Answers
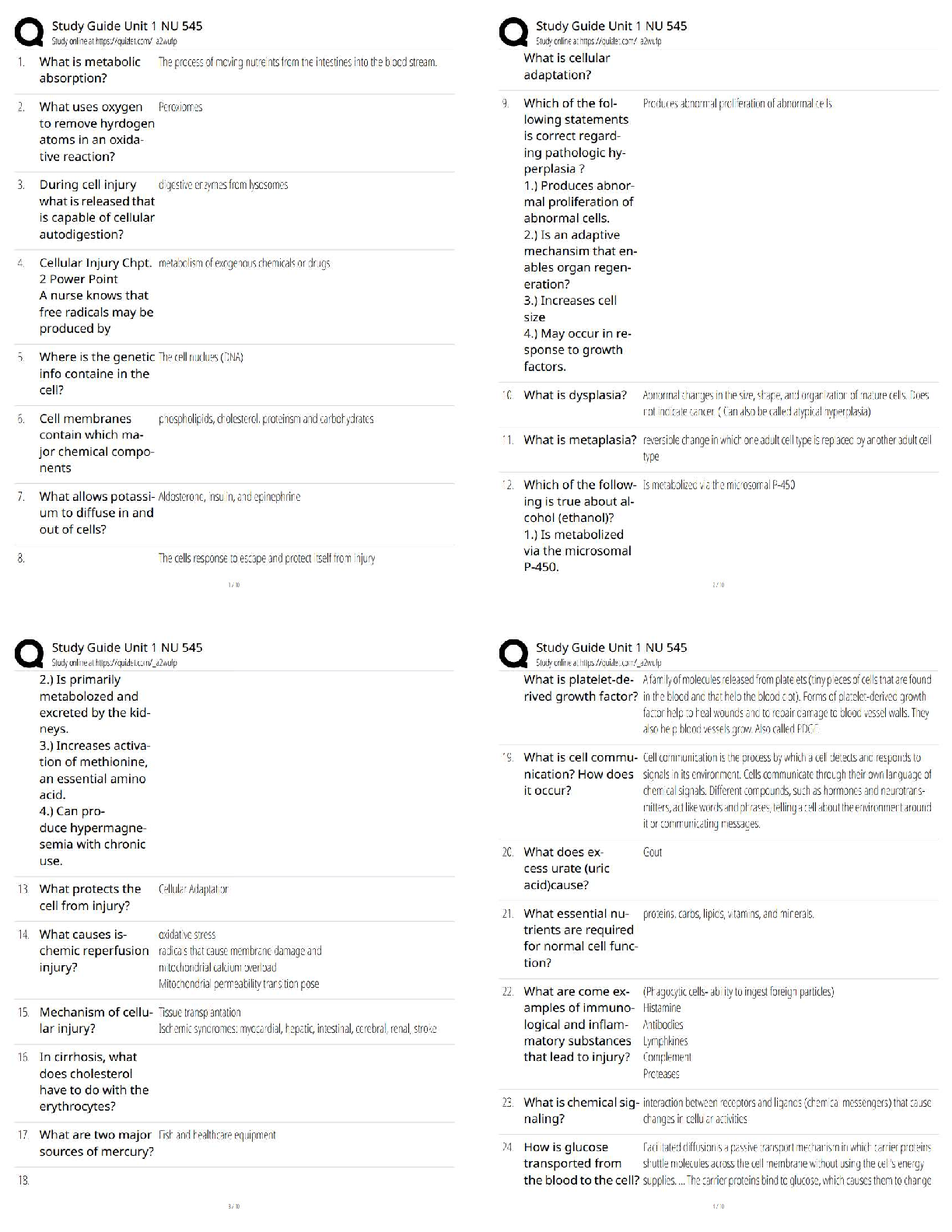
Assignment 1: Biology 235: Human Anatomy and Physiology (2020) (graded A )
Each question is worth 10 marks.
1. Maintenance of calcium ion homeostasis is critical to neurological, cardiac and skeletal muscle
...
Answers
Assignment 1: Biology 235: Human Anatomy and Physiology (2020) (graded A )
Each question is worth 10 marks.
