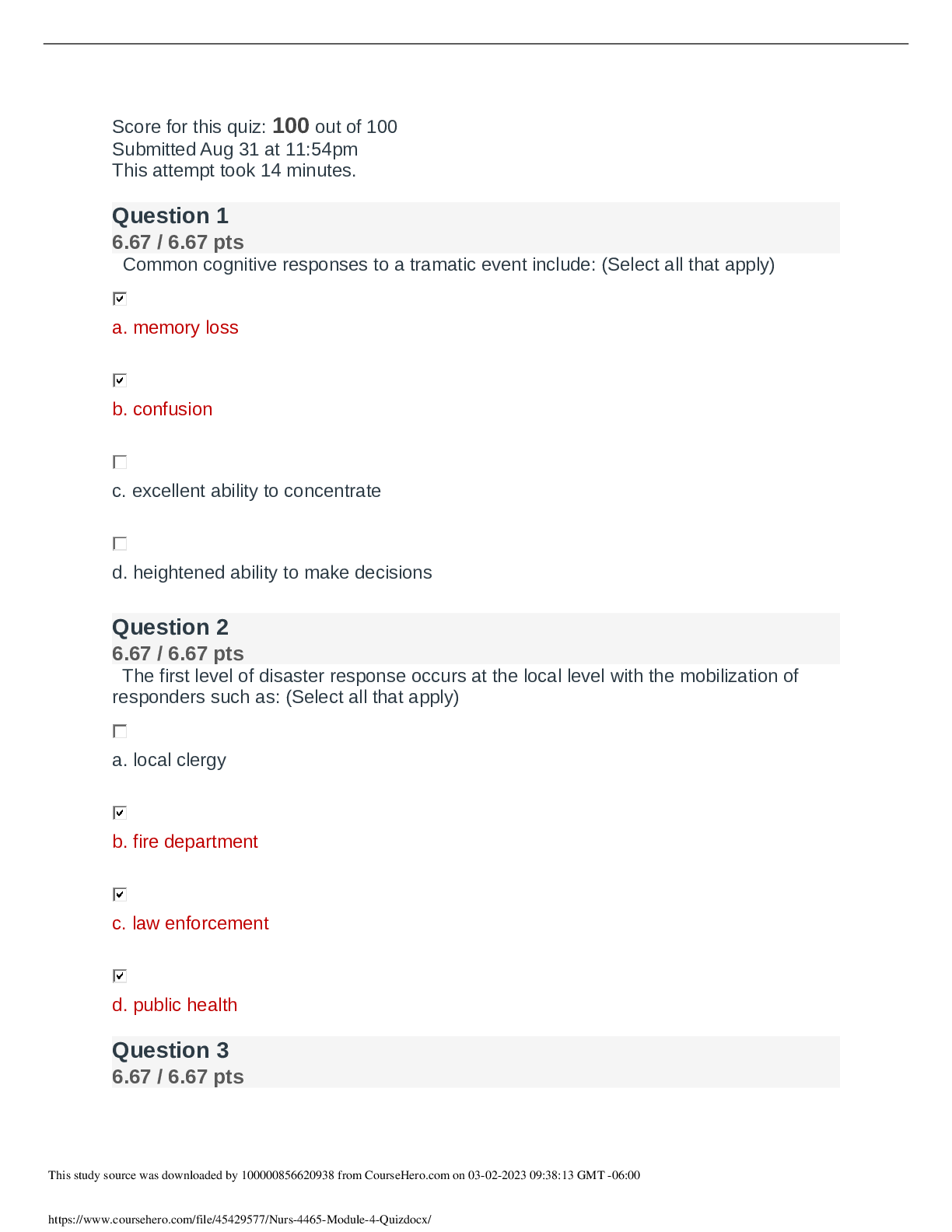
GI and Neuro ATI practice questions and Answers. DETAILED ANSWER KEY
Document Content and Description Below
A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving total parenteral nutrition (TPN). The pharmacy is delayed in supplying the client’s next container of TPN. Which of the following fluids should the n... urse infuse until the next container arrives? Rationale: TPN contains high concentrations of certain nutrients. Infusing dextrose 5% in water could cause rapid shifts in serum levels of some substances. A. Dextrose 5% in water Rationale: TPN contains high concentrations of certain nutrients. Infusing 0.9% sodium chloride could cause rapid shifts in serum levels of some substances. B. 0.9% sodium chloride Rationale: TPN contains high concentrations of dextrose and proteins. To avoid hypoglycemia, the nurse should infuse dextrose 10% or 20% in water until the next container of TPN solution arrives. C. Dextrose 10% in water Rationale: TPN contains high concentrations of certain nutrients. Infusing lactated Ringer’s solution could cause rapid shifts in serum levels of some substances. D. Lactated Ringer’s solution 1. A nurse is providing discharge teaching for a client who has chronic pancreatitis. Which of the following statements by the nurse is appropriate? Rationale: Clients who have chronic pancreatitis are at risk for malnutrition and should increase their caloric intake in order to maintain weight. A. “You should decrease your caloric intake when abdominal pain is present.” Rationale: Clients who have chronic pancreatitis should consume a diet that is high in protein. B. “You should increase your daily intake of protein.” Rationale: Clients who have chronic pancreatitis should consume a low-fat diet to prevent stimulation of the pancreas and steatorrhea. C. “You should increase fat intake when experiencing loose stools.” Rationale: Clients who have chronic pancreatitis should avoid alcohol intake to prevent stimulation of the pancreas. D. “You should limit alcohol intake to 2-3 drinks per week.” 2. CAA_DetailedAnswerKey created 10/07/2015 page 1 of 53 Detailed Answer Key GI/Neuro Med Surg A nurse monitors for increased intracranial pressure (ICP) on a client who has a leaking cerebral aneurysm. If the client manifests increased intracranial pressure, which of the following findings should the nurse