Health Care > EXAM > Physiological Health Problems Exam | Questions, Answers and Rationales (All)
Physiological Health Problems Exam | Questions, Answers and Rationales
Document Content and Description Below
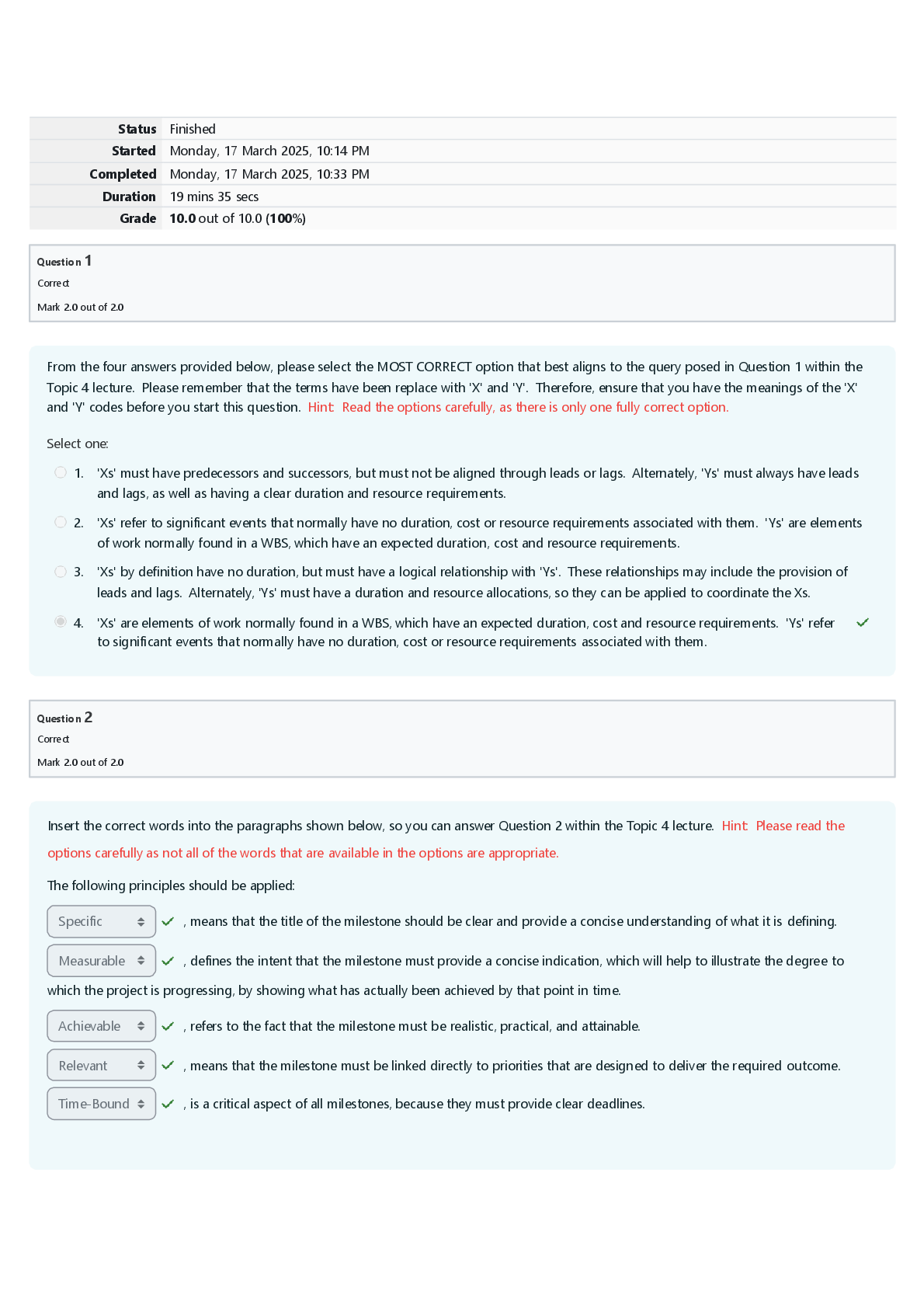
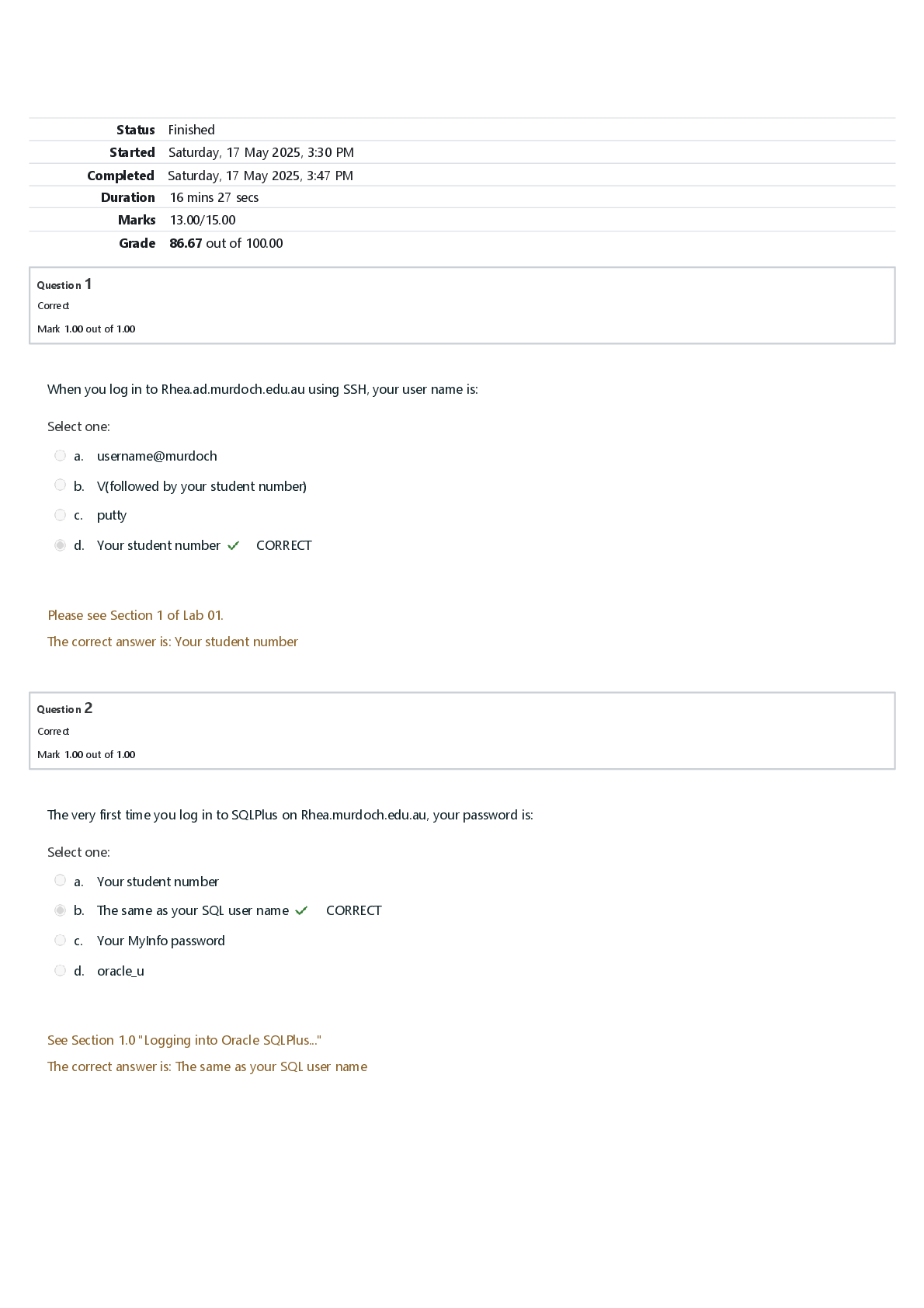
Physiological Health Problems Exam | Questions, Answers and Rationales A client who experienced a brain attack (stroke) exhibits right-sided unilateral neglect. The nurse caring for this client plan ... s to place the client's personal care items: Within the client's reach on the right side Rationale: Unilateral neglect is unawareness of one side of the body. The client behaves as if that part is not there. The client does not look at the paralyzed limb when moving about. Unilateral neglect results in increased risk for injury. It is possible for the client to relearn to look for and to move the affected limb(s). Therefore in this condition the client's personal care items are placed within the client's reach on the right side. Hemiparesis is a weakness of the face, arm, and leg on one side. The client with one-sided hemiparesis benefits from having objects placed on the unaffected side and within reach. This reduces client frustration and aids in ensuring client safety because the client does not have to strain and reach for needed items. The nurse adapts the client's environment to the deficit by focusing on the client's unaffected side and by placing the client's personal care items on the affected side within reach. Placing items out of the client's reach presents a risk of injury. The emergency department nurse assesses a client who has a diagnosis of left-sided heart failure. Which findings does the nurse expect to note? Select all that apply. Crackles on auscultation of the lungs. Rationale: Signs of left-sided heart failure result from decreased cardiac output and increased pulmonary venous congestion, and the nurse would note signs related to the respiratory system, such as cough, dyspnea, and crackles and wheezes on auscultation of the lungs. Right-sided heart failure is associated with increased systemic venous pressure and congestion, and the nurse would note signs such as neck vein distention, dependent edema, abdominal distention, and weight gain. A home care nurse has provided instructions to the father of a child with croup regarding treatment measures. Which statement by the father indicates a need for further instruction? "I should put a steam vaporizer in her room." Rationale: Steam from running water in a closed bathroom and cool mist from a bedside humidifier or a freezer are effective in reducing mucosal edema. A cool mist humidifier is recommended over a steam vaporizer, which presents a danger of scald burns. Taking the child out into the cool humid night air may also relieve mucosal swelling. A mother calls the clinic and tells the nurse that her newborn's umbilical cord site looks red and swollen. The nurse should tell the mother: To bring the newborn to the clinic. Rationale: Symptoms of cord infection include moistness, oozing, discharge, swelling, and a reddened base. If symptoms of infection occur, the newborn must be seen by the healthcare provider. Telling the mother to increase the number of times that the cord is cleansed each day or to place an ice pack on the umbilical cord site and stating that this is a normal occurrence are inappropriate nursing interventions. The wife of a client with angina pectoris calls the physician's office and reports to the nurse that her husband is experiencing chest pain and has taken 2 sublingual nitroglycerin tablets 5 minutes apart, with no relief. The nurse tells the client's wife to: Give her husband a third tablet and, if no relief is obtained, call an ambulance to have him transported to the ED. Rationale: Chest pain that is unrelieved by rest and three doses of nitroglycerin taken 5 minutes apart may be not typical anginal pain but instead a sign of myocardial infarction (MI). Because the risk of sudden cardiac death is greatest in the 24 hours after MI, it is imperative