NRSG 663: Advanced Pathophysiology
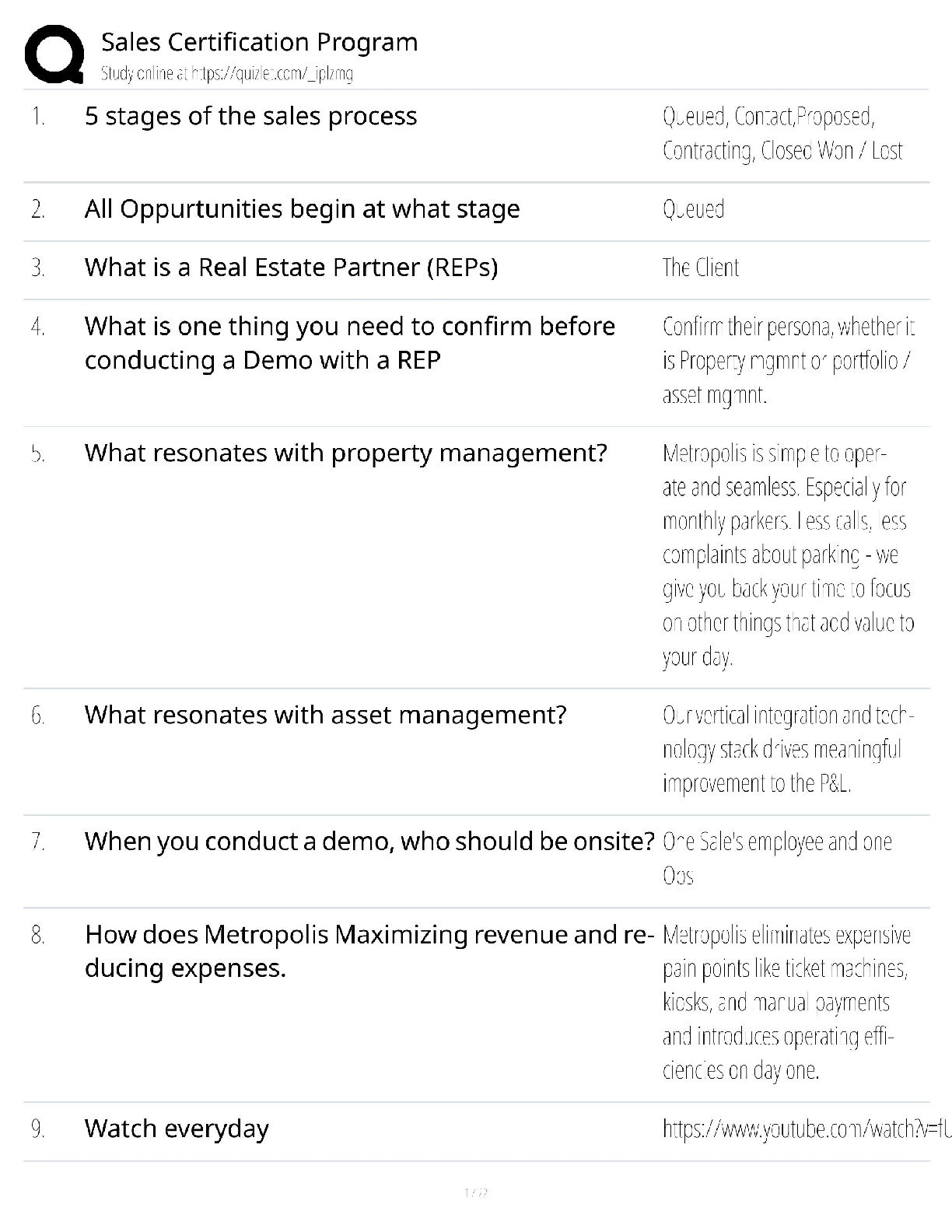
Exam 1 – Week 2
Chapter 1
Chapter 1: Cellular Biology
Know vocabulary and pathophysiology associated with vocabulary
The Eight Chief Cellular Functions:
1.) Movement- Muscle cel
...
