Economics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > ECONOMICS: Chapter 07: The Balance of Payments, Exchange Rates, and Trade Deficits (WITH CORRECT ANS (All)
ECONOMICS: Chapter 07: The Balance of Payments, Exchange Rates, and Trade Deficits (WITH CORRECT ANSWERS) ALREADY GRADED A
Document Content and Description Below
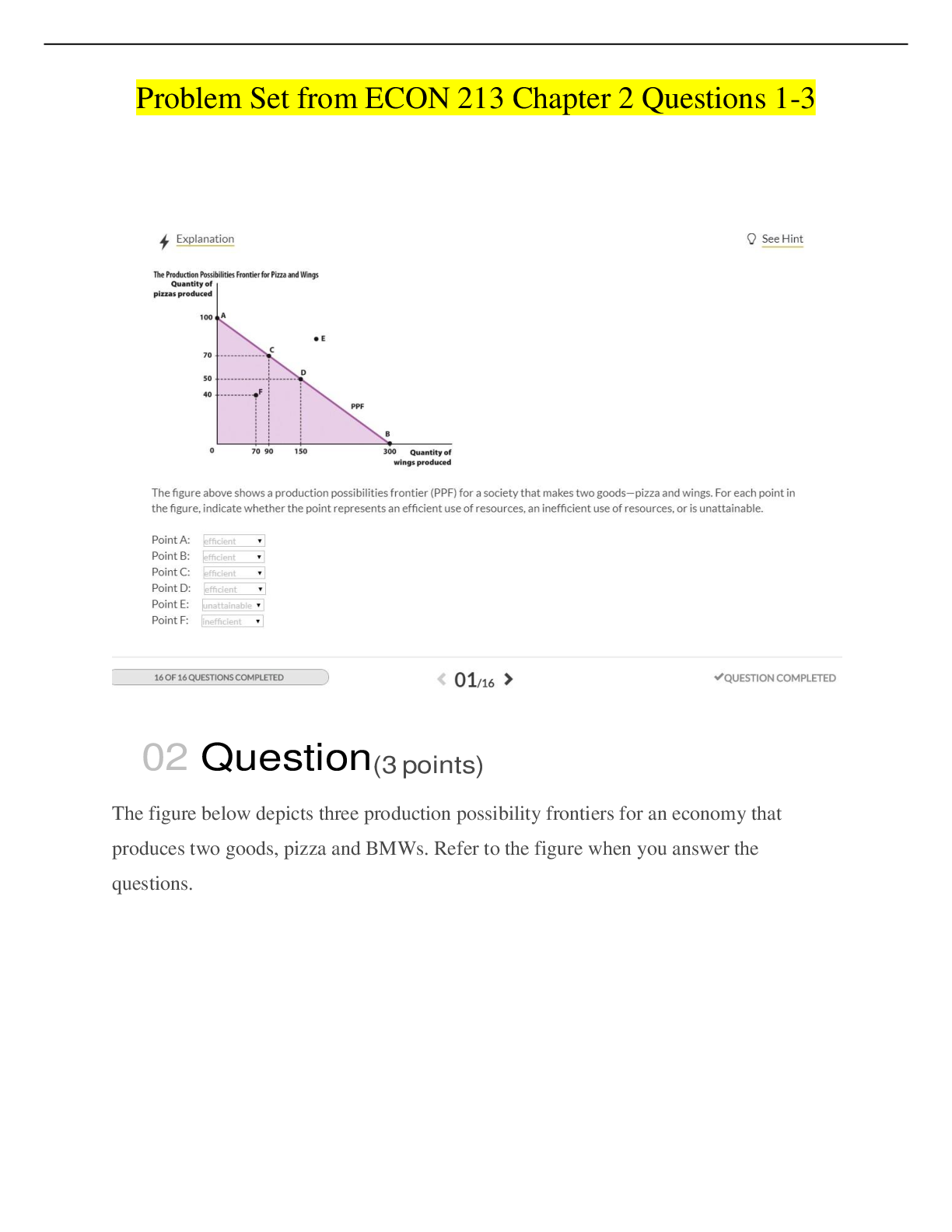
Chapter 07: The Balance of Payments, Exchange Rates, and Trade Deficits [QUESTION] 1. U.S. exports create a: A. Supply of foreign currencies to the United States and a demand for dollars in for... eign countries B. Demand for foreign currencies in the United States and a supply of dollars to foreign countries C. Supply of foreign currencies to the United States and a supply of dollars to foreign countries D. Demand for foreign currencies in the United States and a demand for dollars in foreign countries [QUESTION] 2. U.S. imports represent two flows: A. An outflow of goods or services, and an outflow of payments B. An inflow of goods or services, and an outflow of payments C. An outflow of goods or services, and an inflow of payments D. An inflow of goods or services, and an inflow of payments [QUESTION] 3. U.S. businesses are demanders of foreign currencies because they need them to: A. Produce goods and services exported to foreign countries B. Pay for goods and services imported from foreign countries C. Receive interest payments from foreign governments D. Receive interest payments from foreign businesses [QUESTION] 4. French and German farmers wanting to buy equipment from an American manufacturer based in the U.S. will be: A. Supplying dollars and also supplying euros in the foreign exchange market B. Demanding dollars and also demanding euros in the foreign exchange market C. Supplying dollars and demanding euros in the foreign exchange market D. Supplying euros and demanding dollars in the foreign exchange market [QUESTION] 5. U.S. imports: A. Increase the foreign demand for foreign currencies B. Increase the domestic demand for foreign currencies C. Decrease the foreign supply of foreign currencies D. Increase the domestic supply of foreign currencies [QUESTION] 6. If a financial portfolio manager in the U.S. buys British company stocks in the London Stock Exchange, this would involve: A. A demand for British pounds in the foreign exchange market B. A supply of British pounds in the foreign exchange market C. No effect on the demand for British pounds in the foreign exchange market D. A demand for US dollars in the foreign exchange market [QUESTION] 7. The purchase of a British Rolls-Royce by a U.S. citizen would result in all of the following except a(n): A. Supply of payments to England B. Sale of dollars and the purchase of British pounds C. Increase in imports to the United States D. Gain of foreign exchange for the United States [QUESTION] 8. U.S. exports of computers, aircraft, and chemicals create a: A. Foreign demand for foreign currencies B. Domestic demand for foreign currencies C. Domestic supply of foreign currencies D. Foreign supply of foreign currencies [QUESTION] 9. Which of the following statements about the financing of international trade is correct? A. International trade means the trading of financial assets for foreign exchange B. Most international transactions are made with gold C. Imports are more important than exports to the economy of a nation D. Exports provide the foreign currencies needed to pay for imports The Balance of Payments [QUESTION] 10. A nation's balance of trade on goods is equal to its exports of goods less its imports of: A. Goods B. Capital C. Financial assets D. Official reserves [QUESTION] 11. A nation's current account balance is equal to its exports less its imports of: A. Goods and services B. Goods and services, minus U.S. purchases of assets abroad C. Goods and services, plus net investment income and net transfers D. Goods and services, plus foreign purchases of assets in the United States [QUESTION] 12. The current account on a nation's balance of payments statement includes all of the following except: A. The nation's goods exports B. The nation's goods imports C. Net investment income D. Net purchases of assets abroad [QUESTION] 13. Which transaction represents a debit in the current account section of the U.S. balance of payments? A. The Arab Capital Investment Corporation makes a loan to a U.S. firm B. A U.S. subsidiary exports raw materials to the Canadian parent company C. U.S. tourists in Great Britain purchase pounds with dollars in order buy souvenirs D. U.S. firms and individuals receive dividends from their investments in Latin America [QUESTION] 14. When a Japanese company buys a U.S. software company, this transaction will be a: A. Credit on the current account of the U.S. balance of payments B. Debit on the current account of the U.S. balance of payments C. Credit on the financial account of the U.S. balance of payments D. Debit on the financial account of the U.S. balance of payments [QUESTION] 15. When a U.S. importer buys 100,000 pairs of pants from a Hong Kong company, this transaction will be a: A. Credit on the current account of the U.S. balance of payments B. Debit on the current account of the U.S. balance of payments C. Credit on the financial account of the U.S. balance of payments D. Debit on the financial account of the U.S. balance of payments [QUESTION] 16. When a U.S. agribusiness sells 10,000 units of cow vaccine to a company in France, this transaction will be a: A. Credit on the current account of the U.S. balance of payments B. Debit on the current account of the U.S. balance of payments C. Credit on the financial account of the U.S. balance of payments D. Debit on the financial account of the U.S. balance of payments [QUESTION] 17. Which of the following transactions represents a credit on the financial account of the U.S. balance of payments? A. Oil is imported from Venezuela B. United States firms pay dividends to foreigners C. United States citizens purchase foreign securities D. A