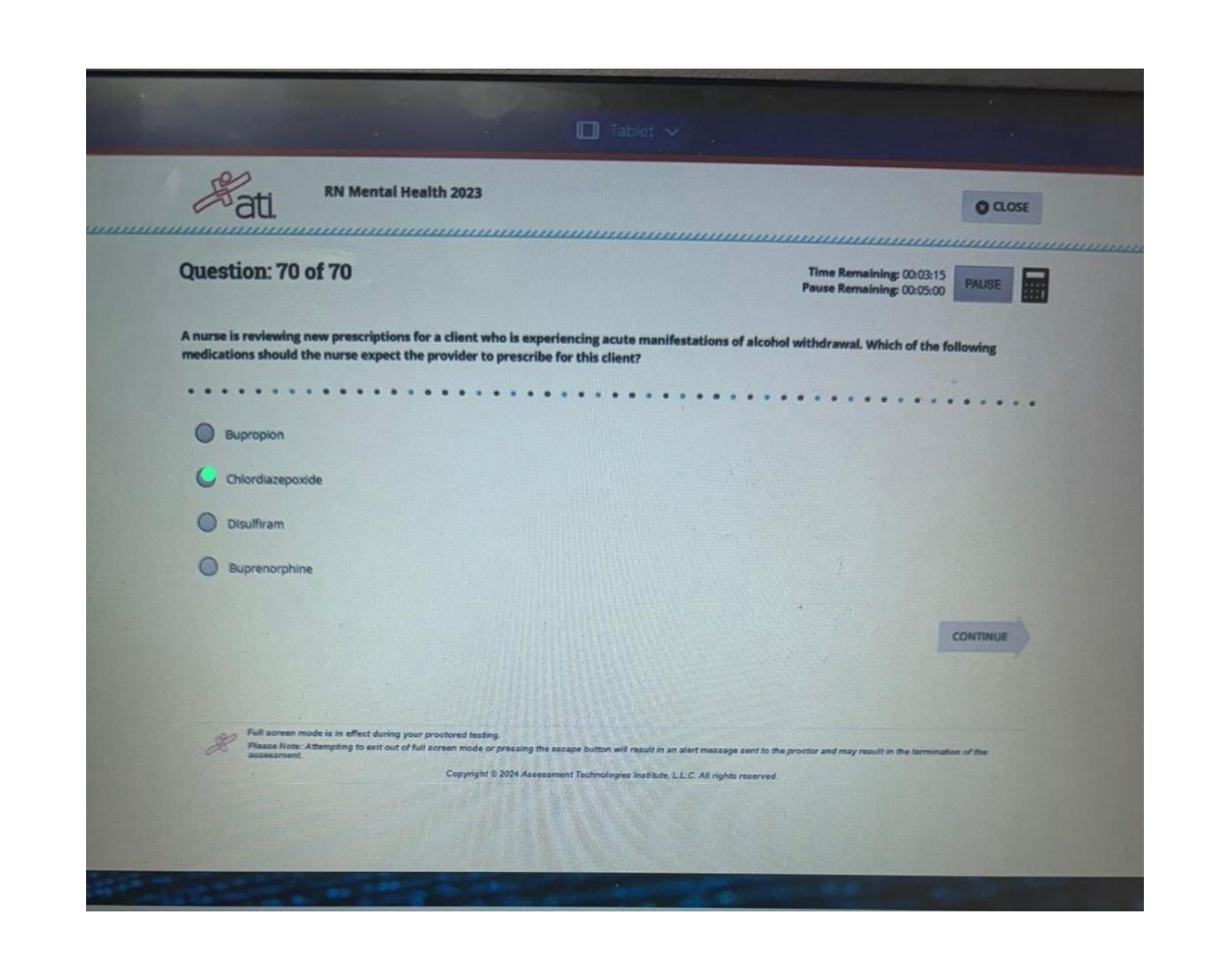
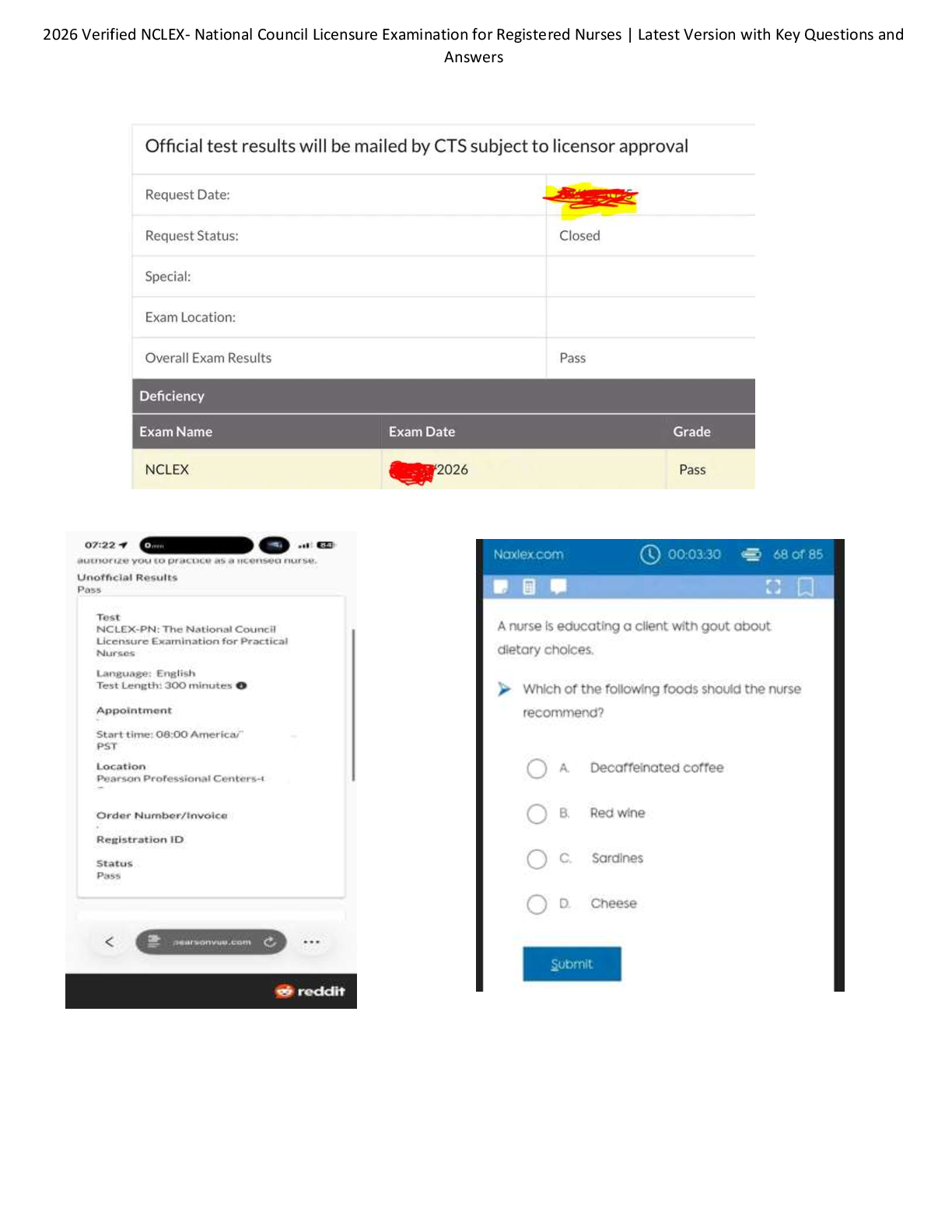
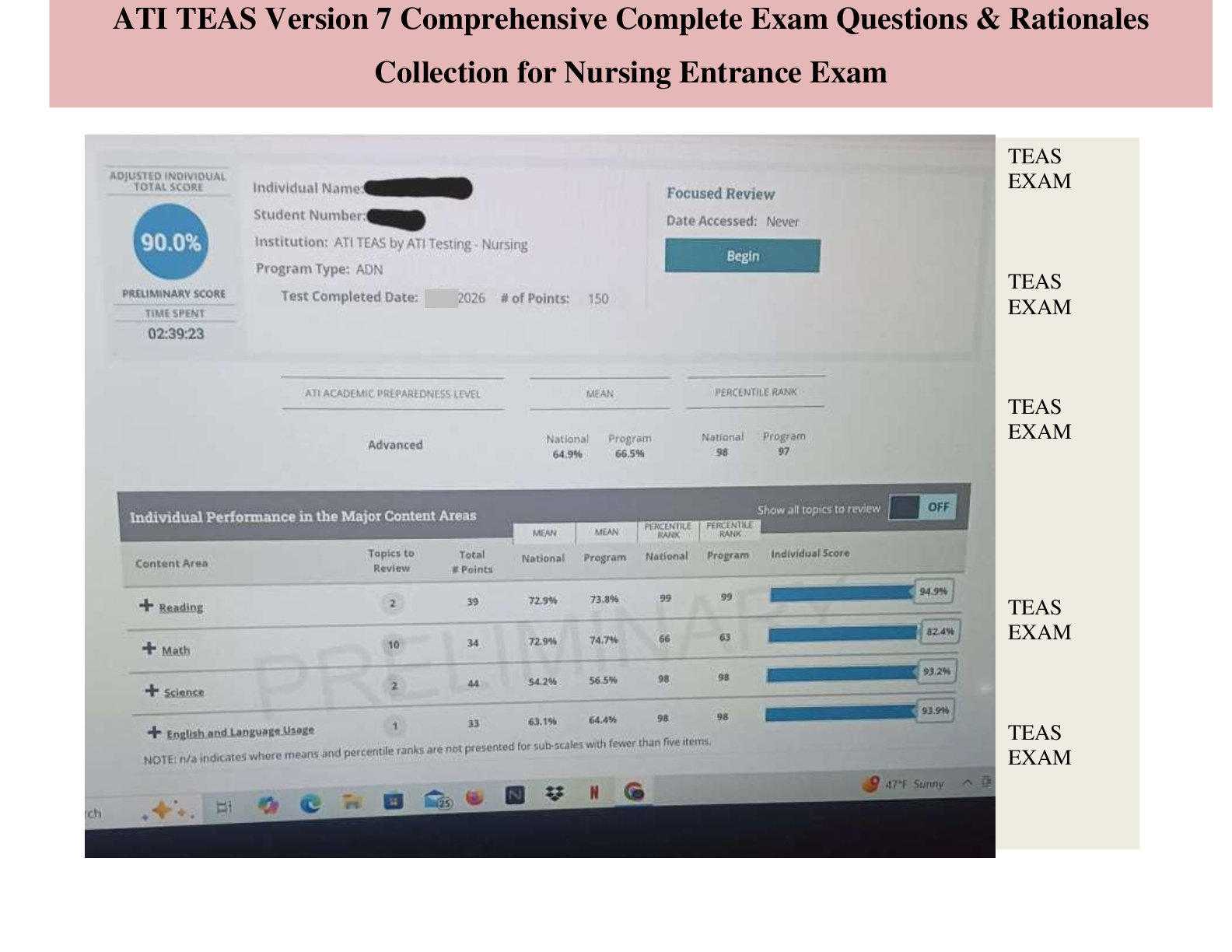
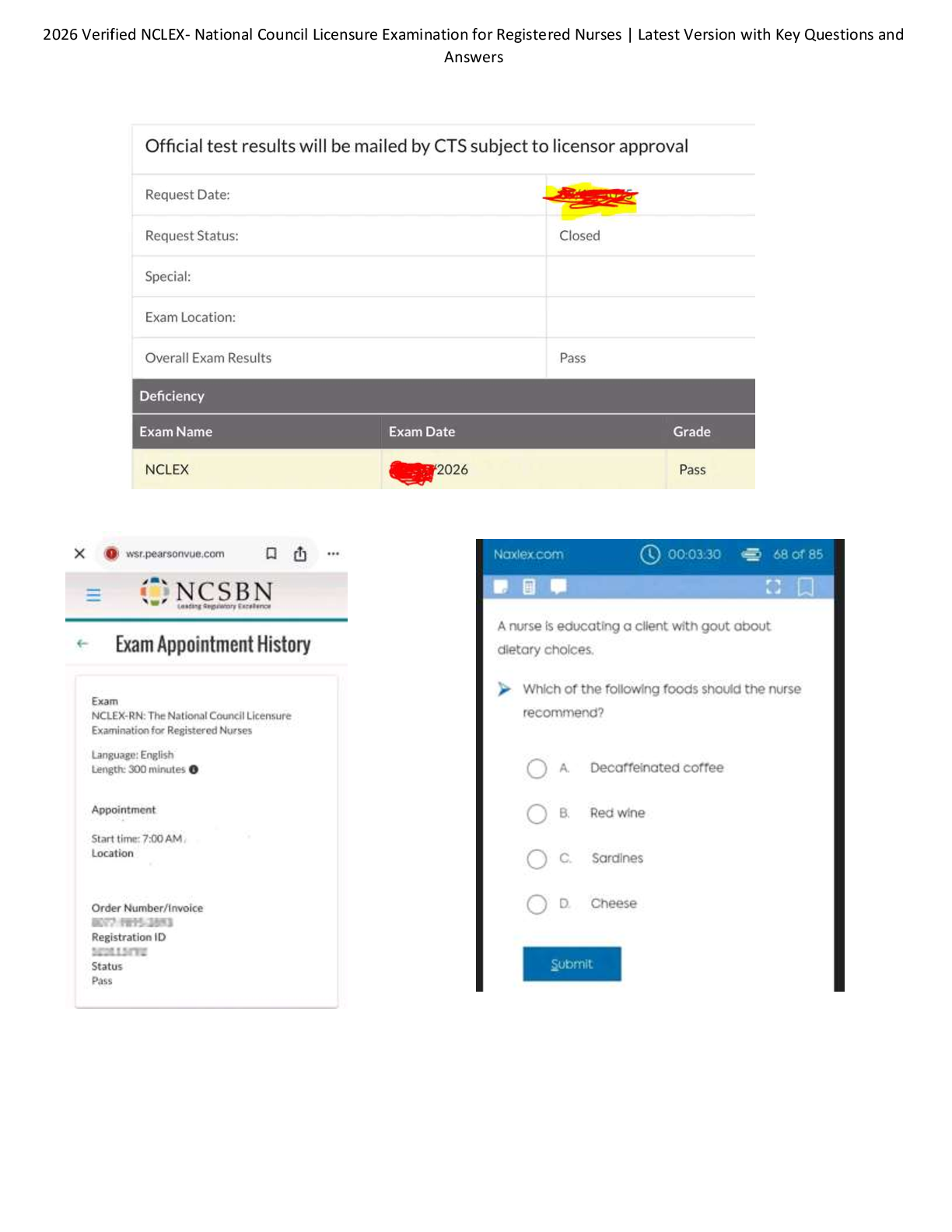
COM 312 Exam 2 Study Guide 59 Questions with Verified Answers
Define Interpersonal Violence - CORRECT ANSWER when a person imposes will (wants, desires, needs, etc.) on a relational partner through physical and/or v
...
COM 312 Exam 2 Study Guide 59 Questions with Verified Answers
Define Interpersonal Violence - CORRECT ANSWER when a person imposes will (wants, desires, needs, etc.) on a relational partner through physical and/or verbal intimidation.