NRSG 663: Advanced Pathophysiology
Exam 1 – Week 2
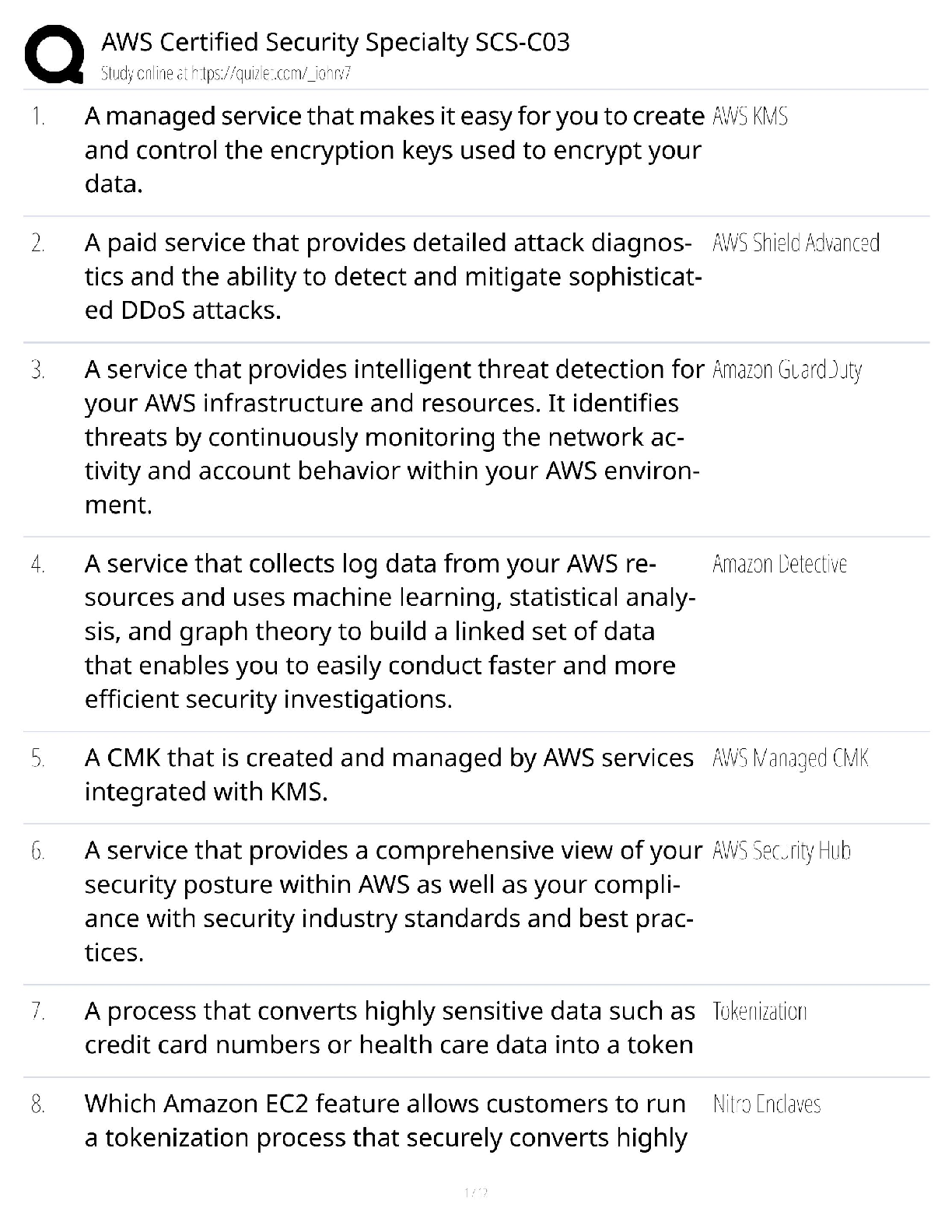
Chapter 1
Chapter 1: Cellular Biology
Know vocabulary and pathophysiology associated with vocabulary
The Eight Chief Cellular Functions:
1.) Movement- Muscle cells; generate forces that produce motion. skeletal muscle cells promote limb movement, hollow organs like intestines produce contraction that moves food, poop, pee, etc through.
2.) Conductivity-Conduction from stimuli results in wave of excitement, electrical potential goes from cell surface to other parts. chief fxn of nerve cells.
3.) Metabolic Absorption- All cells take in and use nutrients from surroundings. Intestine and renal cells carry out absorption. kidney tubule and intestinal epithelial cells reabsorb fluids and synthesize proteins.
4.) Secretion- Mucus cells absorb one substance and can secrete another substance to be used somewhere else. Adrenal, testis, ovaries secrete hormones.