Canadian firm increases its direct investment in its U.S. branch [QUESTION] 18. When a U.S. company purchases a factory in Singapore, this will be a: A. Credit on the current account of the U.S. balance of payments B. Debit on the current account of the U.S. balance of payments C. Credit on the financial account of the U.S. balance of payments D. Debit on the financial account of the U.S. balance of payments [QUESTION] 19. Which of the following shows the net difference between how much Americans forgave in debts owed to them by foreigners compared with how much foreigners forgave debts owed to them by Americans? A. Current account B. Capital account C. Financial account D. Net transfers [QUESTION] 20. Which one of the following is part of the financial account on the U.S. balance of payments? A. Net transfers B. Net investment income C. U.S. goods exports D. U.S. purchases of assets abroad [QUESTION] 21. Which is an item in the current account of the balance of payments for the United States? The purchase of: A. A U.S. company by a foreign company B. Stock in a foreign corporation by a U.S. company C. Insurance in the United States by a foreign company D. A United States Treasury bond by a wealthy foreigner [QUESTION] 22. Remittances of Mexican workers in the U.S. to their families in Mexico are included in the U.S. balance of payments as a debit in the section on: A. Trade in services B. Net international transfers C. Financial accounts D. Capital accounts [QUESTION] 23. Which of the following appears as a positive item on the balance of payments account for the United States? A. U.S. government sending aid to natural-disaster victims in Asia B. American tourists spending money in the other countries C. The buying of U.S. Treasury bonds by a foreign bank D. The payment of stock dividends by U.S. firms to foreign shareholders [QUESTION] 24. In one year the United States had a current account deficit of $161 billion. The balance on the capital account was –$5 billion. What was the balance on the financial account? A. –$415 billion B. +$415 billion C. –$425 billion D. +$425 billion [QUESTION] 25. In the Balance of Payments statement, a current account surplus will be matched by a: A. Capital and financial accounts deficit B. Capital and financial accounts surplus C. Trade deficit D. Trade surplus [QUESTION] 26. Official reserves used to achieve a balance of payments between nations engaging in international trade are held by: A. Private businesses engaging in trade B. Central banks of the nations engaged in trade C. Commercial banks which make loans to businesses engaging in trade D. Commercial banks which make loans to governments which engage in trade [QUESTION] 27. The settling of any net deficit in the combined current, and capital and financial accounts is done with: A. Capital reserves B. Official reserves C. Net transfers D. Net investment income [QUESTION] 28. If there is a small surplus in the combined current account plus capital and financial account for a certain year, then to make the two accounts balance there will be: A. An increase in the exchange rate B. A decrease in the exchange rate C. An increase in official reserve holdings D. A decrease in official reserve holdings [QUESTION] 29. Which of the following would be an indication that a nation has a balance of payments deficit? A. It is buying gold abroad B. Its imports exceed its exports C. Its holdings of official reserves are declining D. It is borrowing abroad to finance capital investments [QUESTION] 30. A trade deficit means a net: A. Inflow of payments for goods and services B. Outflow of goods and services C. Inflow of goods and services D. Excess of exports over imports [QUESTION] 31. A nation's annual balance of payments statement must always balance because: A. A nation's imports are limited to the value of its exports B. A nation's exports and imports are always paid with dollars C. All international transactions must be settled in one way or another D. A trade deficit must be matched by an equal surplus of investment income Reference: 07-32 Use the following to answer questions 32-38: The following table contains hypothetical data for the U.S. balance of payments in a year. Answer the following questions on the basis of these data. All figures are in billions of dollars. U.S. goods exports +$390 U.S. goods imports –498 U.S. service exports +133 U.S. service imports –107 Net investment income +12 Net transfers –22 Capital account –5 Foreign purchases of U.S. assets +156 U.S. purchases of foreign assets –59 [QUESTION] 32. Refer to the above table. The data indicate that there was a trade: A. Deficit in goods and also a trade deficit in services B. Surplus in goods and also a trade surplus in services C. Deficit in goods and a trade surplus in services D. Surplus in goods and a trade deficit in services [QUESTION] 33. Refer to the above table. The balance of trade in goods and services was: A. $107 billion surplus B. $82 billion deficit C. $115 billion deficit D. $55 billion surplus [QUESTION] 34. Refer to the above table. The balance on the current account was a: A. $51 billion surplus B. $92 billion deficit C. $22 billion surplus D. $82 billion deficit [QUESTION] 35. Refer to the above table. The figure for net transfers indicates that the United States: A. Received a net public and private transfer of $22 billion from the rest of the world B. Sent a net public and private transfer of $22 billion in remittances to the rest of the world C. Sent a net private transfer of $22 billion to the rest of the world D. Received a net private transfer of $22 billion from the rest of the world [QUESTION] 36. Refer to the above table. What does the figure for net investment income indicate? A. Americans invested more abroad than the amount foreigners invested in the U.S. B. The size of the net inflow of foreign investment to the United States in that year C. The net amount Americans received as interest and dividends on existing American investments abroad D. The net amount Americans