Study guide for QMA Latest Update with
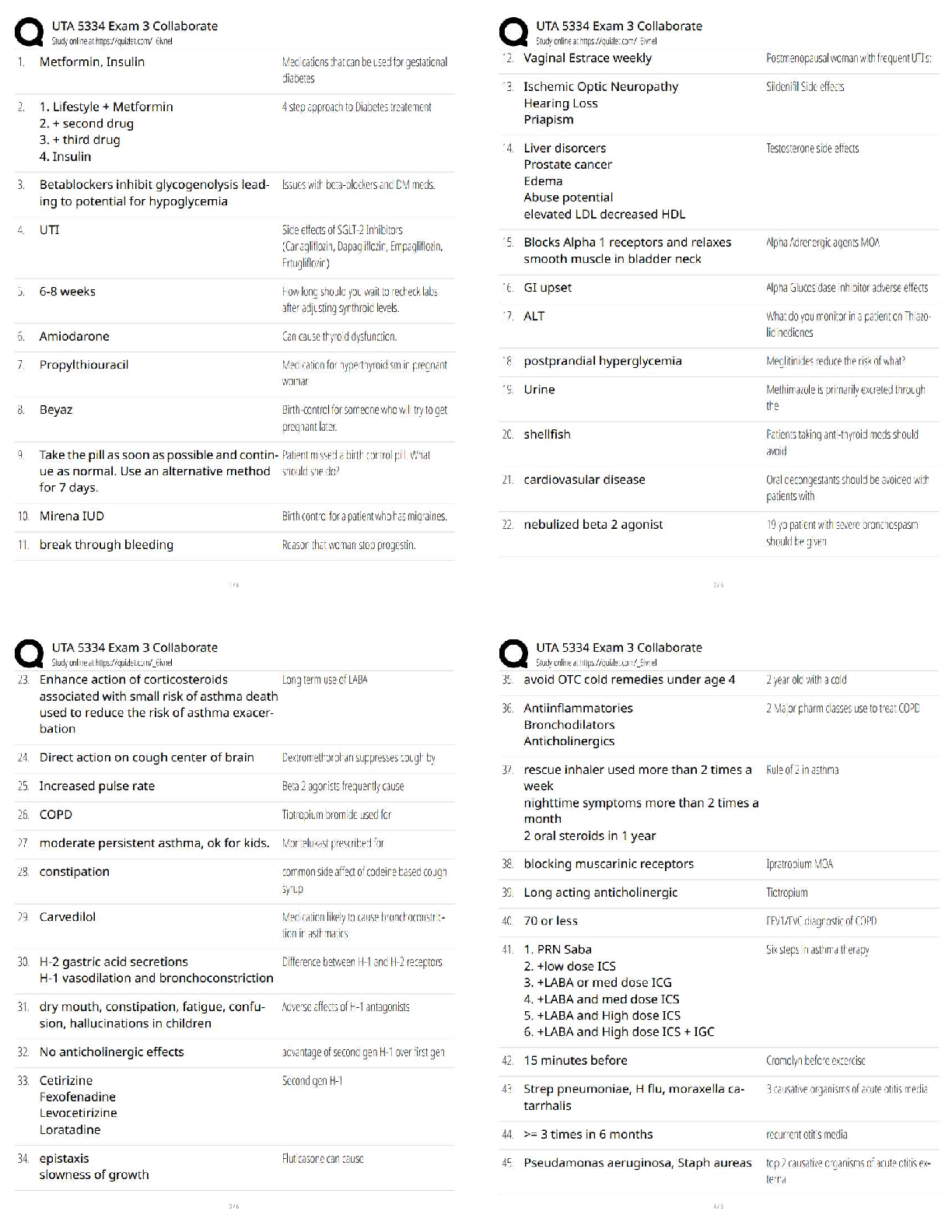
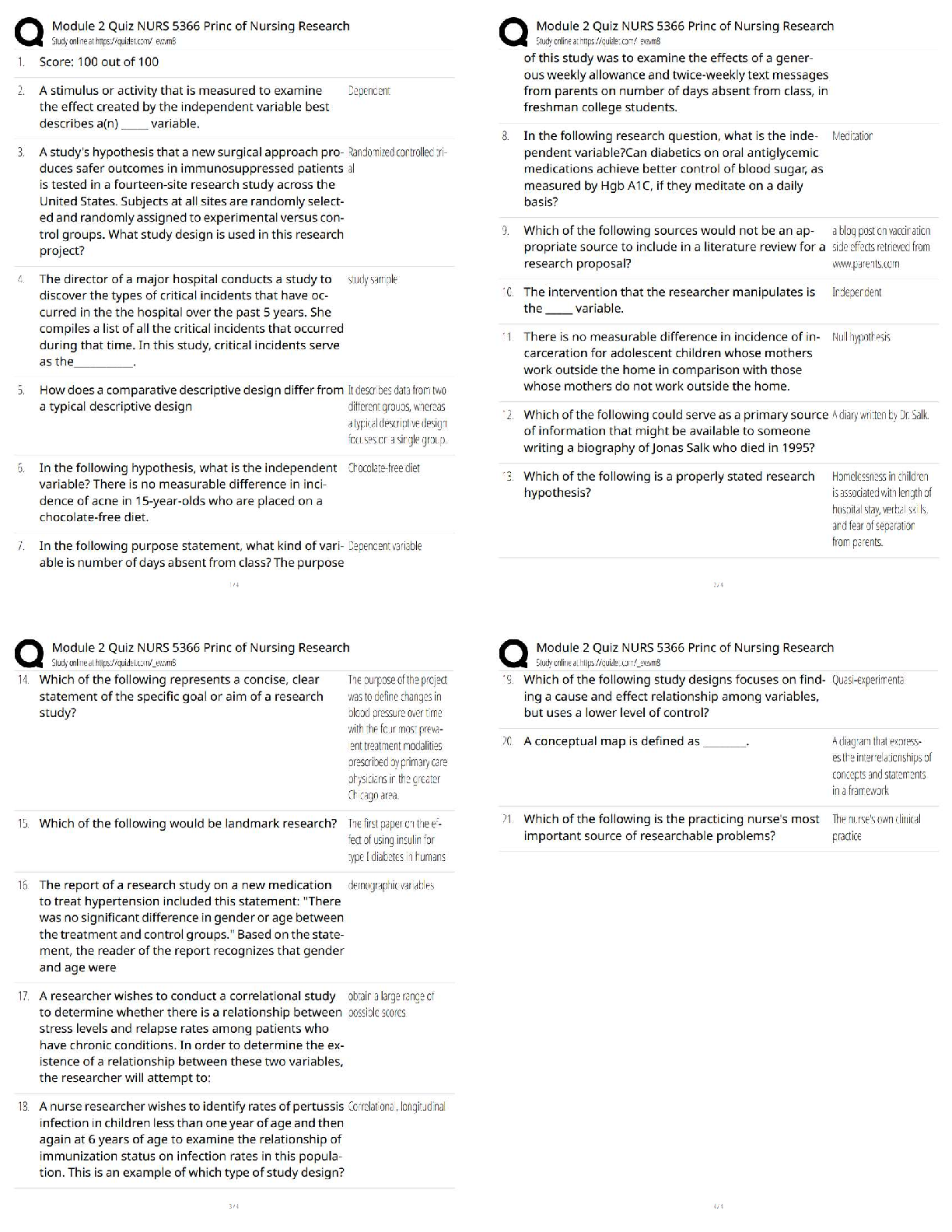
Verified Solutions
Tasks the QMA is PROHIBITED from performing. ✔✔Assess a resident's condition. Call a
physician. Take a physician's written or verbal order. Administer medicati
...
Study guide for QMA Latest Update with
Verified Solutions
Tasks the QMA is PROHIBITED from performing. ✔✔Assess a resident's condition. Call a
physician. Take a physician's written or verbal order. Administer medication by injection.
Administer any medication inhalation treatment OTHER than a metered dose inhaler. Administer
medication per nasogastric tube. Instill irrigation fluids of any type including, but not limited to,
colostomy, catheter and enema, EXCEPT a commercially packed prepared disposable enema.
