*NURSING > TEST BANKS > TEST BANK: Child Development; Children with Exceptionalities (PSYCH2043), Exam Questions & Answers, (All)
TEST BANK: Child Development; Children with Exceptionalities (PSYCH2043), Exam Questions & Answers, All Chapters Answered
Document Content and Description Below
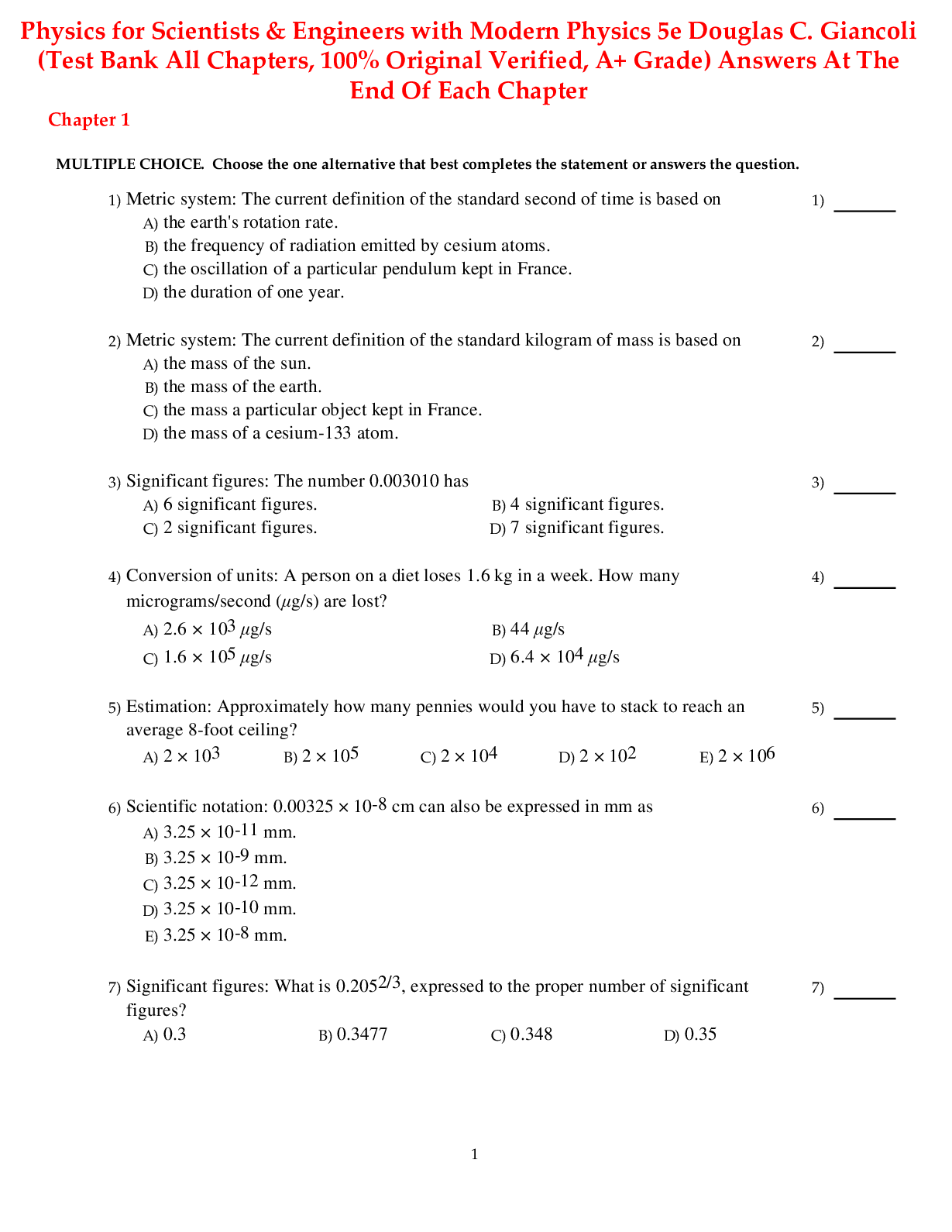
TEST BANK: Child Development; Children with Exceptionalities (PSYCH2043), Exam Questions & Answers, All Chapters Answered-1. Legally recognized categories of exceptionality are defined by a. the Indi... viduals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act (IDEA). b. the laws of individual states. c. No Child Left Behind (NCLB). d. the Council for Exceptional Children (CEC). ANSWER: a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child with Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Remembering 2. Which of the following exceptionalities does NOT have its own defined category under IDEA, 2004? a. Autism b. ADHD c. Traumatic Brain Injury d. Emotional Disturbance ANSWER: b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child with Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Understanding 3. Children with are the only exceptional children not covered under federal legislation. ANSWER: special gifts and talents POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child with Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Remembering 4. From an educator's point of view, identification of a student as exceptional is necessary when the student a. has an obvious interindividual difference. b. has an obvious intraindividual difference. c. requires special adaptations in the educational program. d. has a parent who wants services. ANSWER: c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child With Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Understanding 5. In defining the term children with exceptionalities, which characteristic is most central? a. The child deviates from the normal population in intellectual ability. b. The child is from a lower socioeconomic background. c. The child shows evidence of multiple disabilities. d. The child's deviation is extensive enough to warrant modification of educational services or practices. ANSWER: d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child with Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Understanding 6. Intraindividual differences a. consider how a child compares to other children. b. are not useful in developing individual plans of instruction. c. are the differences in abilities within the same child. d. are stable as the child ages. ANSWER: c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child with Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Understanding 7. Shannon, who is 10 years old, has the intelligence of a 12-year-old and the social behavior of a 8-year-old. This discrepancy is referred to by the authors of your text as an a. aberration. b. anomaly. c. interindividual difference. d. intraindividual difference. ANSWER: d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child with Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Understanding 8. Interindividual differences are differences that exist a. between a child and other children. b. between a child and his or her environment. c. but are not observable in a child. d. between different areas of a single child's development. ANSWER: a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child with Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Remembering 9. Contrast interindividual differences and intraindividual differences and explain how cultural context influences our perception of these differences. ANSWER: Interindividual differences are substantial differences between people. These differences are often in academic performance, physical development, or social development. It