paid as interest and dividends on existing foreign investments in the United States [QUESTION] 37. Refer to the above table. The balance on the financial account was a: A. $92 billion surplus B. $97 billion surplus C. $92 billion deficit D. $97 billion deficit [QUESTION] 38. Refer to the above table. If there was an inpayment of $7 billion in official reserves to the capital and financial account that year, the United States experienced a balance-of-payments: A. Surplus of $7 billion B. Deficit of $7 billion C. Surplus of $99 billion D. Deficit of $99 billion Reference: 07-39 Use the following to answer questions 39-41: Answer the next questions on the basis of the following balance of payments data for the hypothetical nation of Alfina. All figures are in billions of dollars. (1) Goods exports +$220 (2) Goods imports –328 (3) Exports of services +54 (4) Imports of services –55 (5) Net investment income +18 (6) Net transfers –11 (7) Capital account –1 (8) Foreign purchases of Alfina assets+124 (9) Alfina purchases of foreign assets –21 [QUESTION] 39. Refer to the above table. Alfina's balance of trade in goods and services shows a: A. Net inflow of payments of $109 billion B. Net outflow of payments of $109 billion C. Net inflow of payments of $108 billion D. Net outflow of payments of $108 billion [QUESTION] 40. Refer to the above table. Alfina's balance on the current account shows a: A. Deficit of $91 billion B. Deficit of $102 billion C. Deficit of $109 billion D. Surplus of $109 billion [QUESTION] 41. Refer to the above table. Alfina’s balance of on the capital and financial account is a: A. Deficit of $110 billion B. Surplus of $92 billion C. Surplus of $102 billion D. Surplus of $103 billion Reference: 07-42 Use the following to answer questions 42-44: The following table contains data for the U.S. balance of payments in a prior year. Answer the next question(s) on the basis of this information. All figures are in billions of dollars. U.S. goods exports +$793 U.S. goods imports –1573 U.S. exports of service +280 U.S. imports of services –222 Net investment income +5 Net transfers –81 Capital account –5 Foreign purchases of assets in the U.S. +1198 U.S. purchases of foreign assets –395 [QUESTION] 42. Refer to the above table. There was a: A. Trade deficit, but a current account surplus B. Trade surplus, but a current account deficit C. Trade surplus, and a current account surplus D. Trade deficit, and a current account deficit [QUESTION] 43. Refer to the above table. The data indicate that Americans: A. Bought foreign assets abroad more than foreigners bought assets in the U.S. B. Invested abroad more than foreigners invested in America C. Earned more from their investments abroad than foreigners earned from their investments in America D. Sold more products to buyers abroad than what foreign producers sold to buyers in America [QUESTION] 44. By how much did Americans forgive debt owed to them by foreigners than foreigners forgave debt owed to them by Americans? A. +$5 billion B. –$5 billion C. +$72 billion D. –$72 billion Flexible Exchange Rates [QUESTION] 45. Foreign exchange rates refer to the: A. Price at which purchases and sales of foreign goods take place B. Movement of goods and services from one nation to another C. Price of one nation's currency in terms of another nation's currency D. Difference between exports and imports in a particular nation [QUESTION] 46. To Americans buyers, there is a decrease in the relative prices of Japanese goods when the: A. Yen appreciates B. Dollar appreciates C. Inflation rate in the United States is higher than the inflation rate in Japan, and there are flexible exchange rates D. Inflation rate in Japan is higher than the inflation rate in the United States and there are fixed exchange rates [QUESTION] 47. If an American can purchase 40,000 British pounds for $90,000, the dollar rate of exchange for the pound is: A. $0.44 B. $0.23 C. $2.25 D. $2.00 Answer: C Topic: Flexible Exchange Rates Difficulty: 1 Easy Learning Objective: 07-03 Bloom’s: Level 3 Apply AACSB: Analytic [QUESTION] 48. If a Japanese importer could buy $1000 U.S. for 122,000 yen, the rate of exchange for one dollar would be: A. 8.19 yen B. 122 yen C. 820 yen D. 1220 yen [QUESTION] 49. If the exchange rate is $1 = 0.7841 euro, then a French DVD priced at 20 euros would cost to an American buyer (excluding taxes and other fees): A. $15.68 B. $20.78 C. $25.51 D. $27.84 Answer: C Topic: Flexible Exchange Rates Difficulty: 2 Medium Learning Objective: 07-03 Bloom’s: Level 3 Apply AACSB: Analytic [QUESTION] 50. If a European importer can buy $10,000 for 11,100 euros, the exchange rate for the euro is: A. 1 euro = $0.80 B. 1 euro = $0.90 C. 1 euro = $0.95 D. 1 euro = $1.11 [QUESTION] 51. An increase in the dollar price of the British pounds will: A. Increase the pound price of dollars B. Decrease the pound price of dollars C. Leave the pound price of dollars unchanged D. Cause Britain's terms of trade with the United States to deteriorate [QUESTION] 52. In one year the dollar would buy 162 Japanese yen, but ten years later, it would buy only 123 yen. Relative to the yen, the value of the dollar: A. Increased by about 32 percent B. Decreased by about 24 percent C. Decreased by about 32 percent D. Increased by about 24 percent [QUESTION] 53. Assume an exchange rate of $1 = .60 British pounds. A U.S. product sells in Britain for 18 pounds. By what percentage will dollar revenues change if the dollar price of a pound falls to .50 pounds? A. –20 percent B. –16 percent C. +16 percent D. +20 percent [QUESTION] 54. If the Canadian dollar price of United States dollars increases from C$.80 to C$1.00, it can be concluded that: A. Both countries are on the international gold standard B. The Canadian dollar has appreciated in value relative to the United States dollar C. The United States dollar has depreciated in value relative to the Canadian dollar D. The Canadian dollar has depreciated in value relative to the United States dollar [QUESTION] 55. In