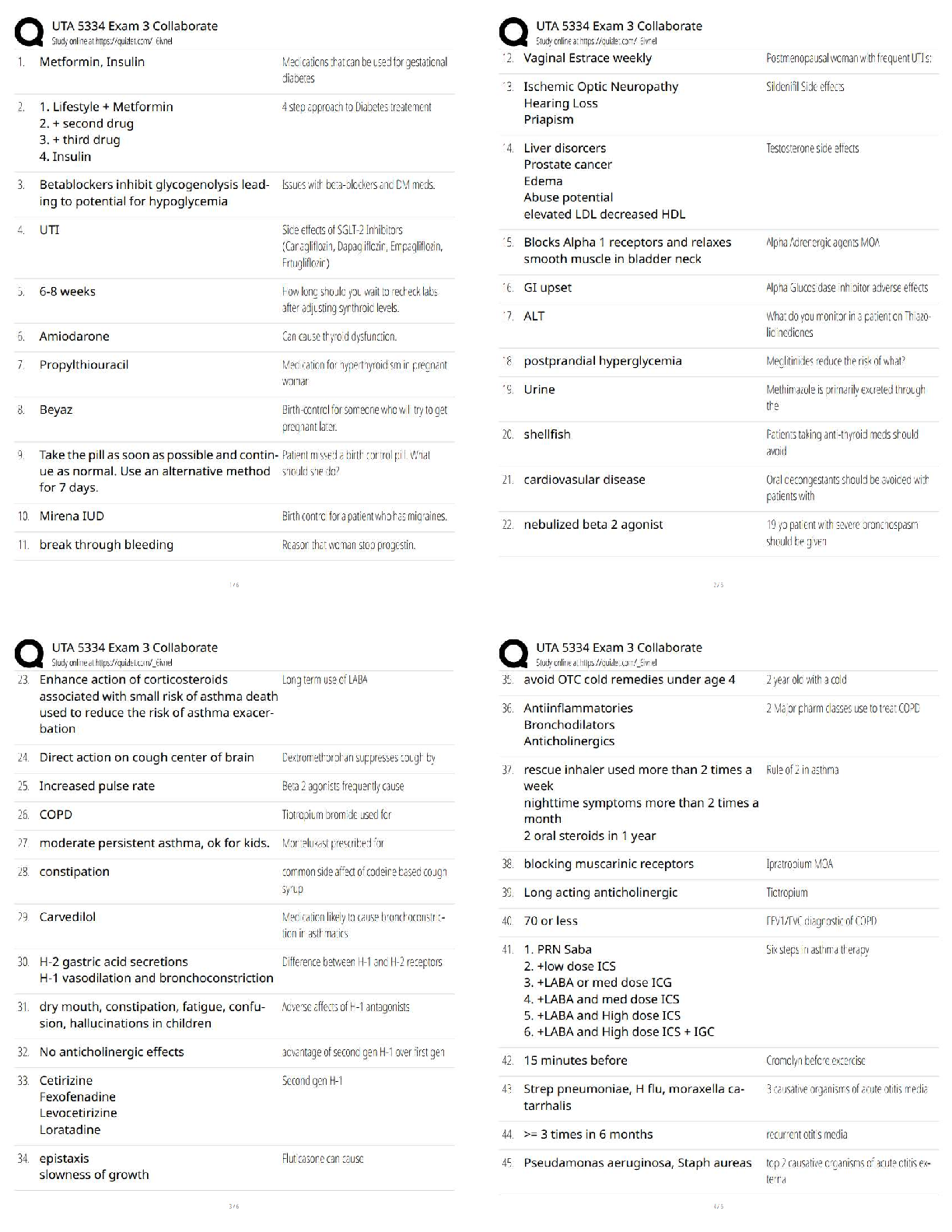
Administer a treatment that involves an advanced skin condition, including Stage II, III, and IV
decubitus ulcers.