that the client receive emergency cardiac care. If the client needs to go to the ED, the nurse must instruct the client's wife to call an ambulance to transport her husband. The client's wife must not drive the client, because the client should not exert energy and place an increased workload on the heart and the client's wife would not be able to provide care if an emergency arose during transport to the hospital. Telling the wife that she will have to discuss the situation with the physician, who will call her as soon as he gets to his office, delays necessary interventions. Having her husband rest delays necessary interventions; also, the usual procedure is to have the client take three nitroglycerin tablets before seeking medical attention. Mastitis is diagnosed in a client who recently gave birth. The nurse tells the woman that: Moist heat will increase circulation and may be used before the breasts are emptied. Rationale: Antibiotic therapy and continued decompression of the breasts, by means of breastfeeding or with a breast pump, is prescribed for the client with mastitis. In most cases the mother may continue to feed with both breasts. If the affected breast is too sore, the mother may pump the breast gently. Regular emptying of the breast is important in preventing abscess formation. Antibiotic therapy helps resolve mastitis within 24 to 48 hours. Additional supportive measures include moist heat or ice packs, breast support, and analgesics. Moist heat promotes comfort and increases circulation. A shower or hot packs should be used before the breasts are emptied or before feeding. A nurse is conducting an assessment of a client with mild preeclampsia. Which sign indicates improvement in the client's condition? Trace protein in the urine. Rationale: Preeclampsia is considered mild when the systolic blood pressure is 140 mm Hg or greater but less than 160 mm Hg and the diastolic blood pressure is 90 mm Hg or greater but less than 110 mm Hg, proteinuria is 1+ on a random dipstick, and symptoms such as headache, visual disturbances, and abdominal pain are absent. In addition, signs of kidney or liver involvement are absent. An increased BUN level indicates kidney damage, a result of the preeclampsia. A nurse is assessing a child with increased intracranial pressure who has been exhibiting decorticate posturing. The nurse notes extension of the upper and lower extremities, with internal rotation of the upper arms and wrists and the knees and feet. The nurse determines that the child's condition: Indicates deterioration in neurological function. Rationale: In decorticate posturing, the upper extremities are flexed and the lower extremities are extended. In decerebrate posturing, the upper and lower extremities are extended and the upper arms and wrists and the knees and feet are internally rotated. The progression from decorticate to decerebrate posturing usually indicates deteriorating neurological function and warrants physician notification. The remaining options are inaccurate interpretations. During a client's yearly eye examination, the nurse checks the intraocular pressure. The nurse notes that the pressure in the right eye is 12 mm Hg and 19 mm Hg in the left. The nurse tells the client: That the intraocular pressure in both eyes is normal. Rationale: Normal intraocular pressure ranges from 10 to 21 mm Hg. Therefore this client's intraocular pressure is normal. Increased intake of fluids is unrelated to increasing intraocular pressure. A nurse provides instructions to a client with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) about the positions that are most effective in alleviating dyspnea. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further instruction? "I should lie on my right side in bed." Rationale: Positions that will help the client with COPD breathe more freely include sitting up and leaning on an overbed table, sitting up and resting with the elbows on the knees, sitting up in a chair, and standing and leaning against the wall. These positions allow for the greatest expansion of the lungs and respiratory cage in all directions. Lying on the side is not effective. A stapedectomy is performed on a client with otosclerosis. During the preparations for discharge, which home care instruction does the nurse give the client? Avoid rapidly moving the head and bending over for at least 3 weeks. Rationale: The client must avoid rapidly moving the head, bouncing, and bending over for at least 3 weeks to prevent disruption of the surgical site. The client should keep the affected ear dry at all times and should avoid getting the head wet, washing the hair, or showering for 1 week. The client should not rinse out the ear. The client also needs to avoid drinking through a straw for 2 to 3 weeks because the sucking action necessary to use the straw could cause disruption of the surgical site. The client should notify the physician if excessive ear drainage is noted. A nurse is providing instructions to a nursing assistant about effective measures for communicating with a hearing-impaired client. The nurse instructs the nursing assistant to: Face the client when talking, keeping the hands away from the mouth. Rationale: To facilitate communication with a client who is hearing impaired, the nurse should speak in a normal tone, not shout or raise the voice. The nurse should speak clearly and directly while facing the client and keep the hands away from the mouth so that the client can read the nurse's lips. It may be helpful for the nurse to move closer to the client and toward the better ear to facilitate communication, but it is not helpful to talk directly into the client's impaired ear. Smiling while talking will make it difficult for the client to lipread. A client is found to have viral hepatitis, and the nurse provides home care instructions to the client. The nurse should tell the client to: Eat small frequent meals that are low in fat and protein and high in carbohydrates. Rationale: Fatigue is a normal response to hepatic cellular damage. During the acute stage, rest is an essential intervention to reduce metabolic demand on the liver and increase its blood supply, but strict bed rest is unnecessary. The client should avoid taking medications, including acetaminophen (which is hepatotoxic), unless they are prescribed by the healthcare provider. The client must avoid all alcohol consumption. The client should consume small frequent meals that are low in fat and protein and high in carbohydrates to reduce the workload of the liver. A cardiac monitor alarm sounds, and a nurse notes a straight line on the monitor screen. The nurse immediately: Assesses the client. Rationale: If a monitor alarm sounds, the nurse should first assess the clinical status of the client to see whether the problem is an actual dysrhythmia or a malfunction of the monitoring system. Asystole should not be mistaken for an unattached electrocardiogram wire. If the client is alert and the client's status is stable, the problem is likely an unattached cardiac lead or wire. Calling a code and obtaining a rhythm strip from the monitor device are unnecessary if the client's condition is stable. A woman in labor suddenly complains of abdominal tenderness and pain and states that she felt as though "something ripped." For which manifestations does the nurse, suspecting uterine rupture, assess the client? Select all that apply. -Severe chest pain -Absence of fetal heart tones. Rationale: Signs of uterine rupture vary with the degree of rupture. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain and tenderness, chest pain, hypovolemic shock, signs associated with impaired fetal oxygenation, an absence of fetal heart tones, cessation of uterine contractions, and palpation of the fetus outside the uterus if the rupture is complete. Signs of hypovolemic shock include tachycardia; tachypnea; pallor; cool, clammy skin; and anxiety. A client has just had a plaster leg cast applied, and the nurse has given the client instructions on cast care. Which statement by the client indicates the need for further instruction? "I can dry the cast faster if I use a