Quiz Module 07 Public Key Infrastructure and
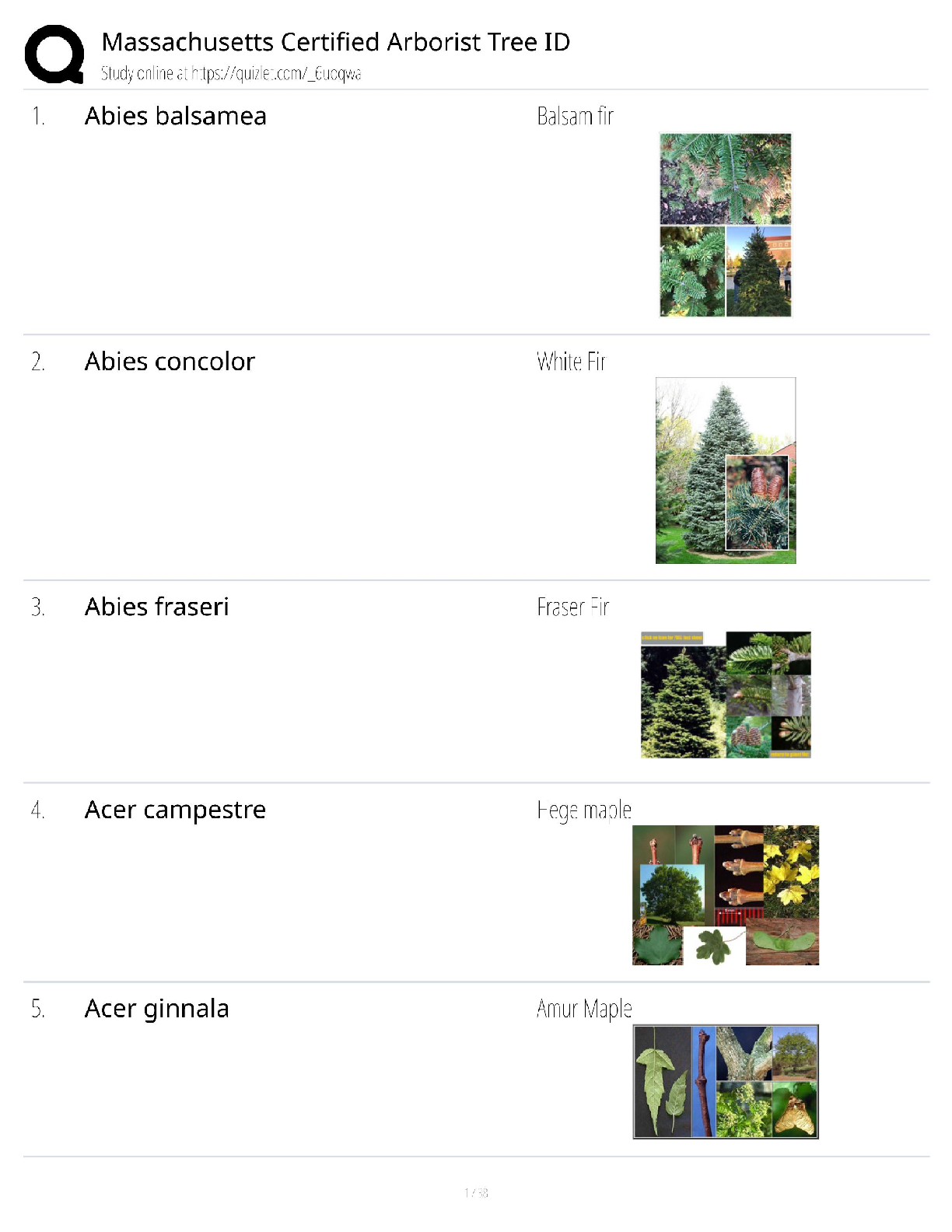
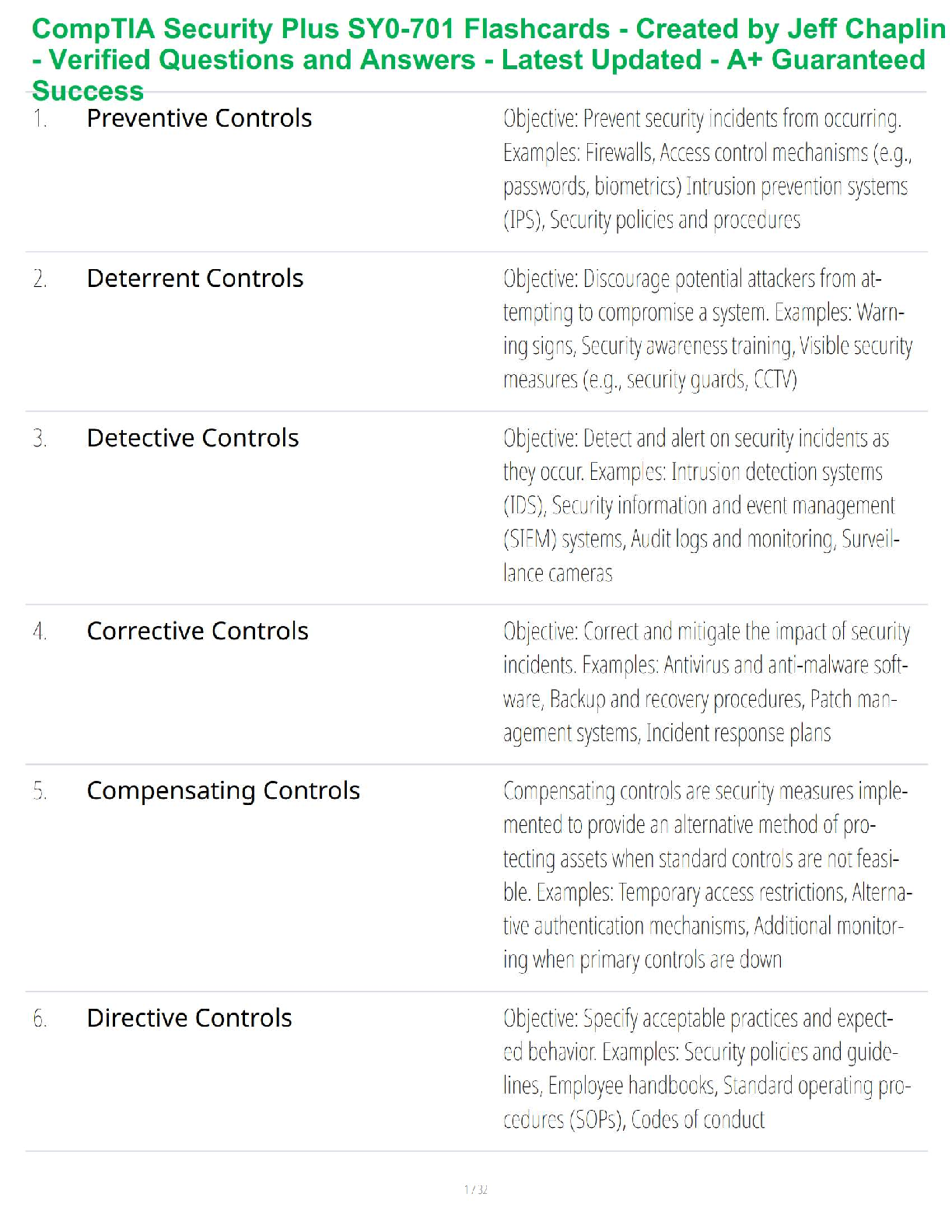
Cryptographic Protocols
What is the strongest technology that would assure Alice that Bob is the sender of a message?
a. Digital certificate
b. Digital signature
c. Diges
...
Quiz Module 07 Public Key Infrastructure and
Cryptographic Protocols
What is the strongest technology that would assure Alice that Bob is the sender of a message?
a. Digital certificate
b. Digital signature
c. Digest
d. Encrypted signature - ✔✔Digital certificate
A digital certificate is a technology used to associate a user's identity to a public key that has
been digitally signed by a trusted third party. This third party verifies the owner and that the
public key belongs to that owner.
Which of the following can a digital certificate NOT be used for?
a. To encrypt messages for secure email communications
b. To verify the identity of clients and servers on the Web
c. To encrypt channels to provide secure communication between clients and servers
d. To verify the authenticity of the CA - ✔✔To verify the authenticity of the CA
A digital certificate does not verify the authenticity of a CA; rather, a CA verifies the
authenticity of a user.
Who verifies the authenticity of a CSR?
a. Signature authority
b. Registration authority
c. Certificate authority
d. Certificate signatory - ✔✔Registration authority
A user electronically signs the CSR by affixing her public key and then sends it to a registration
authority that is responsible for verifying the credentials of the applicant.
Juan needs a certificate that must only authenticate that a specific organization has the right to
use a particular domain name. What type of certificate does he need?
a. Domain validation
b. Root
c. Extended validation
d. Website validation - ✔✔Domain validation
A domain validation digital certificate is a certificate that only verifies the identity of the entity
that has control over the domain name.
Which block cipher mode of operating requires that both the message sender and receiver access
a counter that computes a new value whenever a ciphertext block is exchanged?
a. CD
b. CTR
c. CXL
d. CN - ✔✔CTR
Counter (CTR) mode requires that both the message sender and receiver access a counter, which
computes a new value each time a ciphertext block is exchanged. The weakness of CTR is that it
requires a synchronous counter for both the sender and receiver.
A centralized directory of digital certificates is called a(n) _____.
a. Authorized digital signature (ADS)
b. Digital signature approval List (DSAP)
c. Digital signature permitted authorization (DSPA)
d. Certificate repository (CR) - ✔✔Certificate repository (CR)
A certificate repository (CR) is a publicly accessible centralized directory of digital certificates
that can be used to view the status of a digital certificate. This directory can be managed locally
by setting it up as a storage area that is connected to the CA server.