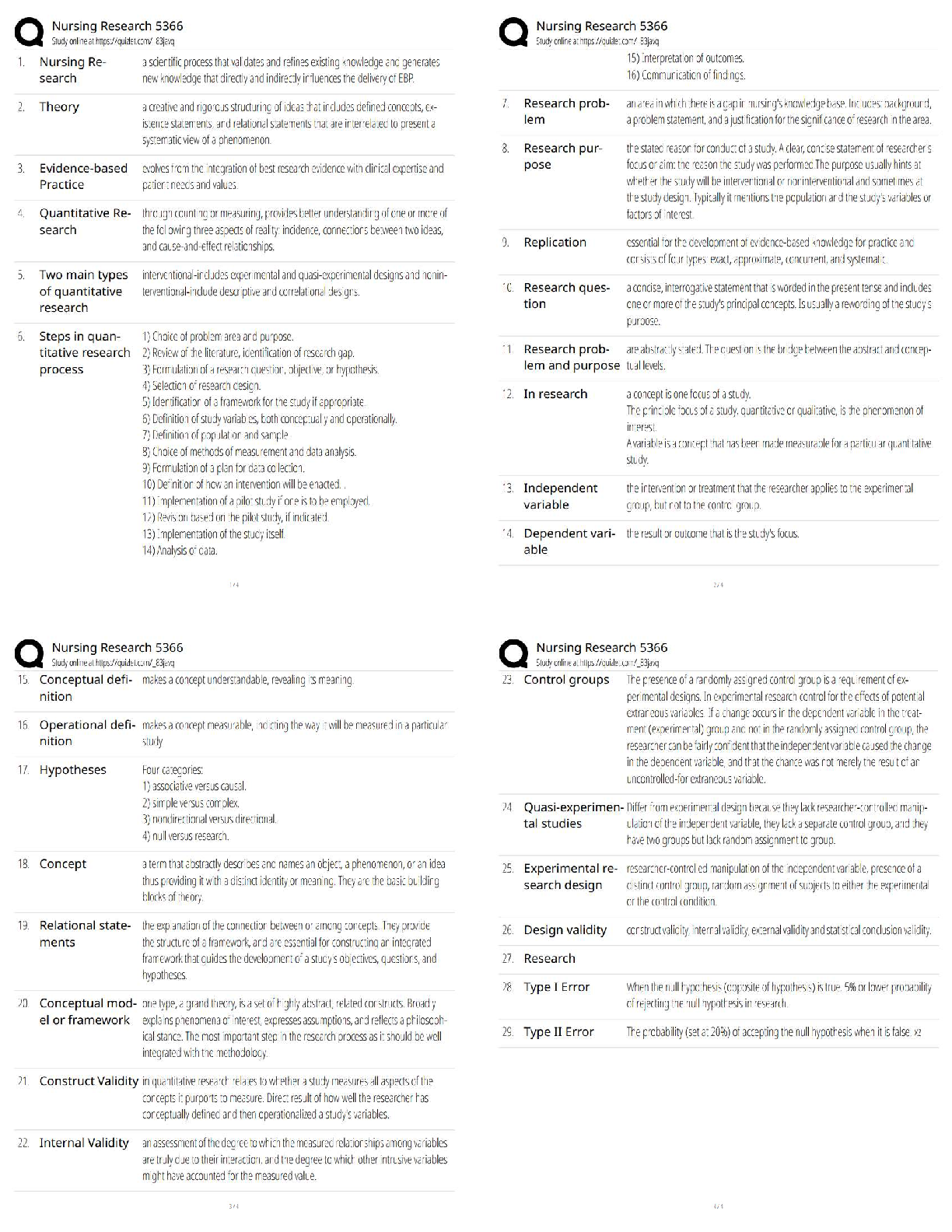
The QMA Scope of Practice ✔✔Observe and report to licensed nurse. Measure and document
vital signs. Administer regularly prescribed meds which the QMA has been trained to administer
only after personally preparing the meds to be administered. Initiate oxygen per nasal cannula or
non sealing mask only in an emergency. Obtain oxygen saturation using oximeter. Administer,
apply physician ordered oral, ophthalmic, otic, nasal, vaginal and rectal meds. Crush and
administer meds if such preparation is appropriate per manufacturer or physicians order. Alter
capsules if prescribed to be administered in this altered manner by the physician. Count,
administer, and document controlled substances. Administer meds per G-tube or J-tube.
Administer previously ordered PRN meds only if authorization is obtained, then the QMA must
chart resident symptoms indicating the need for the med and time symptoms occurred, Chart that
the facility nurse was notified the symptoms of the resident and that permission was granted to
administer med, obtain permission each time the resident needs the med, ensure that the
resident's record is soigné do by the LPN or RN who gave the permission for the PRN meds.