hairdryer on the hot setting." Rationale: Using a blow dryer on the hot setting to dry the cast is not advised because it may burn the client's skin under the cast and crack the cast. While the cast is still damp, the client may feel cold and may experience a decrease in body temperature. The client should never insert any item under the cast because of the risk skin compromise. An odor coming from the cast could indicate the presence of infection, warranting physician notification. A healthcare provider writes a prescription for the administration of intravenous (IV) potassium chloride to a client with hypokalemia. What does the nurse plan to do when preparing and administering this medication? Ensure that the medication is diluted in an appropriate amount of normal saline solution. Rationale: Potassium chloride administered IV must always be diluted in IV fluid. Undiluted potassium chloride given IV can cause cardiac arrest. The intramuscular and subcutaneous routes of administration are not recommended because the medication cannot be adequately diluted for these routes; toxicity could result if the medication is not adequately diluted. Potassium chloride is never administered as a bolus (IV push) injection; an IV push would result in sudden severe hyperkalemia, which could precipitate cardiac arrest. Saline dilution is recommended, but dextrose is avoided because it increases intracellular potassium shifting. Although urine output is monitored carefully during administration, it is not necessary to insert a Foley catheter unless this is specifically prescribed. The physician is notified if the urinary output is less than 30 mL/hr. Potassium chloride should be administered with the use of a controlled IV infusion device to avoid bolus infusion and increased risk of cardiac arrest. A central IV line is not necessary; potassium chloride may be administered through a peripheral IV line. A nurse develops a nursing care plan for a client with a sealed radiation implant. Which stipulation does the nurse include in the plan? Visitors must be limited to one half-hour per day. Rationale: The nurse would limit each visitor to a half-hour per day and be sure that visitors remain at least 6 feet from the radiation source. The nurse would wear the dosimeter badge when caring for the client. The dosimeter badge measures an individual's exposure to radiation and should be used by only one individual. The dosimeter badge is not left in the client's room. The client is assigned to a private room with a private bath to keep other clients from being exposed to radiation. The nurse is administering cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to an adult client. Which compression-ventilation ratio is correct? 30:2 Rationale: A 30:2 ratio of compressions to ventilations is recommended for CPR in adults. The other options are incorrect. A nurse is caring for a client who has undergone resection of an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). Which action should the nurse implement to prevent graft occlusion? Limiting elevation of the head of the bed to 45 degrees. Rationale: To prevent graft occlusion, the nurse limits elevation of the head of the bed to 45 degrees. The nurse does assess the client for signs of graft occlusion, but assessment will not prevent occlusion. The signs of graft occlusion include changes in peripheral pulses, cool-to-cold extremities distal to the graft, white or blue extremities or flanks, severe pain, and abdominal distention. Bowel sounds and urine output are also assessed, but these parameters are unrelated to graft occlusion. A nurse is assessing a client with AIDS for signs of Pneumocystis jiroveci infection. Which sign of the infection is the earliest manifestation? Nonproductive cough. Rationale: The client with P. jiroveci infection usually has a cough as the first symptom, which begins as nonproductive then progresses to productive. Later signs include fever, dyspnea on exertion, and finally dyspnea at rest. A nurse is preparing a teaching plan for the parents of an infant with a ventricular