Health Care > EXAM > REVISED] TNCC 8TH EDITION QUESTION WITH ANSWERS LATEST 2024-2025 A+ GRADE BEST UPDATE (All)
REVISED] TNCC 8TH EDITION QUESTION WITH ANSWERS LATEST 2024-2025 A+ GRADE BEST UPDATE
Document Content and Description Below
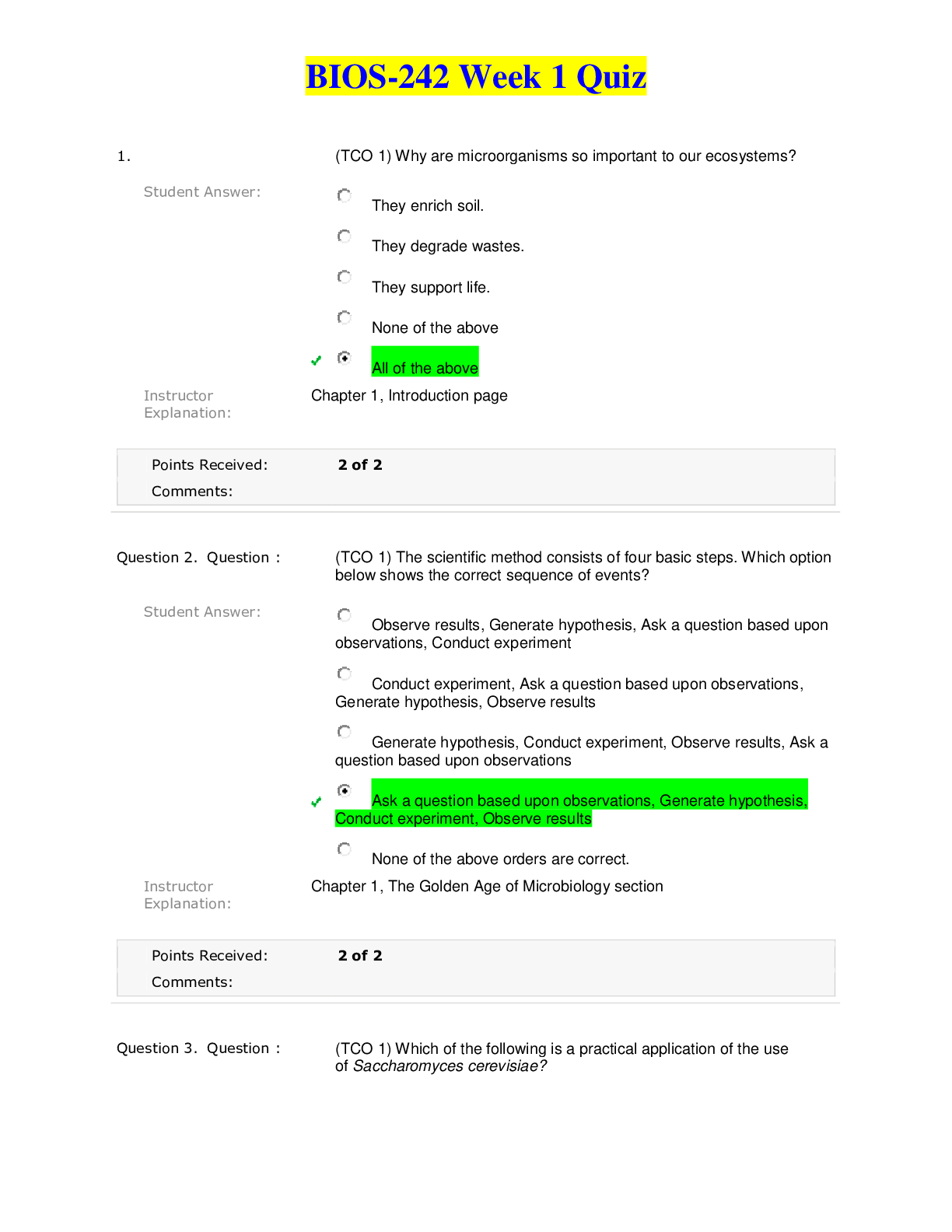
REVISED] TNCC 8TH EDITION QUESTION WITH ANSWERS LATEST 2024-2025 A+ GRADE BEST UPDATE 1. What are the greatest risks for trans- port? 2. According to newtons law which of these two force i... s greater: size or force? 3. What is the relationship between mass and velocity to kinetic energy? Loss of airway patency, displaced ob- structive tubes lines or catheters, dis- lodge splinting devices, need to re- place or reinforce dressings, deterio- ration in patient status change in vital signs or level of consciousness, injury to the patient and/or team members Neither. For each force there is an equal and opposite reaction. Kinetic energy is equal to 1/2 the mass multiplied the square of its ve- locity therefore when mass is doubled so is the net energy, however, when velocity is doubled energy is quadru- pled. 4. What is tension? stretching force by pulling at opposite ends 5. What is compression? Crushing by squeezing together 6. What is bending? Loading about an axis. Bending caus- es compression on the side the per- son is bending toward intention to the opposite side 7. What is shearing? Damage by tearing or bending by ex- erting faucet different parts in oppo- site directions at the same time. 8. What is torsion? Torsion forces twist ends in opposite directions. 9. What is combined loading? Any combination of tension compres- sion torsion bending and/or shear. 10. Blunt, penetrating, thermal, or blast. What are the four types of trauma related injuries? 11. What are contributing factors to in- juries related to blunt traumas? 12. What are the seven patterns of path- way injuries related to motor vehicle accidents? 13. Differentiate between the three im- pacts of motor vehicle impact se- quence. 14. What are the three factors that con- tribute to the damage caused by penetrating trauma's? 15. What causes the primary effects of blast traumas? 16. What causes the secondary effects of blast traumas? 17. 17. The point of impact on the patient's body, the type of surface that is hit, the tissues ability to resist (bone ver- sus soft tissue, air-filled versus solid organs), and the trajectory of force. Up and over, down and under, lateral, rotational, rear, roll over, and ejection. The first impact occurs when the ve- hicle collided with another object. The second impact occurs after the initial impact when the occupant continues to move in the original direction of travel until they collide with the inte- rior of the vehicle or meet resistance. The third impact occurs when internal structures collide within the body cav- ity. The point of impact, the velocity and speed of impact, and the proximity to the object. The direct blast effects. Types of injuries include last long, tympanic membrane rupture and middle ear damage, abdominal hemorrhage and perforation, global rupture, mild Tru- matic brain injury. Projectiles propelled by the explosion. Injuries include penetrating or blunt injuries or I penetration. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 06, 2024
Number of pages
9
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 06, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
37