FISDAP Airway Exam Study Guide
(2022/2023) Rated A+
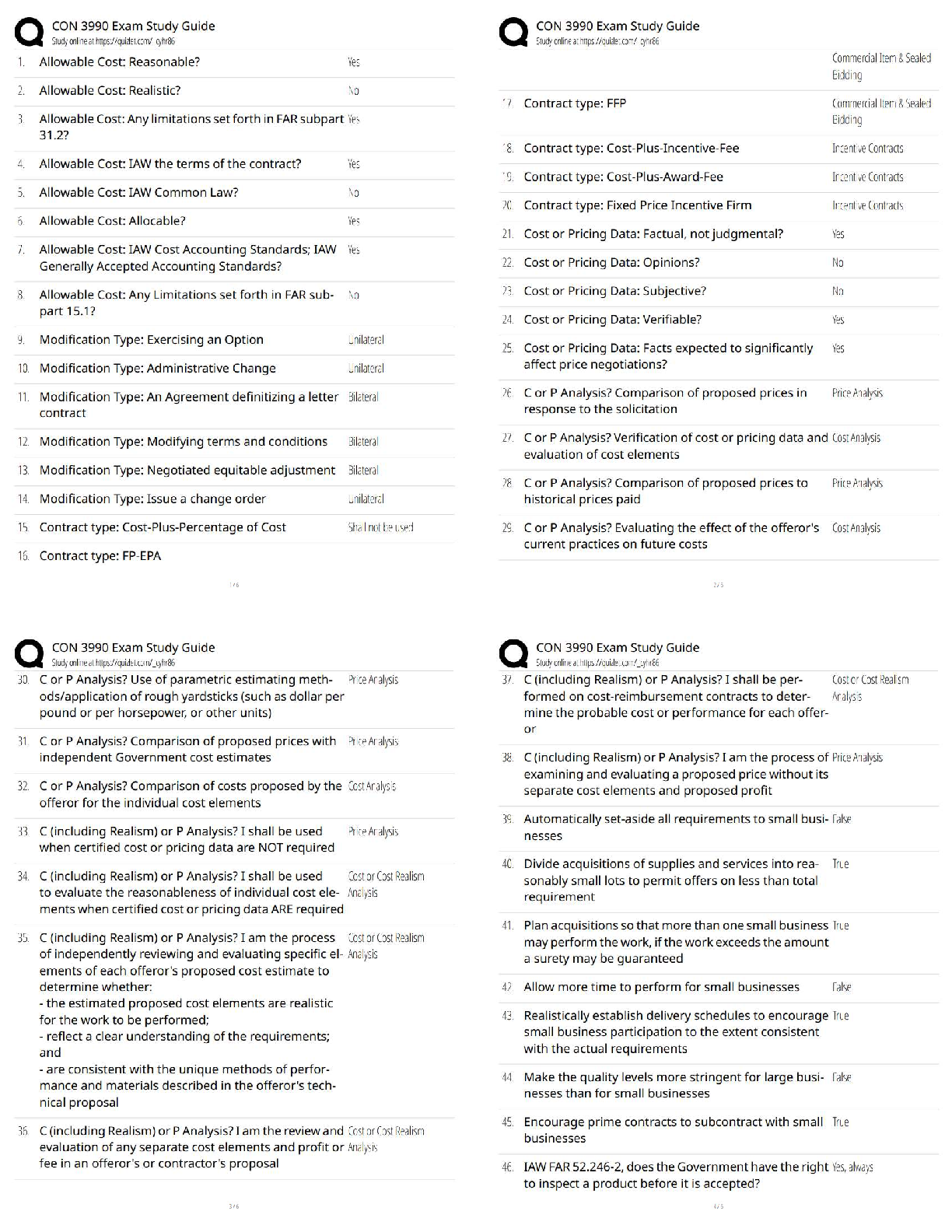
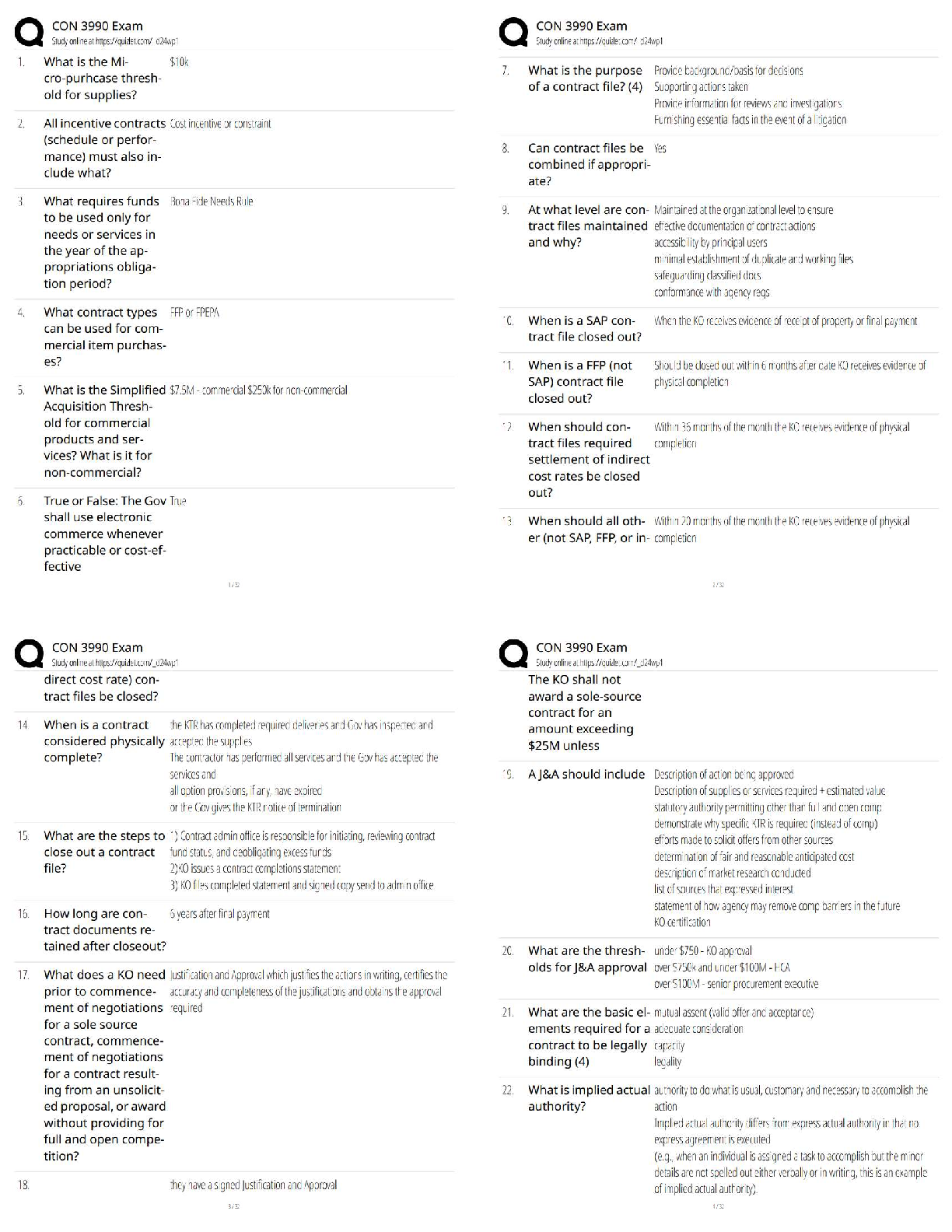
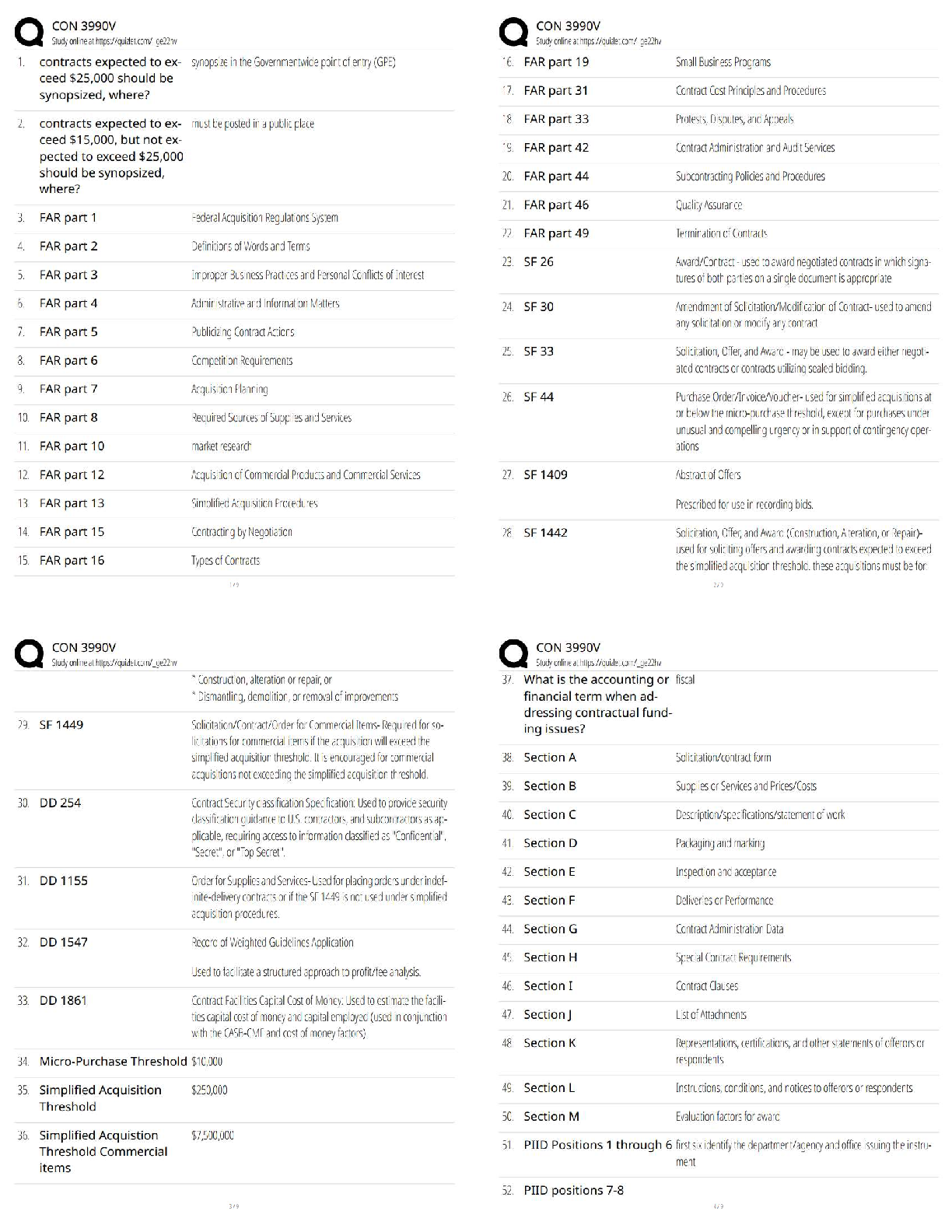
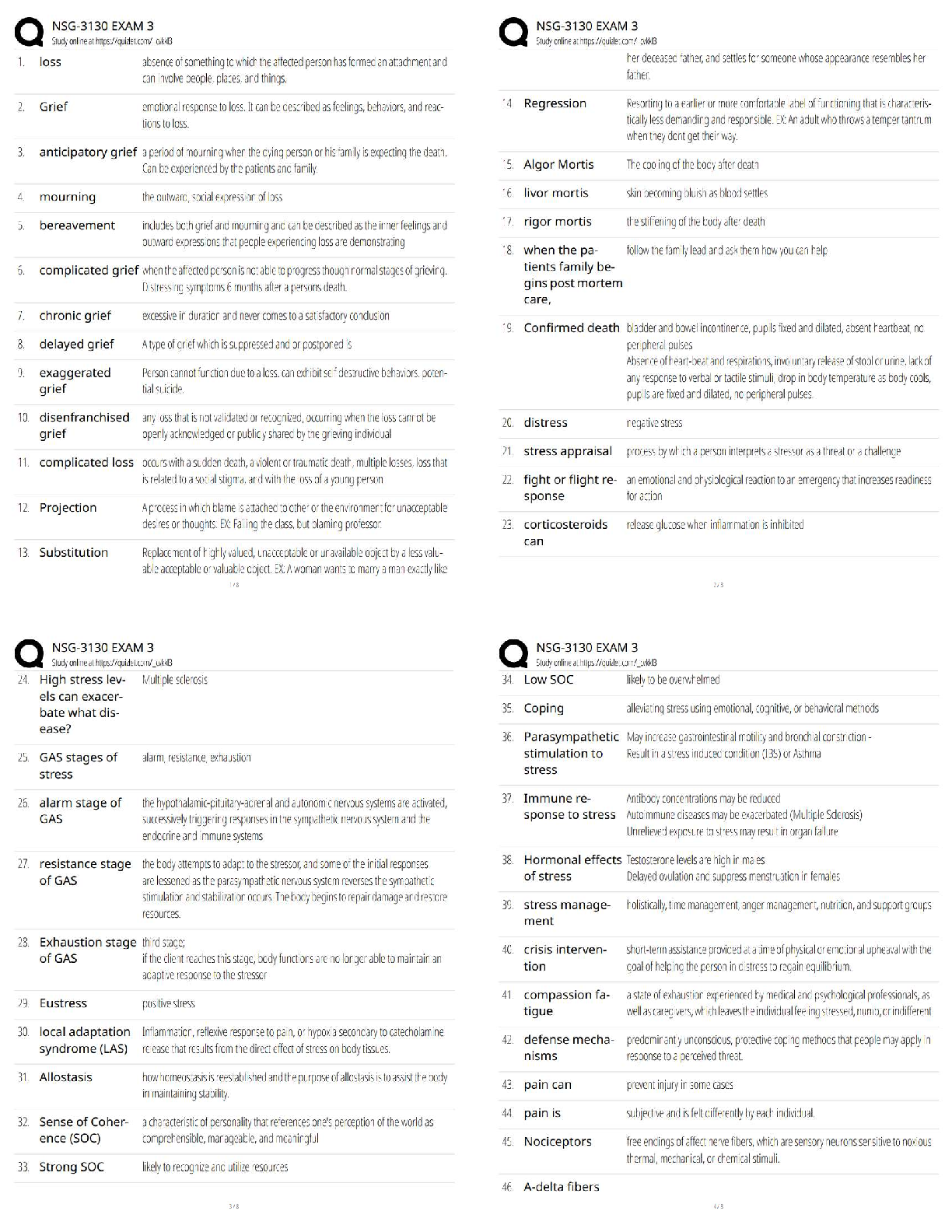
Alveolar air volume ✔✔Amount of air that reaches alveoli for gas exchange (approx. 350 ml.
For adult male) Tidal volume minus dead space
Dead air space ✔✔Anatomical
...
FISDAP Airway Exam Study Guide
(2022/2023) Rated A+
Alveolar air volume ✔✔Amount of air that reaches alveoli for gas exchange (approx. 350 ml.