peritoneal shunt. Which of the following questions does the nurse plan to include? Call the physician if the infant is lethargic. Rationale: If the shunt is broken or malfunctioning, the fluid from the ventricle part of the brain will not be diverted to the peritoneal cavity. cerebrospinal fluid will build up in the cranial area. The result is intracranial pressure, which causes the infant to make a high-pitched cry or induces changes in level of consciousness, such as lethargy. The infant should not be positioned on the side of the shunt, because this will cause pressure on the shunt and skin breakdown. This type of shunt affects the gastrointestinal system, not the genitourinary system, and an increased urine output is not expected. The anterior fontanel normally bulges when the infant cries. The nurse has instructed a client who is about to begin external radiation therapy in how to maintain optimal skin integrity during therapy. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further instruction? "I can use over-the-counter cortisone cream on the radiation site if it gets red." Rationale: The client should use no powders, ointments, lotions, or creams on the skin at the radiation site unless they have been prescribed by the physician. Avoiding sun exposure of the radiation site, not removing marks made on the skin by the radiologist, and washing the skin with mild soap and water and patting it dry are all correct measures. The client should also be instructed to avoid using harsh detergents to wash clothing. A nurse is working in the emergency department. Which of the following clients should be assessed first? A client with new-onset atrial fibrillation with a rate of 118 beats/min. Rationale: The client with new-onset atrial fibrillation is at risk for complications associated with the tachydysrhythmia. This dysrhythmia may result in decreased cardiac output because of ineffective atrial contractions. Thrombi form in the atria as a result of the pooling of blood. All of the other clients will require the nurse's attention, but the client who requires immediate attention and is the most hemodynamically unstable is the one with atrial fibrillation. A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a client after outpatient surgery for cataract removal. The nurse determines that the client needs additional instructions if the client indicates that he will: Expect to experience pain, nausea, and vomiting after the procedure. Rationale: If the client experiences any pain that is unrelieved, redness around the eye, or nausea or vomiting, the physician must be notified, because such findings could be an indication of increased intraocular pressure. Usually the client is given a follow-up appointment on the day after the surgery, and the physician removes the eye patch at this time. The client is instructed to limit activity to sitting in a chair, resting, and walking to the bathroom for 24 hours. Aspirin or medications containing aspirin should not be taken by the client; rather, acetaminophen (Tylenol) should be used to alleviate discomfort. A client arrives in the emergency department for treatment of a surface injury sustained when sand blew into the eye. Which action does the nurse take first? Assessing the client's vision. Rationale: When a client has sustained a surface injury of the eye as a result of the introduction of a foreign body, the nurse must first assess visual acuity. The eye is then assessed for corneal abrasions; this is followed by irrigation with sterile normal saline solution to gently remove the particles. Ice would be placed on the eye if the client had sustained an eye contusion. A nurse attending a recertification course in basic life support (BLS) for healthcare professionals is practicing BLS on an infant mannequin. Where does the nurse place the fingers to assess the infant's pulse? Antecubital fossa of the arm. Rationale: An infant's pulse should be checked at the brachial artery. The relatively short, fat neck of an infant makes palpation of the carotid artery (neck) difficult. Palpation