Pharmacology > EXAM > Pharmacology HESI EXAM QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS AND RATIONALE AT THE LAST PAGES 2021 DOCS (All)
Pharmacology HESI EXAM QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS AND RATIONALE AT THE LAST PAGES 2021 DOCS
Document Content and Description Below
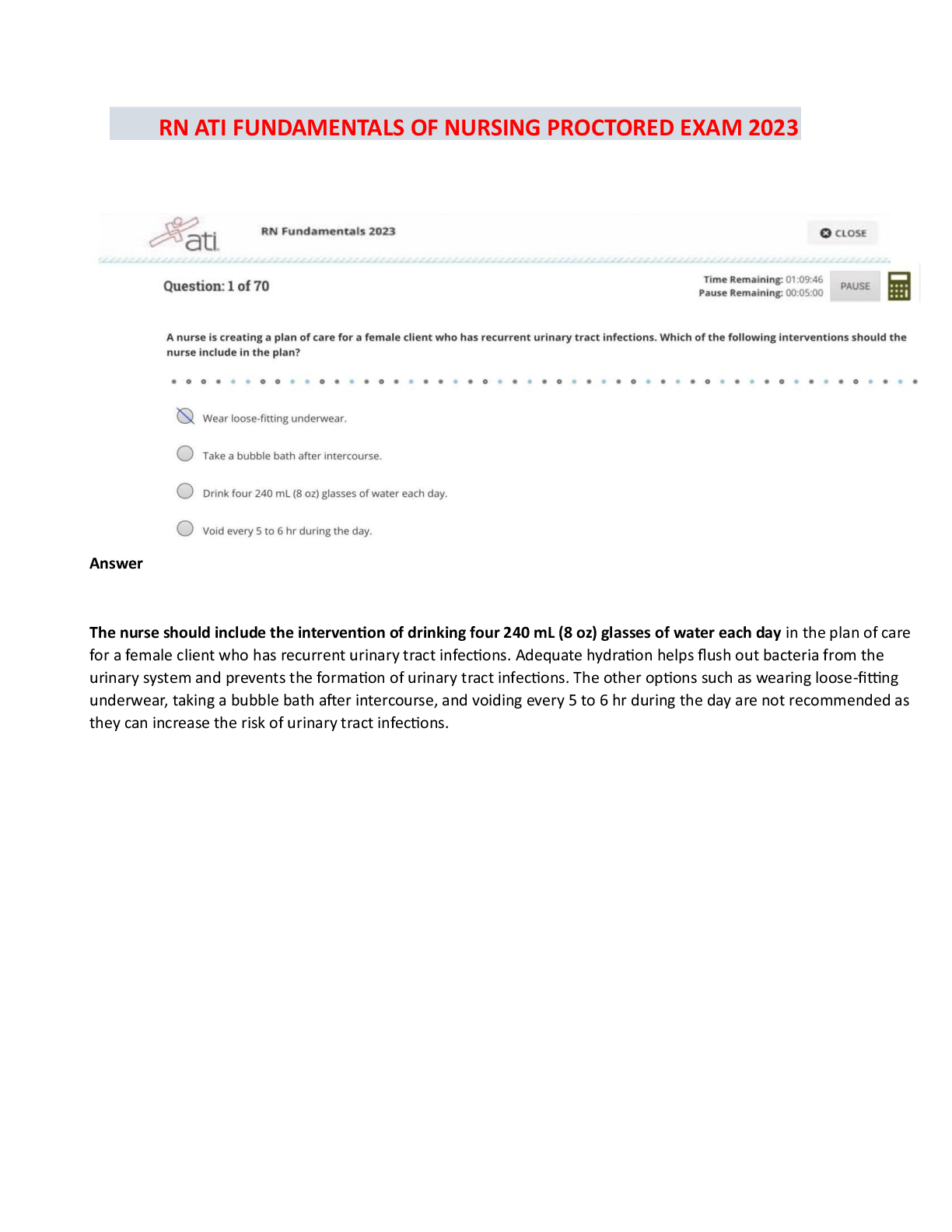
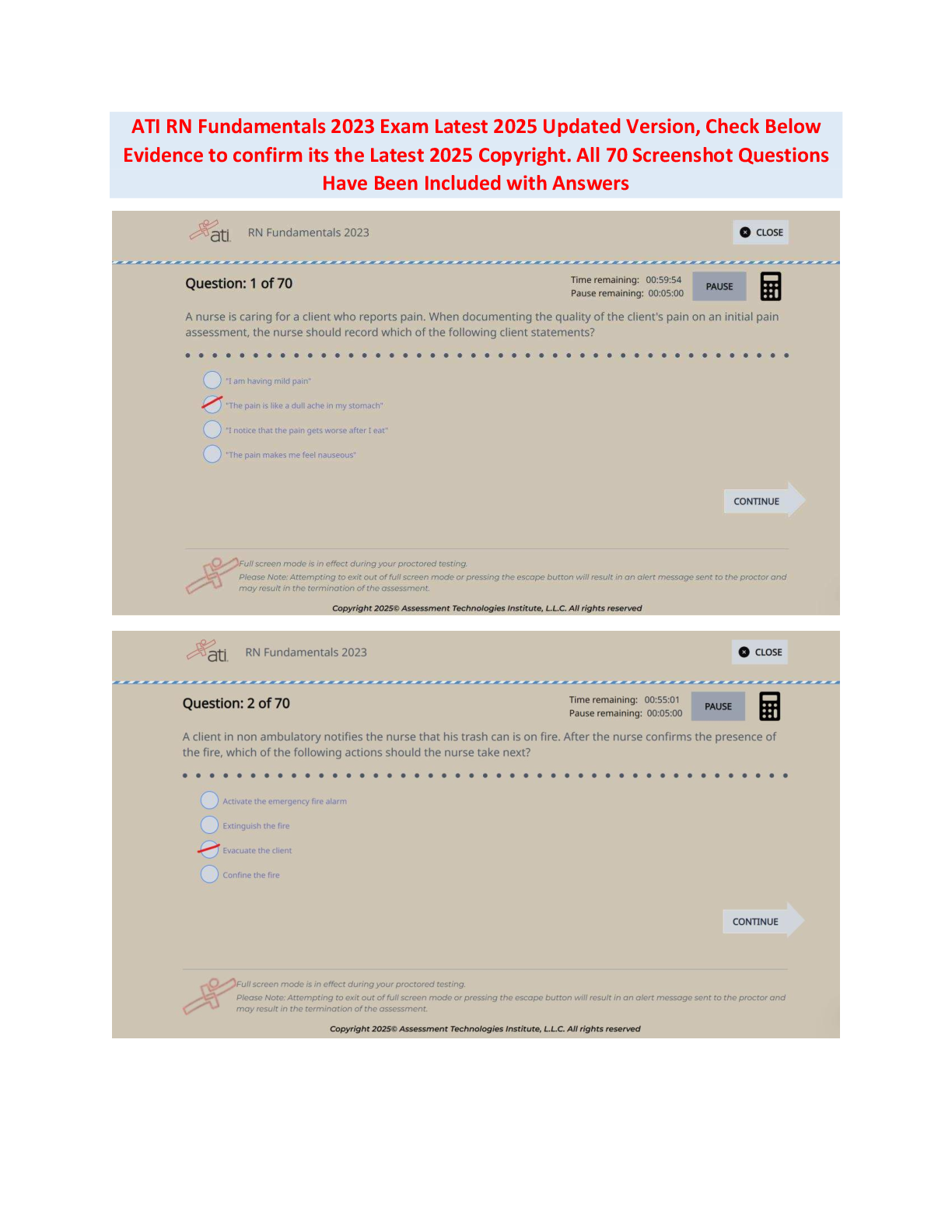
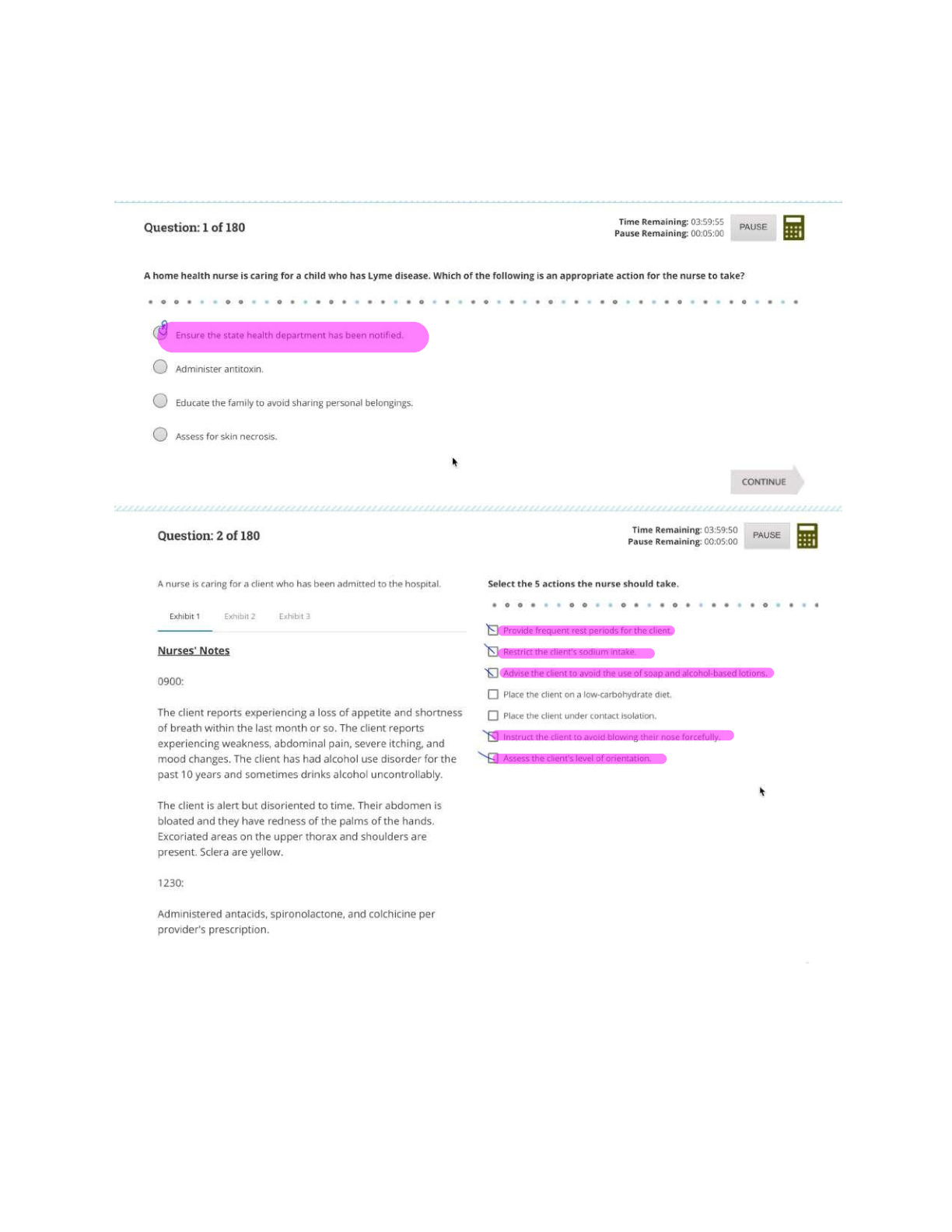
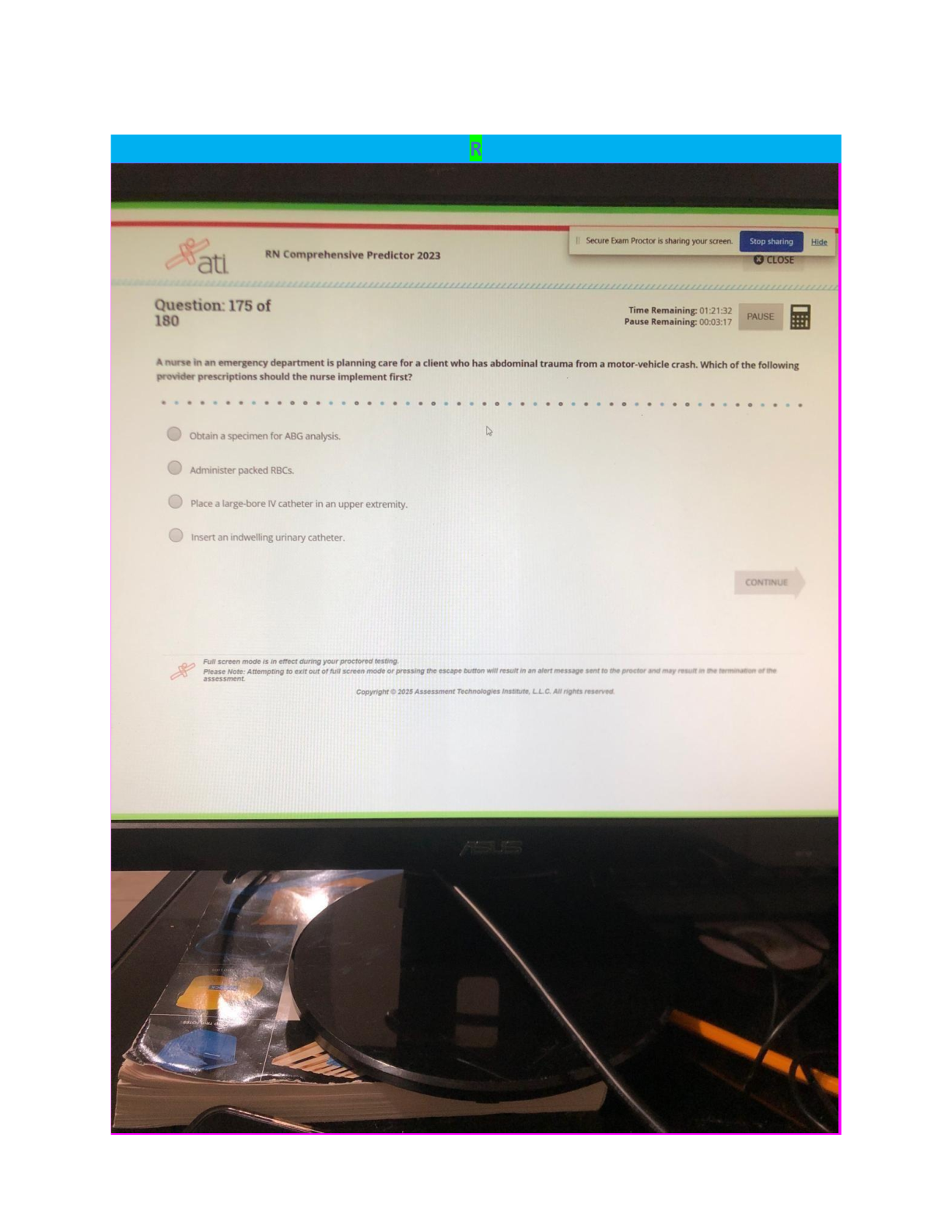
Pharmacology HESI EXAM QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS AND RATIONALE AT THE LAST PAGES 2021 DOCS . A 67-year-old client is discharged from the hospital with a prescription for digoxin (Lanoxin) 0.25 mg daily ... . Which instruction should the nurse include in this client's discharge teaching plan? (2/150) Take the medication in the morning before rising. Take and record radial pulse rate daily. Expect some vision changes due to the medication. Increase intake of foods rich in Vitamin K. Which symptoms are serious adverse effects of beta-adrenergic blockers such as propranolol (Inderal)? (6/150) Headache, hypertension, and blurred vision. Wheezing, hypotension, and AV block. Vomiting, dilated pupils, and papilledema. Tinnitus, muscle weakness, and tachypnea. What medication is useful in treating digoxin (Lanoxin) toxicity? (7/150) Atropine sulfate (Atropine). Isoproterenol (Isuprel) Xylocaine (Lidocaine). Digoxin immune fab (Digibind). When caring for a client on digoxin (Lanoxin) therapy the nurse knows to be alert for digoxin (Lanoxin) toxicity. Which finding would predispose this client to developing digoxin toxicity? (8/150) Low serum sodium. High serum sodium. Low serum potassium. High serum potassium. A 78-year-old client with congestive heart failure receives a cardiac glycoside, digoxin (Lanoxin) 0.25mg po daily. Which observation by the nurse indicates that the medication has been effective? (9/150) Systolic blood pressure readings ranges from 120 to 130. Clear breath sounds anteriorly and posteriorly Jugular venous distention present with supine positioning. Radial pulse volume of +4 bilaterally. The physician prescribes digitalis (Digoxin) for a client diagnosed with congestive heart failure. Which intervention should the nurse implement prior to administering the