For adult male) Tidal volume minus dead space
Dead air space ✔✔Anatomically: structures that hold air, but can't participate in gas exchange.
Physiologically: alveoli or capillaries destroyed by disease
Expiratory reserve volume ✔✔Amount of gas that can be forcefully expired at the end of a
normal expiration
Inspiratory reserve volume ✔✔Amount of gas that can be forcefully inspired in addition to a
normal breaths tidal volume
Internal respiration ✔✔Exchange of gases between blood cells and tissues
Peak expiratory flow ✔✔The greatest rate of airflow during forced expiration when lungs are
fully inflated
Residual volume ✔✔After maximal forced exhalation, amount of air remaining not able to be
expelled
Tidal volume ✔✔Amount of air in a respiratory cycle (500 ml, 5-7ml/kg)
Minute volume ✔✔Amount of gas moved in and out of respiratory tract per minute
Air trapping ✔✔A respiratory pattern associated with an obstruction in the pulmonary tree. Rate
increases to overcome resistance
Angle of Louis ✔✔Angulation of the sternum that indicates the point where the second rib joins
the sternum. (manubriosternal junction)
Anoxia ✔✔total lack of oxygen available to the tissues
Apnea ✔✔Respiratory arrest
Atelectasis ✔✔Abnormal condition characterized by collapse of alveoli, preventing exchange of
co2 and o2 in a part of the lungs
Barrier device ✔✔Thin film of material placed on the patient's face used to prevent direct
contact with the patient's mouth during PPV
Carina ✔✔Where the trachea divides into right and left bronchi
Ronchi ✔✔Rattling or rumbling in the lungs. Inspiration and expiration. Fluid in larger airways
and may be cleared from a cough.