of the pulse in the radial (wrist) and popliteal (behind the knee) area would also be difficult. An emergency department nurse is caring for a client with acute pancreatitis who will be admitted to the hospital. Into which position that will ease the abdominal pain does the nurse assist the client? With the knees drawn up to the chest. Rationale: Helping the client assume the fetal position (legs drawn up to the chest) will ease the abdominal pain of pancreatitis. Other helpful positions include sitting up, leaning forward, and flexing the legs (especially the left leg). Prone, supine with the legs straight, and side-lying with the head of the bed flat are incorrect. A client with chronic renal failure is undergoing his first hemodialysis treatment, and the nurse is monitoring the client for signs of disequilibrium syndrome. For which signs of this syndrome does the nurse monitor the client? Headache and confusion. Rationale: Disequilibrium syndrome most often occurs in clients who are new to hemodialysis. It is characterized by headache, confusion, decreasing level of consciousness, nausea, vomiting, twitching, and, in some cases, seizure activity. It results from rapid removal of solutes from the body during hemodialysis and a higher residual concentration gradient in the brain, caused by the blood-brain barrier. Water goes into cerebral cells because of the osmotic gradient, causing brain swelling and onset of symptoms. It is prevented with the use of shorter dialysis times or dialysis at a reduced blood flow rate. Irritability and generalized weakness, fever and tachycardia, and bradycardia and hypothermia are not associated with disequilibrium syndrome. A nurse in a newborn nursery receives a telephone call from the delivery room and is told that a newborn with spina bifida (meningomyelocele type) will be transported to the nursery. Which item does the nurse, preparing for the arrival of the newborn, make a priority of placing at the newborn's bedside? Sterile dressing. Rationale: The newborn with spina bifida is at risk for infection before the closure of the gibbus. A sterile normal saline dressing is placed over the gibbus to maintain moisture of the gibbus and its contents. This prevents tearing or breakdown of the skin at the site. A flashlight may be needed to closely assess the status of the gibbus but is not a priority item. A cardiac monitor is not necessary. Blood pressure is difficult to assess during the newborn period and is not the best indicator of infection. The blood pressure cuff would not be a priority item. A nurse is administering care to a client with angina pectoris who is attached to a cardiac monitor. The monitor alarm sounds, and the nurse notes the rhythm shown here. How does the nurse interpret the rhythm? Ventricular tachycardia. Rationale: Ventricular tachycardia is characterized by a ventricular rate of 100 to 250 times/min. There is a wide QRS complex and an absence of P waves. The rhythm is usually fairly regular. In atrial fibrillation, multiple rapid impulses from many foci depolarize in the atria in a totally disorganized manner at a rate of 350 to 600 times/min. The atria quiver, which can lead to the formation of thrombi. No definitive P wave is observed, only fibrillatory waves before each QRS. Sinus tachycardia is characterized by a normal sinus rhythm that is rapid (faster than normal) in rate. Sinus bradycardia is characterized by a rhythm that is slower than normal. A nurse is monitoring a client with hyperparathyroidism for signs of hypercalcemia. For which of the following clinical manifestations, associated with this electrolyte imbalance, does the nurse assess the client? Select all that apply. -Muscle weakness -Increased urine output Rationale: Signs of hypercalcemia include muscle weakness, diminished deep tendon reflexes or an absence thereof, increased urine output, decreased gastrointestinal motility, and increased heart rate and blood pressure. Hyperactive deep tendon reflexes, the presence of the Chvostek sign, and paresthesias are signs of hypocalcemia. A nurse