*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Arizona State University NR 507 Week 8 Final Exam Structure and Function of the Renal and Urologic S (All)
Arizona State University NR 507 Week 8 Final Exam Structure and Function of the Renal and Urologic Systems (ALL CORRECT ANSWERS WITH RATIONALE)
Document Content and Description Below
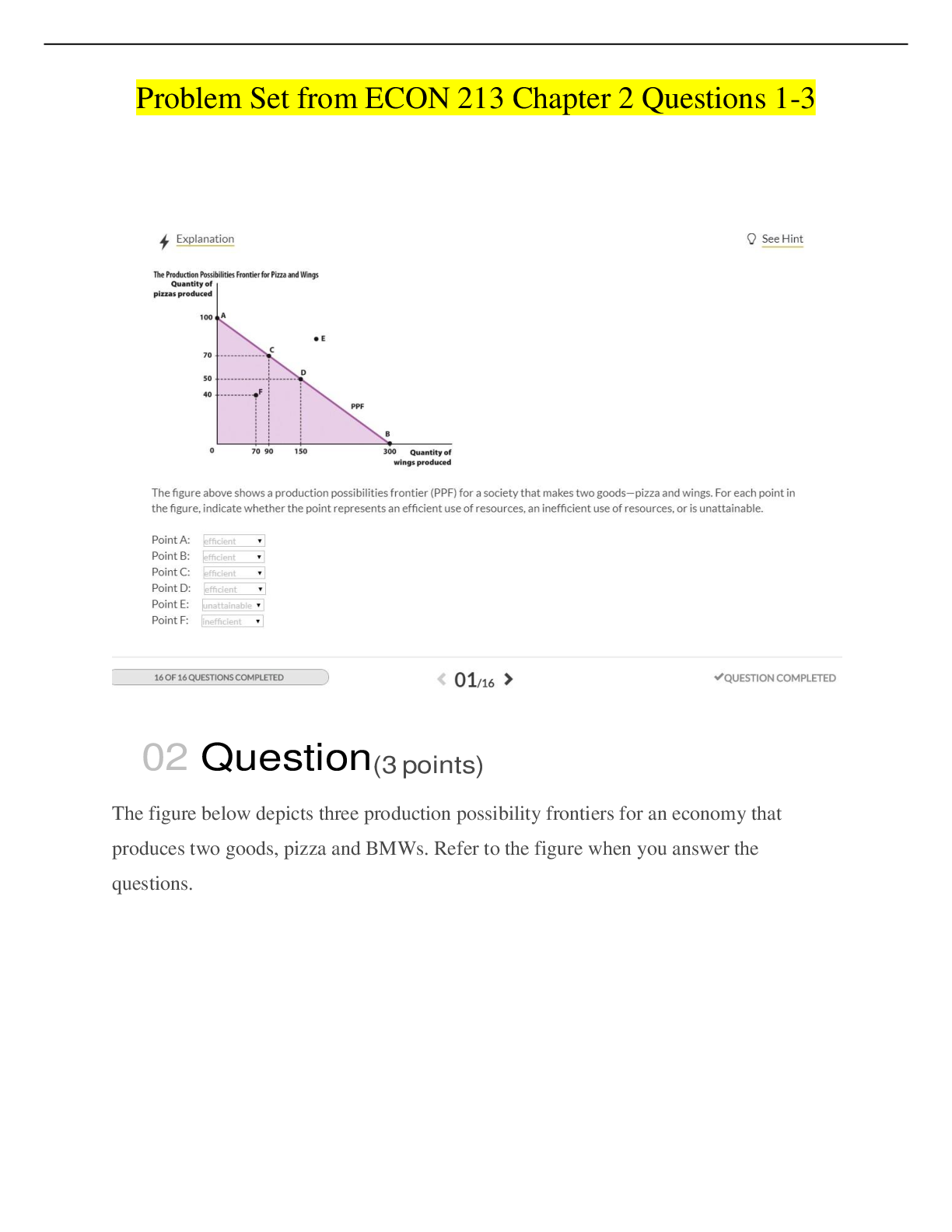
Structure and Function of the Renal and Urologic Systems MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The area of the kidneys that contains the glomeruli and portions of the tubules is called the: a. Medulla c. Pyramids ... b. Cortex d. Columns 2. What is the functional unit of the kidney called? a. Glomerulus c. Collecting duct b. Nephron d. Pyramid 3. Which cells have phagocytic properties similar to monocytes and contract like smooth muscles cells, thereby influencing the glomerular filtration rate? a. Principle cells c. Mesangial cells b. Podocin cells d. Intercalated cells 4. The only surface inside the nephron where cells are covered with microvilli to increase the reabsorptive surface area is called the: a. Proximal convoluted tubules c. Ascending loop of Henle b. Distal tubules d. Descending loop of Henle 5. What part of the kidney controls renal blood flow, glomerular filtration, and renin secretion? a. Macula densa c. Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) b. Visceral epithelium d. Filtration slits 6. Kidney stones in the upper part of the ureter would produce pain referred to which anatomical area? a. Vulva or penis c. Thighs b. Umbilicus d. Lower abdomen 7. Innervation of the bladder and internal urethral sphincter is supplied by which nerves? a. Peripheral nerves c. Sympathetic nervous system b. Parasympathetic fibers d. Tenth thoracic nerve roots 8. How much urine accumulates in the bladder before the mechanoreceptors sense bladder fullness? a. 75 to 100 ml c. 250 to 300 ml b. 100 to 150 ml d. 350 to 400 ml 9. What is the trigone? a. A smooth muscle that comprises the orifice of the ureter b. The inner mucosal lining of the kidneys c. A smooth triangular area between the openings of the two ureters and the urethra d. One of the three divisions of the loop of Henle 10. The glomerular filtration rate is directly related to which factor? a. Perfusion pressure in the glomerular capillaries b. Diffusion rate in the renal cortex c. Diffusion rate in the renal medulla d. Glomerular active transport 11. On average, what percent of cardiac output do the kidneys receive? a. 10% to 20% c. 20% to 25% b. 15% to 20% d. 30% to 35% 12. What effects do exercise and body position have on renal blood flow? a. Exercise and body position activate renal parasympathetic neurons and cause mild vasoconstriction. b. They activate renal sympathetic neurons and cause mild vasoconstriction. c. Both activate renal parasympathetic neurons and cause mild vasodilation. d. They activate renal sympathetic neurons and cause mild vasodilation. 13. Blood vessels of the kidneys are innervated by the: a. Vagus nerve c. Somatic nervous system b. Sympathetic nervous system d. Parasympathetic nervous system 14. When renin is released, it is capable of which action? a. Inactivation of autoregulation b. Direct activation of angiotensin II c. Direct release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) d. Formation of angiotensin I 15. What effect do natriuretic peptides have during heart failure when the heart dilates? a. Stimulates antidiuretic hormones. c. Stimulates renin and aldosterone. b. Inhibits antidiuretic hormones. d. Inhibits renin and aldosterone. 