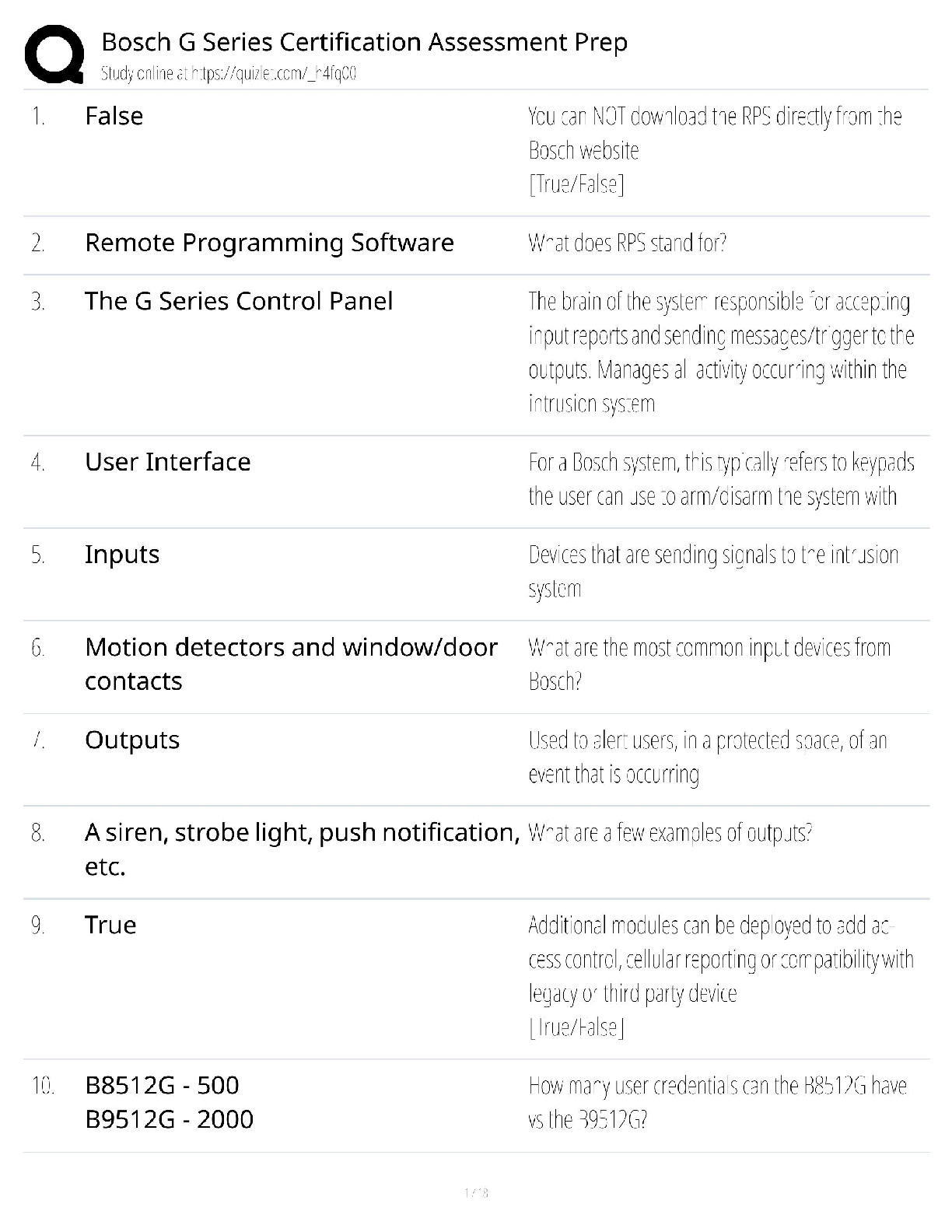
5.) Excretion- All cells get rid of waste products. lysosomes in the cell have enzymes that break down or digest large molecules, turning them into waste products excreted by the cell.
6.) Respiration-Cells absorb oxygen. Oxygen is used to transform nutrients into energy (ATP). Cell respiration (aka oxidation) occurs in mitochondria.
7.) Reproduction- Tissue growth from cells enlarging and reproducing themselves. Not all cells are capable of reproduction.
8.) Communication- Needed to happen between cells in order to function as a “society” of cells. i.e. pancreatic cells secrete insulin to tell muscle cells to absorb sugar for energy. Needed to maintain dynamic steady state.