1. Maintenance of calcium ion homeostasis is critical to neurological, cardiac and skeletal muscle function. Consider the roles of two hormones involved in the regulation of the concentration of calcium ions in the blood. Parathyroid hormone increases the concentration of calcium ions in the blood, while calcitonin decreases the concentration. Based on this information predict the body's response to restore calcium balance if a person swallowed 100 antacid tablets made of a calcium compound in 10 minutes. Include in your answer the definition of homeostasis, the type of feedback loop involved and all of the components of a feedback loop.
2. Provide one important example (in the human body) of each of the following:
A molecule containing ionic bonds
A molecule containing covalent bonds
A molecule containing hydrogen bonds
What is the function of each of these three molecules you have identified in the human body? Explain why each of these three molecules must have its specific types of bonds in order to perform that molecule’s function.
3. Define mitosis and meiosis, and describe the differences between these two processes.
4. List the skin glands and write details about their functions. What would be the consequences if a person’s skin glands stopped functioning?
• Describe how the structures of the epidermis allow it to provide immediate and indirect protection to underlying tissues.
5. Fill in the words or phrases that best complete each of the following sentences.
a. Functions of the skeletal system include support, protection, assisting in movement, homeostasis, production and triglyceride storage.
b. The hollow space inside of long bones that is lined with and filled with yellow marrow is the
c. The protein that provides flexibility and _ strength to bone is f.
d. bone tissue is organized into concentric rings of bone tissue, which are called osteons or
e. accompany blood vessels within bone tissue; the periosteum is enriched with neurons.
f. Ossification may also be called in an embryo, it begins with the organization of tissue into the general shape of bones.
g. ossification occurs between __ connective tissue sheet-like layers that resemble membranes.
h. Activity of the epiphyseal plate causes the _ region of a bone to grow in
i. _____GH__, IGFs, insulin and T3/T4 are the primary stimulators of bone growth before puberty