digoxin? (11/150) Observe respiratory rate and depth. Assess the serum potassium level. Obtain the client's blood pressure. Monitor the serum glucose level. A 59-year-old client with congestive heart failure is taking furosemide (Lasix) 40 mg twice daily. The nurse plans to monitor this client for development of which complication? (12/150) Hyponatremia. Hyperchloremia. Hypercalcemia. Hyponatremia. A male client being discharged with a prescription for theophylline, a bronchodilator, tells the nurse that he understands he is to take three doses of the medication each day. Since, at the time of discharge, timed-release capsules are not available, which dosing schedule should the nurse advise the client to follow? (14/150) 9 a.m., 1 p.m., and 5 p.m. 8 a.m., 4 p.m., and midnight. Before breakfast, before lunch and before dinner. With breakfast, with lunch, and with dinner. A 75-year-old male client taking hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) is admitted to the hospital having "palpitations" and "skipped heart beats." What is the most likely cause of these symptoms given the client's medication history? (15/150) Hypokalemia. Hypermagnesemia. Hyperchloremia. Hyponatremia. Vancomycin (Vancocin) is prescribed for a client who has a history of endocarditis and is to undergo minor dental surgery. The nurse knows that this drug (16/150) should be administered IM. may be administered sub-q. should always be administered IV. may be administered po. Alteration of which laboratory finding represents achievement of a therapeutic goal for heparin administration? (17/150) Prothrombin time. Fibrin split products. Platelet count. Partial thromboplastin time. A client receiving a continuous infusion of heparin intravenously starts to hemorrhage from an arterial access site. What medication should the nurse anticipate administering to prevent further heparin- induced hemorrhaging? (18/150) Vitamin K (Aquamephyton). Protamine sulfate. Warfarin sodium (Coumadin). Prothrombin. A client taking furosemide (Lasix), reports difficulty sleeping. What question is important for the nurse to ask the client? (20/150) What dose of medication are you taking? Are you eating foods rich in potassium? Have you lost weight recently? At what time do you take your medication? A female client who has