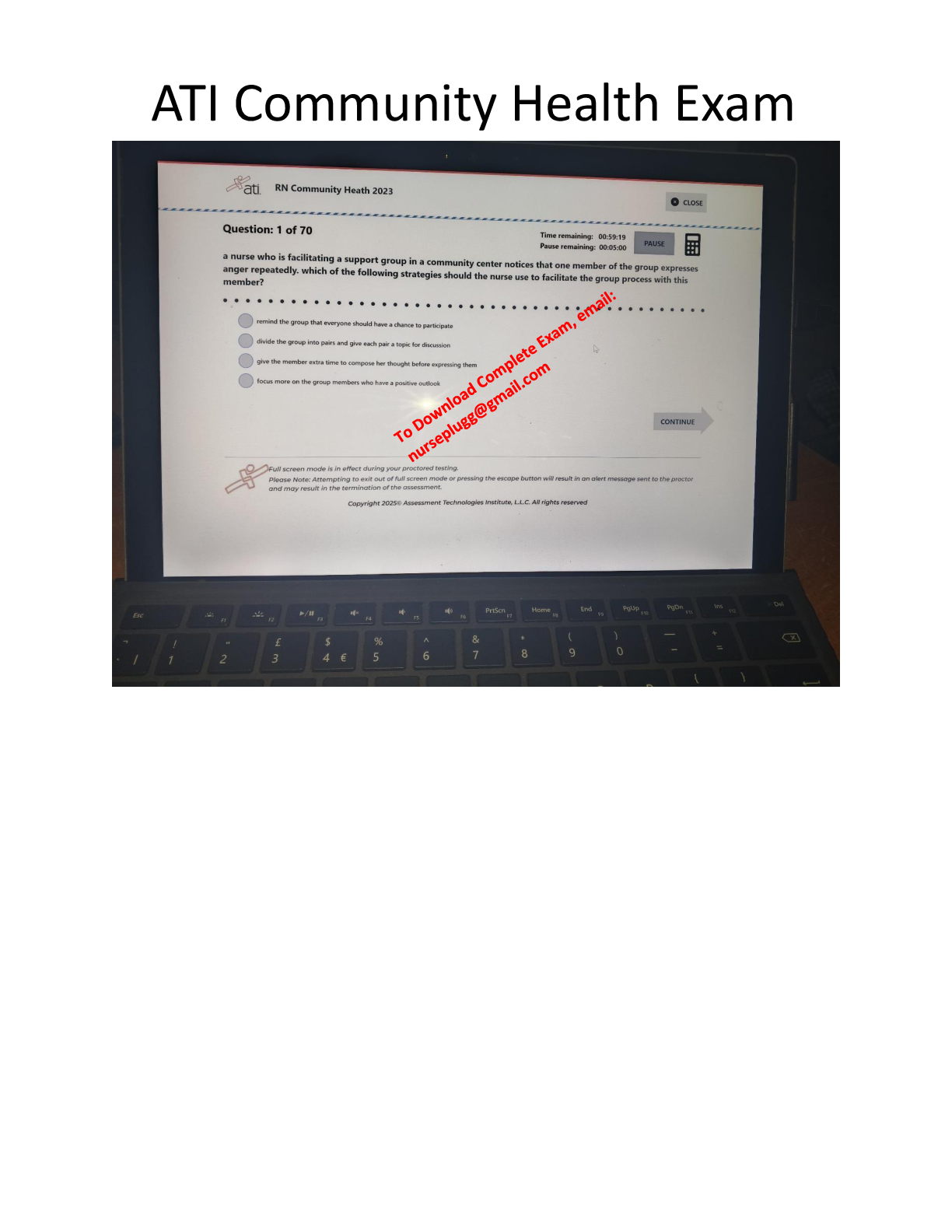
NCP 5.10 LATEST QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
$ 8

eBook [PDF] Advances in Robotics Research From Lab to Market Vol 132 By Antoni Grau, Yannick Morel, Ana Puig-Pey, Francesca Cecchi
$ 30

UNIT 4 Mathematical Methods Modelling / Problem solving task (SAC 2)
$ 8

2023 Wellcare Medicare Certification Test.
$ 17

Test Bank for Maternal Child Nursing Care in Canada 3rd Edition Keenan Lindsay | All Chapters 1-55 | Complete Latest Guide A+ | Perry's Maternal Child Nursing Care
$ 11.5

Chapter 1: Accounting: Information for Decision Making. question and answers