j. _______ is the hormone that _______ the effects of parathyroid hormone.
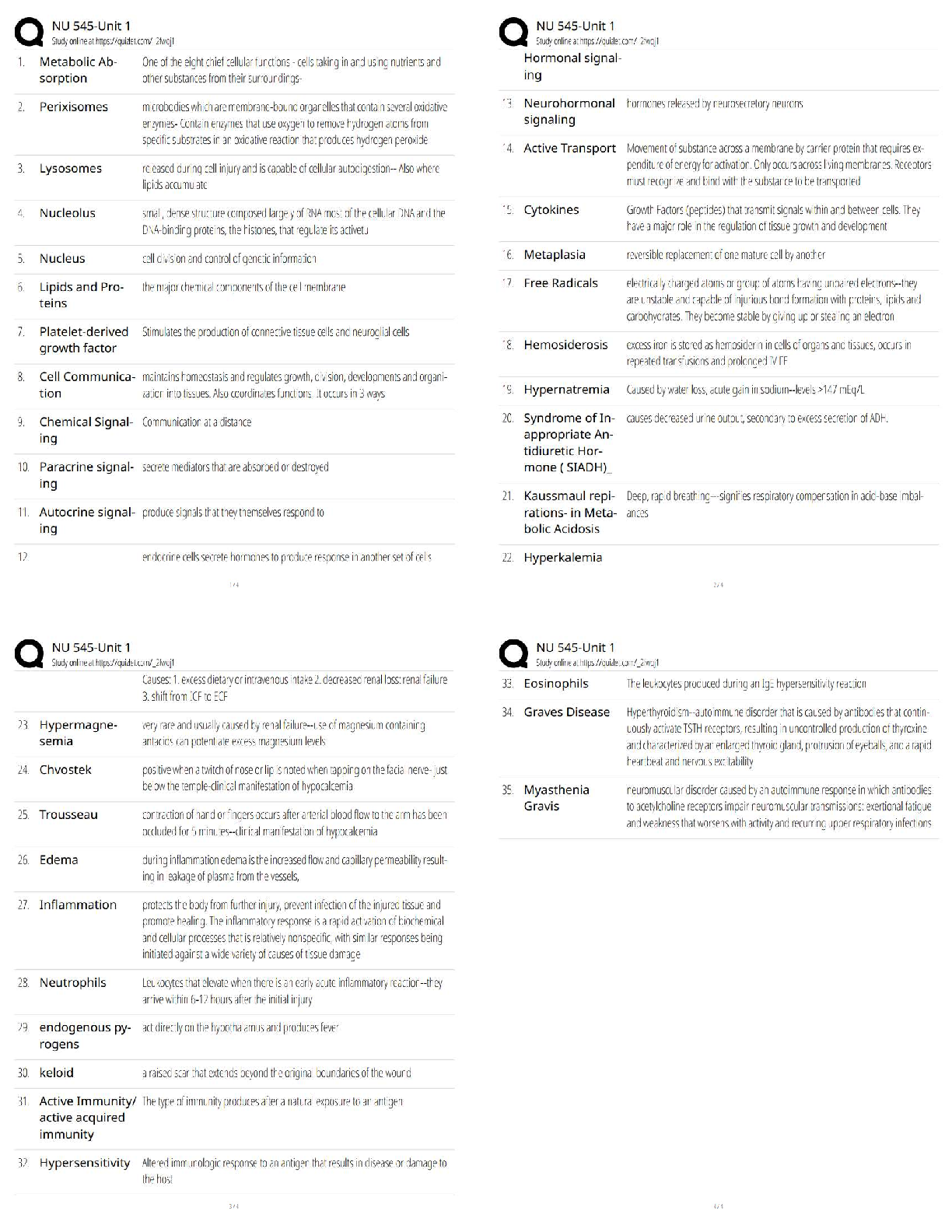
6. Match the items in column A with the descriptions in column B to create the BEST MATCHES.
Items in column A can be used more than once when making matches to column B. However, there is only one correct answer for each blank space.
Column A Column B
a. articular cartilage
b. diaphysis
c. endosteum
d. epiphyses
e. periosteum
f. canaliculi
g. lacunae
h. lamellae
i. osteons
j. trabeculae
k. calcification
l. development of cartilage model
m. development of ossification center
n. development of periosteum
o. osteoblast
p. intramembranous ossification
q. osteoclast
r. zone of hypertrophic cartilage
s. zone of proliferating cartilage
t. zone of calcified cartilage
u. calcitonin
v. calcitriol
w. foramen
x. parathyroid hormone
y. fossa ____ ___ raises blood Ca2+ levels by increasing osteoclast activity and blocking kidney secretion of Ca2+
___ struts or plates within spongy bone that assist in withstanding stresses in a specific direction
_ ______ channels in bone matrix; allow osteocytes to communicate with each other
___ ____ expanded ends of a long bone
__ _____ occurs after development of ossification center during intramembranous bone development; occurs prior to formation of trabeculae
___ ____ lines the marrow cavity
___ ____ protects bone; assists in fracture repair
___ a rounded passageway through a bone that permits blood vessels and/or nerves to pass
____ shaft of a long bone
___ ___ process where the bone develops from mesenchyme, often forming flat bones
____ ___ structural units of compact bone
_____ __ bone cell that breaks down old bone matrix
____ ___ spaces in bone matrix that contain osteocytes
___ tiny channels connecting osteocytes with the central canal of an osteon
____ ___ occurs when mesenchymal cells cluster and differentiate during intramembranous bone development
____ ___ inhibits osteoclastic activity
_____ __ reduces friction and absorbs shock at joints that have a wide range of motion
_______ the highly vascularized mesenchyme on the outside of the new bone that develops in the periosteum
_______ does not occur during intramembranous bone development; must arise from mesenchyme template
___ ____ part of a long bone that is not covered by the periosteum is covered by this structure
7.