Apply topical meds to minor skin conditions such as dermatitis, scabies, pediculosis, fungal
infection, psoriasis, eczema, first degree burn, stage I decubitus ulcer. Administer meds via
metered dose inhaler. Conduct hemoccult testing and report result to licensed nurse. Provide site
care and apply dressing to a healed G-tube or J-tube site (ordered). Empty and change colostomy
bag. Instill a commercially disposable enema (120 ml or 4.5 ozs) after the resident has been
assessed by the nurse. Administer a sitz bath if ordered by a physician. Apply cold, dry compress
as directed by nurse or physician. Conduct diabetic urine testing. Collect fecal or urine
specimens as ordered by physician. CHART CHART CHART anything the QMA see, hears, or
smells and document what is reported to the Q by the resident.
Negligence ✔✔The omission or neglect of any reasonable precaution, care or action. Residents
are protected from health care negligence or malpractice by a law called Duty of Care.
Malpractice ✔✔Any improper or injurious practice, or any unskillful or faulty medical or
surgical treatment.
The Six Rights of Medication administration ✔✔Right Medication. Right Dose. Right Resident.
Right Route. Right Time. (1hr before or 1 hr after). Right documentation.
Initial Steps ✔✔Obtain info from licensed nurse about resident's needs abilities, limitations, and
known allergies. Gather supplies and equipment. Knock on resident's door. Identify yourself.
Explain procedure to the resident. Wash your hands or use antiseptic foam or gel. Wear gloves to
maintain Standard Precautions as necessary.
Final Steps ✔✔Observe resident for any immediate reaction to med or procedure. Assure the
resident is in a comfortable position. Make sure call light is within resident's reach. Remove
supplies and discard of medication cups/disposable supplies. Thank resident. Remove gloves.
Wash hands. Document meds administered or procedure preformed. Report any abnormalities to
the nurse.
Sundowning ✔✔Increased confusion and restlessness in late afternoon, evening, and night.
Hand washing ✔✔Lather all areas of hands and wrists, rubbing vigorously for at least 10
seconds.
Putting on Gloves ✔✔Remove one glove by grasping the outer surface just below the cuff with
the other gloved hand.
Isolation Precautions ✔✔Airborne-pathogens are transmitted on dust particles in air currents
examples are TB, chickenpox, measles.
Droplet-pathogens are transmitted in droplets when a person coughs, sneezes or talks examples
pneumonia, influenza, scarlet fever.
Contact-pathogens are transmitted by direct contact (skin-to-skin) with the resident or indirect
contact with surfaces or care items in the resident's environment examples scabies,
conjunctivitis, impetigo.
Hepatitis ✔✔Contagious disease of the liver caused by a virus and spread by exposure to
infected blood, sexual contact or fecal/oral contact. Symptoms are flu like. Severe infection can
cause permanent liver damage and death. Types A, B, C, D, E
Tuberculosis ✔✔Chronic bacterial infection that usually affects the lung but may affect other
parts of the body such as the kidneys, bones, and the brain. TB is spread through the air in
droplets from sputum of persons with active disease. Symptoms include fever, loss of appetite,
fatigue, productive cough and night sweats.
Acquired ImmuneDeficiency Syndrome ✔✔Results from infection with the Human
Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) which destroys the body's ability to fight infection. Virus is
spread thru infected blood and body fluid. Early symptoms are flu like followed by a symptom
free period which can last many years (one to ten or more). No cure is known, however, new
meds and treatments show promise.
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) ✔✔Bacteria that no longer responds to
antibiotics normally used to treat staphylococcal infections. It is spread on the hands of health
care workers. To prevent spread follow Standard Precautions.
Vancomycin Resistant Enterococcus
(VRE) ✔✔Bacteria that no longer responds to the antibiotic Vancomycin. It is spread on the
hands of health care workers. Use Standard Precautions to prevent spreading.
Body Mechanics/Resident Safety ✔✔Place a pillow against the headboard when moving a
resident up in bed.
Stomatitis ✔✔Inflammation of the mouth. Residents who have stomatitis must receive more
frequent mouth care and removal of excess mucous from the mouth.
Pruritus ✔✔Severe itching without evidence of a rash on the skin. It may occur over the entire
body. Residents who have pruritus must have proper positioning and good skin care.
Pharmacology ✔✔The study of medications and their effect on the body.