equilibrium, if $1 = 0.5 pounds sterling and 1 pound sterling = 40 Swiss francs, the exchange rate between dollar and franc will be: A. 1 franc = $.10 B. 1 franc = $.20 C. $1 = 80 francs D. $1 = 20 francs [QUESTION] 56. When the exchange rate between pounds and dollars moves from $2 = 1 pound to $1 = 1 pound, we say that the dollar has: A. Depreciated B. Appreciated C. Inflated D. Deflated [QUESTION] 57. The exchange rate for the Mexican peso changes from $1 = 5 pesos to $1 = 6 pesos. This change will lead to: A. U.S. goods becoming less expensive for Mexicans B. Mexican goods becoming more expensive for Americans C. An increase in U.S. exports to Mexico D. A decrease in U.S. exports to Mexico [QUESTION] 58. If the U.S. dollar appreciates relative to the British pound, then: A. The pound will appreciate relative to the U.S. dollar B. The pound will depreciate relative to the U.S. dollar C. British goods will be more expensive for Americans D. American goods will be less expensive for the British [QUESTION] 59. All else being equal, increased U.S. exports to nations in the European Union create a: A. Demand for euros B. Supply of euros C. Shortage of euros D. Surplus of euros [QUESTION] 60. In a market graph showing the supply and demand for British pounds in terms of U.S. dollars, the demand-for-pounds curve is downsloping because: A. Fewer British pounds can be purchased if pounds become less expensive B. Fewer U.S. dollars can be purchased if British pounds become less expensive C. More U.S. dollars can be purchased if British pounds become more expensive D. More British pounds can be purchased if pounds become less expensive [QUESTION] 61. In a market graph showing the supply and demand for British pounds in terms of U.S. dollars, the supply-of-pounds curve is upsloping because: A. Fewer British pounds can be purchased per dollar if U.S. dollars become more expensive B. Fewer U.S. dollars can be purchased per pound if the British pounds become less expensive C. The British will purchase more U.S. goods or services when the dollar price of pounds rises D. The British will purchase more U.S. goods or services when the dollar price of pounds falls [QUESTION] 62. Consider the currency market for British pounds and U.S. dollars. A decrease in the supply of British pounds results in: A. An appreciation of the pound and a depreciation of the dollar B. A depreciation of the pound and a depreciation of the dollar C. An appreciation of the pound and an appreciation of the dollar D. A depreciation of the pound and an appreciation of the dollar [QUESTION] 63. Consider the currency market for British pounds and U.S. dollars. An increase in the demand for British pounds results in: A. An appreciation of the pound and a depreciation of the dollar B. A depreciation of the pound and a depreciation of the dollar C. An appreciation of the pound and an appreciation of the dollar D. A depreciation of the pound and an appreciation of the dollar [QUESTION] 64. Consider the currency market for British pounds and U.S. dollars. An increase in the supply of British pounds: A. Results in an appreciation of the pound and a depreciation of the dollar B. Results in a depreciation of the pound and a depreciation of the dollar C. Is equivalent to an increase in the demand for the U.S. dollar D. Is equivalent to a decrease in the demand for the U.S. dollar [QUESTION] 65. Consider the currency market for Japanese yen and U.S. dollars. An increase in the supply of Japanese yen results in: A. An appreciation of the yen and a depreciation of the dollar B. A depreciation of the yen and a depreciation of the dollar C. An appreciation of the yen and an appreciation of the dollar D. A depreciation of the yen and an appreciation of the dollar [QUESTION] 66. Consider the currency market for Japanese yen and U.S. dollars. A decrease in the demand for Japanese yen results in: A. An appreciation of the yen and a depreciation of the dollar B. A depreciation of the yen and a depreciation of the dollar C. An appreciation of the yen and an appreciation of the dollar D. A depreciation of the yen and an appreciation of the dollar Flexible Exchange Rates; Fixed Exchange Rates Reference: 07-67 Use the following to answer questions 67-69: [QUESTION] 67. Refer to the above graph. If Canadians buy more U.S. goods, then: A. The demand curve will shift left B. The demand curve will shift right C. The supply curve will shift left D. The supply curve will shift right [QUESTION] 68. Refer to the above graph. If U.S. citizens flock to Canada for summer vacations and buy more Canadian goods and services, then the: A. The supply curve will shift left B. The demand curve will shift right C. The price of U.S. dollars in Canadian dollars will rise D. The price of U.S. dollars in Canadian dollars will fall [QUESTION] 69. Refer to the above graph. Higher inflation in the United States relative to that in Canada, ceteris paribus, is predicted to cause a(n): A. Decrease in the supply of U.S. dollars B. Increase in the demand for U.S. dollars C. Decrease in the value of the U.S. dollar in terms of the Canadian dollar D. Increase in the value of the U.S. dollar in terms of the Canadian dollar Answer: C Topics: Flexible Exchange Rates; Fixed Exchange Rates Difficulty: 3 Hard Learning Objective: 07-04 Bloom’s: Level 3 Apply AACSB: Analytic Refer To: 07-67 [QUESTION] 70. Other things being equal, an increase in the U.S. rate of inflation is likely to cause an increase in the: A. Quantity of U.S. exports B. Quantity of U.S. imports C. Demand for U.S. dollars D. International value of the U.S. dollar [QUESTION] 71. Which statement is correct? A. Under the gold standard, exchange rates fluctuate without restraint and thereby correct any international balance of payment disequilibrium B. If nations X and Y are on the international gold standard, and X's exports to Y exceed X's imports from Y, gold will flow from X to Y C. If the dollar price of pounds rises, the pound price of dollars will also rise D. American exports tend to