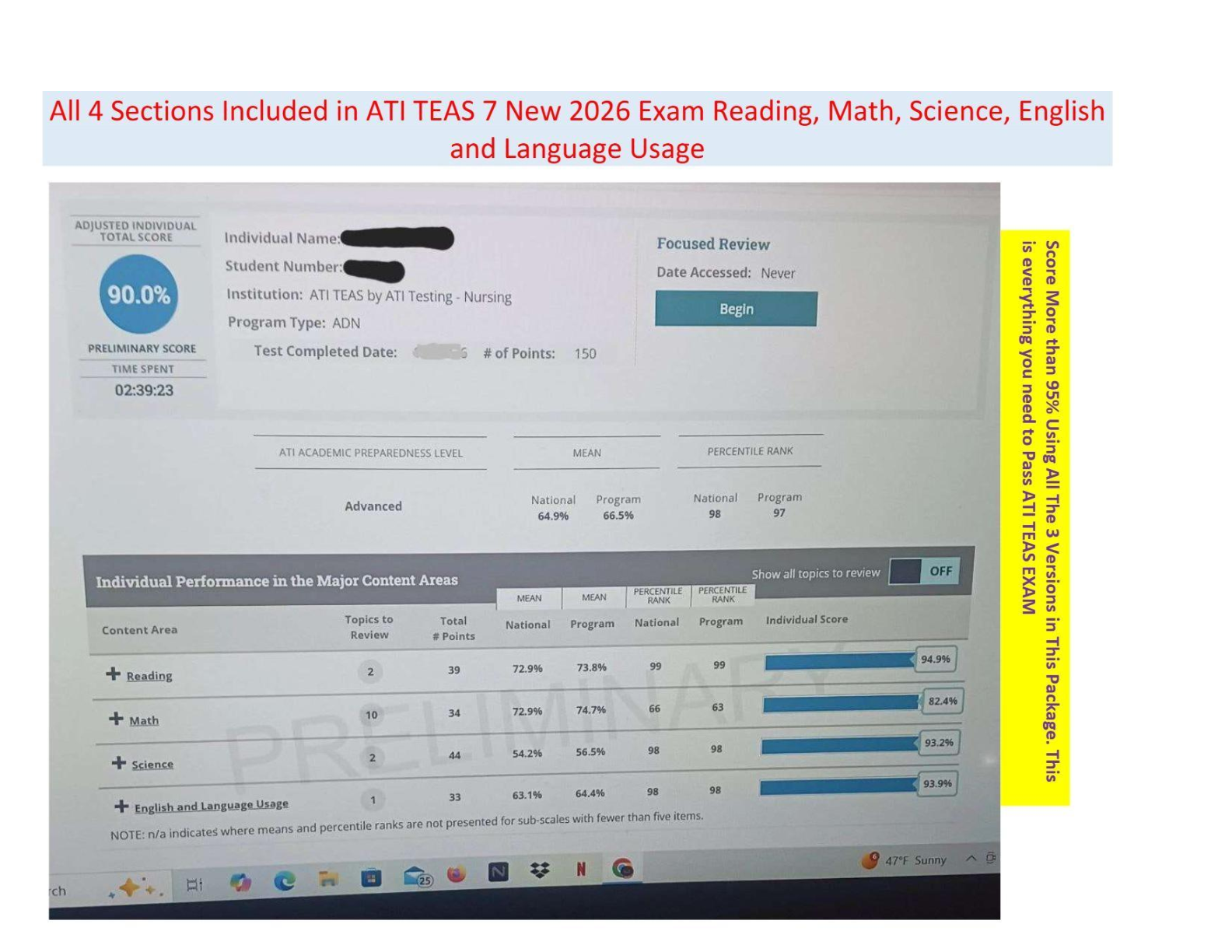
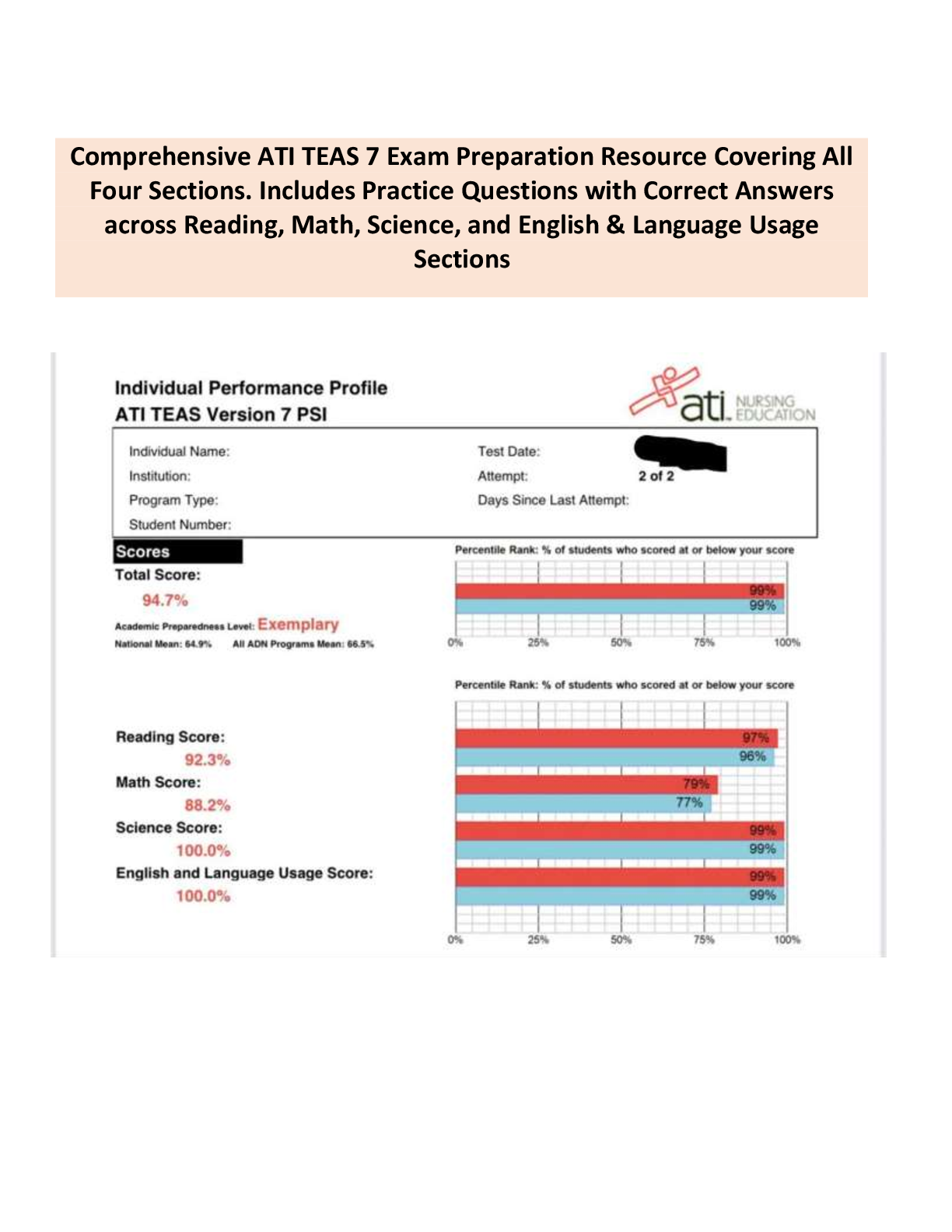
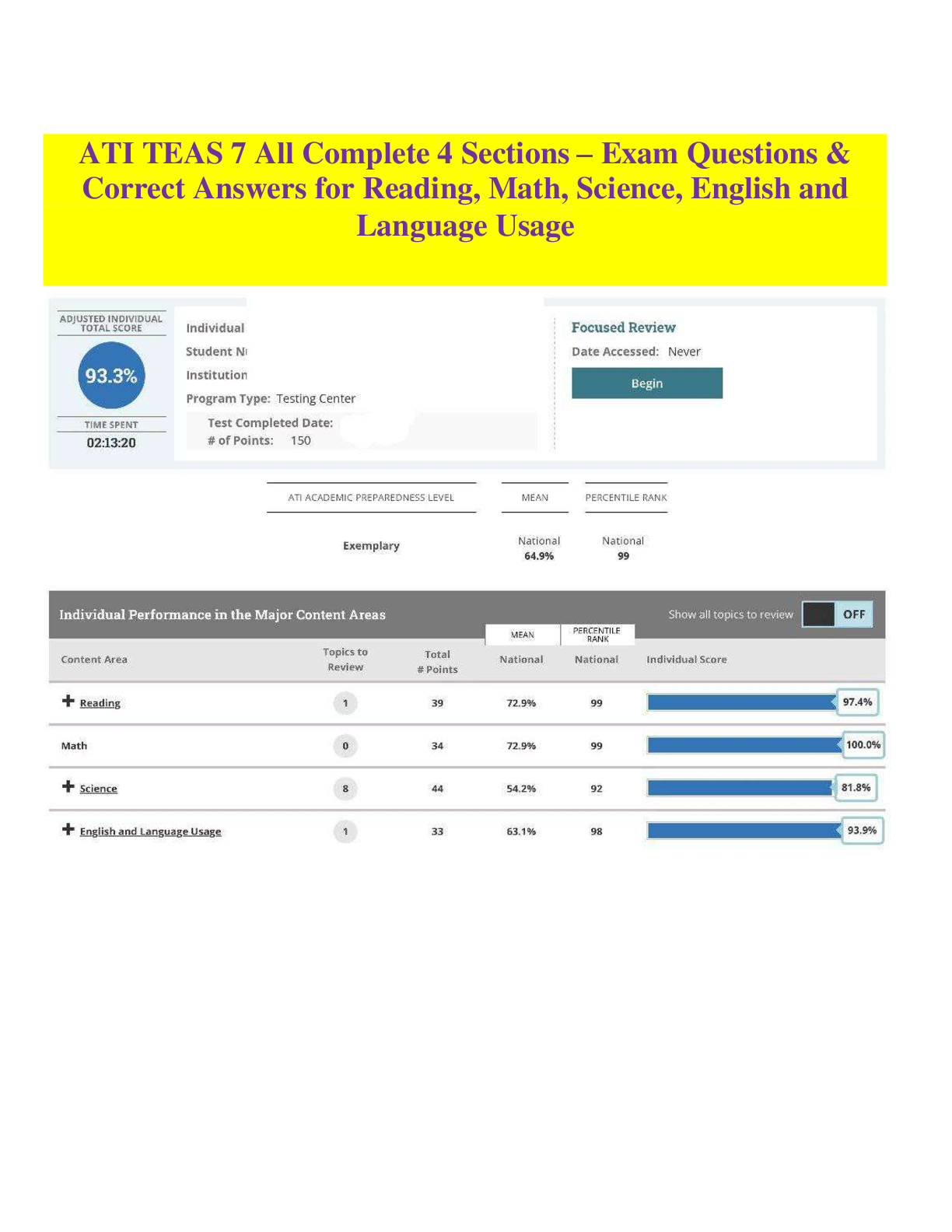
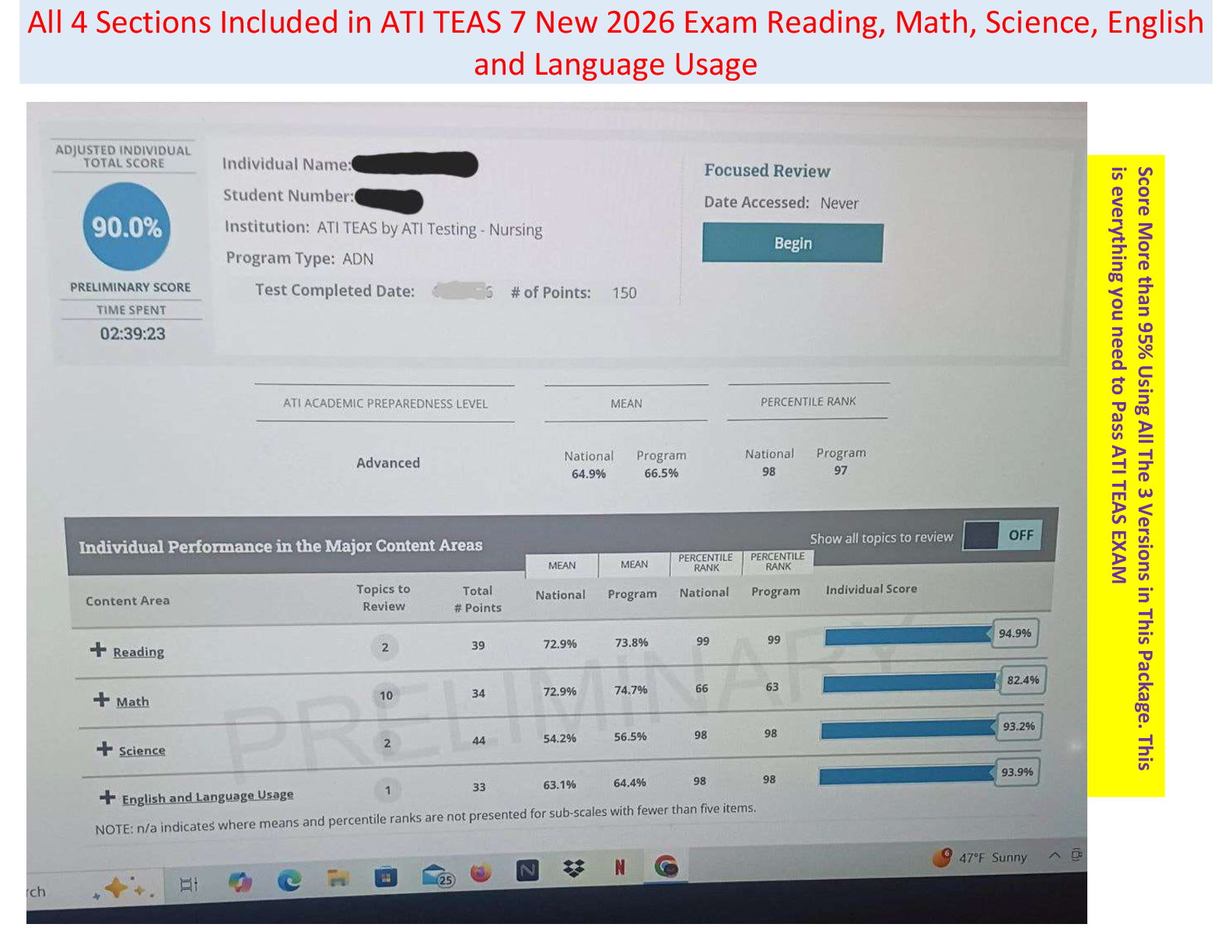
Medicare - for clients over age 65 and/or with permanent disabilities. premiums applied as
insurance program reimburses providers based on DRGs. Premiums applied as Managed Care
Organizations (MCOs) provide enrolled cl
...
Medicare - for clients over age 65 and/or with permanent disabilities. premiums applied as
insurance program reimburses providers based on DRGs. Premiums applied as Managed Care
Organizations (MCOs) provide enrolled clients with comprehensive care overseen by a primary
