Vocabulary: atmosphere, biomass, biosphere, carbon reservoir, carbon sink, fossil fuel, geosphere, greenhouse gas, hydrosphere, lithosphere, photosynthesis
Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.
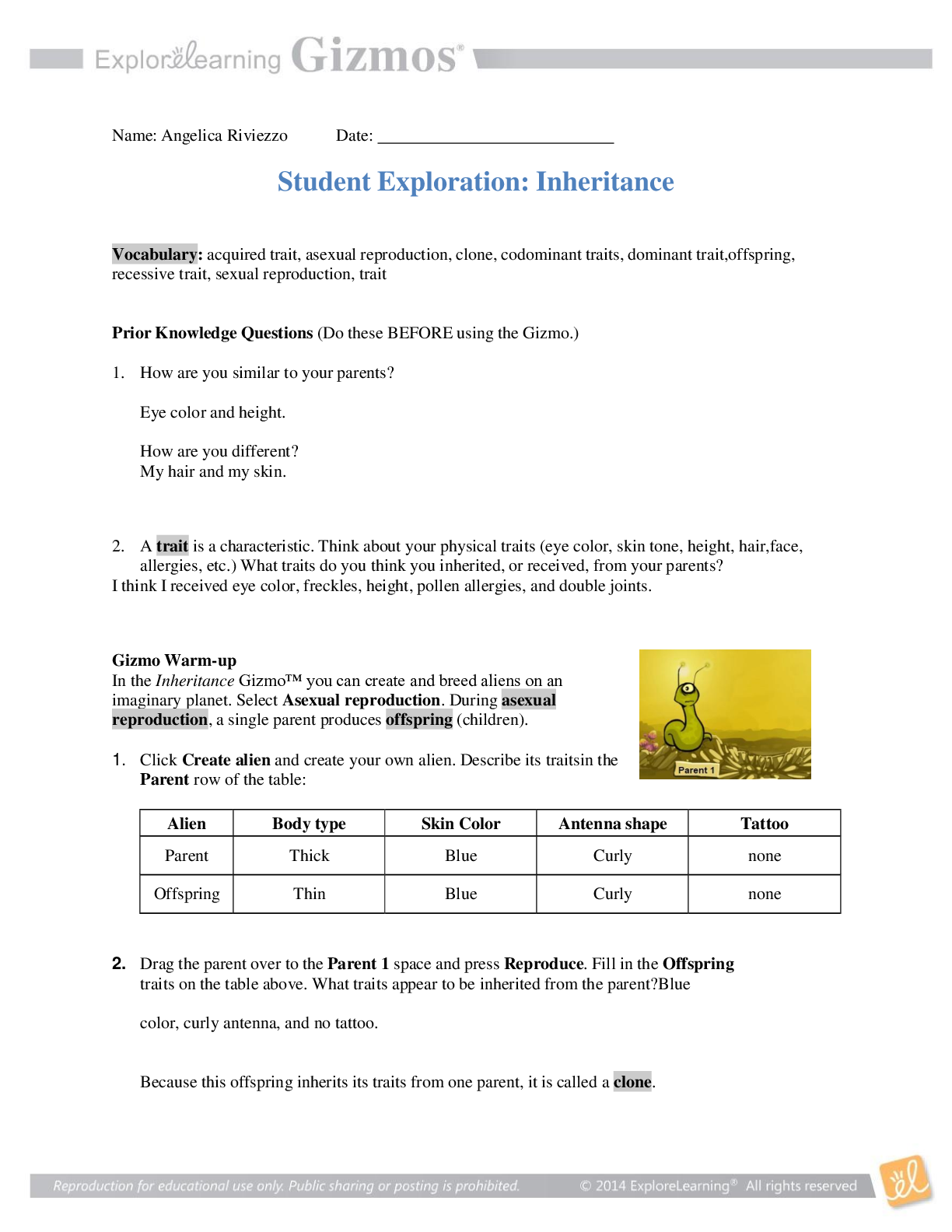
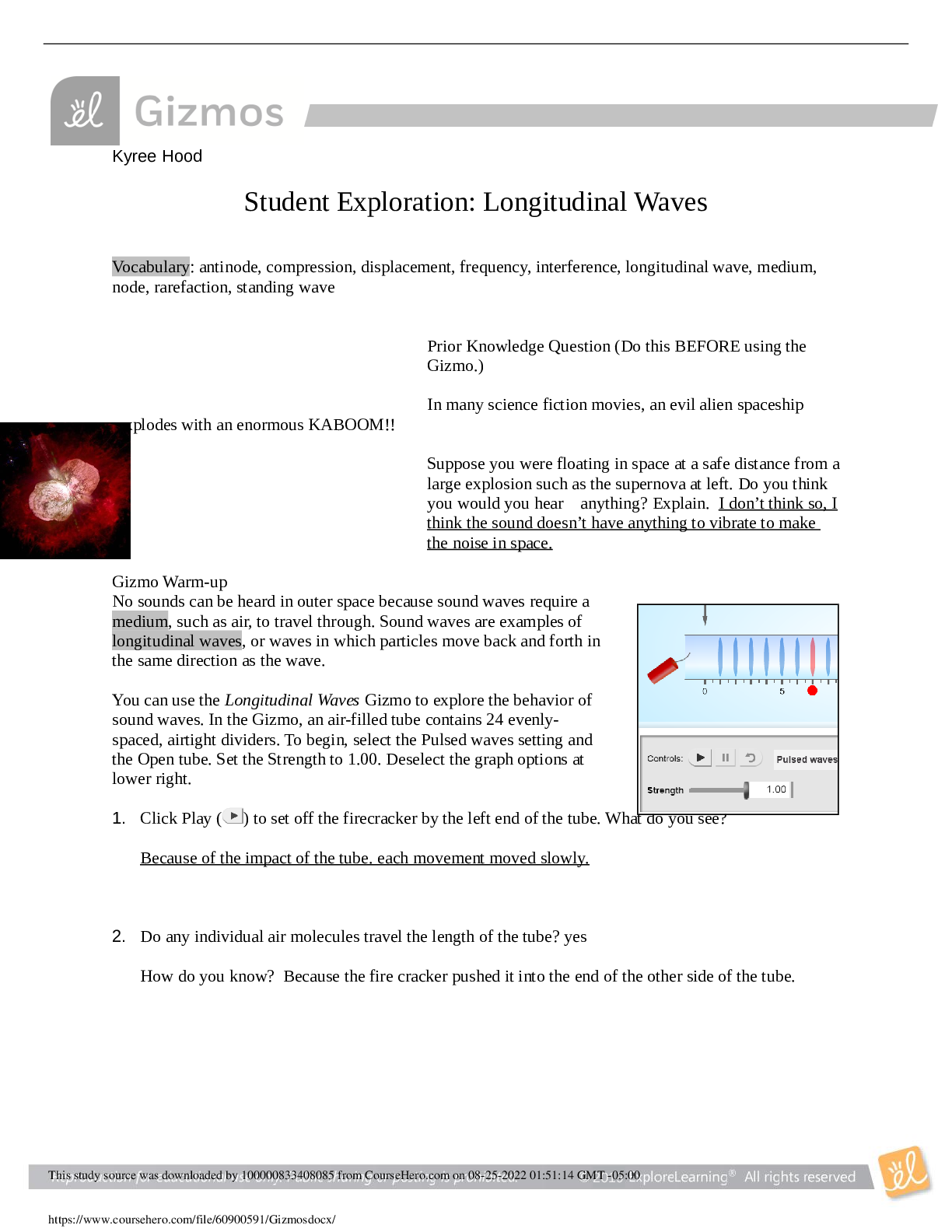
...
Vocabulary: atmosphere, biomass, biosphere, carbon reservoir, carbon sink, fossil fuel, geosphere, greenhouse gas, hydrosphere, lithosphere, photosynthesis
Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
In the process of photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and water (H2O) from the soil. Using the energy of sunlight, plants build molecules of glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2).
1. How do plants on Earth affect the amount of carbon in Earth’s atmosphere?
Since they consume carbon during photosynthesis, they consume carbon.
2. Animals eat plants and produce carbon dioxide and water. How do animals affect the amount of carbon in Earth’s atmosphere? They release carbon in the atmosphere.