started taking long-term corticosteroid therapy tells the nurse that she is careful to take her daily dose at bedtime with a snack of crackers and milk. What is the best response by the nurse? (22/150) Advise the client to take the medication in the morning, rather than at bedtime. Teach the client that dairy products should not be taken with her medication. Tell the client that absorption is improved when taken on an empty stomach. Affirm that the client has a safe and effective routine for taking the medication. The nurse has completed diabetic teaching for a client who has been newly diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. Which statement by this client would indicate to the nurse that further teaching is needed? (24/150) "Regular insulin can be stored at room temperature for 30 days." "My legs, arms, and abdomen are all good sites to inject my insulin." "I will always carry hard candies to treat hypoglycemic reactions." "When I exercise, I should plan to increase my insulin dosage." A client asks the nurse if glipizide (Glucotrol) is an oral insulin. What is the correct answer for the nurse to provide? (25/150) "Yes, it is an oral insulin and has the same actions and properties as intermediate insulin." "Yes, it is an oral insulin and is distributed, metabolized, and excreted in the same manner as insulin." “No, it is not an oral insulin and can be used only when some beta cell function is present." “No, it is not an oral insulin, but it is effective for those who are resistant to injectable insulins." The nurse gives a client NPH insulin 15 units subcutaneously before breakfast (7:30 a.m.). At what time should the nurse be particularly alert for signs or symptoms of a potential hypoglycemic reaction? (26/150) a. 8:30 to 11:30 a.m. b. 1:30 to 3:30 p.m. c. 7:30 to 9:30 p.m. d. 12:00 midnight. The nurse is preparing a teaching plan for a client who is newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Which signs and symptoms should the nurse describe when teaching the client about hypoglycemia? (27/150) Sweating, trembling, tachycardia. Polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia. Nausea, vomiting, anorexia. Fruity breath, tachypnea, chest pain. A 43-year-old female client is receiving thyroid replacement hormone following a