that indicate advanced gestational age include increased hip
flexion and adduction, decreased square angle, flexed response to arm recoil, increasing
resistance with scarf sign maneuver and a low popliteal angle.
In examining the black newborn's eyes, a bright light directed toward the lens reveals a red color
that is reflected back to the examiner. This finding is consistent with
a. an intact lens
b. opacity of the lens
c. retinal detachment - ✔✔A-In examination of the eyes, a red color should be reflected from the
retina when a bright light is directed towrds the lens. This indicates an intact lens.
On physical examination of the hip, a sharp click is heard. This is suggestive of
a. dislocation
b. fracture
c. normal variant - ✔✔A-hip dislocation should be suspected if a sharp click occurs when the
examiner abducts the neonate's legs into the frog position. Soft clicks can be heard and are
common but a sharp click indicates hip dislocation. Clicks are not related to diagnosis of
fractures.
During a physical examination of a 34 week gestational age neonate, the suck/swallow relfex is
intact but the gag reflex cannot be elicited. The nurse should recognize that this is due to
a. esophageal atresia
b. neurological impairment
c. prematurity - ✔✔C-Neonatal reflexes appear in a systematic manner based on maturation of
the CNS. In a 34 week gestational age neonate, suck/swallow reflex is intact but the gag reflex
will not appear until 36 weeks gestation. Therefore, for this neonate, a lack of the gag reflex is
consistent with the stated gestational age.
A preterm neonate who required resuscitation at birth is admitted to the neonatal intensive care
unit in stable condition. Recording of the vital signs for this neonate should occur
a. every 30-60 minutes
b. once or twice during the transition
c. on admission and every 2 hours - ✔✔B-If a neonate is stable when admitted and remains
stable, vital signs should be recorded once or twice during the transition and then at least every
eight hours. If the neonate is unstable (increased heart rate or respiratory distress), vital signs
need to be recorded more frequently, at least every 30-60 minutes until stabilization occurs.
The best intervention to differentiate peripheral from central cyanosis in a 12 hour old neonate is
to
a. check hematocrit
b. check the core temperature
c. warm the infant - ✔✔C- It is essential to differentiate between central and peripheral cyanosis
in the neonate because central cyanosis can portend major cardiac or respiratory disease.
Peripheral cyanosis generally occurs in the neonate and is transient during the first 48 hours of
life. One way to differentiate is to warm the infant and see if the cyanosi improves. If it does, this
is not central cyanosis. Location of cyanosis is also a cue. In peripheral cyanosis, it usually
occurs in the extremities and central cyanosis is more generalized.
A neonate has a flat pink lesion on the face. The lesion is unilateral and has sharply deliniated
borders. Minimal blanching occurs when pressure is applied. The nurse should suspect
a. a hemangioma
b. nevus simplex
c. port wine stain - ✔✔C-The clinical scenario depicted in the question is consistent with port
wine stain. It most often appears on the face, its borders are sharp and delinieated, and blanches
minimally with pressure. Hamangiomas are bright red raised tumors on the face that can appear
on the head, neck, trunk or extremities.
A 2500 gm neonate with birth asphyixia develops hypocalcemia. this is most likely a result of
increased
a. calcitonin
b. 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D resisitance
c. parathyroid hormone - ✔✔A-Hypocalcemia occurs in three primary categories of infants:
those with birth asphyxia, those born to diabetic mothers and those who have very low birth
weight. In birth asphyxiated infants, this occurs due to increased calcitonin levels. In IDMs, it is
due to functional hypothyroidism and in very low birth weight infants, 1 25 dihydroxyvitamin D
is usually the cause.
A neonate is oliguric. A 10ml/kg body weight test dose of crystalloid is given. Oliguria persists
and furosemide is given. If the problem is post renal, the urine output will
a. decrease
b. increase
c. remain unchanged - ✔✔A-When the nature of oliguria is unclear in the neonate, a test dose of
crystalloid will assist in the determination. Following the crystalloid administration, the urine
output will decrease if the problem is postrenal.
Prolonged hypertension can be a result of what resuscitative effort?
a. High dose epinephrine administration
b. Rapid volume overload
c. Repeated Sodium Bicarbonate administration - ✔✔A-Prolonged hypertension can occur with
high dose epinephrine administration. Rapid volume expansion may lead to a brief hypertensive
episode but will more likely result in intraventricular hemorrhage. Repeated sodium bicarbonate
can cause volume overload.
To prevent potential complications during endotracheal intubation, a measure that can be
instituted is to
a. keep the total insertion time to one minute
b. provide free flow oxygen during intubation
c. use a tube size of less than 3.0 - ✔✔B-Thers is a host of complication that can occur with
endotracheal intubation and they include hypoxia, tube malposition, apnea, bradycardia or
trauma including subglottic stenosis. To prevent such complications, administration of free flow
oxygen should be an integral part of any intubation. Intubation should be done quickly and if it
takes more than 20 seconds, the procedure should be stopped to allow the infant to recover. Tube
size is based on the neonate's weight and using the smallest tube may be inappropriate depending
on the total weight of the infant.
[Show More]














.png)