care provider. Is federally funded.
Medicaid - for clients with low income. is federally funded and individual states determine
eligibility requirements.
Traditional Insurance - reimburses for services on fee-for-service basis.
Managed Care Organizations (MCOs) - comprehensive care is overseen by a primary care
provider & focuses on prevention and health promotion
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs) - client chooses from a list of contracted providers.
using non-contracted providers increases the client's out of pocket costs
Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs) - the client chooses from a list of providers within a
contracted organization
Long-Term Care Insurance - provides for long-term care expenses not covered by Medicare
Preventive health care - focuses on educating and equipping clients to reduce and control risk
factors of disease. Examples include immunizations, stress management programs, and seat
belt use
Primary health care - emphasizes health promotion, and includes prenatal and well-baby care,
nutrition counseling, and disease control. is based on a sustained partnership between client
and provider. examples include office or clinic visits and scheduled school/work centered
screenings (vision, hearing, obesity)
Secondary health care - includes the diagnosis and treatment of emergency, acute illness, or
injury. examples include care given in hospital settings (inpatient and EDs), diagnostic centers,
or emergent care centers
Tertiary health care - involves the provision of specialized highly technical care. examples
include oncology centers and burn centers
Restorative health care - involves intermediate follow-up care for restoring health. examples
include home health care, rehab centers, and skilled nursing facilities
Continuing health care - designed to address long-term or chronic health care needs. examples
include hospice, adult day care, and in-home respite care
[Show More]