16. What is the direct action of atrial natriuretic hormone? a. Sodium retention c. Water retention b. Sodium excretion d. Water excretion 17. What term is used to identify the movement of fluids and solutes from the tubular lumen to the peritubular capillary plasma? a. Tubular secretion c. Tubular reabsorption b. Ultrafiltration d. Tubular excretion 18. How high does the plasma glucose have to be before the threshold for glucose is achieved? a. 126 mg/dl c. 180 mg/dl b. 150 mg/dl d. 200 mg/dl 19. Which hormone is required for water to be reabsorbed in the distal tubule and collecting duct? a. Antidiuretic hormone c. Cortisol b. Aldosterone d. Adrenocorticotropin hormone 20. Which glycoprotein protects against urolithiasis and is a ligand for lymphokines? a. Uromodulin c. Urodilatin b. Nephrin d. Cystatin 21. What is the end-product of protein metabolism that is excreted in urine? a. Glucose c. Bile b. Ketones d. Urea 22. What is the action of urodilatin? a. Urodilatin causes vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles. b. It causes vasodilation of the efferent arterioles. c. Urodilatin inhibits antidiuretic hormone secretion. d. It inhibits salt and water reabsorption. 23. The concentration of the final urine is determined by antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which is secreted by which gland? a. Posterior pituitary c. Parathyroid b. Thyroid d. Anterior pituitary 24. Which statement is true regarding urodilatin? a. Urodilatin inhibits sodium chloride and water reabsorption in the medullary part of the collecting duct. b. It inhibits antidiuretic hormone (ADH) to prevent water reabsorption in the medullary part of the collecting duct. c. Urodilatin is stimulated by a rise in blood pressure and an increase in extracellular volume. d. It is stimulated by a fall in blood pressure and a decrease in extracellular volume. 25. What substance stimulates renal hydroxylation in the process of producing vitamin D? a. Erythropoietin c. Calcitonin b. Thyroid hormone d. Parathyroid hormone 26. Which hormone is synthesized and secreted by the kidneys? a. Antidiuretic hormone c. Erythropoietin b. Aldosterone d. Angiotensinogen 27. What provides the best estimate of the functioning of renal tissue? a. Glomerular filtration rate b. Hourly urine output c. Serum blood urea nitrogen and creatinine d. The specific gravity of the solute concentration of the urine 28. Which renal change is found in older adults? a. Sharp decline in glomerular filtration rate b. Sharp decline in renal blood flow c. Decrease in the number of nephrons d. Decrease in urine output 29. Compared with a younger individual, how is the specific gravity of urine in older adults affected? a. Specific gravity of urine in older adults is increased. b. Specific gravity of urine in older adults is considered high normal. c. Specific gravity of urine in older adults is considered low normal. d. Specific gravity of urine in older adults is decreased. 30. What process allows the kidney to respond to an increase in workload? a. Glomerular filtration b. Secretion of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 c. Increased heart rate d. Compensatory hypertrophy 31. Which process makes it possible for ureters to be transplanted successfully? a. Compensatory hypertrophy c. Peristalsis b. Erythropoietin secretion d. Collateral circulation MULTIPLE RESPONSE 32. Which structures are parts of the nephron? (Select all that apply.) a. Loop of Henle b. Renal corpuscle c. Proximal convoluted tubule d. Calyx e. Collecting duct 33. Which forces create passive transport of water in the proximal tubule? (Select all that apply.) a. Peritubular capillary hydrostatic pressure b. Peritubular capillary oncotic pressure c. Interstitial hydrostatic pressure d. Interstitial osmotic pressure e. Peritubular capillary osmotic pressure 34. Which hormones are produced by the kidney? (Select all that apply.) a. Renin b. Erythropoietin c. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 d. Calcitonin e. Aldosterone 35. Which statements are true regarding renal circulation? (Select all that apply.) a. The interlobar arteries travel down into the renal columns. b. The arcuate arteries branch to form the interlobar arteries. c. The arcuate arteries arch over the base of the pyramids. d. The interlobar arteries run parallel to the surface of the kidneys. e. The interlobar arteries run between the pyramids. MATCHING Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms. ______ A. Good estimate of glomerular filtration rate 36. Crystals ______ B. Form in concentrated acidic or alkaline urine 37. Casts ______ C. Cylindric with distinct borders 38. Leukocytes ______ D. Hematuria 39. Creatinine clearance ______ E. Pyuria 40. Erythrocytes 36. 5th ed MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A nurse is teaching the staff about the kidneys. Which information should the nurse include? The region of the kidneys that contains the glomeruli is the: a. Medulla b. Cortex c. Pyramids d. Columns 2. When the nurse is discussing the functional unit of the kidney, what other term should the nurse use? a. Calyx b. Nephron c. Collecting duct d. Pyramid 3. The urologist is teaching about the nephrons that determine the concentration of the urine. The urologist is discussing the _____ nephrons. a. Juxtamedullary b. Midcortical c. Cortical d. Medullary 4. A urologist is discussing the phagocytic cells that lie between the layers of the renal corpuscle. What is the urologist describing? a. Podocytes b. Macula densa cells c. Mesangial cells d. Filtration slits 5. When the nurse discusses the glomerulus and Bowman capsule together, it is referred to as the renal: a. Corpuscle b. Capsule c. Medulla d. Pyramid . 6. When a nurse is checking the urinalysis, plasma proteins should be absent from the urine because: a. All proteins filtered are subsequently reabsorbed. b. All of the plasma proteins are too large to fit through the filtration slits. c. All proteins filtered are subsequently degraded before elimination. d. The negative charge of the glomerular filtration membrane repels the plasma proteins. 7. When the nurse is discussing the sodium-sensing cells of the glomerulus, what term should the nurse use? a. Podocytes b. Macula densa c. Mesangial cells d. Loop of Henle 8. When a nurse is preparing to teach about urine, which information should the nurse include? Just before entering the ureter, urine passes through the: a. Collecting duct b. Renal pelvis c. Urethra d. Major calyx 9. A urologist is discussing a structure that supplies blood to the medulla. What is the urologist describing? a. Renal arteries b. Arcuate arteries c. Peritubular capillaries d. Vasa recta 10. A nurse is describing the trigone. Which information should be included? The trigone is defined as: a. The orifice of the ureter b. The inner area of the kidney c. A triangular area between the openings of the two ureters and the urethra d. The three divisions of the loop of Henle 11. When describing the male urinary anatomy, which information should the nurse include? The portion of the male urethra that is closest to the bladder is the _____ portion. a. Membranous b. Prostatic c. Cavernous d. Vas deferens 13. While reviewing urine lab results, the nurse remembers the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is directly related to the: a. Perfusion pressure in the glomerular capillaries b. Oncotic pressure in the glomerular capillaries c. Vascular resistance in the glomerular arterioles d. Hydrostatic pressure in the Bowman capsule 14. A nurse recalls the blood vessels of the kidneys are innervated by the: a. Vagus nerve b. Sympathetic nervous system c. Somatic nervous system d. Parasympathetic nervous system 15. While planning care for a patient with urinary problems, the nurse recalls that the renin-angiotensin system will be activated by: a. Increased blood volume b. Elevated sodium concentrations c. Decreased blood pressure in the afferent arterioles d. Renal hypertension 16. When a patients renal system secretes rennin, what effect will that cause in the body? It causes the direct activation of: a. Angiotensin I b. Angiotensin II c. Antidiuretic hormone d. Aldosterone 17. A nurse