ATMO Exam 1
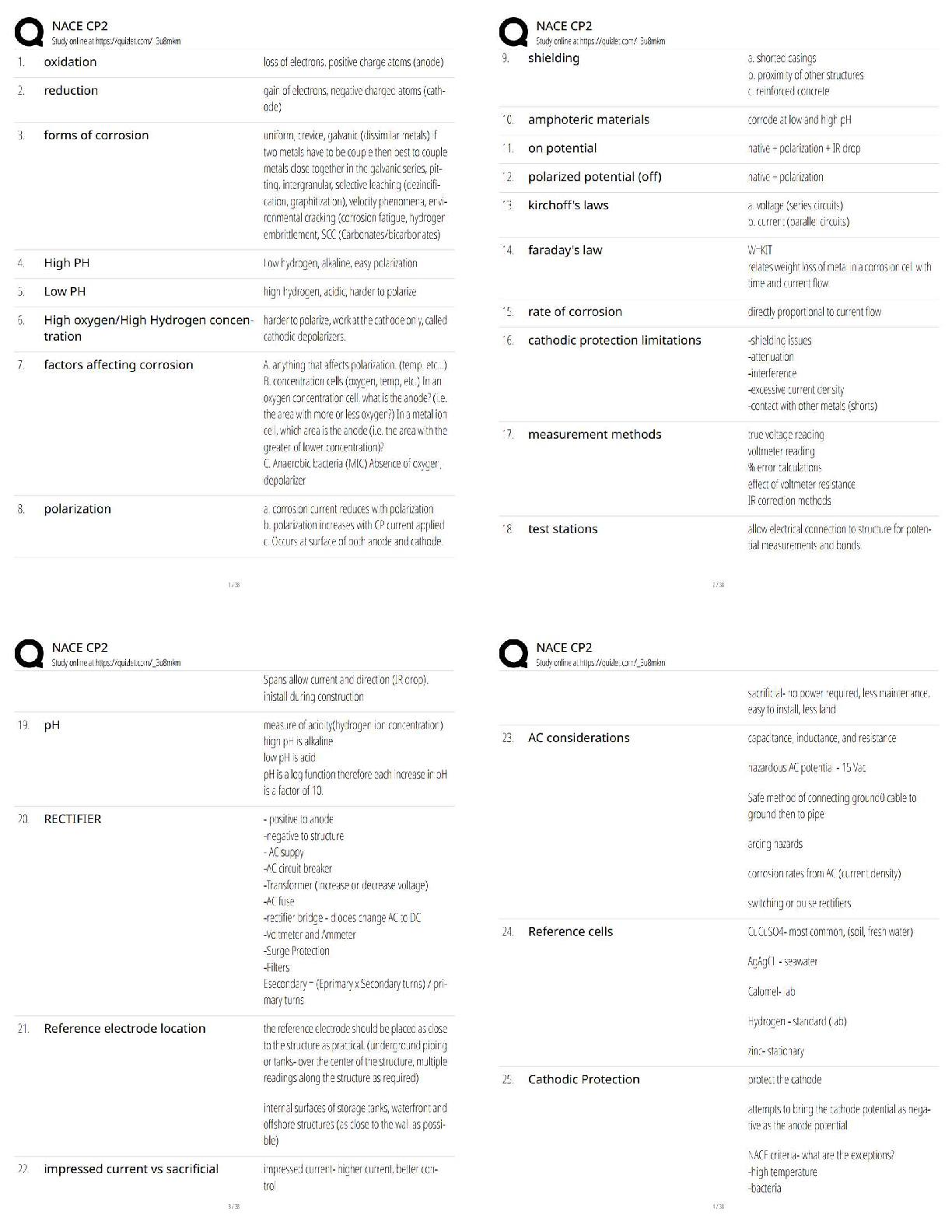
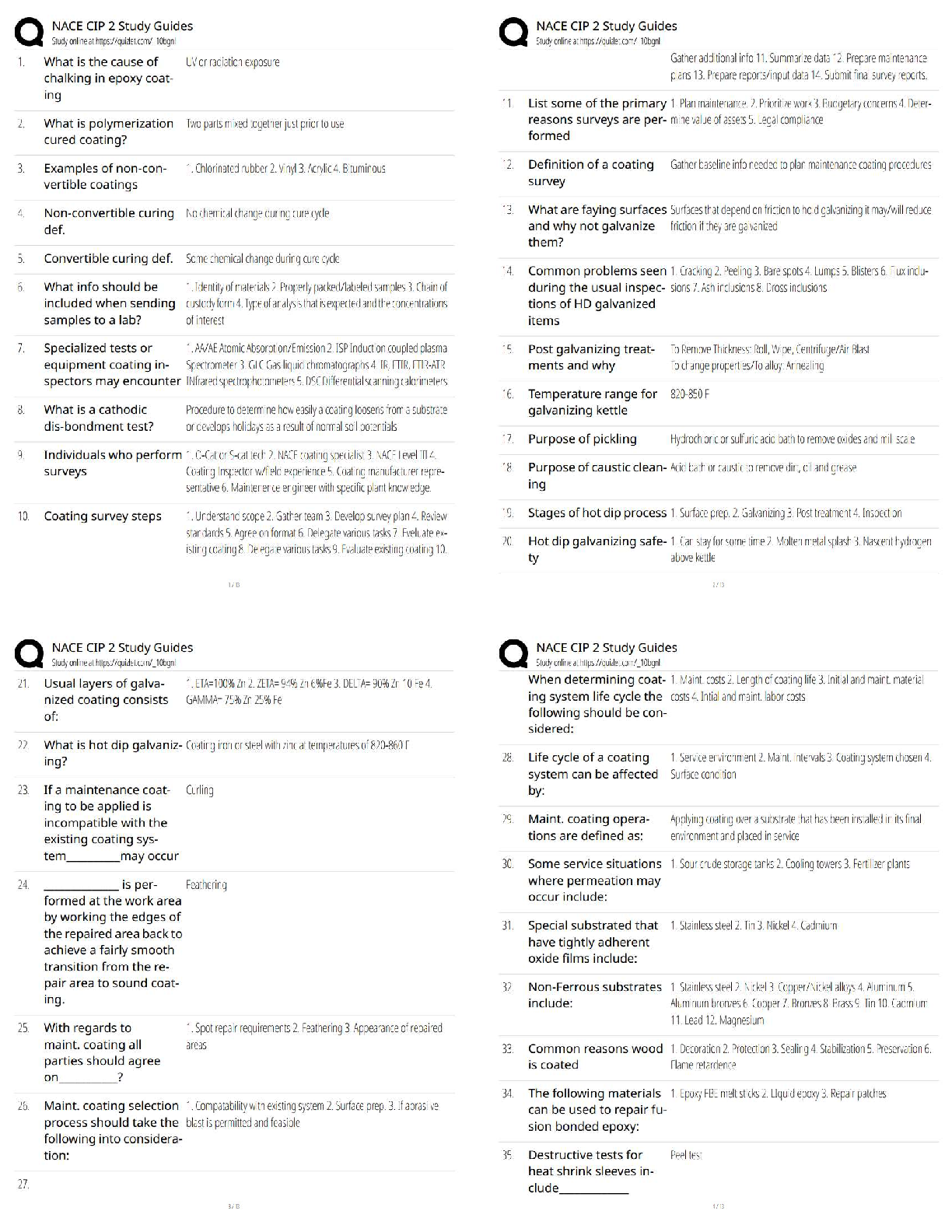
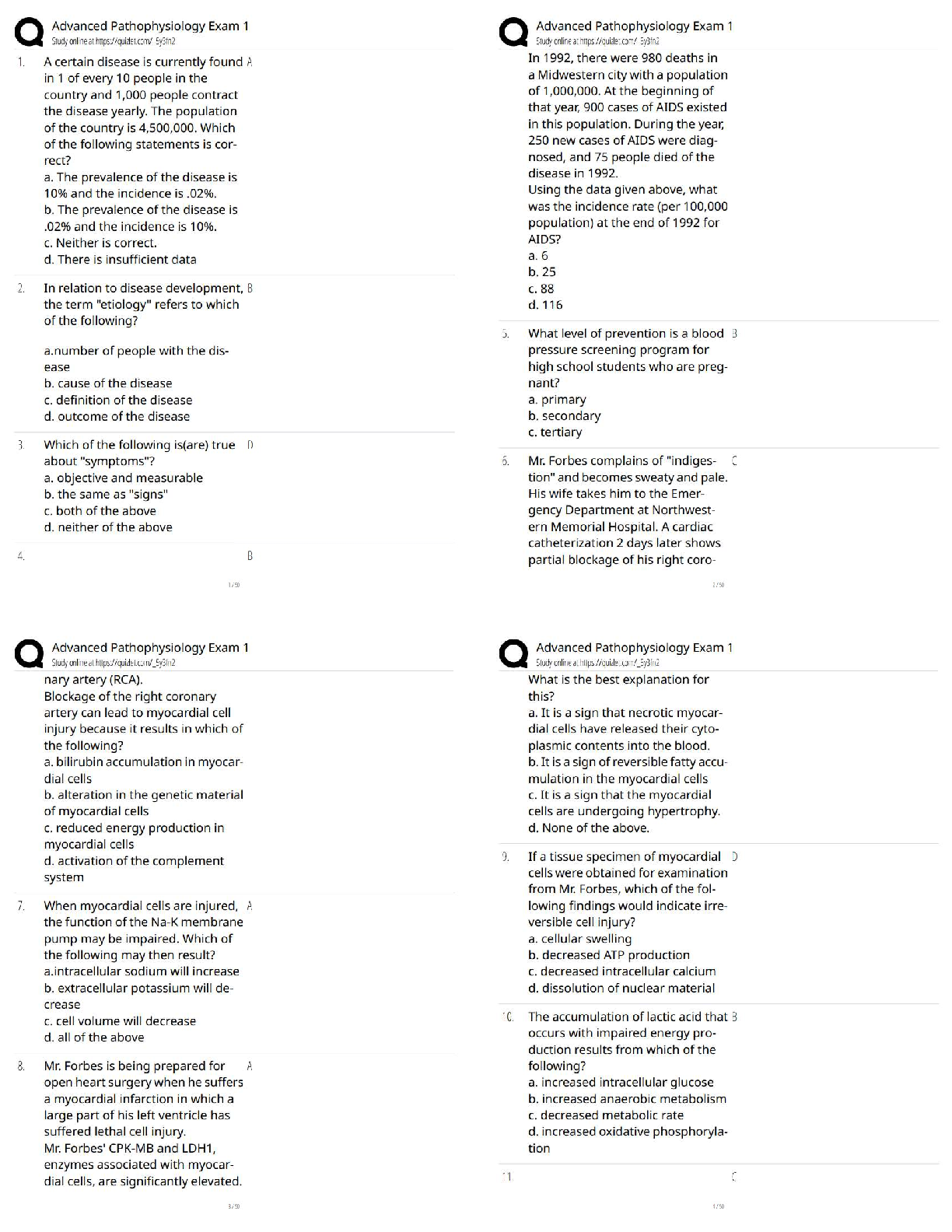
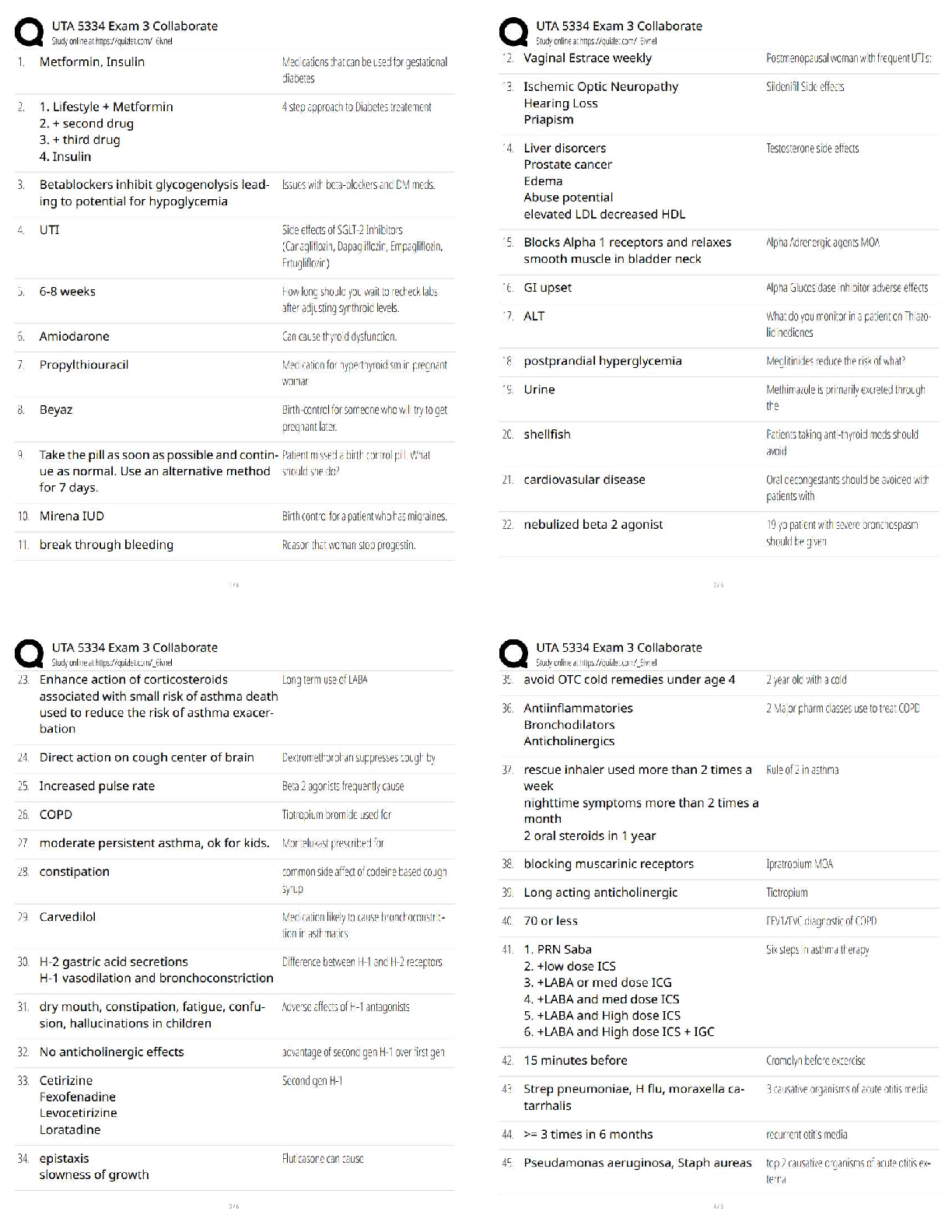
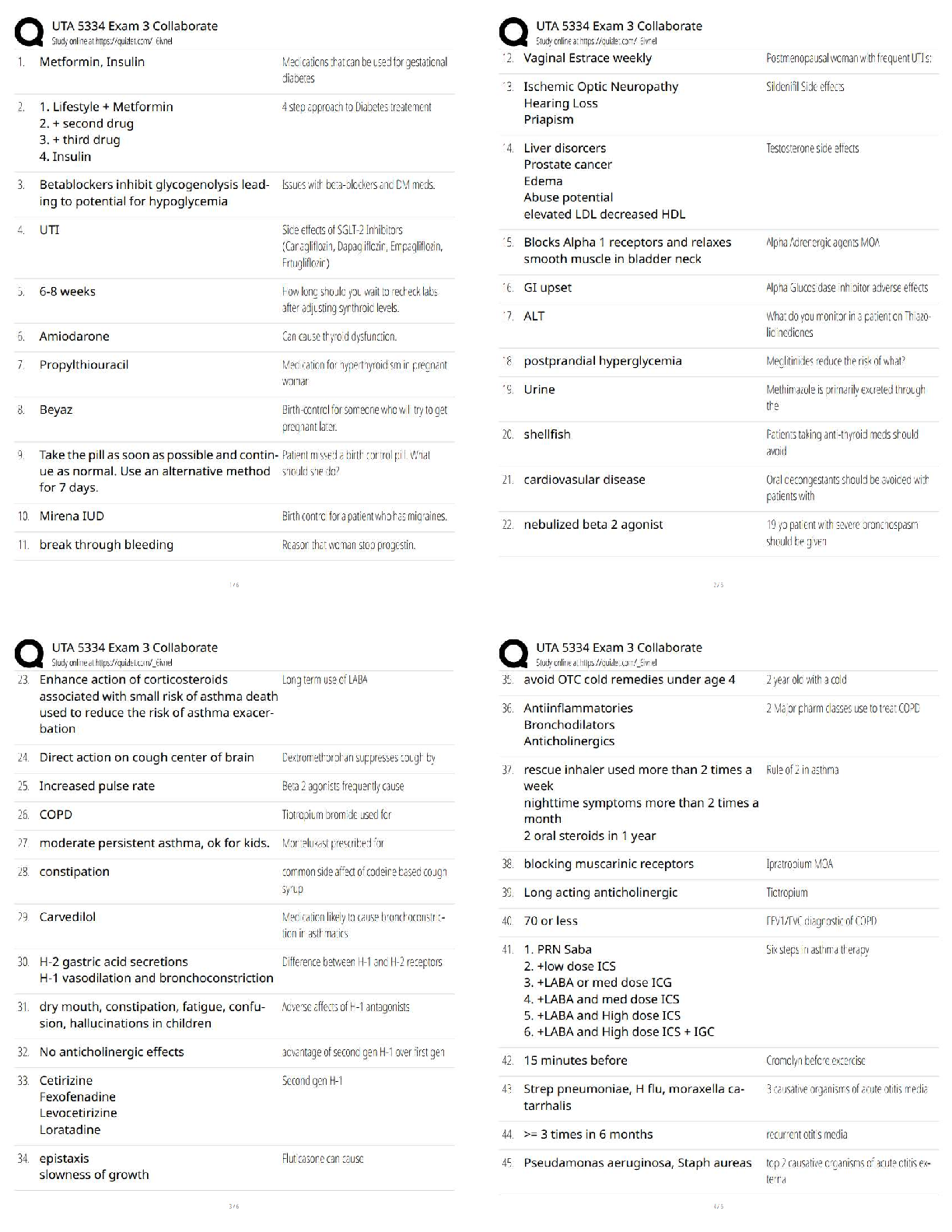
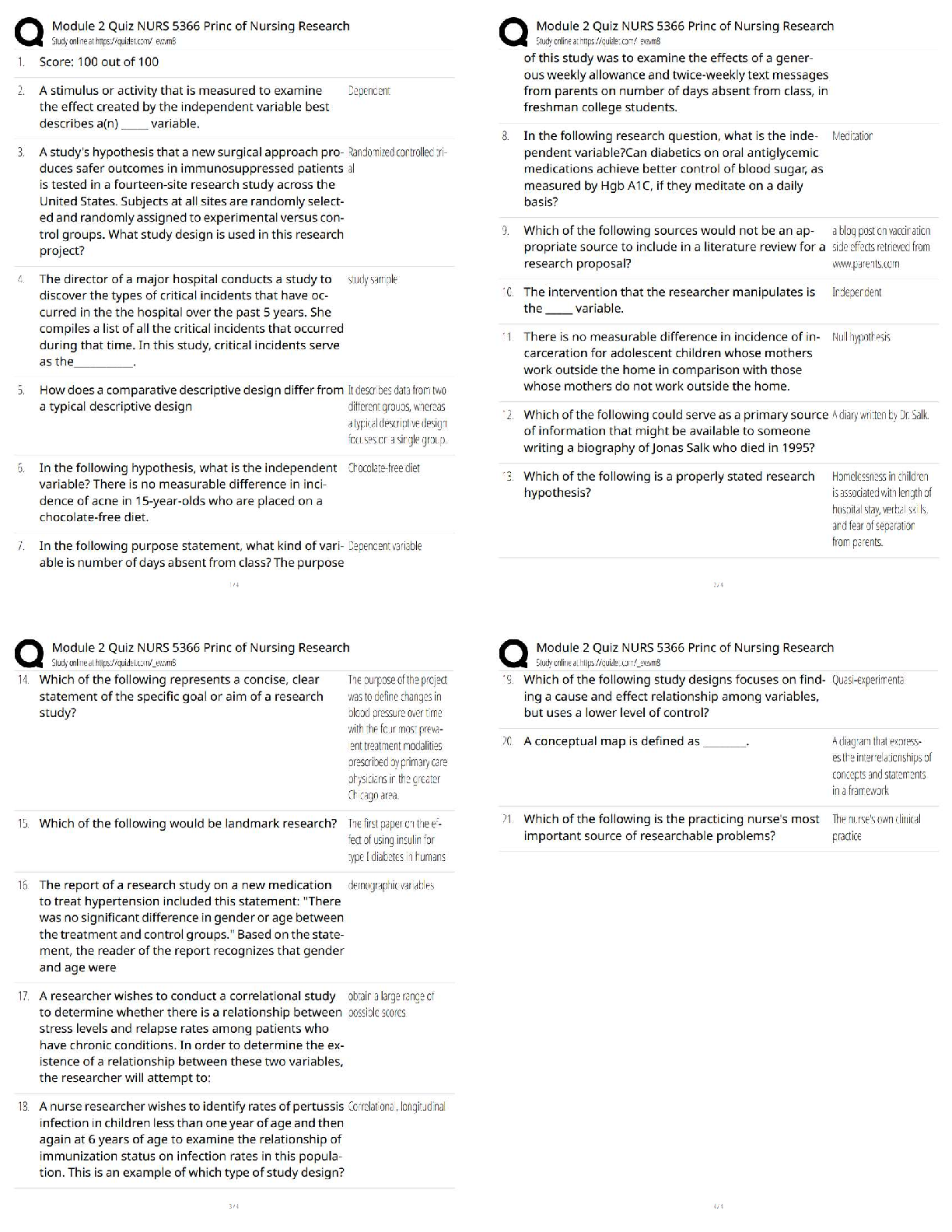
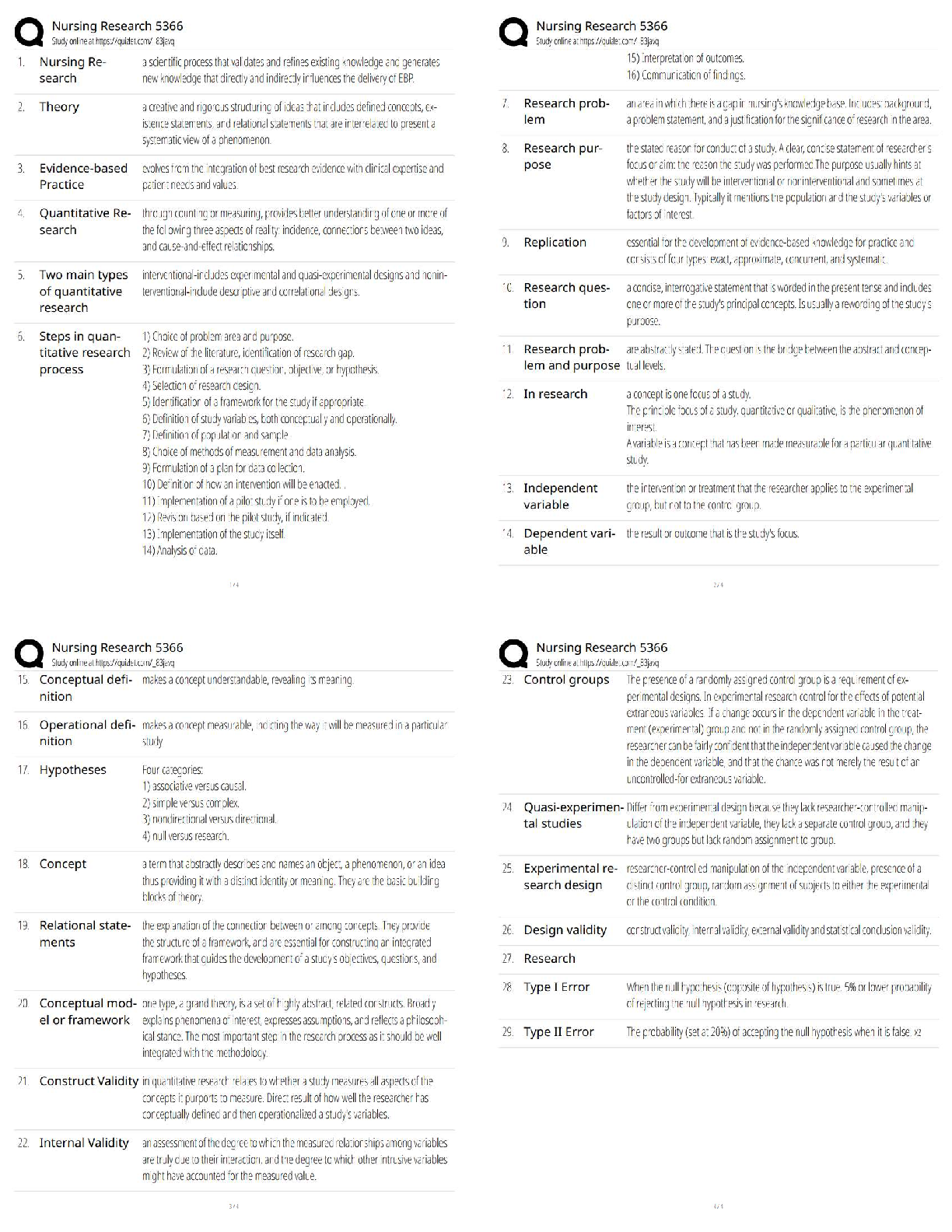
The atmosphere is composed mainly of what two gases? - ✔✔Nitrogen (78%) & Oxygen (21%)
Where is ozone found and why is it important? - ✔✔Stratosphere: it absorbs UV rays (up to
30km)
Troposphere: Near the
...
ATMO Exam 1
The atmosphere is composed mainly of what two gases? - ✔✔Nitrogen (78%) & Oxygen (21%)
