Question 1.1:
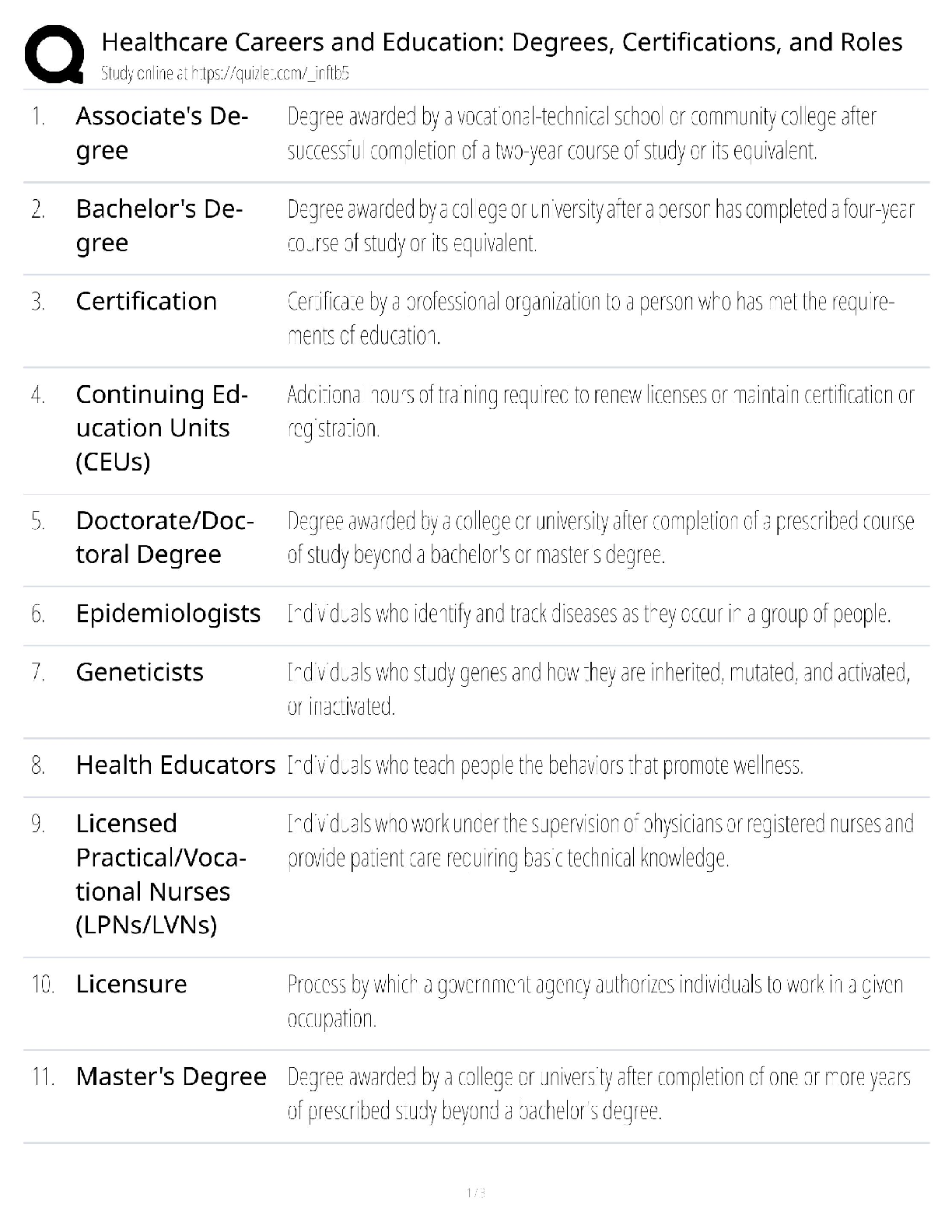
To draw the demand curve, the price for using public transportation must be held constant. If the cost of riding the bus declines, which of the following statements are true? Select all correct statements.
...
Question 1.1:
To draw the demand curve, the price for using public transportation must be held constant. If the cost of riding the bus declines, which of the following statements are true? Select all correct statements.
The commuter’s demand curve for gasoline may change.