is reviewing urinalysis results and notices glucose is present in the urine. A nurse realizes glucose will be excreted in the urine when: a. The maximum rate of glucose filtration is achieved b. The carrier molecules have reached their maximum c. Glucose is consumed d. The ability of the kidneys to regulate blood glucose is lost 18. When teaching about sodium reabsorption, which information should the nurse include? The majority of sodium reabsorption takes place in the: a. Proximal tubule b. Loop of Henle c. Distal tubule d. Collecting duct 19. A kidney has a glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure of 50 mm Hg, a Bowman capsule hydrostatic pressure of 15 mm Hg, and a glomerular capillary oncotic pressure of 12 mm Hg. The net filtration pressure is ____ mm Hg. a. 23 b. 27 c. 35 d. 38 20. A nurse is preparing to teach about the loop of Henle. Which information should be included? The descending segment of the loop of Henle primarily allows for: a. Sodium secretion b. Potassium secretion c. Hydrogen ion reabsorption d. Water reabsorption 21. When a staff member asks which of the following substances are actively secreted by the renal tubules, what is the nurses best response? a. Sodium and chlorine b. Phosphate and calcium c. Hydrogen and potassium d. Bicarbonate and carbonic acid 22. A nurse is preparing to teach about the collecting ducts. Reabsorption of water in the collecting ducts requires which of these hormones? a. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) b. Atrial natriuretic factor (ANP) c. Renin d. Aldosterone 23. When a patient asks what role the kidneys play in vitamin D function, how should the nurse reply? a. Synthesizes vitamin D from cholesterol b. Activates intestinally absorbed vitamin D c. Metabolizes and breaks down vitamin D d. Excretes excess vitamin D 24. A 35-year-old hypertensive male begins taking a diuretic. Which of the following common side effects of this medication should the nurse monitor? a. Hypokalemia b. Hyponatremia c. Increased uric acid secretion d. Hypermagnesemia 25. A patient has searched the Internet for hormones. The patient has a good understanding when she knows that the hormone _____ is synthesized and secreted by the kidneys to stimulate bone marrow production of red blood cells. a. Creatinine b. Aldosterone c. Erythropoietin d. Renin 26. If a nurse wants to obtain the best estimate of renal function, which test should the nurse monitor? a. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) b. Circulating antidiuretic hormone (ADH) levels c. Volume of urine output d. Urine-specific gravity 27. A nurse recalls the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and plasma creatinine (Pcr) concentration are _____ related. a. Directly b. Indirectly c. Inversely d. Not MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. When a student asks what the components of the nephron are, how should the nurse respond? The components of the nephron include (select all that apply): a. Loop of Henle b. Renal corpuscle c. Proximal tubule d. Renal pelvis e. Convoluted tubule 2. When a staff member asks how the urine gets from the nephrons to the calyces, what is the nurses best response? The renal structure that drains directly into the calyces is (are) the (select all that apply): a. Distal tubule b. Collecting duct c. Pyramid d. Renal pelvis e. Loop of Henle COMPLETION 1. A nurse recalls the superficial cortical nephrons account for ____% of all nephrons. 2. On average, _____% of renal plasma flow (RPF) to the glomerulus is filtered into the Bowman capsule. 3. A nurse would chart a patient is experiencing oliguria when a 24-hour urine output is less than ________. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 14 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 15, 2020
Number of pages
14
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 15, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
237