is important to consider cultural factors when interpreting interindividual differences. Variations among individuals may be more of an expression of differences in attitudes, values, customs, and language related to heritage and cultural patterns than a deviation from normal development. Intraindividual differences are differences within a single child. They can show up in any area: intellectual, psychological, physical, or social. The uneven development of specific characteristics may also be affected by family culture. Both inter- and intraindividual differences should be considered in educational planning for the student. POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child with Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Applying 10. Educators use to address the intraindividual differences that require adjustments to the educational program for a child with exceptionalities. ANSWER: individualized education programs (IEPs) POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child with Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Remembering 11. When looking at the historical perspective of services for children with exceptionalities, the 1950s saw a. the passage of new legislation requiring schools to serve these children. b. the beginning of many preschool programs for these children. c. the Council for Exceptional Children being founded. d. the beginning of special programs in some states for these children. ANSWER: d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child with Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Understanding 12. Although children with exceptionalities were not legally guaranteed a free and appropriate education until the 1970s, most children with exceptionalities have received specialized education services for well over 100 years. a. True b. False ANSWER: False POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child with Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Understanding 13. Why have education professionals replaced medical professionals as the primary professionals to address the needs of exceptional children? ANSWER: Even though exceptionalities often have a medical cause and may require medical monitoring, educators spend more time with children with exceptionalities and are in a better position to influence developmental patterns through their intervention. POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child with Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Applying 14. Using tiers to deliver different intensity of instruction and intervention is an example of a. Differential Instruction Methods (DIM). b. Least Restrictive Environment (LRE). c. Response to Intervention (RtI) d. Formal Appropriate Education (FAE). ANSWER: c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child with Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Applying 15. Response to Intervention is a. based only on the use of special education instructional methods. b. a multilevel approach of academic intervention used to provide early, effective assistance to children before referral to special education and identification. c. a variety of materials and techniques for an “independence” curriculum that is totally community-based. d. based upon the extensive use of assistive technology. ANSWER: b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: The Child with Exceptionalities: An Overview LEARNING OBJECTIVES: EDUC.KIRK.14.01.01 - Who is the child with exceptionalities? KEYWORDS: Blooms: Understanding [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 237 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$16.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 13, 2024
Number of pages
237
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 13, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
43