increase, while American imports tend to decrease, the supplies of foreign monies owned by American banks [QUESTION] 72. A currency depreciation on the foreign exchange market will: A. Encourage imports to the country whose currency has depreciated B. Discourage imports to the country whose currency has depreciated C. Discourage exports to the country whose currency has depreciated D. Encourage foreign travel by the citizens of the country whose currency has depreciated [QUESTION] 73. United States exports, foreign travel in the United States, and foreign capital inflow into the United States give rise to: A. Depreciation of the U.S. dollar B. A supply of foreign currencies to the United States C. A demand for foreign currencies in the United States D. Decreased foreign exchange reserves in the United States [QUESTION] 74. When the U.S. dollar decreases in value relative to foreign currencies the: A. Demand for U.S. exports will decrease B. Supply of U.S. exports will decrease C. Demand for U.S. exports will increase D. Supply of U.S. exports will remain constant [QUESTION] 75. All of the following would add to the demand for U.S. dollars except: A. Long-term capital inflows B. Foreign travel by United States citizens C. Exports of commodities from the United States D. Travel by foreigners on United States airlines [QUESTION] 76. Other things being equal, which is a necessary consequence of a depreciation of the U.S. dollar ($) against other currencies? A. The terms of trade will move in favor of the United States B. The United States will experience an increase in the volume of imports C. International speculators will buy U.S. dollars and sell other currencies D. U.S. exports will become cheaper relative to other nations' products [QUESTION] 77. Other things being equal, the international value of foreign currencies will increase against the U.S. dollar ($) if: A. U.S. citizens reduce spending on imports B. The U.S. Federal Reserve raises real interest rates C. There is an increase in the number of foreign tourists in the United States D. There are withdrawals of funds by foreigners from U.S. money markets [QUESTION] 78. When real interest rates fall in the United States as compared to other nations, other things being equal, we would expect the dollar to experience: A. Appreciation B. Depreciation C. Inflation D. Deflation [QUESTION] 79. If Japanese autos increase in popularity in the United States, then this event is most likely to cause the Japanese yen to: A. Appreciate and the U.S. dollar to depreciate B. Depreciate and the U.S. dollar to appreciate C. Appreciate and the U.S. dollar to appreciate D. Depreciate and the U.S. dollar to depreciate [QUESTION] 80. If there is a recession in the United Kingdom, and a reduction in British imports, and an economic boom in the United States, and an increase in U.S. imports, then these events are most likely to cause the British pound to: A. Appreciate and the U.S. dollar to appreciate B. Depreciate and the U.S. dollar to depreciate C. Appreciate and the U.S. dollar to depreciate D. Depreciate and the U.S. dollar to appreciate [QUESTION] 81. If Switzerland has a much lower inflation rate than the United States, then this event is most likely to cause the Swiss franc to: A. Depreciate and the U.S. dollar to depreciate B. Depreciate and the U.S. dollar to appreciate C. Appreciate and the U.S. dollar to appreciate D. Appreciate and the U.S. dollar to depreciate [QUESTION] 82. If real interest rates rise in the United Kingdom relative to the United States, then this event is most likely to cause the British pound to: A. Depreciate and the U.S. dollar to depreciate B. Depreciate and the U.S. dollar to appreciate C. Appreciate and the U.S. dollar to appreciate D. Appreciate and the U.S. dollar to depreciate [QUESTION] 83. If currency speculators believe South Korea will have much lower inflation in the future than the United States, then this event is most likely to cause the South Korean won to: A. Depreciate and the U.S. dollar to depreciate B. Depreciate and the U.S. dollar to appreciate C. Appreciate and the U.S. dollar to appreciate D. Appreciate and the U.S. dollar to depreciate [QUESTION] 84. An increase in the income of country A relative to the income of country B will usually lead to an increase in country: A. A's exports to country B B. B's imports from country A C. A's demand for the currency of country B D. B's demand for the currency of country A [QUESTION] 85. Which would cause the supply of U.S. dollars in the United Kingdom to increase? A. An increase in the U.S. inflation rate B. An increase in real interest rates in the United States C. U.S. rock music becomes more popular in the United Kingdom D. Widespread anticipation that the U.S. economy is about to experience a period of rapid economic growth Reference: 07-86 Use the following to answer questions 86-90: Assume that Japan and the United States are engaged in a system of flexible exchange rates. [QUESTION] 86. Refer to the above graph. If more people in the United States decide to purchase Japanese cars, what effect will this have on the market for yen? A. The price of yen will increase B. The price of yen will decrease C. The supply of yen will increase D. The supply of yen will decrease [QUESTION] 87. Refer to the above graph. If more Japanese decide to visit the United States for their vacations: A. The yen will appreciate and the U.S. dollar will depreciate B. The yen will depreciate and the U.S. dollar will appreciate C. The yen and the U.S. dollar will appreciate D. The yen and the U.S. dollar will depreciate [QUESTION] 88. Refer to the above graph. One U.S. dollar will purchase how many Japanese yen? A. 80 B. 120 C. 125 D. 140 [QUESTION] 89. Refer to the above graph. An increase in the supply of yen will result in: A. An appreciation of the yen B. An appreciation of the U.S. dollar C. A depreciation of the U.S. dollar D. An increase in the dollar price of yen [QUESTION] 90. Refer to the above graph. An increase in the demand for yen