The ceteris paribus assumption is violated.
The commuter may ride the bus more and consume less gasoline.
The demand curve will become upward sloping.
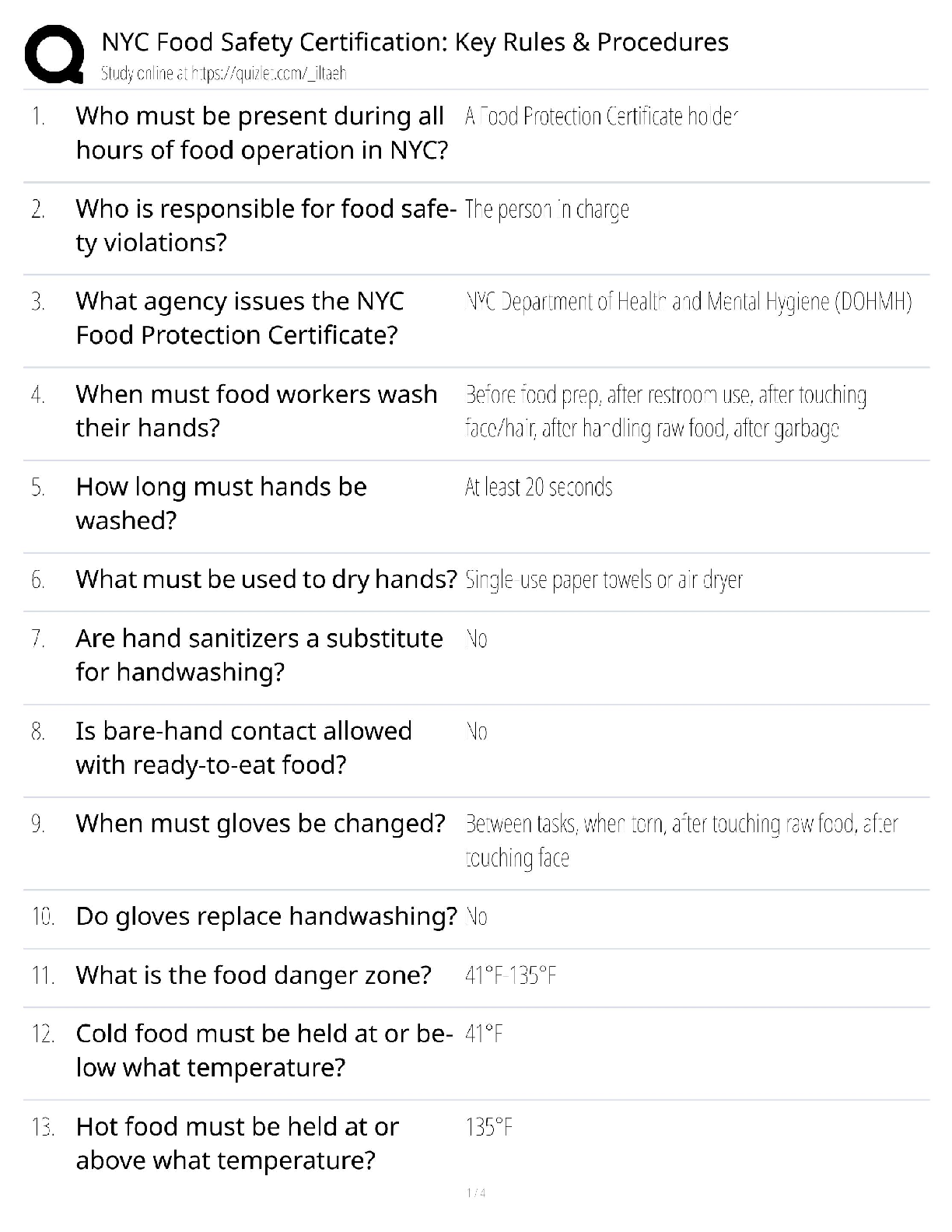
Question 1.2:
As the price of gasoline decreases, the quantity demanded of gasoline Increases
Question 1.3:
What is the total quantity demanded at $3.00 per gallon?
125
175
50
Question 1.4:
What is the total quantity demanded at $4.00 per gallon?