Stridor ✔✔Harsh, high-pitched inspiratory sound best heard over the neck
Rattles (ronchi) ✔✔Inflammation and mucus or fluid in larger airways heard on inspiration.
Associated with bronchitis or pneumonia
Crackles (rales) ✔✔Wet lungs - sounds like hair rolled in finger tips. fluid in smaller airways,
crackling or popping sound on inspiration, sound that indicates presence of fluid in smaller
airways
Croup ✔✔Viral infection in upper airway that sounds like a seal bark
Wheeze ✔✔Whistling sound heard on inspiration or expiration in pharynx, trachea, bronchi
Biots respirations ✔✔Irregular respirations and rate with periods of apnea from increased ICP,
brain damage at medulla, DKA, and OD'ing
Agonal respirations ✔✔Slow, shallow, irregular from anoxic brain injury
Central neurogenic hyperventilation ✔✔Similar to Kussmaul respirations, deep and rapid
breathing from increased ICP
Cheyne-Stokes respiration ✔✔A pattern of gradually increasing rate and depth of breathing that
tapers to slower and shallower breathing with a period of apnea before the cycle repeats
Hering-Breuer reflex ✔✔Reflex that limits inspiration and prevents overinflation
Hiccup ✔✔Spasm of the diaphragm
Benign tumor ✔✔Not spreading aggressively
Malignant tumor ✔✔Aggressively spreads
Secondary tumor ✔✔Spread from its original location
Primary tumor ✔✔Collection of cells that grow out of control, in excess of normal rate. Tumor
that develops in only 1 tissue
Acute Respiratory Distress syndrome (ARDS) ✔✔Collection of fluid in the alveoli of the lung,
usually from trauma or illness
Compliance ✔✔Resistance of the patient's lung tissue to ventilation
Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure Device (BiPAP) ✔✔Air pressure during inhalation and lower
pressure to during exhalation
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) ✔✔Slight PPV throughout the respiratory cycle to
prevent airway collapse
Costal angle ✔✔Angle formed by the margins of the ribs and the sternum
Coughing ✔✔Protective mechanism from mucosal irritation. Can clear bronchioles and bronchi
Crepitation ✔✔Crackling sound from bones grinding
Cricothyroid membrane ✔✔Fibrous membrane between cricoid and thyroid cartilage
Cricothyrotomy ✔✔Emergency entrance into the airway
Dyspnea ✔✔Uncomfortable awareness of one's breathing
Functional reserve capacity ✔✔At end of normal expiration, the volume of air remaining in
lungs
External respiration ✔✔Exchange of gases between alveoli and pulmonary capillaries
Fraction of Inspired Oxygen (FiO2) ✔✔The percentage of oxygen in inspired air. This
percentage increases with supplemental oxygen. This value is commonly given as a decimal (Ex:
room air is 21% O2, so FiO2 = 0.21).
Gagging ✔✔Brooks on a friday night
Gag reflex ✔✔Something brooks is working on getting rid of.
Glottis ✔✔True vocal cords and space between them
Hemoglobin ✔✔A protein
Hilum ✔✔Point of entry for bronchial vessels, bronchi, and nerves in lung
Hypoxemia ✔✔Deficiency in the concentration of oxygen in arterial blood.
Hypoxia ✔✔Inadequate oxygenation of the cells
Orthopnea ✔✔Dyspnea relieved by a change in position, SLEEPING UPRIGHT with pillows,
usually CHF pulmonary edema problem.