expect? (Select all that apply) A. Violent headache B. Neck pain and stiffness C. Slurred speech D. Projectile vomiting E. Rapid loss of consciousness 3. Rationale: Violent headache is correct. The client who manifests ICP should display a violent headache Neck pain and stiffness is incorrect. The client who manifests ICP should not display neck pain and stiffness Slurred speech is correct. The client who manifests ICP may display slurred speech. Projectile vomiting is correct. The client who manifests ICP may display sudden onset of projectile vomiting. Rapid loss of consciousness is correct. The client who manifests ICP may display a sudden rapid loss of consciousness. CAA_DetailedAnswerKey created 10/07/2015 page 2 of 53 Detailed Answer Key GI/Neuro Med Surg A nurse is assessing an adult who has meningococcal meningitis. Which of the following is an appropriate finding by the nurse? Rationale: The nurse should find as a sign of meningococcal meningitis severe headache due to meningeal inflammation. A. Severe headache Rationale: The nurse should find as a sign of meningococcal meningitis tachycardia not bradycardia. B. Bradycardia Rationale: The nurse should find as a sign of meningococcal meningitis decreased not increased muscle tone. C. Increased muscle tone Rationale: The nurse should find as a sign of meningococcal meningitis disorientation not orientation to time, person, and place. D. Oriented to time, person, place 4. A nurse admits a client who has a concussion for overnight observation. Alert and oriented on admission, the client reports a headache along with neck pain and generalized muscle aches. The nurse knows that a manifestation considered an early indication of increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is Rationale: Alterations in vital signs, including increased systolic pressure, widening pulse pressure and bradycardia may be later signs of increased ICP. A. bradycardia. Rationale: Ipsilateral or bilateral pupil dilation occurs when increasing intracranial pressure displaces the brain ag [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 53 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$20.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 03, 2021
Number of pages
53
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 03, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
84



.png)



.png)



.png)













