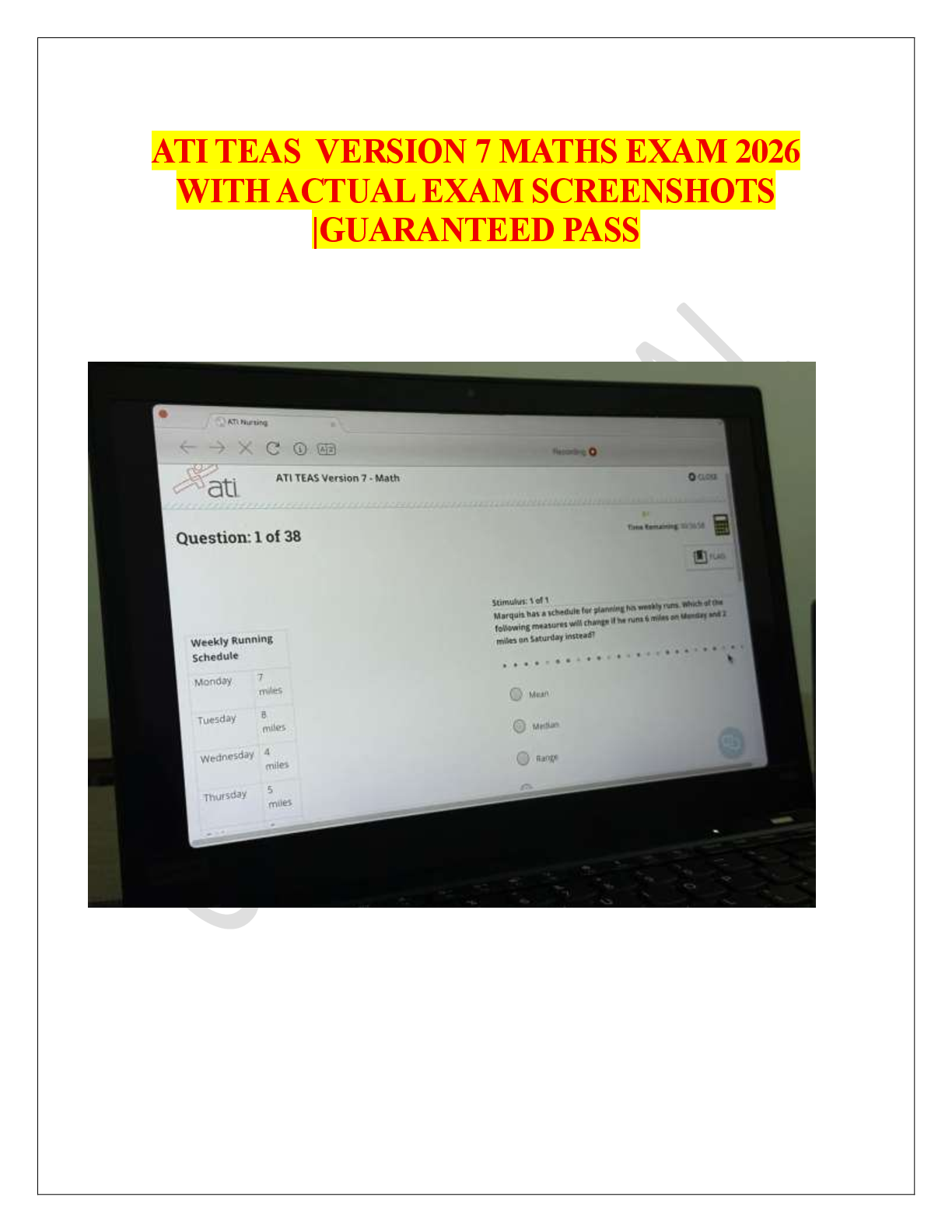
HESI A2 Entrance Exam (Math) Final Test (Qns & Ans) 2025
$ 12

ATI Pediatric Practice B Questions And Answers (Latest Update)
$ 12

OCR GCSE Chemistry A (Gateway Science) J248/02: Paper 2 (Foundation tier) General Certificate of Secondary Education Mark Scheme for June 2022
$ 6

Sophia Statistics Unit 5 Milestone Questions and Answers with Complete Solutions
$ 13

Case Notes & Answer for ChimpChange How to Raise Capital to Grow By Stephen Sapp
$ 15