Gizmo Warm-up
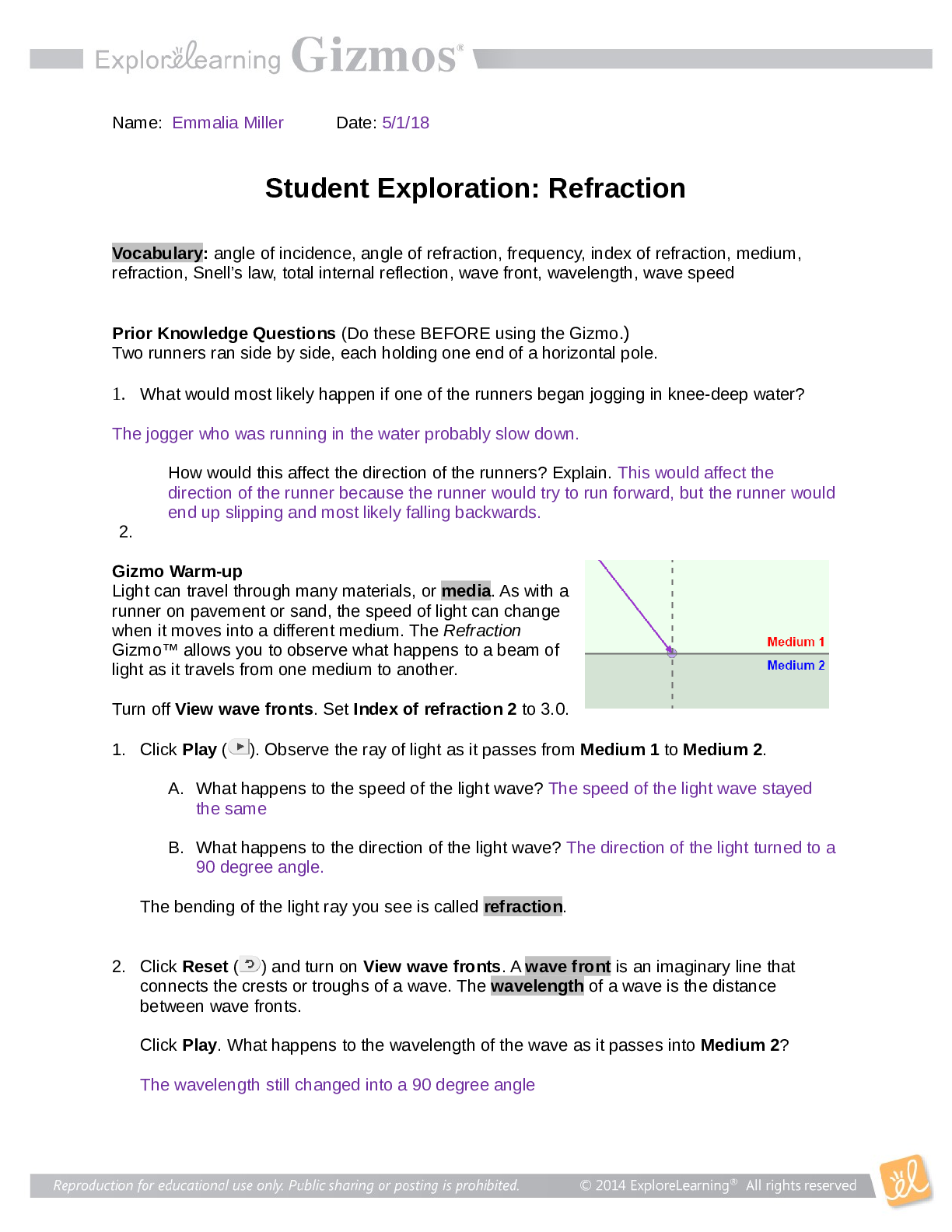
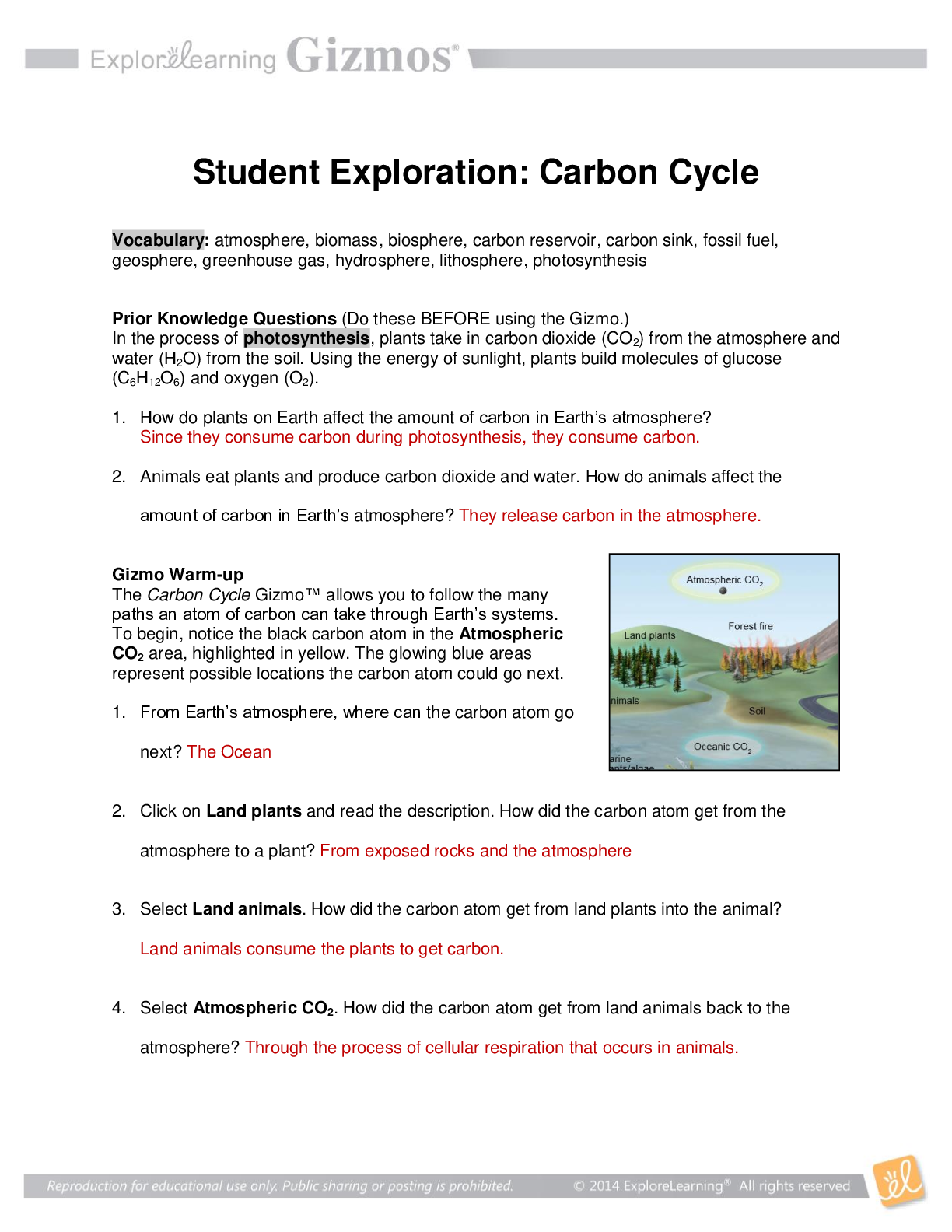
The Carbon Cycle Gizmo™ allows you to follow the many paths an atom of carbon can take through Earth’s systems. To begin, notice the black carbon atom in the Atmospheric CO2 area, highlighted in yellow. The glowing blue areas represent possible locations the carbon atom could go next.
1. From Earth’s atmosphere, where can the carbon atom go next? The Ocean
2. Click on Land plants and read the description. How did the carbon atom get from the atmosphere to a plant? From exposed rocks and the atmosphere
3. Select Land animals. How did the carbon atom get from land plants into the animal?
Land animals consume the plants to get carbon.
4. Select Atmospheric CO2. How did the carbon atom get from land animals back to the atmosphere? Through the process of cellular respiration that occurs in animals.
Activity A:
Carbon pathways Get the Gizmo ready:
• Click Reset.