Trade or Brand name of meds ✔✔First letter is capatilized. Identified with the symbol ® which
indicates the name is registered or patented by a company or individual.
Generic name of meds ✔✔First letter is lowercase. This is the OFFICIAL name of the
medication. Usually a combination of chemicals in the medication, not patented.
Body mechanics/resident safety ✔✔Place a pillow against the headboard when,living a resident
up in bed.
Semi synthetic combination of man made and plants, animals or minerals ✔✔Examples-Tylox
(acetaminophen and opium)
Local effect ✔✔Limited to the area of the body where the medication is applied.
Systemic effect ✔✔Affects the entire body
Tolerance ✔✔The body becomes increasingly resistant to a drug or other substance through
continued exposure to the substance.
Primary effect ✔✔The reason the medication was ordered.
Secondary effect ✔✔Any additional effect from the medication
Idiosyncrasy ✔✔Unusual effect from the drug
Side effect ✔✔Outcomes that are not intended; the action or effect of a medication other than
that desired. Commonly undesired, such as nausea, headache, insomnia, etc.
Adverse effect (ADR) ✔✔An undesired side effect or toxicity.
Cumulative effect ✔✔Build up of a substance that could lead to toxicity.
**tetracycline should not be administered with milk or milk products**
Chemical reactions
(Positive) ✔✔A beneficial chemical reaction is potassium K+ and Sodium Na+. At the correct
ratios these two chemicals cause the heart to beat.
Chemical reaction
(Negative) ✔✔A negative reaction of chemicals could be serving a patient spinach when the
resident is taking Coumadin (blood thinner).
Coated ✔✔Improves taste.
Enteric coated ✔✔To prevent irritation or absorption in the stomach. These medications are not
recommended for crushing.
Methods of administration ✔✔Oral-by mouth
Topical-particular location of body
Parenteral-by injection
Instillation-administering a liquid drop by drop
Insertion-placed into a specific area of the body
Inhalation-draw in by breathing
Transdermal-absorbs through the skin
Enteral-tube feedings
Legend medications ✔✔Medications that can only be obtained with a prescription filled by a
licensed pharmacist.
Non legend medications ✔✔Over the counter medications
Orders medications to be administered ✔✔Type of medication
Amount of medication
Form of medication
Time and frequency of administration
Absorption ✔✔Occurs when medication moves from the site of administration into the
bloodstream.
**food may prevent some medications from being absorbed** example milk with tetracycline
Distribution ✔✔Medication is carried to body cells through the bloodstream.
Half life ✔✔The time it takes half of the medication to leave the bloodstream. If the half life is
two hours, then 50 percent of the medication will be gone from the bloodstream in two hours.
Metabolism ✔✔Or biotransformation is the process by which a substance is changed into a form
that is more easily excreted by the body.
Excretion ✔✔The process by which a medication is eliminated from the body.
Labeling of the medication container ✔✔Resident's full name
Prescribing physician's name
Pharmacy prescription number
Name, strength and amount of the medication dispensed
Expiration date of all timed medications
Date if issuance
Warning labels if needed
Physician's direction for use
Labels on containers of controlled substances must have the following warning "Caution:
Federal Law prohibits the transfer of this medication to any person other than the person for
whom it was prescribed."
Name, address and the telephone number of the issuing pharmacy.
Schedule I ✔✔Have the highest potential for abuse
These meds must could also be called high market street meds.
Examples include heroin and cocaine
Schedule II ✔✔Have a high potential for abuse
Examples of these medications include Percodan and Dilaudid
Schedule III ✔✔Have a moderate potential for abuse
Examples of these medications are Percocet, Vicodin and Codeine
Schedule IV ✔✔Have a minimal potential abuse
Examples of these medications include Talwin, Darvon, Ambien
Schedule V ✔✔Are routinely administered medications
Examples of these medications include Lasix, Digoxin, Dilantin.
Physician's orders (verbal) ✔✔If the order is over the phone the physician the signs the order on
his or her next visit to the facility.
Apothecary system ✔✔Is more accurate than the household measure system, but less accurate
than the metric system.
1 Liter ✔✔1000 mL
30 cc ✔✔1 ounce
1 teaspoon ✔✔5 mL
1 tablespoon ✔✔15 mL
[Show More]













.png)