*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Dosage Calculation of Intravenous Solutions and Drugs (All)
Dosage Calculation of Intravenous Solutions and Drugs
Document Content and Description Below
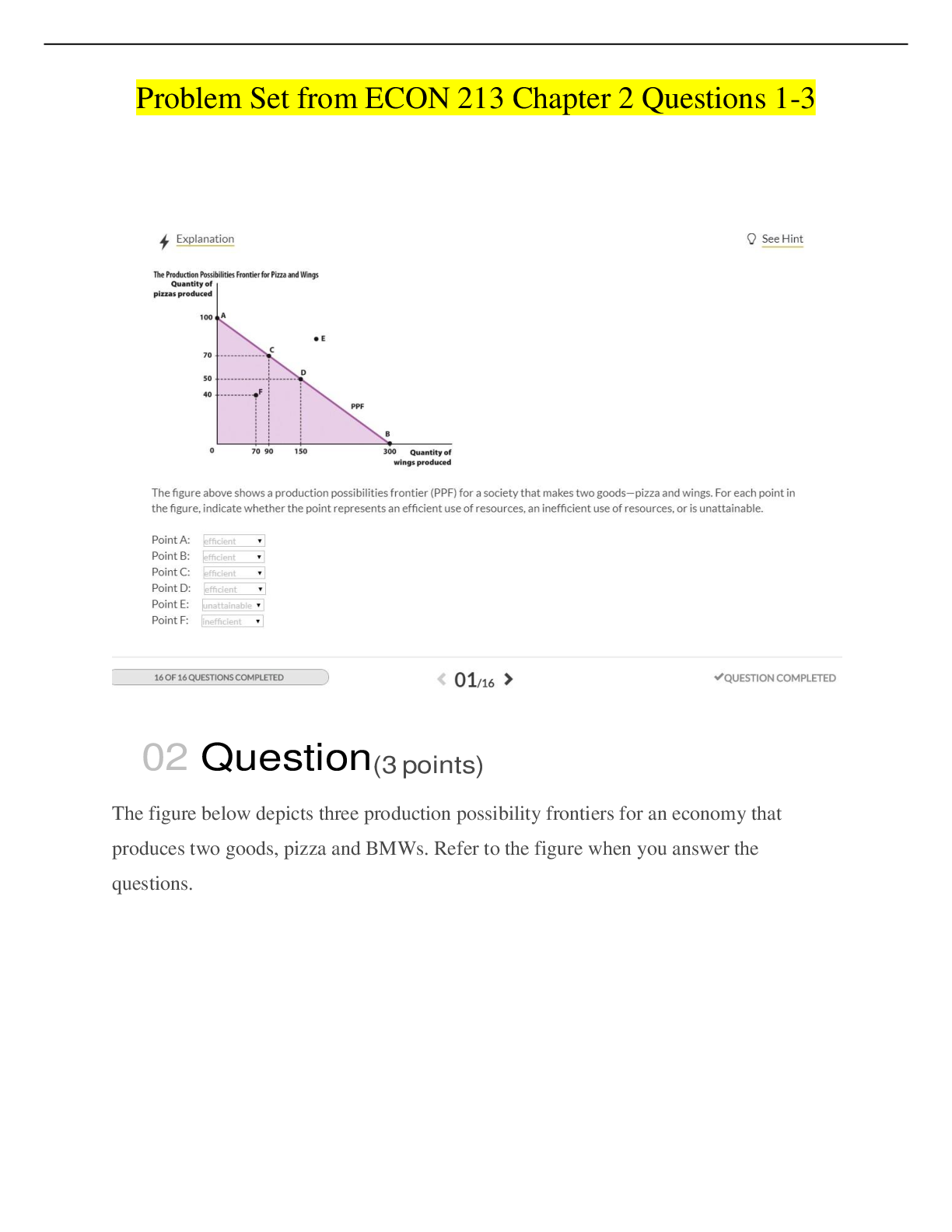
Dosage Calculation of Intravenous Solutions and Drugs Workman & LaCharity: Understanding Pharmacology: Essentials for Medication Safety, 2nd Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What does the term infil ... tration mean? a. Leakage of intravenous fluid into the surrounding tissue b. Infusion of intravenous fluids at a faster rate than was prescribed c. Plugging up or clotting off the needle during intravenous infusion d. Infusion of intravenous fluids without the use of a pump or controller 2. How many drops per milliliter (mL) does a microdrip chamber and tubing provide? a. 15 b. 20 c. 60 d. 100 3. Which term describes how much fluid is to be infused intravenously? a. Rate b. Infusion c. Volume d. Duration 4. On an infusion pump, what does the abbreviation “VTBI” indicate? a. Amount of fluid already infused b. Amount of fluid remaining in the bag or bottle c. Total amount of fluid prescribed for the day d. How fast the infusion should be run 5. If an IV scheduled to have a duration of 6 hours is started at 5:00 p.m., what is the expected stop time? a. 5:00 a.m. b. 11:00 a.m. c. 1:00 a.m. d. 11:00 p.m. 6. What sign or symptom is an indication of IV extravasation? a. Fever b. Purulent drainage c. Pain at the infusion site d. Strong blood return when the IV bag is positioned below the level of the IV site 7. Under which conditions should a microdrip setup for an IV infusion always be used? a. When the patient is an infant b. When whole blood is to be infused c. When the patient has only a few veins available for infusion d. When a very large amount of fluid needs to be infused quickly 8. What is the most important advantage for intravenous (IV) infusion of drugs? a. Anyone can administer IV drugs. b. The drug reaches the bloodstream immediately. c. Drugs given intravenously cost less than drugs given orally. d. The patient is not required to be alert to swallow the drug. 9. How does the “drop factor” affect IV infusions? a. Fluid with a larger drop factor infuses more slowly than fluid with a smaller drop factor. b. Smaller drop factors occur with smaller needles (or cannulas) and larger drop factors occur with larger needles. c. The smaller the drop factor, the fewer the number of drops needed to administer 1 mL of infusion fluid. d. The larger the drop factor, the fewer the number of drops needed to administer 1 mL of infusion fluid. 10. A patient is to receive 1000 mL intravenously of dextrose 5% in lactated Ringer’s solution in 8 hours. When you check the intravenous (IV) bag after 2 hours, 700 mL remain in the bag. How many milliliters have already infused? a. 100 b. 300 c. 700 d. 1000 11. How is extravasation different from infiltration? a. Infiltration occurs in the hand, whereas extravasation occurs in the arm. b. Both conditions lead to swelling, but extravasation causes tissue damage. c. Infiltration is swelling accompanied by pain, whereas extravasation is not painful. d. Extravasation causes phlebitis along with tissue swelling, whereas infiltration causes fluid overload along with swelling. 12. An IV infusion order for a patient reads “1000 mL dextrose 5% in normal saline intravenously, immediately.” What additional information does the prescriber need to provide for it to be a valid order? a. Drip rate b. Drop factor c. Duration d. Start time 13. Which problem is a major disadvantage of an intravenous (IV) pump? a. The alarms are so sensitive that nurses tend to ignore them when they sound frequently. b. Patients and families can override the automatic features and reset the infusion rate. c. It can “run away” and cause a patient to experience fluid overload. d. It can continue to push fluid into the tissue when infiltration occurs. 