thyroidectomy. What adverse effects associated with thyroid hormone toxicity should the nurse instruct the client to report promptly to the physician? (29/150) Tinnitus and dizziness. Tachycardia and chest pain. Dry skin and intolerance to cold. Weight gain and increased appetite. The nurse is preparing a teaching plan for a client who has received a new prescription for levothyroxine sodium (Synthroid). Which instruction should be included? (30/150) "Take this medication with a high protein snack at bedtime." "You may change at anytime to a less expensive generic brand." "Take your pulse daily, and if it exceeds 100, contact the physician." "Return to the clinic weekly for serum blood glucose testing." The physician prescribes aluminum and magnesium hydroxide (Maalox), 1 tablet PO PRN, for a client with chronic renal failure who is complaining of indigestion. What intervention should the nurse implement? (32/150) Administer 30 minutes before eating. Evaluate the effectiveness 1 hour after administration. Instruct the client to swallow the tablet whole. Question the physician's prescription. Which antidiarrheal agent should be used with caution in clients taking high dosages of aspirin for arthritis? (34/150) Loperamide (Imodium). Probanthine (Propantheline). Bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto Bismol). Diphenoxylate hydrochloride with atropine (Lomitil). A client with dysphagia has been diagnosed with duodenal ulcers and is being discharged from the hospital with a prescription for the proton pump inhibitor lansaprozole (Prevacid) 15mg PO daily. The medication comes in capsule form. What instruction should the nurse include in the discharge teaching plan for this client? (41/150) Capsule contents can be sprinkled on pudding or applesauce. Chew the medication thoroughly to enhance absorption. Take the drug at the same time as famotidine (Pepcid). This drug must be ingested 30 minutes after a meal. A 52-year-old client is admitted to the hospital for possible duodenal ulcers. The physician prescribes ranitidine hydrochloride (Zantac) 150 mg b.i.d., PO. Which data would indicate that this medication is effective? (42/150) Analysis of gastric secretions indicate a pH level below 3. Hemoccult testing is positive on 2 different occasions. The client reports a