GRE psychology practice 159 Questions with Verified Answers,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
GRE psychology practice 159 Questions with Verified Answers
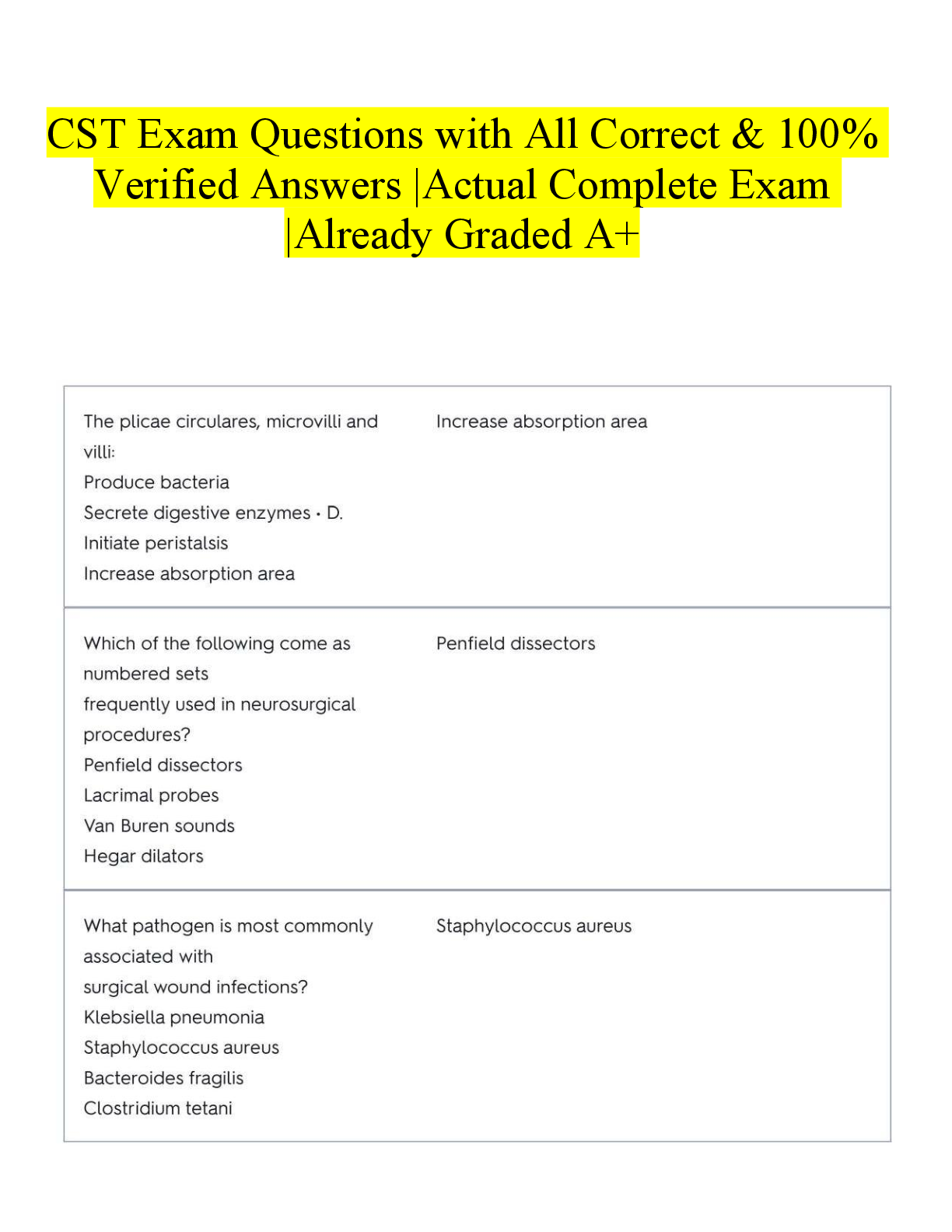
Acetycholine - CORRECT ANSWER neurotransmitter associated with voluntary movement, sleep and wakefulness. Too little is associated with A
...
lzheimer's
Analysis of Variance/ANOVA - CORRECT ANSWER inferential statistical procedure used to compare 2 or more means to see if the difference is not chance (need p<.05 for statistical significance)
Aphasia - CORRECT ANSWER impairment of ability to communicate either through oral or written discourse as a result of brain damage. Ex. Wernicke's ________ or Broca's __________
Optimum Arousal Theory - CORRECT ANSWER Theory stating that we are motivated by our innate desire to maintain an personally preferred level of arousal.