ATI PN Comprehensive Exit Exam 2023-2024 Update | PN ATI Comprehensive Exit Exam Verified Questions and Correct Answers Rated A+
$ 15
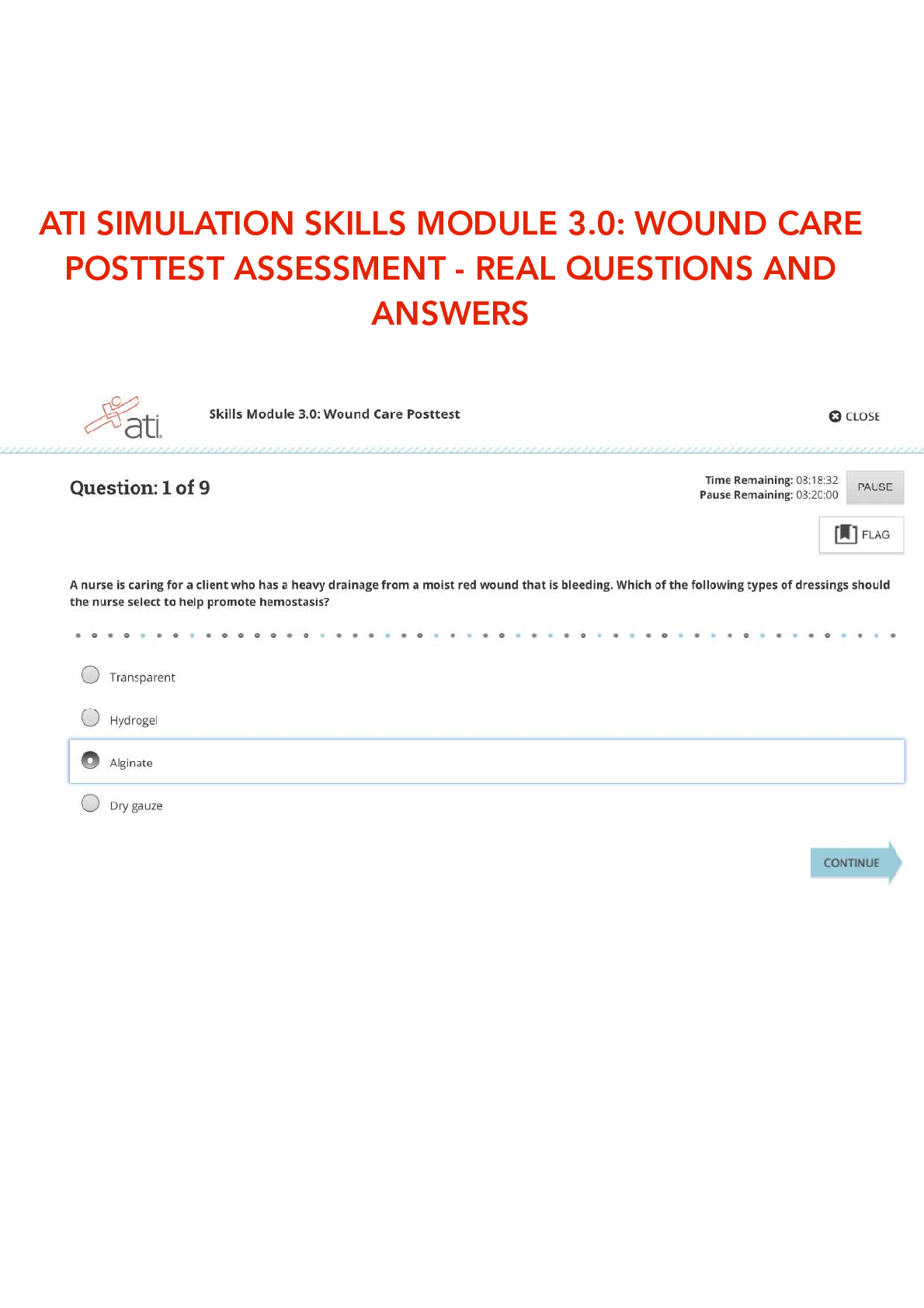
ATI SIMULATION SKILLS MODULE 3.0: WOUND CARE POSTTEST ASSESSMENT - REAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
$ 11.5

COMUPTER S CS6310Quiz_ Quiz 3_ Unified Modeling Language (UML). Georgia Institute Of Technology.ALL ANSWERS CORRECT.1005 SCORE
$ 9