Identify the potential communication behaviors evident in interpersonal violence. - CORRECT ANSWER -Interrupting
-Dominating
-Stereotyping
-Glaring eye contact
-Invading posture
-Intimidating
Define Verbal Abuse - CORRECT ANSWER Attacking someone's self-concept to cause psychological pain
Give some examples of Verbal Abuse - CORRECT ANSWER - Character Attacks (belittling someone)
- Threats
Define Nonverbal Aggression - CORRECT ANSWER Causing physical harm to others
What are the gender differences in violent communication? - CORRECT ANSWER 1. Men are more likely to use physical violence toward female partners than vise-versa in heterosexual relationships
2. More women report feeling stalked
3. 25% of women and 8% of men report physical/sexual assault in life
Explain the Prelude stage in the Interpersonal Violence Cycle. - CORRECT ANSWER perceptions of past unresolved conflict and episodes of violence
Explain the Triggering Event stage in the Interpersonal Violence Cycle. - CORRECT ANSWER Disagreement happens; the abused feel fear; the abuser feels aggression
Explain the Initiation stage in the Interpersonal Violence Cycle. - CORRECT ANSWER Overt conflict begins, generally through competing and destructive messages (verbal abuse)
Explain the Differentiation stage in the Interpersonal Violence Cycle. - CORRECT ANSWER Verbal abuse escalates and can escalate from verbal to physical violence.
Explain the Resolution stage in the Interpersonal Violence Cycle. - CORRECT ANSWER Conflict is NOT resolved. Issues are dropped or suppressed. (accommodate/avoid)
What is the "Chilling Effect" Cycle? - CORRECT ANSWER which one person in a relationship withholds grievances from the other, usually due to fear of alienating the other person or fear of the other person's severe reaction.
Abusive partners struggle to manage... - CORRECT ANSWER Dialectical Tensions
What are the competing but equally essential needs/demands? - CORRECT ANSWER Autonomy (independence) vs. Connection
Stability vs. Change
How do mothers who have been abused tend to view their children's activities? - CORRECT ANSWER They are more likely to control their child's choices during game/play - they treat these activities as tasks to accomplish rather than enjoyment.
Define Patriarchal Violence. - CORRECT ANSWER male-female dating or marital relationship in which the man severely and regularly beats the woman, who is left feeling frightened and isolated.
Define Relation Control-Motivated Aggression. - CORRECT ANSWER refers to the use of power tactics such as intimidation, coercion and threats, emotional abuse, minimization and denial, using the children, isolation, and economic deprivation.
What is Authoritarian Parenting? - CORRECT ANSWER demand compliance, loyalty and perfection, and resort to physical punishment if "needed".
What are AVPs? - CORRECT ANSWER Alternatives to Violence Projects (AVPs)
What is Conflict Climate? - CORRECT ANSWER The psychological atmosphere that influences each conflict.
What are the 4 components of Conflict Climate? - CORRECT ANSWER 1. Equity vs. Power imbalance
2. Cooperation vs. Competition
3. Trust vs. Distrust
4. Nurturing vs. harmful (combination of 1,2, and 3)
Define Communication Climate. - CORRECT ANSWER The overall feeling, or emotional mood of a relationship -- shaped by verbal and nonverbal interaction between people
What is Group Think? - CORRECT ANSWER Committment to people/goals/ideas of group at expense of engaging in necessary conflict.
- Maintaining image of cohesion
What is the Abeline Paradox? - CORRECT ANSWER We do not voice our opinion in a group because:
- we have anxiety about choosing
- we fear separation from the group and negative outcomes from them
- We don't want to "rock the boat"
What is the "Lucifer Effect"? - CORRECT ANSWER - Point in time when normal, ordinary people first cross the boundary to increase in evil action
- Don't question what others are doing
- Lack of separation from person to role
- Based off of the Stanford Prison Studies
Important Dates for the Politeness Theory. - CORRECT ANSWER 1600 - Shakespeare: "All the world's a stage"
1967 - Goffman: Dramaturgical Perspective
1987 - Brown and Levinson's: Politeness Theory
Politeness Theory Key Concept - CORRECT ANSWER Focuses on the specific ways that people manage and save face using communication.
According to Politeness Theory, what is someone's "Face"? - CORRECT ANSWER The public self image that people want to claim.
According to Politeness Theory, what is "Self-Presentation"? - CORRECT ANSWER The presentation of that image to others through communication.
According to Politeness Theory, what is "Impression Management"? - CORRECT ANSWER Strategic attempts to manage aspects of one's identity in ways that make a good impression.
