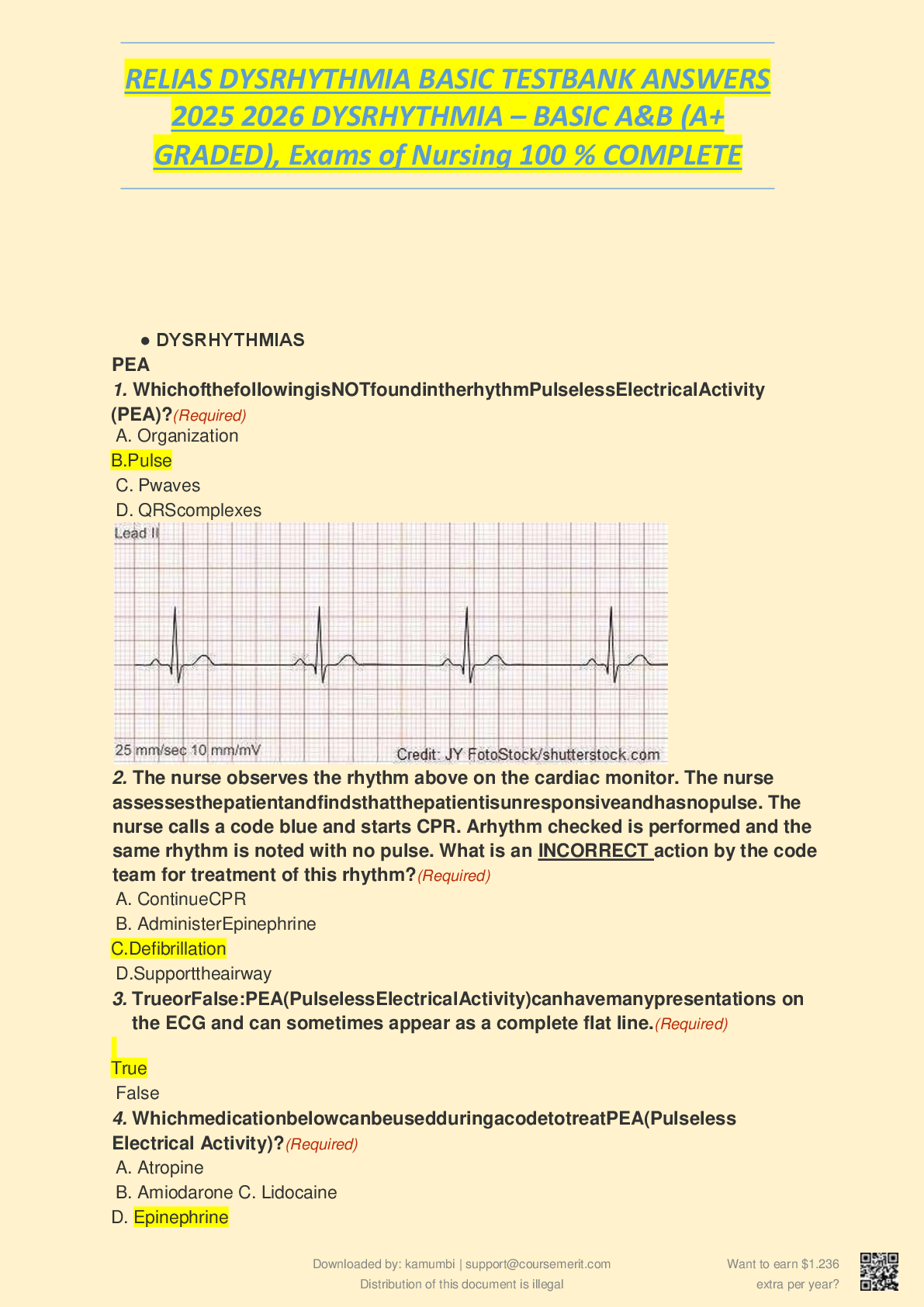
1. A 72-year-old woman with a recent onset of syncopal episodes has been referred to a cardiology group by her family physician. As part of the patient's diagnostic workup, the nurse practitioner conducting the intake as
...