9.) Osmolality- measure of number of milliosmoles per kilo. concentration of molecules per weight of water. controls distribution and movement of water between body compartments.
10.) Osmolarity- measure of the number of milliosmoles per liter of solution. concentration of molecules per volume of solution.
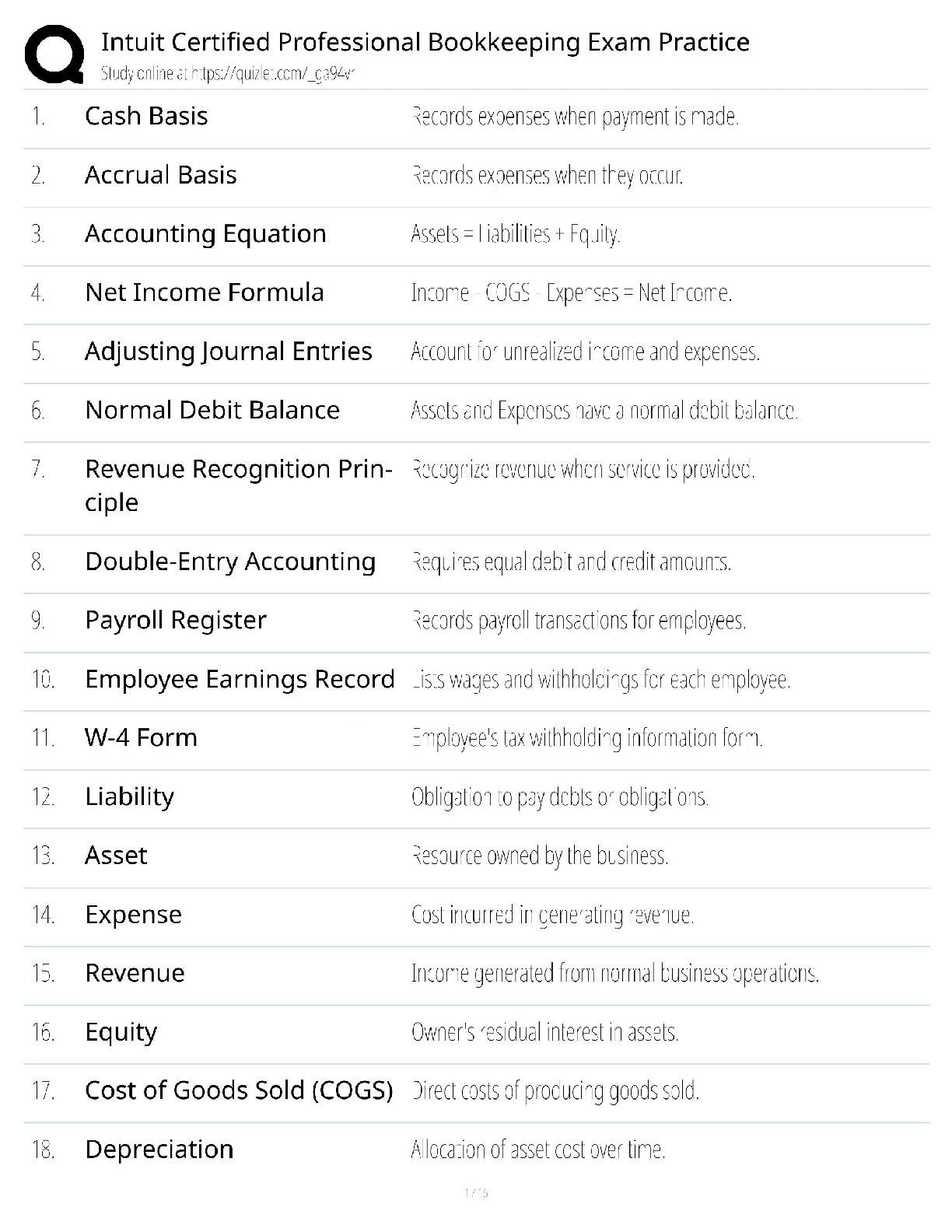
Cellular Components and Their Function
Nucleus- located at the center of cell. largest membrane-bound organelle. Covered by nuclear envelope (2 membranes), contains nucleolus (houses DNA & RNA & histones- cause dna to fold into chromosomes) Functions: cell division and control of genetic info. Other fxns: replication/repair of D
[Show More]
.png)