decrease in the epigastric "burning." Within 4 hours after eating, the client denies having pain. A 46-year-old female client is instructed to take Lugol's solution (strong iodine solution) in preparation for thyroidectomy surgery. Which food should the nurse instruct this client to remove from her diet? (43/150) Canned vegetables. Cheeses. Citrus fruits. Shrimp. An 83-year-old woman is recovering from a myocardial infarction. The cardiologist prescribes docusate sodium and casantrol (Peri-colace) 1 tab PO, b.i.d. What theraputic effect does this medication provide for this client? (45/150) Maintaining soft stools to prevent straining on defecation. Increasing cardiac blood flow by dilating the coronaries. Replacing serum potassium lost with diuretic therapy. Preventing the occurrence of stress ulcers in the duodenum. The physician has prescribed a low molecular weight heparin, enoxaparin (Lovenox), 30 mg IVP b.i.d. for a client following hip replacement. Prior to administering the first dose, which intervention is most important for the nurse to implement? (55/150) Assess the client's IV site for signs of inflammation. Evaluate the client's degree of mobility. Instruct the client regarding medication side effects. Contact the physician to clarify the prescription. A client is receiving antiinfective drug therapy for a post-operative infection. Which complaint should alert the nurse to the possibility that the client has contracted a superinfection? (56/150) "My mouth feels sore." "I have a headache." "My ears feel plugged up." "I feel constipated." The nurse is assessing the effectiveness of high dose aspirin therapy for an 88-year-old client with arthritis. The client reports that she is can't hear the nurse's questions because her ears are ringing. What action should the nurse implement? (59/150) Refer the client to an audiologist for evaluation of her hearing. Advise the client that this is a common side effect of aspirin therapy. Notify the health care provider of this finding immediately. Ask the client to turn off her hearing aid during the exam. Which outcome would the nurse expect a client to have who is receiving cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril)? (61/150) Elevated mood with improved responsiveness to family. A decrease in joint pain