Where is ozone found and why is it important? - ✔✔Stratosphere: it absorbs UV rays (up to
30km)
Troposphere: Near the ground, it acts as a pollutant (10-17km)
Which component has the biggest variation from place to place? - ✔✔Water vapor is the main
variable constituent (up to 4%),
followed by CO2
A compound is added to the air at a rate of 2 Tg/year, and removed at this same rate. If the total
amount of this compound in the atmosphere is 4000 Tg, what is the residence time? -
✔✔Residence Time = Rate of Creation// Rate of Destruction
1 year(?)
What does density measure? Suppose we cool the air without changing the pressure. How would
the density change? - ✔✔Measures the amount of a substance present in a given amount of
space. D= M/V
Density increases
What does pressure measure? How is it related to weight of the atmosphere? - ✔✔The force
exerted by a given volume of air outward on its surroundings. Pressure= outward force exerted /
area of surface
The weight of the air above a certain point is held up by a the pressure force exerted by the air
below.
Why are the record high pressures found in places like Siberia and Montana (and not Hawaii or
Texas)? - ✔✔
If the surface pressure is 1000 mb, what percentage of the atmosphere (by weight or mass) is
above 700 mb? - ✔✔Below: [(1000-700)/1000]*100= 30%
Above: 70%
In the stratosphere, the temperature increases with height, while the pressure decreases. So how
does the density change with height? - ✔✔As temperature increases with height, density
decreases
What are the four main layers of the atmosphere and how does temperature vary across each? -
✔✔4)Thermosphere (temp. increases w/ height)
3)Mesosphere (temp. decrease w/ height)
2)Stratosphere (temp. increases w/ height)
1) Troposphere (temp. decrease w/ height)
Why does temperature decrease with height in the troposphere but then increase with height in
the stratosphere? - ✔✔In the absence of solar absorption, the temperature tends to decrease with
height (Troposphere/Mesosphere)
How many degrees Celsius are between freezing and boiling? How many degrees F? And K? -
✔✔Celcius: 100
Fahrenheit: 180
Kelvin: 100
A temperature of 25 C is what in F? - ✔✔77 F
180 Degrees Fahrenheit for every 100 of Celsius (9 Degrees for every 5 Degrees of Celsius + 35
degrees F)
Why does land heat up faster than water on a hot day? And how does this diff
erence result in the sea breeze? - ✔✔Specific Heat of Water is higher than that of Land (more
energy is required to increase the temp. of water). This causes the air over the ocean to be cooler
(high pressure) than the air over the land (low pressure); high pressure moves to low pressure
Based on my experiments, cats have a higher specfi
c heat than squirrels. Suppose I stuff
a cat and a squirrel of roughly equal size into a toaster oven: Which
will heat up faster? - ✔✔Squirrels
Ok, so land heats up faster than water during the day....what do you think happens at night?