Broca's Aphasia - CORRECT ANSWER Loss of function associated with damage to a specific area of the left frontal lobe, demonstrated by impairment in producing understandable speech.
Egocentric - CORRECT ANSWER young child's inability to understand another person's perspective - typical of Piaget's preoperational stage
Concrete Operational Stage - CORRECT ANSWER According to Piaget - stage of cognitive development where child between ages of 7 and 12 begins thinking more globally and outside of the self but are still deficient in abstract thought.
Construct Validity - CORRECT ANSWER Validity answers the question of whether or not the measuring device actually measures the theoretical idea under question.
Convergence - CORRECT ANSWER Binocular cue to distance referring to fact that the closer an object is, the more inward our eyes need to turn in order to focus
Dopamine Hypothesis - CORRECT ANSWER Theory that schizophrenia is caused by an excess amount of dopamine in brain. Research has found that medication to reduce dopamine can reduce the positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
Endorphins - CORRECT ANSWER neurotransmitter involved in pain relief, and feelings of pleasure and contentedness.
Epinephrine - CORRECT ANSWER neurotransmitter involved in energy and glucose metabolism.
External Validity - CORRECT ANSWER The extent to which data collected from a sample can be generalized to the entire population.
Factor Analysis - CORRECT ANSWER A statistical technique used combine data into similar groups
Frequency Effect - CORRECT ANSWER The phenomenon in memory which states that we tend to remember information better if it is repeated.
Formal Operational Stage - CORRECT ANSWER Piaget's fourth and final stage of cognitive development where thinking becomes more abstract. 12+ years
Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis - CORRECT ANSWER Theory arguing that aggression is the natural reaction to frustration.
g factor - CORRECT ANSWER Basic intelligence of Spearman's theory. Typically compared to s which represents specific intelligences.
Gender Identity - CORRECT ANSWER Internal sense of being either male or female. Usually congruent with biological gender, but not always.
Hawthorne Effect - CORRECT ANSWER Phenomenon that subject behavior changes by mere fact that they are being observed.
Introspection - CORRECT ANSWER The process of examining one's own consciousness used by Structuralists and Functionalist researchers
Legitimate Power - CORRECT ANSWER Power derived through one's position, such as a police officer or elected official.
Motive - CORRECT ANSWER Internal states that provide direction for one's behaviors.
Norepinephrine - CORRECT ANSWER neurotransmitter associated with eating and alertness. Too little has been associated with depression in addition to serotonin
Overlearning - CORRECT ANSWER A technique used to improve memory where info is learned to the point that it can be repeated without mistake more than one time. Continuted rehearsal after material is leanred - Ebbinghaus
Phi Phenomenon - CORRECT ANSWER The perception of motion based on two or more stationary objects (e.g., perception of chaser lights brought about by different lights blinking at different times).
Criterion Validity - CORRECT ANSWER A measurements ability to predict scores on another measurement that is related or purports to measure the same or similar construct
Preoperational Stage - CORRECT ANSWER Piaget's second stage of cognitive development in which a child develops objects permanency and language. 2-7 years
Proactive Interference - CORRECT ANSWER Interference in memory due to prior learning.
r - CORRECT ANSWER Symbol used for the Pearson-product moment correlation (correlation coefficien
Reaction Formation - CORRECT ANSWER defense mechanism where unacceptable impulses are converted to their opposite.
Reticular Formation (Reticular Activating System) - CORRECT ANSWER Part of brain stem involved in arousal and attention, sleep and wakefulness, and control of reflexes.