will result in: A. A depreciation of the Japanese yen B. An appreciation of the U.S. dollar C. A depreciation of the U.S. dollar D. A decrease in the dollar price of yen [QUESTION] 91. Which of the following would tend to raise the value of the U.S. dollar in foreign exchange markets? A. A rise in U.S. interest rates B. An easy monetary policy in the United States C. A expansionary budget policy in the United States D. An increase in the U.S. demand for foreign oil Reference: 07-92 Use the following to answer questions 92-94: Assume that U.S. and European governments adopt a system of flexible exchange rates, and the figure below shows the market for euros. [QUESTION] 92. Refer to the above graph. If more people in Europe decide to purchase U.S. cars, what effect will this have on the market for euros? A. Demand will decrease B. Demand will increase C. Supply will increase D. Supply will decrease [QUESTION] 93. Refer to the above graph. One U.S. dollar will purchase how many euros? A. 0.90 euro B. 1.00 euro C. 1.11 euro D. 1.90 euro [QUESTION] 94. Refer to the above graph. If currency traders think the European economy will experience a recession and the U.S. economy will not, then this event will most likely cause the: A. Euro to appreciate B. Euro to depreciate C. U.S. dollar to depreciate D. The supply of euros to decrease [QUESTION] 95. With flexible exchange rates, an increase in U.S. interest rates can be expected to: A. Adversely affect U.S. exporters B. Encourage investment spending by U.S. firms C. Lower the foreign exchange value of the dollar D. Cause a net outflow of foreign capital from the United States [QUESTION] 96. To maintain a fixed exchange rate, the government can use the following tools, except: A. Currency market intervention B. Controlling the flow of trade through various barriers C. Rationing of foreign exchange D. Keep its level of international reserves strictly fixed Reference: 07-97 Use the following to answer questions 97-100: The figure below shows the supply and demand graphs for dollars. [QUESTION] 97. Refer to the above diagram. Assume the initial demand for and supply of dollars are shown by D1 and S1. The exchange rate will be: A. $5 equals 1 pound B. $4 equals 1 pound C. $1 equals 5 pounds D. $0.20 equals 1 pound [QUESTION] 98. Refer to the above diagram. Assume the initial demand for and supply of dollars are shown by D1 and S1. Now suppose that Great Britain increases its imports of American products. Assuming freely floating exchange rates: A. The pound price of dollars will fall to 1/5 pound equals $1 B. The pound price of dollars will rise to 1/4 pound equals $1 C. The dollar price of pounds will increase to $5 equals 1 pound D. A dollar shortage of MN will result in Britain [QUESTION] 99. Refer to the above diagram. Assume the initial demand for and supply of dollars are shown by D1 and S1. Assume Britain's demand for dollars increases from D1 to D2. If the British government wishes to fix the exchange rate at the initial level, then it would be faced with a problem of: A. Deteriorating terms of trade B. Rationing LM dollars among British importers who would like to acquire LN dollars C. A rise in the pound price of dollars D. Rationing LN dollars among British importers who would like to acquire LM dollars [QUESTION] 100. Refer to the above diagram. Assume the initial demand for and supply of dollars are shown by D1 and S1. Assume Britain's demand for dollars increases from D1 to D2. If the British government wishes to fix the exchange rate at the initial level, one possible way to do this is for the government to: A. Buy and add more to its dollar reserves B. Sell pounds in exchange for U.S. dollars C. Encourage the British to import more U.S. products D. Sell some of its dollar resreves Reference: 07-101 Use the following to answer questions 101-103: [QUESTION] 101. Refer to the above graph, which shows the supply and demand for British pounds. D1 and S1 represent the initial demand and supply curves. What will be the new equilibrium as indicated in the graph if there is a large decrease in the number of foreign tourists visiting Britain because of the threat of terrorism? A. E B. G C. B D. I [QUESTION] 102. Refer to the above graph, which shows the supply and demand for British pounds. D1 and S1 represent the initial demand and supply curves. What will be the new equilibrium as indicated in the graph if there is an increase in consumer spending by the British for American products and a decrease in consumer spending by Americans for British products? A. A B. C C. H D. J [QUESTION] 103. Refer to the above graph, which shows the supply and demand for British pounds. D1 and S1 represent the initial demand and supply curves. What will be the new equilibrium as indicated in the graph if the domestic price level rises rapidly in the United States and remains constant in Britain? A. I B. J C. H D. A [QUESTION] 104. A market basket of goods costs $260 in the United States and 200 pounds in the United Kingdom. The "purchasing power parity rate" is 1 pound = $1.50. According to purchasing power parity theory, the market basket of goods in the United States should cost: A. $67 B. $77 C. $260 D. $300 [QUESTION] 105. Which is not a serious disadvantage associated with freely fluctuating exchange rates? A. Uncertainty which tends to diminish trade B. Greater instability in unemployment levels C. Longer lags in eliminating balance of payments surpluses or deficits D. Swings in the terms of trade related to currency appreciation or depreciation Answer: C Topics: Flexible Exchange Rates; Fixed Exchange Rates Difficulty: 2 Medium Learning Objective: 07-04 Bloom’s: Level 1 Remember AACSB: Analytic [QUESTION] 106. Fixed exchange rates are often maintained by using all of the following except: A. Open speculation by individual traders in foreign currency markets B. International monetary reserves held by central banks C. Controls on imports and exports such as tariffs and quotas D. Domestic macroeconomic adjustments using