is reviewing the assessment findings and laboratory results of a child with a diagnosis of new-onset glomerulonephritis. Which of the following findings would the nurse expect to note? Hypertension. Rationale: Hypertension is a common finding in glomerulonephritis. Gross hematuria resulting in dark-brown or smoky tea-colored urine is also a classic symptom of glomerulonephritis. The blood urea nitrogen and creatinine levels are increased only when there is an 80% decrease in glomerular filtration rate and renal insufficiency is severe. A high potassium level results from inadequate glomerular filtration. A nurse is conducting the initial assessment of a child with rheumatic fever. Which question does the nurse ask the parents to elicit information specific to the development of the disease? "Has he had a sore throat in the last few months?" Rationale: Rheumatic fever characteristically presents 2 to 6 weeks after an untreated or partially treated group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection of the upper respiratory tract. The nurse first determines whether the child had a sore throat or an unexplained fever within the past 2 months. Asking the parents whether the child has had any loss of appetite, complained of backache recently, or been excessively tired or lethargic will elicit information unrelated to rheumatic fever. A nurse provides home care instructions to a client with Ménière disease about measures to control and treat vertigo. The nurse should tell the client to: Limit sodium in the diet. Rationale: Limiting and fluids in the diet will help reduce the amount of endolymphatic fluid, which is excessive in Ménière disease. The client's room should be darkened to reduce the acute symptoms of vertigo. The client should limit head movement to prevent worsening of the symptoms of vertigo. A nurse answers the call bell of a client who has been fitted with an internal cervical radiation implant, and the client states that she thinks that the implant has fallen out. The nurse checks the client and sees the implant lying in the bed. Which action should the nurse take first? Using long-handled forceps to place the implant in a lead container. Rationale: A lead container and long-handled forceps should be kept in the client's room at all times during internal radiation therapy. If the implant is dislodged, the nurse should pick it up with long-handled forceps and place it in the lead container. Reinserting the implant into the vagina and picking up the implant with gloved hands and placing it in sterile water are both incorrect nursing actions. The physician is called after action is taken to maintain the safety of the client. An ambulatory care nurse is providing home care instructions to the mother of a child who had a tonsillectomy. The nurse determines that the mother needs further instruction if she indicates that she will: Have her child use a straw to make drinking easier. Rationale: Introduction of a straw, fork, or any other pointed object into the mouth could result in accidental contact with the surgical site and disrupt its integrity. Citrus fruits are avoided because they could irritate the throat. Acetaminophen is used for pain relief. A foul mouth odor is normal and can be relieved by drinking fluids. A client is found to have AIDS. What is the nurse's highest priority in providing care to this client? Instituting measures to prevent infection in the client. Rationale: The client with AIDS has inadequate immune bodies and is at risk for infection. The priority nursing intervention is protecting the client from infection. The nurse would also provide emotional support to the client. Discussing the cause of AIDS and the ways in which AIDS is contracted are not priority interventions. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 5 out of 28 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$17.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 03, 2024
Number of pages
28
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 03, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
30