Retinal Disparity - CORRECT ANSWER Binocular cue to distance referring to distance between the two images sent to the brain by our eyes. The farther apart these images, the closer the object.
Retroactive Interference - CORRECT ANSWER Interference in memory created by later learning.
Self Serving Bias - CORRECT ANSWER The tendency to assign internal attributes to successes and external factors to failures.
Sensorimotor Stage - CORRECT ANSWER The first stage in Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development where a child's primary way of learning about the world is through the senses and movement. 0-2 years
Structuralism - CORRECT ANSWER Wundt and Titchner school of thought from the 19th century focused on the gathering of psychological information through the examination of the structure of the mind.
Type I Error - CORRECT ANSWER The error that is committed when a true null hypothesis is rejected erroneously. The probability of a Type I Error is abbreviated with the lowercase Greek letter alpha.
Type II Error - CORRECT ANSWER The error that is committed when a false null hypothesis is accepted erroneously. The probability of a Type II Error is abbreviated with the uppercase Greek letter beta.
Variance - CORRECT ANSWER A measure of spread within a distribution (the square of the standard deviation).
Wernicke's Aphasia - CORRECT ANSWER Aphasia resulting from damage to a specific area of left temporal lobe. Affects written and spoken language.
visual capture - CORRECT ANSWER the tendency for vision to dominate the other senses
feature detectors - CORRECT ANSWER nerve cells in the brain's visual cortex that respond to specific features of the stimulus, such as shape, angle, or movement
bipolar cells - CORRECT ANSWER eye neurons that receive information from the retinal rods and cones and distribute information to the ganglion cells
ganglion cells - CORRECT ANSWER the specialized cells which lie behind the bipolar cells whose axons form the optic nerve which takes the information to the brain
glial cells - CORRECT ANSWER cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons and make myelin
congruence - CORRECT ANSWER consistency between one's ideal self and actual self that results in a positive self concept - Rogers
incongruence - CORRECT ANSWER inconsistency between one's ideal self and actual self that results in a negative self concept - Rogers
belief bias - CORRECT ANSWER the tendency for one's preexisting ideas to distort logical reasoning, sometimes by making invalid conclusions seem valid, or valid conclusions seem invalid
belief perseverance - CORRECT ANSWER Clinging to one's initial conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited
Reciprocal determinism - CORRECT ANSWER Bandura's model in which cognition's, behaviors, and environmental factors both influence and are influenced by each other
basic anxiety - CORRECT ANSWER Horney's term for feelings of helplessness and insecurity as a result of being a small child in a world full of adults.
moving away - CORRECT ANSWER Horney's term for avoiding people as a way of coping with ones anxiety toward them (detached personality)
moving toward - CORRECT ANSWER Horney's term for connecting positively to others and seeking acceptance. (Compliant personality)
moving against - CORRECT ANSWER Horney's term for seeking control and power over people as a way of coping (aggressive personality)
cardinal trait - CORRECT ANSWER a trait that is so pervasive that the person is almost identified with the trait - Allport
central trait - CORRECT ANSWER in Gordon Allport's trait theory of personality, a major characteristic such as honesty or sensitivity that defines a person most of the time
secondary trait - CORRECT ANSWER In Allport's theory, a characteristic seen only in certain situations, such as "uncomfortable in large crowds" and "likes to drive sports cars."