monetary and fiscal policies [QUESTION] 107. In using exchange controls, a nation attempts to eliminate a balance of payments deficit by: A. Limiting its imports to the dollar value of its exports B. Decreasing the nation's domestic price level C. Limiting its exports to the dollar value of its imports D. Appreciating the value of its currency [QUESTION] 108. Which statement is true of a world system of fixed exchange rates compared with floating rates? A. It requires less world liquidity or reserves B. It creates less confidence about future values of currencies C. It facilitates the transmission of economic conditions between countries D. It increases the role of the central banks in foreign exchange markets Reference: 07-109 Use the following to answer questions 109-110: [QUESTION] 109. Refer to the above graph, which shows a change in the demand for pounds from DD to D'D'. Under a system of flexible exchange rates, the: A. Price of a pound will increase to $3 B. Price of a dollar will increase to 3 pounds C. Shortage equal to ab would be met using international monetary reserves D. Payment deficit will cause changes in domestic price and income levels, shifting demand to the left, supply to the right, and reestablishing the original exchange rate [QUESTION] 110. Refer to the above graph, which shows a change in the demand for pounds from DD to D'D'. Under a system of fixed exchange rates, the: A. Price of a pound will increase to $3 B. Price of a dollar will increase to 3 pounds C. Shortage equal to ab would be met using international monetary reserves D. Payment deficit will cause changes in domestic price and income levels, shifting demand to the left, supply to the right, and reestablishing the original exchange rate Reference: 07-111 Use the following to answer questions 111-114: The table below shows the supply and demand schedules for the European euro. [QUESTION] 111. Refer to the above table. Under a flexible exchange rate system, what will be the rate of exchange for one euro? A. $0.80 B. $0.90 C. $1.00 D. $1.10 [QUESTION] 112. Refer to the above table. Under a flexible exchange rate system, what will be the euro rate of exchange for one U.S. dollar? A. 0.95 euro B. 1.00 euros C. 1.11 euros D. 1.23 euros [QUESTION] 113. Refer to the above table. If the U.S. government decides to fix or peg the price of the euro at $1.00, it would have to: A. Buy 100 euros B. Buy 360 euros C. Sell 160 euros D. Sell 360 euros [QUESTION] 114. Refer to the above table. If European governments decided to fix the price of a euro at $0.80, they would have to: A. Buy 286 euros B. Buy 114 euros C. Sell 114 euros D. Sell 286 euros The Current Exchange Rate System: The Managed Float [QUESTION] 115. The current monetary system for conducting international trade is usually described as a system of: A. Fixed exchange rates B. Freely floating exchange rates C. A managed gold standard D. Managed floating exchange rates [QUESTION] 116. Which system would be accompanied by occasional currency interventions by central banks to stabilize or alter rates to avoid persistent balance of payments deficits or surpluses? A. The gold standard B. Fixed exchange rates C. Flexible exchange rates D. Managed floating exchange rates [QUESTION] 117. The basic type of intervention by central banks under the managed floating exchange rate system is to: A. Readjust the peg for exchange rates B. Buy and sell currencies to influence supply and demand C. Renegotiate the rate at which foreign currencies can be converted into gold D. Make pronouncements but then do nothing and let the market set the exchange rate [QUESTION] 118. Which of the following is a G-8 nation? A. China B. Brazil C. Italy D. India [QUESTION] 119. The United States, Germany, Japan, Britain, France, Italy, Canada, and Russia are: A. G-8 nations B. Adjustable peg nations C. Gold standard nations D. Nations using the Bretton Woods System [QUESTION] 120. The G-8 nations is one group that sometimes influences the exchange rates between major currencies. For example, in 2000 the G-8 governments agreed to sell U.S. dollars in order to: A. Counter the depreciation of the euro B. Counter the depreciation of the U.S. dollar C. Support the appreciation of the Swiss franc D. Support the appreciation of the Japanese yen [QUESTION] 121. Proponents of the managed floating exchange rate system argue that it has: A. Added the volatility needed by the exchange rate market B. Been effective because it is a "non-system" without fixed rules C. Been sufficiently flexible to weather major economic turbulence D. Resolved major problems in balance of payments surpluses and deficits [QUESTION] 122. Critics of the managed floating exchange rate system argue that it: A. Is dominated by G-8 nations B. Is a "non-system" with unclear rules C. Increased the growth in world trade at too fast a rate D. Puts too much reliance on the adjustable-peg mechanism for stabilizing exchange rates Recent U.S. Trade Deficits [QUESTION] 123. During the period 2001–2009, U.S. trade deficits: A. Increased rapidly from 2001 to 2006 and increased even faster in the recession of 2007-2009 B. Initially decreased, but then increased significantly in the recession of 2007-2009 C. Increased rapidly from 2001 to 2006, but then decreased in the recession of 2007-2009 D. Decreased throughout the entire decade [QUESTION] 124. Which one of the following is a major factor that has contributed to large trade deficits in the United States in recent years? A. A U.S. economy growing slower than its trading partners B. A declining saving rate and increasing investment rate in the U.S. C. Large trade deficits with Canada D. Large trade surpluses with Mexico [QUESTION] 125. Which of the following contributed to the United States' trade deficits between 2001 and 2006? A. The weakness of the dollar against foreign currencies B. Low levels of debt in the less developed nations of the world C. Relatively faster rates of economic growth in the U.S. than in other industrialized nations D. Higher