Introduction: Earth can be divided into four systems. The atmosphere is the air above Earth’s surface. The hydrosphere is composed of all of Earth’s water. The geosphere is the rocky, non-living part of Earth. The biosphere consists of all living things, including people. Some scientists use the term “anthroposphere” to describe everything made or modified by humans.
Question: How does carbon move between the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and geosphere?
1. Explore: Use the Gizmo to create a path for carbon that begins and ends in the atmosphere. Fill in the steps in the path below. Then, label each location with the system it represents. Finally, summarize very briefly how the carbon atom got to that location.
Carbon path System How it got there
Atmospheric CO2
Atmosphere Atmospheric CO2 comes from volcanoes, burning fossil fuels, and other sources.
Exposed Rock
Geosphere Plants and exposed rocks consume carbon through photosynthesis.
Oceanic CO2
Hydrosphere It travels from the plants into the water when some of it is released
Atmospheric CO2
Atmosphere It goes from the water to the atmosphere from it being released.
2. Create: Click Reset. Use the Gizmo to create a path in which the carbon atom goes from the atmosphere to the hydrosphere, biosphere and geosphere. Describe each transition briefly.
Atmosphere Hydrosphere Biosphere Geosphere
Atmospheric CO2 Oceanic CO2 Marine Plants/Algae
Exposed Rock
Volcanoes, burning fossil fuels, and other sources. It travels from the atmosphere into the water when some of it is released It goes from the ocean to the ocean plants during photosynthesis It travels from the marine plants into the rocks when it is released
Activity A (continued from previous page)
3. Explore: Use the Gizmo to create three more carbon paths, each starting and ending in the atmosphere. Label each location with A for atmosphere, B for biosphere, G for geosphere, or H for hydrosphere. (You can also use P for anthroposphere if you like, or just include it in the biosphere.)
Path 1:
Atmosphere Ocean Atmosphere
Path 2:
Atmosphere Land Plants Forest Fire Atmosphere
Path 3:
Atmosphere Land Plants Land Animals Atmosphere
4. Explain: Based on the Gizmo, explain how the following transitions might take place:
A. Describe at least two ways that carbon can get from a land plant to the atmosphere.
It can get there when the plant goes through cellular respiration. Also when the plant is consumed by a land animal and the animal goes through cellular respiration.
B. Describe at least two ways that carbon can get from the atmosphere to the hydrosphere. It can go from the atmosphere into the ocean. It can also go from the atmosphere to plants and then the ocean through cellular respiration.
C. Can you find two ways that carbon can get from the ocean to the lithosphere? (The lithosphere is the rigid layer of the Earth, including the crust and part of the mantle.)
If it goes from the atmosphere to the rocks and the rock become part of the lithosphere. If it goes from the atmosphere to the plants and they die to form a rock.
D. Describe at least two ways that carbon can get from seashells to the atmosphere.
From the seashell to the ocean to the atmosphere. Also, from a seashell to the marine animals to marine plants to the ocean to the atmosphere.
Activity B:
Human activities Get the Gizmo ready:
• Click Reset.
Introduction: Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, formed over millions of years from the remains of ancient plants and animals. The burning of fossil fuels, as well as other human activities, increases the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Question: How does human activity affect the carbon cycle?
1. Describe: Using the Gizmo, determine how coal and petroleum (oil) are formed. Describe the steps required to form each fuel from atmospheric CO2.
Coal: It goes from the atmosphere to plants in photosynthesis. When the plant is compressed after it dies, coal is formed.
Petroleum: It goes from the atmosphere to plants in photosynthesis. The plant goes to soil and to sediments. Then to petroleum.
2. Explore: Natural gas is a mixture of methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), and other gases. Find two ways that natural gas forms. List the steps of the two carbon pathways below:
Path 1: Atmosphere Land Plants Natural Gas
Path 2: Atmosphere Soil Land Plants Natural Gas
How is the formation of natural gas related to the formation of coal and petroleum?
Natural gas is in coal and petroleum.
Describe: Fossil fuels are used in many ways. Using the Gizmo, describe the main use for each fuel.
Coal: Machines such as trains
Petroleum: Machines such as cars
Natural gas: Warmth in a home
In each case, what is the end product of burning the fossil fuel, and where does it go?
The atmosphere
The End
[Show More]