experienced with osteoarthritis. Improved range of motion during physical therapy exercises. Fewer absence seizures with lengthened attention span. A physician prescribes naloxone (Narcan) for a client in the emergency room. Which assessment data would indicate that the naloxone has been effective? (77/150) The client's statement that the chest pain is better. The client's respiratory rate is 16 breaths/minute. The client's seizure activity has stopped temporarily. The client's pupils are constricted bilaterally. A client with cancer who has been receiving fentanyl (Duragesic) for several weeks reports to the nurse that the medication is not effectively controlling the pain. Which intervention should the nurse initiate? (81/150) Instruct the client about indications of opioid dependence. Monitor the client for symptoms of opioid withdrawal. Notify the physician of the need to increase the dose. Administer naloxone (Narcan) per PRN protocol for reversal. Before administering an antiinfective agent to a client with a urinary tract infection, which nursing intervention is most important? (94/150) Obtain a clean catch urine specimen. Assess the urine pH for acidity. Insert an indwelling catheter. Assess for complaints of dysuria. A client taking a thiazide diuretic for the past six months has a serum potassium level of 3. 0. The nurse anticipates which change in prescription for the client? (96/150) The dosage of the diuretic will be decreased. The diuretic will be discontinued. A potassium supplement will be prescribed. The dosage of the diuretic will be increased. Phenazopyridine (Pyridium) is commonly prescribed for clients with urinary tract infections. What statement should be included by the nurse when teaching clients about the administration of phenazopyridine (Pyridium)? (97/150) Stop taking the drug if the urine turns a red-orange color. This medication is an antispasmodic for bladder spasms. Take this medication with food to decrease gastric irritation. Take for the full two weeks to avoid growing resistant organisms. A client has a positive skin test for tuberculosis. What prophylactic drug should the nurse expect to administer to this client? (104/150) Isoniazid (INH). Rifampin (Rifadin). Acyclovir (Zovirax). Griseofulvin (Grisactin). The nurse is teaching a client