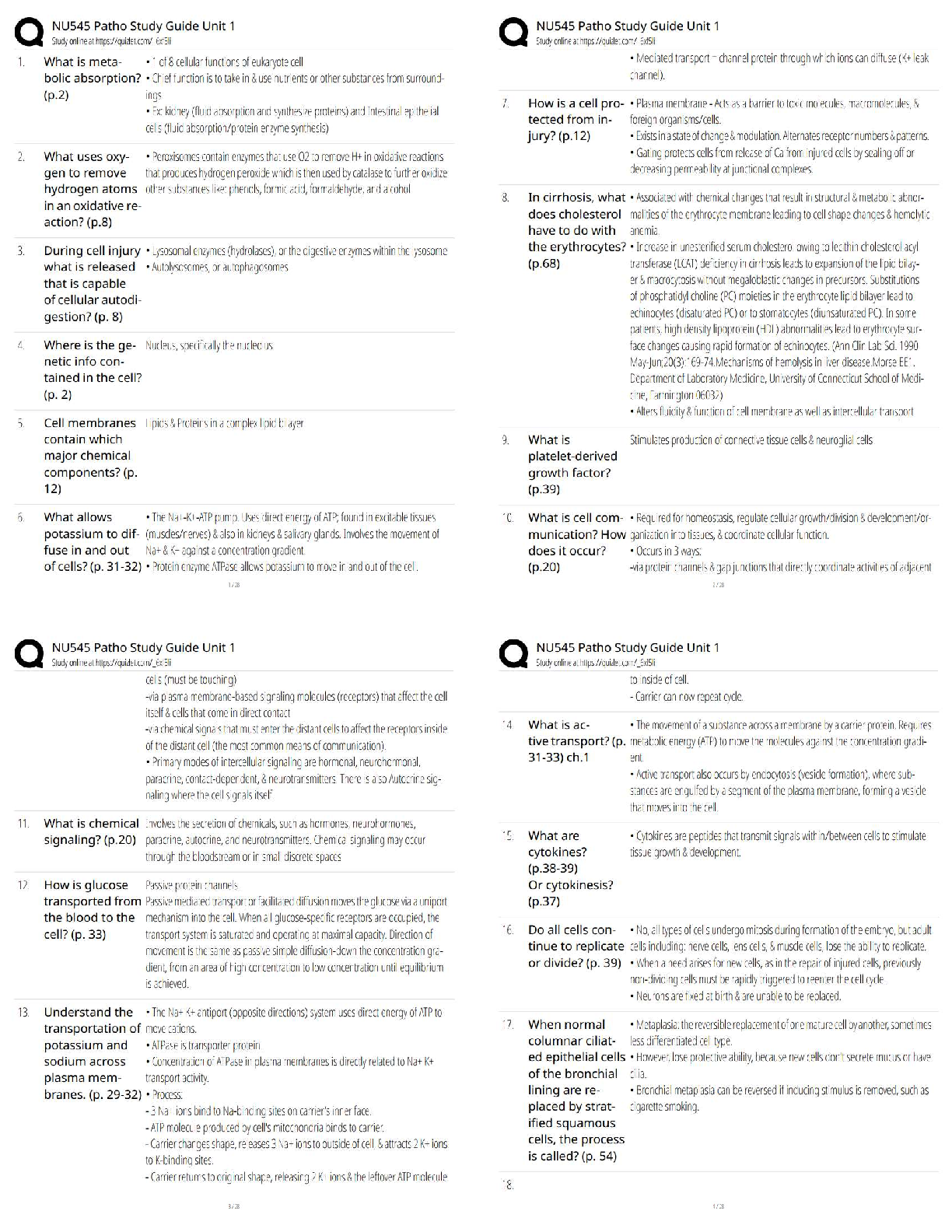
a. Match the items in column A with the descriptions in column B to create theBEST MATCHES.
Items in column A can be used more than once when making matches to column B. However, there is only one correct answer for each blank space.
Column A Column B
1. pronation
2. abduction
3. inversion
4. gliding
5. depression
6. dorsiflexion
7. extension
8. retraction
9. lateral flexion
10. circumduction
11. plantar flexion
12. elevation
13. adduction
14. hyperextension
15. flexion
16. medial rotation
17. eversion
18. protraction
19. supination
20. lateral rotation a. _______ straightening the elbow joint
b. ___1oving the arm anteriorly
c. _____ spreading the fingers apart
d. _______ opening the jaw
e. _______ bending the ankle joint so that the foot moves downward
f. _____ moving a thigh straight toward the other thigh
g. _______ bending the wrist joint so that the hand moves posteriorly
h. ____bending the head so that it moves toward the right shoulder
i. _______ bending the knee joint
j. _______ moving the thumb around in a circle
b. From the movements listed in column B, list the scientific names of the bones (learned in earlier chapters) that meet at each joint, i.e., where each movement occurs.