14. Which drop factor allows the greatest volume of intravenous fluid to be delivered per hour at a drip rate of 50 gtt per minute? a. 10 b. 15 c. 20 d. 60 15. What will the drip rate of an intravenous infusion with a drop factor of 20 need to be in order to deliver 1000 mL in 8 hours? a. 13 gtt/min b. 31 gtt/min c. 42 gtt/min d. 60 gtt/min 16. Which precaution is most important to teach a patient who is receiving intravenous (IV) drug therapy? a. “Turn on your call light if the IV machine starts to beep for any reason.” b. “Do not use the arm that has the IV running in it for any reason whatsoever.” c. “Call me immediately if you start to feel any pain or burning in the arm with the IV.” d. “If you think the IV is running too slowly, just push the up-arrow button on the machine once or twice.” 17. While examining a patient’s peripheral intravenous (IV) site, you observe a red streak along the length of the vein. On palpation, the vein feels hard and cordlike. What is your best action? a. Check for a blood return and notify the prescriber. b. Discontinue the infusion and remove the IV needle. c. Apply ice packs to the vein and continue the infusion. d. Change the IV fluid to normal saline and redress the site. 18. A patient is to receive 125 mL of intravenous fluid per hour and the drop factor is 10 gtt/mL. You count the 15-second drip rate to be 8 gtt/min. What is your best action? a. Nothing, the IV flow rate is correct. b. Turn the rate down to 5 gtt/15 s. c. Turn the rate up to 11 gtt/15 s. d. Turn the rate up to 15 gtt/15 s. 19. The intravenous (IV) site of a patient who has been receiving IV therapy for 2 days is red and has a small amount of pus oozing from around the needle. What is your action? a. Document the finding as an expected response to long-term IV therapy as the only action. b. Immediately notify the prescriber to get an order to discontinue the IV therapy. c. Use an iodine solution to clean the site and replace the dressing. d. Discontinue the IV therapy and notify the prescriber. 20. A patient is receiving an intravenous (IV) infusion of 1000 mL normal saline solution containing 60 mEq/L of potassium chloride over 6 hours. How many mEq of potassium chloride are delivered per 10 mL of this solution? a. 0.06 b. 0.6 c. 6 d. 60 21. A patient’s IV is supposed to have a drip rate of 42 gtt/min. You count 8 gtt in 15 seconds. What is your best action? a. Nothing, the IV flow rate is correct. b. Increase the drip rate to 10 gtt/15 seconds. c. Increase the drip rate to 15 gtt/15 seconds. d. Decrease the drip rate to 6 gtt/15 seconds. COMPLETION 1. What is the hourly flow rate for 250 mL of normal saline to be administered over 2 hours? _____ mL/h DIF: Cognitive Level: Understanding REF: p. 80 2. A patient is to receive 1000 mL of D5W intravenously over 6 hours. The tubing set has a drop factor of 15 gtt/mL. How many drops per minute are needed to infuse this fluid in the prescribed time? _____ gtt per minute 3. A patient is to receive 100 mL of normal saline over the next 5 hours with microdrip tubing. How many drops per minute are required to infuse this fluid in the prescribed time? _____ gtt per minute [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 14, 2020
Number of pages
9
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 14, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
44