1. A 72-year-old woman with a recent onset of syncopal episodes has been referred to a cardiology group by her family physician. As part of the patient's diagnostic workup, the nurse practitioner conducting the intake assessment has ordered a Holter monitor for 24 hours. Which of the following statements best captures an aspect of Holter monitoring? (Points : 0.4)
A Holter monitor is preferable to standard ECG due to its increased sensitivity to cardiac electrical activity.
The primary goal is to allow the cardiologist to accurately diagnose cardiomyopathies.
Accurate interpretation of the results requires correlating the findings with the activity that the woman was doing at the time of recording.
Holter monitors are normally set to record electrical activity of the heart at least once per hour.
Question 2.2. As part of the diagnostic workup for a male patient with a complex history of cardiovascular disease, the care team has identified the need for a record of the electrical activity of his heart, insight into the metabolism of his myocardium, and physical measurements, and imaging of his heart. Which of the following series of tests is most likely to provide the needed data for his diagnosis and care? (Points : 0.4)
Echocardiogram, PET scan, ECG
Ambulatory ECG, cardiac MRI, echocardiogram
Serum creatinine levels, chest auscultation, myocardial perfusion scintigraphy
Cardiac catheterization, cardiac CT, exercise stress testing
Question 3.3. An 81-year-old female patient of a long-term care facility has a history of congestive heart failure. The nurse practitioner caring for the patient has positioned her sitting up at an angle in bed and is observing her jugular venous distention. Why is jugular venous distention a useful indicator for the assessment of the patient's condition? (Points : 0.4)
Increased cardiac demand causes engorgement of systemic blood vessels, of which the jugular vein is one of the largest.
Blood backs up into the jugular vein because there are no valves at the point of entry into the heart.
Peripheral dilation is associated with decreased stroke volume and ejection fraction.
Heart valves are not capable of preventing backflow in cases of atrial congestion.
Question 4.4. A physical assessment of a 28-year-old female patient indicates that her blood pressure in her legs is lower than that in her arms and that her brachial pulse is weaker in her left arm than in her right. In addition, her femoral pulses are weak bilaterally. Which of the following possibilities would her care provider be most likely to suspect? (Points : 0.4)
Pheochromocytoma
Essential hypertension
Coarctation of the aorta
An adrenocortical disorder
Question 5.5. A 6-year-old boy has been brought to the emergency department by ambulance after his mother discovered that his heart rate was “so fast I couldn't even count it.” The child was determined to be in atrial flutter and his mother is seeking an explanation from the health care team. Which of the following points should underlie an explanation to the mother? (Points : 0.4)
The child is experiencing a reentry rhythm in his right atrium.
The resolution of the problem is dependent on spontaneous recovery and is resistant to pacing interventions.
The child is likely to have a normal ECG apart from the rapid heart rate.
The boy's atria are experiencing abnormal sympathetic stimulation.
Question 6.6. A 66-year-old patient's echocardiogram reveals a hypertrophied left ventricle, normal chamber volume, and a normal ejection fraction from the heart. What is this patient's most likely diagnosis? (Points : 0.4)
Mitral valve regurgitation
Aortic valve stenosis
Mitral valve stenosis
Aortic valve regurgitation
Question 7.7. A 70-year-old male patient presents to the emergency department complaining of pain in his calf that is exacerbated when he walks. His pedal and popliteal pulses are faintly palpable and his leg distal to the pain is noticeably reddened. What would his care provider's preliminary diagnosis and anticipated treatment most likely be?(Points : 0.4)
Acute arterial occlusion that will be treated with angioplasty
Raynaud disease that will require antiplatelet medications
Atherosclerotic occlusive disease necessitating thrombolytic therapy
Giant cell temporal arteritis that will be treated with corticosteroids
Question 8.8. A patient in the intensive care unit has a blood pressure of 87/39 and has warm, flushed skin accompanying his sudden decline in level of consciousness. The patient also has arterial and venous dilation and a decrease in systemic vascular resistance. What is this patient's most likely diagnosis? (Points : 0.4)
Hypovolemic shock
Septic shock
Neurogenic shock
Obstructive shock
[Show More]