(Remember: Objects with high specfi
c heat are more resistant
to temperature changes....both warming and cooling.) And how might this result in a so-called
land breeze? - ✔✔The land will cool faster than the ocean thus causing it to have high air
pressure and the air above the ocean to be low pressure, resulting in the land-breeze
Relative wavelengths for the different types of radiation (e.g., gamma, x-rays, visible, IR,
Microwave, TV, and radio). - ✔✔Radio: Long
TV: Long
Microwave: Middle
IR: Middle
Visible: Middle/Short
X-Rays: Short
Gamma: Short
Blackbody - ✔✔A substance that absorbs all incident wavelengths completely. Ex. Sun, Earth
Given a blackbody, will a warmer body emit more or less radiation? Longer or shorter
wavelengths? - ✔✔Warmer bodies emit more energy with shorter wavelengths
What does it mean to be a selective absorber? For the atmosphere, which wavelengths are
absorbed most strongly? Least strongly? - ✔✔Selective Absorber: An object that absorbs some
wavelengths better than others.
Longwaves (IR) are absorbed effectively, while shortwave
(Visible) is barely absorbed at all.
What group of gasses are selective absorbers? - ✔✔Atmospheric Gasses, specifically CO2 and
H2O
What is the effect of select absorption on Earth's surface? - ✔✔Incoming shortwave radiation
from the Sun passes through atmo. (absorbed by the ground).
The outgoing longwave radiation from the surface is then
largely absorbed by the atmosphere, and part of the
longwave is re-radiated back to the ground.
Result: The net incoming radiation at the surface is increased, resulting in higher surface
temperatures
Without an atmosphere, the equilibrium temperature of the earth would be roughly 255 K.
(What's that in degrees F?) So why is the actual temperature more like 288 K? - ✔✔-0.67
degrees F
T(°F) = T(K) × 9/5 - 459.67
How does the green-house e
ffect work? What gets absorbed, what gets emitted, etc - ✔✔Sunlight absorbed by the Earth and
re-emitted as IR
For a planet with an atmosphere, what does it mean to be in radiative equilibrium....i.e., what
gets balanced by what? - ✔✔Equal incoming and outgoing radiative heat flux and egligible heat
transfer by conduction and convection
T ~ 255 K (no atmosphere)
T ~ 288 K (selectively absorbing atmosphere)
Why is the sky blue when you look away from the sun? And why are sunsets red? - ✔✔Blue
light: Scattered Light
The Reds/Oranges can be seen once the blue light has scatted away.
What's the definition of albedo? And what's the albedo for the Earth? - ✔✔~ 30% of the
incoming solar radiation is scattered or reflected back to space.
Energy efficient windows typically have a layer of air (or something similar) between two panes
of glass. Why....i.e., why not just glass? - ✔✔Because air is a good insulator
What are conduction and convection, and how are they di
fferent? Which is more efficient in the atmosphere? - ✔✔Conduction: When heat diffuses
through an object, passing from molecule to molecule.
Convection: When heat is moved from place to place due to warm and cold air masses moving
around.
Convection is most efficient in the atmosphere
Evaporation from the land or water surface is essentially a way of transferring heat to the
atmosphere. What do I mean by that? And when does this heat actually show up? -
✔✔Evaporation works to cool the air around it.
The troposphere absorbs very little of the incoming radiation from the sun. So then where does
the troposphere get its energy? - ✔✔(?) From the Earth's surface that absorbs the Sun's radiation
What factor governs the rate at which molecules escape from a fluid layer? And which factor
governs the rate at which they return? - ✔✔Vapor Content and Temp.
Under what conditions is the air said to be saturated? - ✔✔The number of molecules returning to
the layer exactly
balances the number escaping. Vapor content and temperature are perf!
Suppose we have a mass of air that's sub-saturated (Evaporation is taking place). How could we
make this air saturated, but without changing the amount of vapor in the air? - ✔✔Decrease the
Temp.