What are the 2 types of Face? - CORRECT ANSWER 1. Positive
2. Negative
What is Positive Face? - CORRECT ANSWER The favorable image that a person presents and hopes to have validated by others (reflects the desire to be liked)
- want people to view you positively
What is Negative Face? - CORRECT ANSWER Reflects a person's desire to be free from imposition and restraint and to have control of his/her time, property, space, and resources.
Ex: someone asks you to cover their shift at work and you say no, because you want control over your time.
What are the 2 factors of Face Loss? - CORRECT ANSWER 1. In the wrong face
2. Out of face
Define "In the wrong face" - CORRECT ANSWER Information that contradicts or challenges one's image is brought forth
Define "Out of face" - CORRECT ANSWER A person is unable to put forth the image that is expected or required.
Provide an example of "Out of face" - CORRECT ANSWER Ex: Someone's family member died, but you don't know how to empathize because you have never lost a family member.
What is Corrective Facework? - CORRECT ANSWER Strategic communication that is used to help restore face after it is lost.
- usually to restore positive face
What are some Corrective Facework Strategies? - CORRECT ANSWER - Apologies
- Accounts (an excuse for something)
- Remediation (physically repairing something)
- Humor
- Avoidance
- Aggression
What is a Face-Threatening Act (FTA)? - CORRECT ANSWER Behaviors that detract from an individual's identity.
- usually threatens your positive face
What are the 5 types of FTAs? - CORRECT ANSWER 1. Bald on Record
2. Positive Politeness
3. Negative Politeness
4. Off the Record
5. Do not do the FTA
Explain Bald on Record. - CORRECT ANSWER "You need to help me with this...."
Explain Positive Politeness. - CORRECT ANSWER First you give someone a compliment, then you make your demand.
- Sandwhiching
Explain Negative Politeness. - CORRECT ANSWER "I know you're busy and I hate to ask, but can you help me with my homework?"
Explain off the record. - CORRECT ANSWER "God, I am so bad at math. I wish someone would help me out."
- a hinting strategy
Explain Do not do the FTA. - CORRECT ANSWER You don't make a request and hope that someone sees you struggling and helps.
Ex: Struggling with groceries
Define Stress. - CORRECT ANSWER a biochemical reaction within our bodies due to the way in which we interpret and respond to external pressures, which may be positive or negative.
- Conflict situations can produce stress, but the opposite is also true; conflict itself is a reaction to stress.
What are the 4 types of stress? - CORRECT ANSWER 1. Eustress
2. Hypostress
3. Hyperstress
4. Distress
Explain Eustress. - CORRECT ANSWER short term; encourages positive actions and attitudes
Provide an example of Eustress. - CORRECT ANSWER Ex: a batter may feel eustress before he goes to the plate to hit the ball.
Explain Hypostress. - CORRECT ANSWER Underload; anxiety from boredom or lack of challenges
Provide an example of Hypostress. - CORRECT ANSWER Ex: you may feel hypostress when your relationship with your girlfriend has been stagnant and repetitive because there is no excitement.
Explain Hyperstress. - CORRECT ANSWER Too many tasks pile up; unable to adapt or cope
Provide an example of Hyperstress. - CORRECT ANSWER Ex: Having 3 tests in 2 days during finals week and trying to study for them.
Explain Distress. - CORRECT ANSWER Lose control of the situation and source of stress; supress real issues, stress about one thing manifested into others (long-term)
What are 4 strategies to managing stress? - CORRECT ANSWER 1. Activities Approach
2. ABC model of stress
3. Positive Self-Talk
4. Develop a Playful Spirit
What is the Activities Approach? - CORRECT ANSWER - exercising, art, yard work, discuss stress with friend
What does the ABC model of stress stand for? - CORRECT ANSWER A = Activating event or stressor
B = Beliefs or relevant thoughts
C = Consequences and reaction to stressor
What does Positive Self-Talk mean? - CORRECT ANSWER - Notice when you "should" yourself too much
- Don't overgeneralize ("always", "never")
[Show More]