proper use of an inhaler. When should the client administer the inhaler- delivered medication to demonstrate correct use of the inhaler? (110/150) Immediately after exhalation. During the inhalation. At the end of three inhalations. Immediately after inhalation. Heparin 20,000 units in 500 ml D5W at 50 ml/hour has been infusing for 5 1/2 hours. How much heparin has the client received? (115/150) 11,000 units. 13,000 units. 15,000 units. 17,000 units. A peak and trough level must be drawn for a client receiving antibiotic therapy. What is the optimum time for the nurse to obtain the trough level? (116/150) Sixty minutes after the antibiotic dose is administered. Immediately before the next antibiotic dose is given. When the next blood glucose level is to be checked. Thirty minutes before the next antibiotic dose is given. The physician prescribes furosemide (Lasix) 15 mg IV stat. On hand is Lasix 20 mg/2ml. How many milliliters should the nurse administer? (119/150) 1.0 ml. 1.5 ml. c. 1.75 ml. d. 2.0 ml. A client is to receive 10 mEq of KCl diluted in 250 cc of normal saline over 4 hours. At what rate should the nurse set the client's intravenous infusion pump? (123/150) 13 cc/hour. 63 cc/hour. 80 cc/hour. 125 cc/hour. A client is taking hydromorphone (Dilaudid) PO q4h at home. Following surgery, Dilaudid IV q4h PRN and butorphanol tartrate (Stadol) IV q4h PRN are prescribed for pain. The client received a dose of the Dilaudid IV four hours ago, and is again requesting pain medication. What intervention should the nurse implement? (126/150) Alternate the two medications every four hours PRN for pain Alternate the two medications every two hours PRN for pain. Administer only the Dilaudid every four hours PRN for pain. Administer only the Stadol every four hours PRN for pain. A client with congestive heart failure (CHF) is being discharged with a new prescription for captopril (Capoten), an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. The nurse's discharge instruction should include reporting which problem to the health care provider? (129/150) Weight loss. Dizziness. Muscle cramps. Dry mucus membranes. Following heparin treatment for a pulmonary embolism, a client is being discharged with a prescription for warfarin (Coumadin). In conducting discharge teaching, the