2024 HESI NCLEX-RN Fundamentals Updated Spring Guaranteed A+ Actual Questions and Answers, Complete 100%
$ 14

Criminal Justice Q&A _ What is a forensic palynologist? Describe the case that Mildenhall worked on in New Zealand.
$ 5.5

SDGEOGM Assignment 3 Portfolio
$ 10

Right of Way Portion of QAC Test Solved 2023
$ 9

Chemistry for Today General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10th Edition by Seager, Slabaugh, Hansen Chapter 1-25 | Solution Manual
$ 23
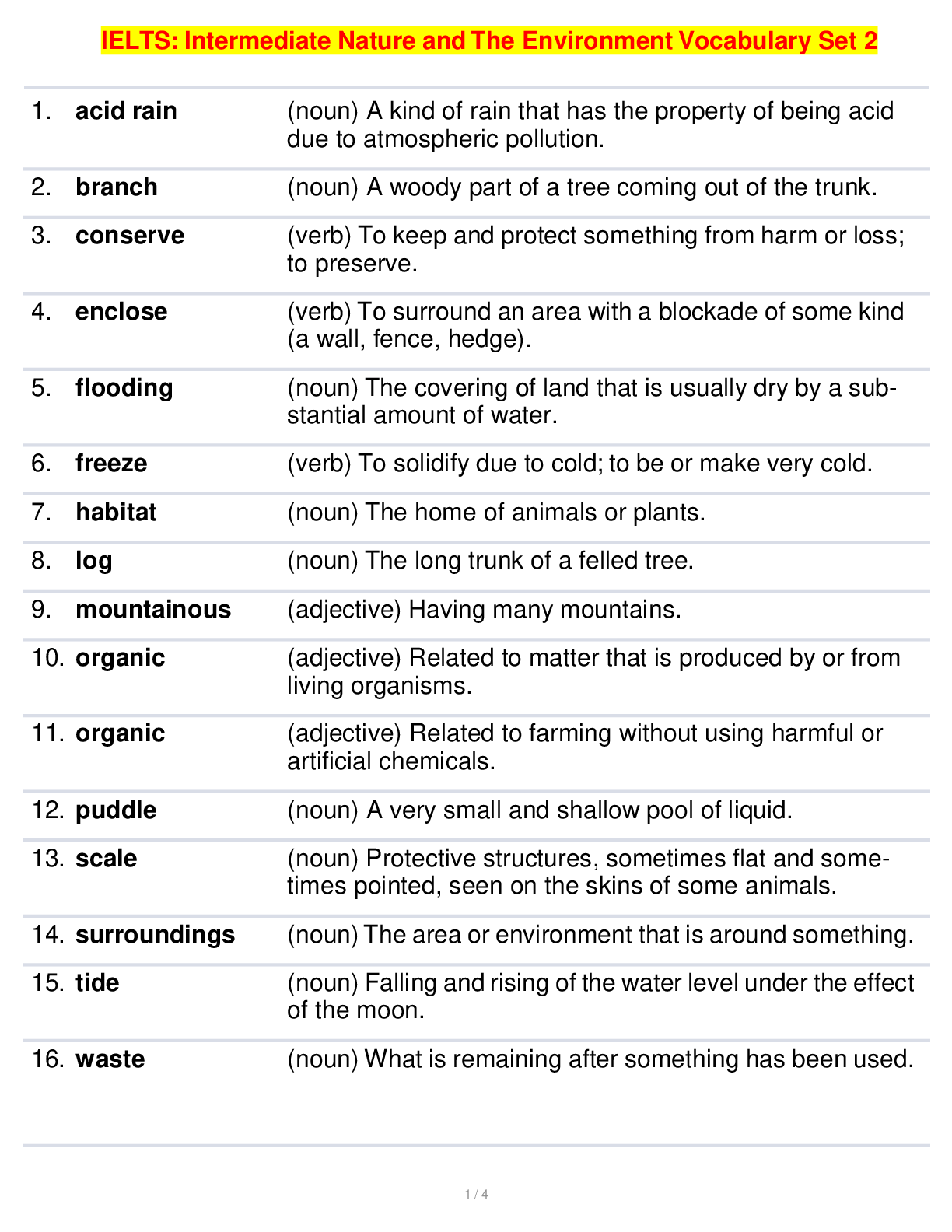
IELTS: Intermediate Nature and The Environment Vocabulary Set 2
$ 5.5