Note: The spaces below require one or two bones of a certain region. Be very specific when required.
a. _ articulates with ___
b. articulates with _ ______
c. _ _____ articulates with __ ____
d. _e______ articulates with _ ______
e. _ _____ articulates with __ _____
f. ____r___ articulates with __f_____
g. _ _____ articulates with ___ ____
h. _ articulates with _
i. __ articulates with ___
j. __ _____ articulates with __
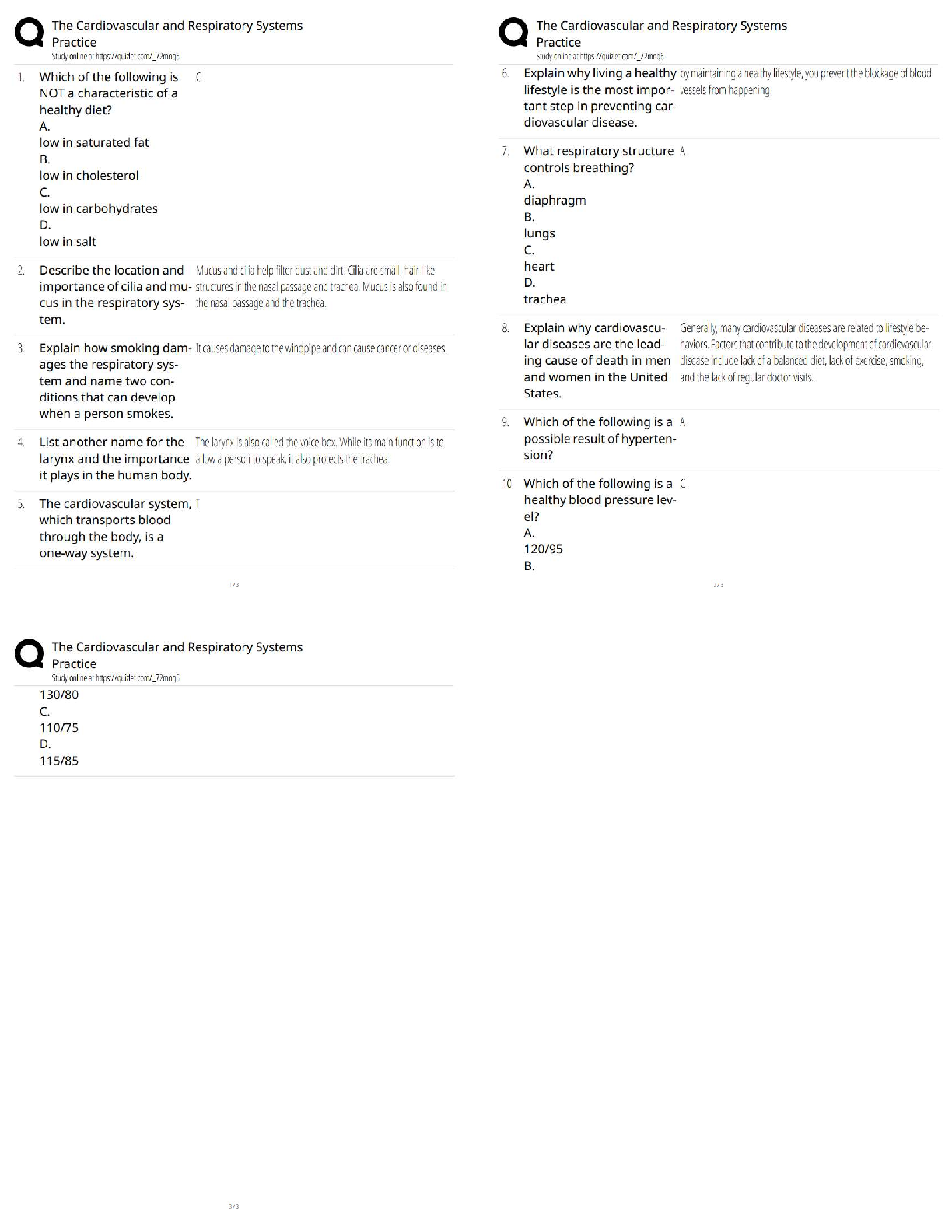
8. Compare the organization and functions of axial and appendicular skeletons, and describe in detail the girdles of the latter.
The adult human skeleton is a framework of 206 bones and is anatomically divided into two parts, the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
The core of the skeleton is referred to as the axial skeleton. It consists of the following 80 bones.
Attached to the axial skeleton is the appendicular skeleton, which consists of 126 bones.
Functionally, the bones give support to the appendages and protect fragile organs of the body such as the brain, spinal cord, heart, and lungs. Additionally, the bumps, ridges, and grooves on the surface of bones serve as attachment sites for the skeletal muscles.
[Show More]