rates of inflation and unemployment in the United States compared to other nations [QUESTION] 126. What are the effects on U.S. imports and exports when the U.S. experiences stronger economic growth than its major trading partners? A. U.S. imports will increase more than U.S. exports B. U.S. exports will increase more than U.S. imports C. U.S. imports will increase, but U.S. exports will decrease D. There will be no effect on U.S. imports and exports [QUESTION] 127. What are two major outcomes from the large U.S. trade deficits? A. An increase in domestic consumption and U.S. indebtedness B. A decrease in domestic consumption and U.S. indebtedness C. An increase in domestic consumption and a decrease in U.S. indebtedness D. A decrease in domestic consumption and an increase in U.S. indebtedness [QUESTION] 128. A trade deficit for the United States is generally financed by: A. Lending to the Federal government B. Borrowing from the Federal government C. Buying securities or assets from other nations D. Selling securities or assets to other nations [QUESTION] 129. If the United States wants to regain ownership of domestic assets sold to foreigners, it will have to: A. Increase domestic consumption B. Increase its national debt C. Export more than it imports D. Import more than it exports [QUESTION] 130. Which of the following factors had helped maintain the large U.S. trade deficits? A. A decline in investment B. Capital and financial account surpluses C. A decrease in economic growth D. An increase in U.S. net exports [QUESTION] 131. The trade deficit has had the effect of: A. Decreasing the Federal budget deficit B. Increasing economic growth in less developed nations C. Increasing direct foreign investment in the United States D. Decreasing protectionist pressure among U.S. businesses [QUESTION] 132. An inflow of investment funds into the United States from overseas is likely to result from a(n): A. Decline in expectations for economic growth in the United States B. Growing belief among investors that the U.S. dollar ($) is overvalued C. Rise in U.S. interest rates relative to world interest rates D. Increase in the U.S. inflation rate [QUESTION] 133. Comparing everything that the United States owes to other nations, and what they owe to the United States, the United States is currently a(n): A. Net creditor B. Net debtor C. International banking asset D. International banking liability Last Word Questions [QUESTION] 134. Speculation in foreign exchange markets could be: A. Negative because it reduces the fluctuations in exchange rates B. Positive because it reduces the fluctuations in exchange rates C. Negative because it relies on the supply and demand for gold D. Positive because it relies on the supply and demand for gold [QUESTION] 135. In foreign exchange markets, speculators help: A. Decrease the influence of the futures market because their trades demand current payments B. Increase fluctuations in exchange rates because of wild buying and selling C. Decrease the value of most currencies because they tend to hedge the market D. Increase international trade because they absorb risk which others do not want to bear True/False Questions [QUESTION] 136. U.S. exports to Japan create a supply of dollars and a demand for yen in the foreign-exchange market. [QUESTION] 137. The current account on a nation's balance of payments statement includes net investment income. [QUESTION] 138. The flow of payments for purchases and sale of financial assets is included in the current account balance of nation. [QUESTION] 139. In the balance of payments statement, a current account deficit is matched by a capital and financial accounts surplus. [QUESTION] 140. An in-payment or accumulation of official reserves in the capital and financial account indicates that there is a balance-of-payments surplus. [QUESTION] 141. The purchase of a foreign hotel by a U.S. company is recorded as a credit in a nation's financial account in its balance-of-payments statement. [QUESTION] 142. In the dollar/yen market, if the supply of yen increases other things being equal, the dollar will appreciate. [QUESTION] 143. Relatively high rates of U.S. inflation compared to other countries will increase the supply of, and decrease the demand for, dollars in foreign exchange markets. [QUESTION] 144. The purchasing-power-parity theory holds that exchange rates equate the purchasing power of various currencies. [QUESTION] 145. The expectations of speculators in the United States that the exchange rate for the euro will fall in the future will increase the supply of euros in the foreign exchange market and decrease the exchange rate for the euros. [QUESTION] 146. If a nation has a balance of payments deficit and exchange rates are flexible, the price or value of that nation's currency in the foreign exchange markets will rise. [QUESTION] 147. Fixed exchange rates usually provide more certainty to those engaged in international trade. [QUESTION] 148. The exchange rate system that we now have for major currencies like the US dollar, yen, and euro is a fully floating or flexible system. [QUESTION] 149. One of the causes of the rising trade deficits of the past decade has been a declining saving rate in the United States. Topic: Recent U.S. Trade Deficits [QUESTION] 150. At the time when a trade deficit is occurring, U.S. consumers benefit from having more goods and services available. [QUESTION] 151. Improved economic growth in the major economies of the major trading partners of the United States would reduce its trade deficit. [QUESTION] 152. Faster economic growth in the United States relative to other nations tends to worsen the U.S. trade deficit. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 50 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$17.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 25, 2020
Number of pages
50
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 25, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
146











 ALREADY GRADED A.png)