Suppose the relative humidity is 40%. What does this mean? Relative to what? - ✔✔RH=
(Actual Vapor Content/ Content Needed for Saturation) * 100
Define Emission Spectrum - ✔✔The energy emitted by an object as a function of wavelength
How thick is the troposphere? - ✔✔Approximate thickness for the troposphere (10 to 12 km in
midlatitudes)
What are the typical values for the surface pressure? - ✔✔(1013 mb, 14.7 psi)
What are the freezing and boiling points in both F, C, and K? - ✔✔Fahrenheit: boiling point:
212/ freezing point: 32
Celcius: boiling point: 100/ freezing point: 0
Kelvin: boiling point: 373/freezing point: 273
What are the wavelength ranges for visible and IR? - ✔✔Visible: 0.4-0.7m
IR: 1-100m
What are the emission peaks for the sun and Earth? - ✔✔Sun: 0.5m
Earth: 10m
What is the pressure at the top of the Burj Kalifa? - ✔✔13.3 lbs/in^2
Define Absorption Spectrum - ✔✔The fraction (or percentage) of incident energy absorbed by
an object as a function of the wavelength
What warms the air around it? - ✔✔Condensation, Freezing, and Deposition (vapor to solid)
What cools the air around it? - ✔✔Melting, Evaporation, and Sub-limation (solid to vapor)
When does Latent Heat occur? - ✔✔Transformations between these phases (i.e., phase changes)
are accompanied by either the release or the absorption of heat
Pressure depends on ______ and ________. - ✔✔Speed; # of air molecules
Which layer of the atmosphere has most of the atmosphere's mass? - ✔✔Troposphere
What is the residency time of CO2? - ✔✔150 years
Consider a layer of water with air above it. If water vapor content is high and the temperature is
low, then we might expect to have... - ✔✔Net Condensation to the layer
A commuter flight to Houston is flying at a pressure of 850 mb. If the surface pressure is roughly
1000 mb, what percentage of the atmosphere by mass is below the plane? - ✔✔[(1000-
850)/1000]*100= 15%
Macroscopic Perspective - ✔✔Look at things in a holistic way (ex. weight)
Microscopic Perspective - ✔✔Looking at things more closely (ex. molecules)
What does temperature measure? - ✔✔A measure of the heat energy stored in a substance; The
speed at which the molecules of air are moving around (on average)
Weight=? - ✔✔Mass*Gravity
Pressure (increases/decreases) with Height - ✔✔Decreases
The Ideal Gas Law expresses the relationship of what 3 things? - ✔✔Pressure, Temperature, &
Density (pressure increases with both density and temperature)
Define Inversion and give an example - ✔✔A layer where temperature increases with height Ex.
Statosphere, Thermosphere
Weather variability can cause how much in a difference of GDP? - ✔✔3 to 4% change in US
GDP in a given year (at most $500 billion per year)
Define Relative Humidity - ✔✔The measure of how close the air is to being
saturated with vapor
How do you calculate relative impact? - ✔✔Worst Weather Year- Baseline Case (mildest year in
past 20 years)
What economic sectors most influenced by weather in percentage? In dollars? - ✔✔Mining
(14.4%); Finance, Insurance, Real Estate ($210 billion)
What is responsible for the majority of deaths related to weather? - ✔✔Heat (43%)
99% of the atmosphere is below ____ km by mass - ✔✔30 km
What is the English measure of pressure? Metric System? - ✔✔psi: Pounds per Square Inch;
Pascal (Pa)
What is the standard atmospheric pressure in metric units? - ✔✔~1013 hPa (1013*100= Pa)
What does Millibars measure? - ✔✔Pressure (it is the same as hPa)
When can air support water droplets and clouds? - ✔✔Only when the air is Saturated or SuperSatureated
Define Energy - ✔✔The capacity to do work (or loosely, the potential to
make something happen). Energy can be transferred in the form of heat or radiation (among
other processes)
Define Power - ✔✔The rate at which energy is transferred from one object
to another (i.e., the energy per unit time)
Define Heat - ✔✔The energy transferred between objects because of
differences in temperature
Define Specific Heat - ✔✔Given a gram of some substance, the amount of heat needed to raise
the temperature by 1°C
By how much is the specific heat of water greater than that of land? - ✔✔~ 2 to 5 times
Define Radiation - ✔✔The energy transmitted by electromagnetic waves (or
waves of electric and magnetic force). Radiation differs from heat in that it travels from emitter
to absorber without affecting the intervening space
What are the units for wavelength? - ✔✔Micrometers (Mu-m) and Meters (m)
The wavelength of peak emission is given by... - ✔✔Wien's law
Characteristics of a planet with no atmosphere - ✔✔Planet interacts directly with space
(Incoming Visible rays absorbed; Outgoing IR are outgoing) Not increase in energy, everything
is in balance. Balanced State. Relative Equilibrium is Te=255K
Characteristics of a planet with selective absorbing atmosphere - ✔✔Incoming Visible rays
absorbed; Outgoing IR are partially absorbed. IR emitted. Relative Equilibrium Te=288K
Where are X-ray and gamma-ray absorbed? - ✔✔Thermosphere
[Show More]







.png)












.png)



.png)


















.png)