100
40
140
Question 1.5:
Which arrow on the graph shows a change in Quantity Demanded?
A
B
Both
The distinction between a change in demand and a change in the quantity demanded is an important one. A change in the quantity demanded of a good is caused by a change in the price of the good, therefore, “all else equal” creates a ceteris paribus condition. As such, a change in the quantity demanded of a good is represented by a movement along the demand curve. This is in contrast to a change in demand which is caused by a change in anything that affects demand other than the price (e.g. income or the price of a related good changes). This occurs when the ceteris paribus assumption does not hold and the demand curve shifts to a new position.
Question 1.6:
Which arrow on the graph shows a change in Demand?
A
B
Both
Question 1.7:
For Emma, gasoline is an inferior good because as her income increases she purchases a house closer to her work’s downtown office and thus has a shorter commute. Emma receives a large raise at work. By dragging the demand curve left or right or selecting the quantity demanded, show the effect that this event will have on Emma’s demand for gasoline.
The demand curve shifts left.
Question 1.8:
When people retire from work they, on average, drive less because they do not have a daily commute. In the United States, according to the Current Population Survey, from 2003 to 2012 the proportion of the population over 65 increased from 12% to 13.4%. By dragging the demand curve left or right or selecting the quantity demanded, show the effect that this event will have on the market for gasoline. The demand curve shifts left.
Question 1.9:
Gasoline and electric cars are substitute goods. By dragging the demand curve left or right or selecting the quantity demanded, show the effect that a government subsidy that lowers the price of electric vehicles would have on the demand for gasoline. The demand curve shifts left.
Question 1.10:
Following the terrorist attacks of September 11th, 2001, citizens of the United States were hesitant to travel by airplane. As a result, Americans who would have previously flown began driving more often. By dragging the demand curve left or right or selecting the quantity demanded, show the effect that this event will have on the market for gasoline. The demand curve shifts right.
Question 1.11:
Gasoline prices over the past few weeks have fallen. By dragging the demand curve left or right or selecting the quantity demanded, show the effect that this event will have on the market for gasoline.
The quantity demanded increases
Question 2.1:
To draw the supply curve, the number of refineries must be held constant. If a hurricane in the Gulf Coast forces the refineries at Galveston and Shreveport to suspend operations, which of the following statements are true? Select all correct answers.
The firm’s supply curve for gasoline will change.
The ceteris paribus assumption is violated.
The firm will supply less gasoline at all prices.
The firm’s supply curve will become downward sloping.
The ceteris paribus assumption is violated.
The supply curve will move to a different place.
The quantity of gasoline supplied at each price will change.
Question 2.2:
As the price of gasoline increases, the quantity supplied of gasoline by the Gulf Coast Refining Company increases.
Question 2.3:
What is the total quantity supplied at $3.00 per gallon?
100
300
200
Question 2.4:
What is the total quantity supplied at $4.00 per gallon?
300
450
150
Question 2.5:
Which arrow on the graph shows a change in Quantity Supplied?
A
B
Both
Question 2.6:
Which arrow on the graph shows a change in Supply?
A
B
Both
Question 2.7:
The states of Texas and Louisiana relax regulations on where gasoline refineries can operate resulting in more refineries. By dragging the supply curve left or right or selecting the quantity supplied, show the effect that this event will have on the gasoline market. In this scenario, presume the relaxed regulations increases the number of gasoline refineries in operation.
The quantity supplied shifts right
The price of crude oil, the primary input to gasoline, increases sharply. By dragging the supply curve left or right or selecting the quantity supplied, show the effect that this event will have on the gasoline market. The quantity supplied shifts left
Question 2.8:
The Environmental Protection Agency approves stricter pollution regulations increasing the marginal cost of refining gasoline. By dragging the supply curve left or right or selecting the quantity supplied, show the effect that this event will have on the gasoline market. The quantity supplied shifts left
n improvement in technology allows firms to process a higher percentage of their oil input into gasoline. By dragging the supply curve left or right or selecting the quantity supplied, show the effect that this event will have on the gasoline market. The quantity supplied shifts right
Question 2.9:
Gasoline refineries can use crude oil to produce either conventional gasoline or petroleum diesel, they are production substitutes. From March 2015 to March 2016, the price of petroleum diesel decreased relative to the price of conventional gasoline. By dragging the supply curve left or right or selecting the quantity supplied, show the effect that this event will have on the gasoline market. The quantity supplied shifts right
Question 2.10:
Gasoline prices today have decreased. By dragging the supply curve left or right or selecting the quantity supplied, show the effect that this will have on the gasoline market. The quantity supplied decreases.