scaffolding - CORRECT ANSWER Vygotsky's idea that learners should be given only just enough help so that they can reach the next level
Place Theory - CORRECT ANSWER in hearing, the theory that links the pitch we hear with the location where the cochlea's membrane is stimulated
Frequency Matching Theory - CORRECT ANSWER theory holding that the firing rate of a neuron matches the frequency of a sound wave to determine pitch
subordinate goals - CORRECT ANSWER how can I achieve that for which I strive, goals that can be achieved only by cooperating and working with others - used to reduce prejudice
long term potentiation - CORRECT ANSWER an increase in a synapse's firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation. believed to be a neural basis for learning and memory
confabulation - CORRECT ANSWER when a person "remembers" info that was never stored in the memory
somnambulism - CORRECT ANSWER the condition of walking or performing some other activity without awakening; also known as sleepwalking - stage 4
pineal gland - CORRECT ANSWER located in the center of the brain, functioning to secrete melatonin
syntax - CORRECT ANSWER grammatical arrangement of words in sentences
grammar - CORRECT ANSWER in a language, a system of rules that enables us to communicate with and understand others
language acquisition devise - CORRECT ANSWER built-in mechanism for acquiring language - Chomsky's nature theory for language development
rooting - CORRECT ANSWER a reflex in which a newborn turns its head in response to a gentle stimulus on its cheek
babinski - CORRECT ANSWER infant reflex that causes toes to fan out when soles of feet are touched
moro - CORRECT ANSWER reflex when baby is startled or playdropped, it puts out arms and then brings limbs to midline
eros - CORRECT ANSWER Freud's term from the Greek word for love - the life instinct or the will to live
thanatos - CORRECT ANSWER Freud's term from the Greek word for death - the death or aggressive instinct which operates invisibly
AcH - CORRECT ANSWER neurotransmitter involved in memory and movement - too little is associated with Alzheimer's
identification - CORRECT ANSWER process by which, according to Freud, children incorporate their parents' values into their developing superegos - children align with their same sex parent to resolve the Oedipus Complex
eidetic - CORRECT ANSWER visual imagery of almost photographic accuracy
phenomenological view - CORRECT ANSWER focuses on the individuals unique self and experiences
Barnum effect - CORRECT ANSWER The tendency to agree with and accept personality interpretations that are provided.
Pick's disease - CORRECT ANSWER disease of the frontal and temporal lobes characterized by changes in personality
trichotillomania - CORRECT ANSWER OCD/anxiety disorder with an intense desire to pull out your hair; reported more in women, men have equal causes but are less likely to report it
parasomnias - CORRECT ANSWER Abnormal behavioral and physiological events during sleep, no problems with sleeping
Tay-Sachs disease - CORRECT ANSWER recessive disorder that is of the nervous system and the child usually dies by the age of 4
Klinefelter's syndrome - CORRECT ANSWER a disorder in which a male receives 2 X chromosomes and 1 Y chromosome
Korsakoff's syndrome - CORRECT ANSWER memory disorder related to thiamine deficiency generaly associated with chronic alcoholism; fail to recall many items or events of the past
Osmoreceptors - CORRECT ANSWER The sensors in the hypothalamus that create the thirst sensation.
orienting reflex - CORRECT ANSWER The tendency to turn toward an object that has touched you.
prosopagnosia - CORRECT ANSWER inability to recognize faces
purkinje shift - CORRECT ANSWER is the way that perceived color brightness changes with the level of illumination in the room. With lower levels of illumination, the extremes of the color spectrum( especially red) are seen as less bright
Ponzo illusion - CORRECT ANSWER Both horizontal rectangles are the same size but the top one looks longer because of linear perspective (railroad)
minimum principle - CORRECT ANSWER is the tendency to see what is easiest or logical to see.
Pragnanz - CORRECT ANSWER The fundamental principle of Gesalt perception is the law of pragnanz (German for consciousness) which says that we tend to order our experience in a manner that is regular, orderly, symetric, and simple
McCollough effect - CORRECT ANSWER Afterimages that appear after staring at a color for a long period of time
Point-Biserial correlation - CORRECT ANSWER used for dichotomous "either-or" variables such as male/female/
Chi-square - CORRECT ANSWER used when cases/data are categorical--looks at patterns or distributions not differences in means
selective attrition - CORRECT ANSWER The tendency for some kinds of people to be more likely than others to drop out of a study.