CLOUD COMP CT097-3-3 Cloud Infrastructure and Service_CT097-3-3-CSVC Exam. Q&A
$ 10.5
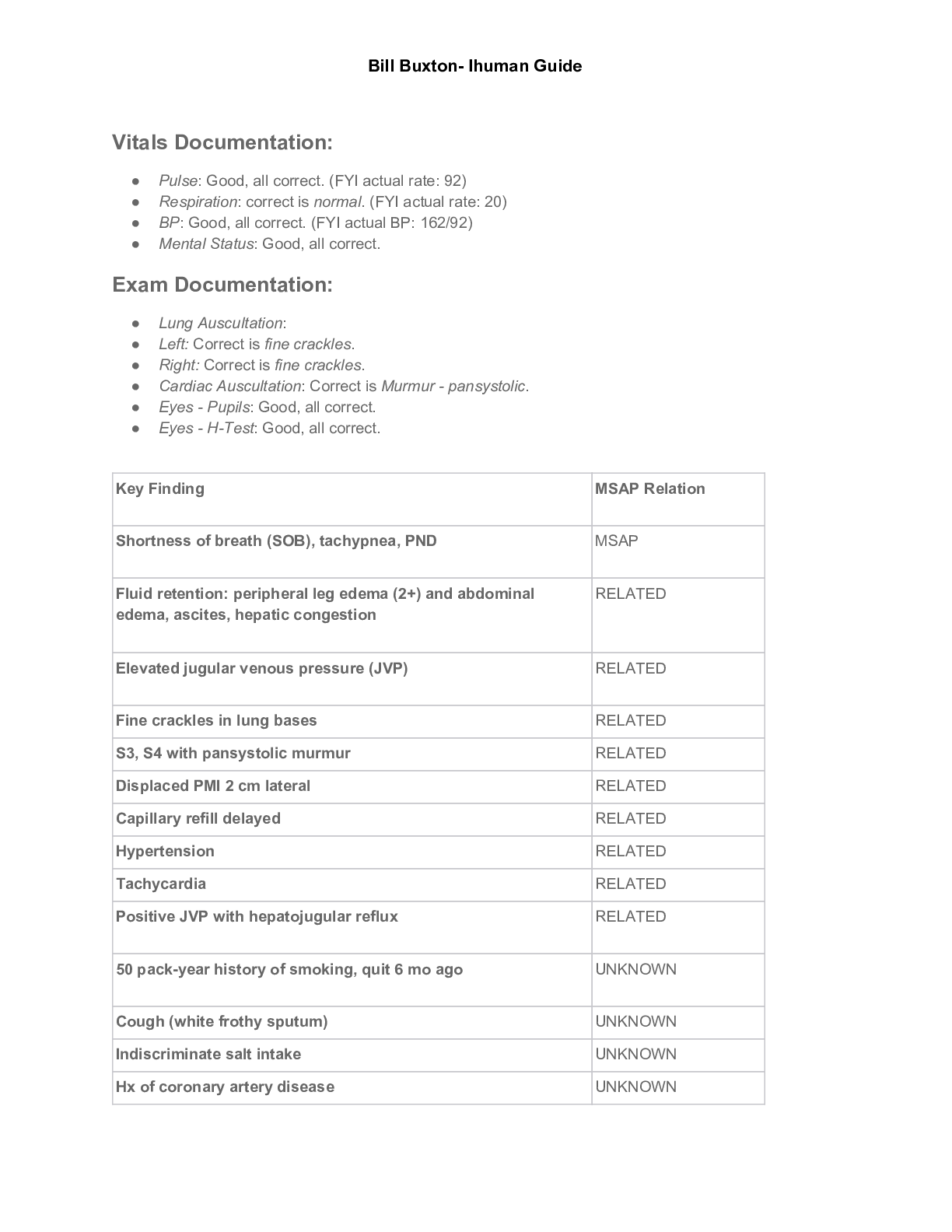
Bill Buxton Ihuman Latest Guide
$ 8

[eTextBook] [PDF] Juvenile Justice Policies, Programs, and Practices 5th Edition By Robert Taylor, Eric Fritsch
$ 29

eBook [PDF] Financial Accounting, Tools for Business Decision Making, 8th Edition By Paul Kimmel, Jerry Weygandt, Donald Kieso