PATHO370 QUIZ REVIEW CHAPTERS 16-20
Document Content and Description Below
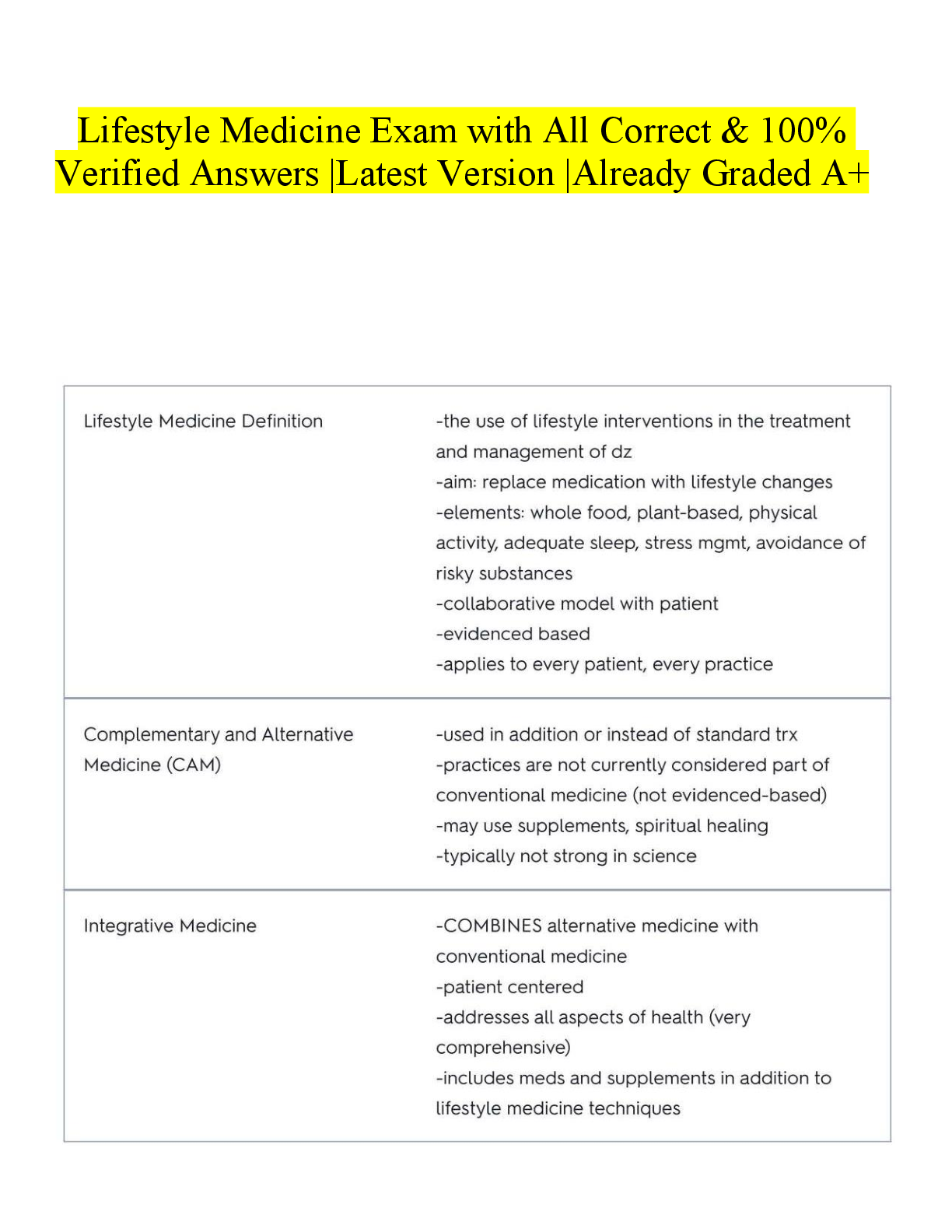
PATHO370 QUIZ REVIEW CHAPTERS 16-20 secondary hypertension - ans-high blood pressure caused by the effects of another disease pericarditis - ans-inflammation of the pericardium Pericardial ... Effusion - ans-accumulation of fluid in the pericardial cavity cardiac tamponade - ans-acute compression of the heart caused by fluid accumulation in the pericardial cavity Constrictive pericarditis - ans-fibrous scar tissue making the pericardium stick to the heart Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) - ans-damage to the heart from the complete or partial blockage of the arteries that provide oxygen to the heart CHD is broken into two types : - ans-Chronic ischemic heart disease Acute coronary syndrome acute coronary syndrome - ans-Ranges from unstable angina to myocardial infarction Stable angina - ans-When the hearts oxygen demand increases variant angina - ans-pain when coronary arteries spasm Comes and goes silent myocardial ischemia - ans-myocardial ischemia without pain Acute coronary syndrome ECG changes - ans-T wave inversion ST segment depression or elevation abnormal Q wave Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) - ans-A heart attack due to reduced oxygen to heart myocardial disease - ans-Weakness or thickening of the heart muscle Cardiomyopathy AV values (atrial ventricular) - ans-Mitral L tricuspid R semilinar valves - ans-Aortic L Pulmonary R Valve Defects - ans-stenosis and regurgitation Cause murmurs Stenosis - ans-the valve does not open completely and blood flow through the valve is reduced Regurgitant - ans-Valves do not close Leaky When will you hear a murmur is the valve is stenotic? - ans-When it is OPEN When will you hear a murmur when the valve is regurgitant? - ans-When it SHOULD BE CLOSED congenital heart defects - ans-abnormalities present in the heart at birth atrial septal defect - ans-Congenital heart defect Allows blood flow between atrias endocardial cushion defect - ans-No separation between the chambers of the heart ventricular septal defect - ans-Allows blood flow between ventricles coarctation of the aorta - ans-narrowing of the aorta patent ductus arteriosus - ans-passageway between the aorta and the pulmonary artery remains open after birth Pulmonary stenosis (congenital defect) - ans-Pulmonary valve is harder to open Transposition of the great vessels - ans-a congenital abnormallity where the aorta is attached to the righ ventricle and the pulmonary artery to the left ventricle (this is backwards and leads to two separate blood routes) Shunts - ans-opening or connection that lets blood move from one side of the circulation to the other left to right shunt - ans-diverts blood from the left heart to the right heart Less blood to the body More blood to the lungs right to left shunt - ans-Deoxygenated blood goes to body less blood goes to lungs [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 13 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 14, 2024
Number of pages
13
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 14, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
42