Oxyhemoglobin ✔✔Hemoglobin with oxygen bound to it
Partial pressure ✔✔Pressure exerted by an individual gas in a mixture
Positive End-Expiratory Pressure (PEEP) ✔✔Amount of pressure above atmospheric pressure
present in the airway at the end of the expiratory cycle
Respiration ✔✔Exchange of gas
Saturation of peripheral oxygen ✔✔SpO2
Sellick maneuver ✔✔Technique used to compress the cricoid against the cervical vertebrae,
occluding the esophagus
Surfactant ✔✔Specialized cells that keep alveoli from collapsing
Tracheal stoma ✔✔Surgical opening in neck
Tracheostomy ✔✔Surgical creation of a hole in the anterior trachea for breathing
Uvula ✔✔Fleshy tissue resembling a grape that hangs down from soft palate
Vallecula ✔✔Depression or pocket between the base of the tongue and the epiglottis
Ventilation ✔✔Mechanical process of moving air
Alveoli ✔✔Functional units of the respiratory system. Area in the lungs where the majority of
the gas exchange takes place
Aspiration pneumonitis ✔✔Inflammation of the bronchi and alveoli caused by inhaled foreign
objects.
Bacterial tracheitis ✔✔Potentially serious bacterial infection of trachea
Barotrauma ✔✔Injury that results from rapid or extreme changes in pressure
Bronchiolitis ✔✔Acute infectious inflammatory disease of the upper and lower respiratory tracts
that results in obstruction of the small airways
Bronchitis ✔✔Inflammation of the lower respiratory tract
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia ✔✔Respiratory condition in infants usually arising from preterm
birth
Carbon Dioxide narcosis ✔✔Mostly seen in COPD where CO2 is excessively retained causing
ALOC
Carpopedal spasm ✔✔Cramping of extremities from hyperventilation
Circumoral paresthesia ✔✔A feeling of tingling around lips
Collapsed lung ✔✔Brooks sucks
Costochondritis ✔✔Inflammation of the cartilage in the anterior chest that is painful
Cystic Fibrosis (CF) ✔✔Genetic disease marked by hyper-secretion of glands, including mucous
in lungs
Emphysema ✔✔Destruction of the alveoli
Esophagoduodenoscopy ✔✔Endoscope is used to look at the esophagus, stomach, and
duodenum
Hamman's sign ✔✔Crunching sounds occasionally heard on the heart when air is in
mediastinum
Mainstem bronchi ✔✔Each of two main breathing tubes off the trachea
Mediastinitis ✔✔Infection in the mediastinum
Mediastinoscopy ✔✔Surgical procedure of looking into mediastinum with an endoscope
NCPE (Non-Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema) ✔✔Fluid collection in the alveoli of the lung that
does not result from heart failure
Ostomy ✔✔A hole, usually referring to a surgically made hole.
Pallor ✔✔Pale washed out coloration of skin
Peak flow meter ✔✔Device used to assess severity of respiratory distress
Pleural effusion ✔✔Fluid in the pleural space, usually fluid that seeped from lung or chest wall
Pleurisy ✔✔Painful rubbing of pleural lining
Pneumomediastinum ✔✔Air entrapped within the mediastinum.
Pneumonia ✔✔Infection in lungs
Pulmonary abscess ✔✔Collection of pus within the lung
Pulmonary bleb ✔✔Cavity in the lung much like a balloon
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) ✔✔Clot lodged in pulmonary artery
Respiratory failure ✔✔Inadequate blood oxygenation and or ventilation to meet the metabolic
demands of body tissue
Retractions ✔✔Use of accessory muscles
Supraglottic ✔✔Airway structure above vocal chords
Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (SIMV) ✔✔Vent setting that generally allows
the patient to inspire at will and to the depth that he or she desires
Tuberculosis (TB) ✔✔Highly contagious bacterial infection known for causing pneumonia and
infecting other parts of the body
Peritonsillar abscess (PTA) ✔✔Infection of tissue between the tonsil and pharynx
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) ✔✔A virus linked to bronchiolitis in infants and children
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) ✔✔Any of several bacterial strains of S.
aureus resistant to methicillin (a penicillin) and related drugs
Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) ✔✔Viral syndrome causing nasal congestion and fever
Vancomycin Resistant Enterococcus (VRE) ✔✔Bacteria resistant to vancomycin
[Show More]