What entity calls in crypto modules to perform cryptographic tasks?
a. Crypto service provider
b. OCSP
c. Certificate Authority (CA)
d. Intermediate CA - ✔✔Crypto service provider
A crypto service provider allows an application to implement an encryption algorithm for
execution. Typically, crypto service providers implement cryptographic algorithms, generate
keys, provide key storage, and authenticate users by calling various crypto modules to perform
the specific tasks.
Which is an IPsec protocol that authenticates that packets received were sent from the source?
a. PXP
b. AH
c. DER
d. CER - ✔✔AH
IPsec authenticates that packets received were sent from the source. This is identified in the
header of the packet to ensure that no specific attacks took place to alter the contents of the
packet. This is accomplished by the Authentication Header (AH) protocol.
What is the purpose of certificate chaining?
a. To lookup the name of intermediate RA
b. To hash the private key
c. To ensure that a web browser has the latest root certificate updates
d. To group and verify digital certificates - ✔✔To group and verify digital certificates
Grouping and verifying digital certificates relies on certificate chaining. Certificate chaining
creates a path between the trusted root CAs (of which there are a few) and intermediate CAs (of
which there are many) with the digital certificates that have been issued.
What is the name of the fields in an X.509 digital certificate that are used when the parties
negotiate a secure connection?
a. PFX
b. Certificate attributes
c. Electronic Code Book (ECB) repositories
d. CTR - ✔✔Certificate attributes
There are several different certificate attributes that make up an X.509 digital certificate. These
attributes are used when the parties negotiate a secure connection.
What is the name of the device protected by a digital certificate?
a. CN
b. RCR
c. TLXS
d. V2X2 - ✔✔CN
The common name (CN) is the name of the device protected by the digital certificate. The CN
can be a single device (www.example.com) or a wildcard certificate (*.example.com) but is not
the URL (https://example.com).
Which refers to a situation in which keys are managed by a third party, such as a trusted CA?
a. Trusted key authority
b. Key authorization
c. Key escrow
d. Remote key administration - ✔✔Key escrow
Key escrow refers to a process in which keys are managed by a third party, such as a trusted CA.
In key escrow, the private key is split and each half is encrypted. The two halves are registered
and sent to the third party, which stores each half in a separate location.
Olivia is explaining to a friend about digital certificates. Her friend asks what two entities a
digital certificate associates or binds together. What would Olivia say?
a. The user's identity with their public key
b. A private key with a digital signature
c. The user's symmetric key with the public key
d. The user's public key with their private key - ✔✔The user's identity with their public key
A digital certificate is a technology used to associate a user's identity to a public key and that has
been digitally signed by a trusted third party.
Which is the first step in a key exchange?
a. The web browser sends a message ("ClientHello") to the server.
b. The web server sends a message ("ServerHello") to the client.
c. The web browser verifies the server certificate.
d. The browser generates a random value ("pre-master secret"). - ✔✔The web browser sends a
message ("ClientHello") to the server.
The web browser sends a message ("ClientHello") to the server that contains information
including the list of cryptographic algorithms that the client supports.
Which is a protocol for securely accessing a remote computer in order to issue a command?
a. Secure Shell (SSH)
b. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
c. Secure Hypertext Transport Protocol (SHTTP)
d. Transport Layer Security (TLS) - ✔✔Secure Shell (SSH)
Secure Shell (SSH) is an encrypted alternative to the Telnet protocol that is used to access
remote computers. SSH is a Linux/UNIX-based command interface and protocol for securely
accessing a remote computer.
Which of the following is NOT a means by which a newly approved root digital certificate is
distributed?
a. Application updates
b. OS updates
c. Web browser updates
d. Pinning - ✔✔Application updates
Updates to applications cannot contain root digital certificates.
What is the file extension for a Cryptographic Message Syntax Standard based on PKCS#7 that
defines a generic syntax for defining digital signature and encryption?
a. .P7B
b. .P12
c. .cer
d. .xdr - ✔✔P7B
Cryptographic Message Syntax Standard with an extension of .P7B defines a generic syntax for
defining digital signature and encryption.
_____ are symmetric keys to encrypt and decrypt information exchanged during the session and
to verify its integrity.
a. Encrypted signatures
b. Session keys
c. Digital certificates
d. Digital digests - ✔✔Session keys
The master secret is used to create session keys, which are symmetric keys to encrypt and
decrypt information exchanged during the session and to verify its integrity.
How is confidentiality achieved through IPsec?
a. ESP
b. AuthX
c. ISAKMP
d. AHA - ✔✔ESP
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) is an IPsec protocol that encrypts packets.
Elton needs his application to perform a real-time lookup of a digital certificate's status. Which
technology would he use?
a. Certificate Revocation List (CRL)
b. Real-Time CA Verification (RTCAV)
c. Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP)
d. Staple - ✔✔Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP)
Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) performs a real-time lookup of a certificate's status.
OCSP is called a request-response protocol. The browser sends the certificate's information to a
trusted entity like the CA, known as an OCSP Responder. The OCSP Responder then provides
revocation information on that one specific certificate.
[Show More]














.png)