Question 3.1:
If the current price is above the equilibrium price then there is a surplus and the price will fall.
Question 3.2:
Given a surplus of a good, as the price declines to equilibrium quantity demanded increases and quantity supplied declines.
Given a shortage of a good, as the price increases to equilibrium quantity demanded declines and quantity supplied increases.
Question 3.4:
That is correct. If the price of gasoline is $4.00 there will be a surplus of gasoline of 60.00 million gallons.
Question 3.5:
That is correct If the price of gasoline is $2.00 there will be a shortage of gasoline of 60.00 million gallons.
Change in demand. If the demand for gasoline were to increase, this will shift the demand curve to the right and as a result the equilibrium price and quantity both rise. Change in supply. If the supply of gasoline decreases, this will shift the supply curve to the left and as a result the equilibrium price rises while quantity falls.
Question 3.6:
Gasoline is a normal good because as incomes increase people tend to drive more. Assume the median income declines. By dragging the demand or supply curve left or right, and holding everything else constant, show the effect that this event will have on equilibrium price and quantity. The demand curve shifts left.
Following the terrorist attacks of September 11th, 2001, citizens of the United States were hesitant to travel by airplane. As a result, Americans who would have previously flown began driving more often. By dragging the demand or supply curve left or right, and holding everything else constant, show the effect that this event will have on equilibrium price and quantity. The demand curve shifts right.
Question 3.7:
Caroline decides to exercise more by cycling to work rather than driving. By dragging the demand or supply curve left or right, and holding everything else constant, show the effect that this event will have on equilibrium price and quantity. The demand curve shifts left.
For Wayland, gasoline and road-trip vacations are complement goods. The price of a hotel room declines making the cost of a road trips less expensive. By dragging the demand or supply curve left or right, and holding everything else constant, show the effect that this event will have on equilibrium price and quantity.
The demand curve shifts to the right
Question 3.8:
The price of crude oil, the primary input to gasoline, decreases sharply. By dragging the demand or supply curve left or right, and holding everything else constant, show the effect that this event will have on equilibrium price and quantity. The supply curve shifts right
Question 3.9:
The Environmental Protection Agency approves stricter pollution regulations increasing the marginal cost of refining gasoline. By dragging the demand or supply curve left or right, and holding everything else constant, show the effect that this event will have on equilibrium price and quantity. The quantity supplied shifts left
Question 3.10:
A hurricane in the Gulf of Mexico shuts down a number of gasoline refineries. By dragging the demand or supply curve left or right, and holding everything else constant, show the effect that this event will have on equilibrium price and quantity. The supply curve shifts left
Question 3.11:
The price of crude oil, the primary input to gasoline, increases sharply. By dragging the demand or supply curve left or right, and holding everything else constant, show the effect that this event will have on equilibrium price and quantity. The supply curve shifts left
Question 4.7:
As the price of oil increased during the first half of 2008, the supply of gasoline decreased causing the equilibrium price of gasoline to increase and the equilibrium quantity of gasoline to decrease .
Question 4.8:
As the price of oil decreased during the first half of 2008, the supply of gasoline increased causing the equilibrium price of gasoline to increase and the equilibrium quantity of gasoline to increase.
Question 4.9:
During what season does the graph indicate higher gasoline prices generally occur?
Fall
Summer
Winter
Question 4.10:
During what season does the graph indicate lower gasoline prices generally occur?
Spring
Summer
Winter
Question 4.11:
How will refinery maintenance affect the market for gasoline?
Demand will decrease
Supply will increase
Supply will decrease
Demand will increase
Question 4.12:
How does adverse summer weather affect the market for gasoline?
Supply will decrease
Demand will increase
Demand will decrease
Supply will increase
[Show More]