reactance - CORRECT ANSWER Negative reactions to threats to one's personal freedom. Reactance often increases resistance to persuasion and can even produce negative attitude change or opposite to what was intended
Rosenthal effect - CORRECT ANSWER the concern that researchers may inadvertently alert subjects to the purpose of the study
Acquiescence - CORRECT ANSWER when people agree with opposing statements
parallel play - CORRECT ANSWER Two children playing side by side at the same activities, paying little or no Attention to each other; the earliest kind of social interaction between toddlers(2-3 years old)
symbolic play - CORRECT ANSWER children pretend to be something or someone else; chlidren pretend an object is something else (1-2 years old)
autonomy vs shame and guilt - CORRECT ANSWER resolution: find independence
18 mo - 3 years
initiative vs guilt - CORRECT ANSWER (3 to 5 years) Children learn to assume more responsibility by taking initiative but will feel guilty if they overstep limits set by parents--resolution: purpose
industry vs inferiority - CORRECT ANSWER Age 6 to puberty. Kids master cognitive and social skills, learn to work industriously, and cooperate with peers. Success will give sense of competence, but failure will give feeling of inadequacy. resolution: compentency
identity vs role confusion - CORRECT ANSWER Erikson stage - teenagers work at refining a sense of self by testing roles and integrating them to form a single identity, or they become confused on who they are. resolution: sense of self
intimacy vs isolation - CORRECT ANSWER resolution: Love. Young adults attempt to find someone to share their life with.
productivity vs stagnation - CORRECT ANSWER middle age--resolution:productive and caring
ego integrity vs despair - CORRECT ANSWER (Erikson) People in late adulthood either achieve a sense of integrity of the self by accepting the lives they have lived or yield to despair that their lives cannot be relived
Palmar reflex - CORRECT ANSWER the grasping reflex that a newborn infant exhibits when an object is placed in his or her hand
Zeigarnik effect - CORRECT ANSWER The tendency to recall uncompleted tasks better than completed ones.
Saccades - CORRECT ANSWER Quirk, jerky movements of the eyes as they jump from one fixation to another in the reading of continuous text
Analogical representations - CORRECT ANSWER share some features or characteristics of the things to which they refer
symbolic representations - CORRECT ANSWER A type of mental representation that does not correspond to the physical characteristics of that which it represents. Thus, the word mouse does not resemble the small rodent it represents.
garden-path sentences - CORRECT ANSWER sentences that suggest one interpretation that turns out to be wrong
Overextension - CORRECT ANSWER the use of words to refer to objects or things that are outside the bounds of the category named by the word--call a sheep a dog
Telegraphic speech - CORRECT ANSWER meaningful two word sentences, usually a noun and a verb, and usually in the correct order uttered by 2 year olds
overregularization - CORRECT ANSWER a grammatical error, usually appearing during early language development, in which rules of the language are applied too widely, resulting in incorrect linguistic forms
prosody - CORRECT ANSWER refers to the pitch, loudness, tempo, and rhythm of language. (the meaning of a written sentence, punctuation)
morphology/morphological rule - CORRECT ANSWER grammar rules; how to group morphemes
hyperphagia - CORRECT ANSWER overeating; due to inadequate leptin secretion or unresponsive receptors
Agraphia - CORRECT ANSWER inability to write
Alexia - CORRECT ANSWER inability to read
agnosia - CORRECT ANSWER failure to recognize or identify objects despite intact sensory function
apraxia - CORRECT ANSWER impaired ability to carry out motor activities despite intact motor function
basal ganglia - CORRECT ANSWER group of structures which coordinate movement; located in the forebrain (telencephalon)
inferior colliculus - CORRECT ANSWER an essential auditory center in the midbrain
superior colliculus - CORRECT ANSWER an essential visual center between the retina and the striate cortex
Triarchic thoery of intelligence - CORRECT ANSWER Components: metacomponents, performance components, knowledge-acquisition components; types of intelligence: analytical, practical, and creative
Metacomponents - CORRECT ANSWER Higher-order processes used to plan and regulate task performance; triarchic theory of intelligence- Sternberg
Performance component - CORRECT ANSWER Actual processes used to perform the task; triarchic theory of intelligence- Sternberg