nurse advises the client to have which diagnostic test monitored regularly after discharge? (130/150) Perfusion scan. Prothrombin Time (PT/INR). Activated partial thromboplastin (APTT). Serum Coumadin level (SCL). The nurse would be correct in withholding a dose of digoxin in a client with congestive heart failure without specific instruction from the physician if which finding was documented? (131/150) Serum digoxin level is 1.5. Blood pressure is 104/68. Serum potassium level is 2.5. Apical pulse is 68/minute. Following the administration of sublingual nitroglycerin, which assessment finding indcates the medication was effective? (133/150) Relief of chest pain. Clear bilateral breath sounds. Increase in blood pressure. Increase in urinary output. A client is receiving propylthiouracil (PTU) prior to thyroid surgery. Which diagnostic test results indicate that the medication is producing the desired effect? (137/150) Increased hemoglobin and hematocrit. Increased serum calcium. Decreased white blood cell count (WBC). Decreased T3 and T4. The physician prescribes an H2 antagonist, famotidine (Pepcid) 20 mg in the morning and at bedtime. What statement regarding the action of H2 antagonists offers the correct rationale for administering the medication at bedtime? (138/150) Gastric acid secreted at night is buffered, preventing pepsin formation. Hydrochloric acid secreted during the nighttime is blocked. The drug relaxes stomach muscles at night to reduce acid. Ingestion of the medication at night offers a sedative effect, promoting sleep. A 45-year-old woman is receiving alprazolam (Xanax) for anxiety. Which client behaviors would indicate that the drug is effective? (141/150) Personal hygiene is maintained by the client for the first time in a week. The client has an average resting heart rate of 120 beats/minute. The staff observe the client sitting in the day room reading a book. The nurse records that the client lost two pounds of body weight in the past week. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 13 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$13.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 13, 2021
Number of pages
13
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 13, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
91