Knowledge-acquisition Component - CORRECT ANSWER Allow us to learn from our experiences, store information in memory, and combine new insights with previously acquired information; triarchic theory of intelligence- Sternberg
Flynn effect - CORRECT ANSWER "rising curve" phenomenon; population score on intelligence has raised 3 points per decade since 1910
Outcome bias - CORRECT ANSWER Refers to the extent that a test underestimates a persons true intellectual ability
Predictive bias - CORRECT ANSWER Occurs if the test successfully predicts criterion measures for some groups but not for other groups
Behavioral activation system (BAS) - CORRECT ANSWER roused to action by signals of potential reward and positive need gratification--prefrontal area in left hemisphere (goal directed and planning behavior)
Behavioral inhibition system (BIS) - CORRECT ANSWER responds to stimuli that signal potential pain, nonreinforcement, and punishment--limbic system and right frontal lobe
Self-determination theory - CORRECT ANSWER focuses on three fundamental psychological needs: competence, autonomy, and relatedness
competence motivation - CORRECT ANSWER master challenges and perform skills (self-determination theory)
autonomy motivation - CORRECT ANSWER greater freedom and regulation by the self (self-determination theory)
relatedness motivation - CORRECT ANSWER form meaningful bonds with others (self-determination theory)
leptin - CORRECT ANSWER hormone secreted by fat cells that decreases appetite and increases energy expenditure
achievement goal theory - CORRECT ANSWER focuses on the manner in which success is defined both by the individual and within the achievement situation itself: mastery and ego orientations
mastery orientation - CORRECT ANSWER focus is on personal improvement, giving maximum effort and perfecting new skills (achievement goal theory)
ego oreintation - CORRECT ANSWER goal is to outperform others (hopefully with as little effort as possible)--achievement goal theory
ego avoidance - CORRECT ANSWER center on avoiding negative judgments by oneself or others
personal fable - CORRECT ANSWER part of adolescent ego-centrism-overestimate the uniqueness of their feelings and experineces
Identity diffusion - CORRECT ANSWER not yet gone through identity crisis-unconcerned or cynical about identity issues
Foreclosure - CORRECT ANSWER not yet gone through identity crisis because already committed to one due to automatic peer-groups of parental values
Moratorium - CORRECT ANSWER want to establish a clear identity and currently in crisis--not yet resolved
Identity achievement - CORRECT ANSWER gone through an identity crisis and successfully achieved a coherent set of values (an identity)
Cognitive-affective personality system (CAPS) - CORRECT ANSWER organized system of five variables that interact continuously with one another and with the environment: encodings and personal constructs, expectancies and beliefs, goals and values, affects, competencies and self-regulatory processes
hardiness - CORRECT ANSWER stress-protective factor cromprising of three beliefs: commitment, control (internal locus), challenge (look at situations as challenges or opportunities not threats)
Transtheoretical model - CORRECT ANSWER six stages in the change process: precontemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, maintenance, and termination
motivational interviewing - CORRECT ANSWER leads the person to his or her own conclusions by asking questions that focus on discrepancies between the current state and the individual's ideal self-image, behaviors, and outcome
harm reduction - CORRECT ANSWER prevention strategy that is designed to reduce the harmful effects of a behavior, not the elimination of the behaivor
abstinence violation effect - CORRECT ANSWER person becomes upset and self-blaming over the lapse and view it as proof that he or she will never be strong enough to resist temptation
social causation hypothesis - CORRECT ANSWER attributes the higher prevalence of schizophrenia to the higher level of stress that low-income people experience
social drift hypothesis - CORRECT ANSWER proposes that as people develop schizophrenia, their personal and occupational functioning deteriorates so that they drift down the socioecomonic ladder
ABCD model - CORRECT ANSWER cognitive therapy: activating system (trigger emotion), belief system (appraisal of A), consequences (consequences of appraisal B), disputing ( changing maladaptive/erroneous belief system B)
[Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages