Supply Chain Management > EXAM > Supply Chain Exam 2 (Chapter 9) | Q & A with 100% Correct Answers (All)
Supply Chain Exam 2 (Chapter 9) | Q & A with 100% Correct Answers
Document Content and Description Below
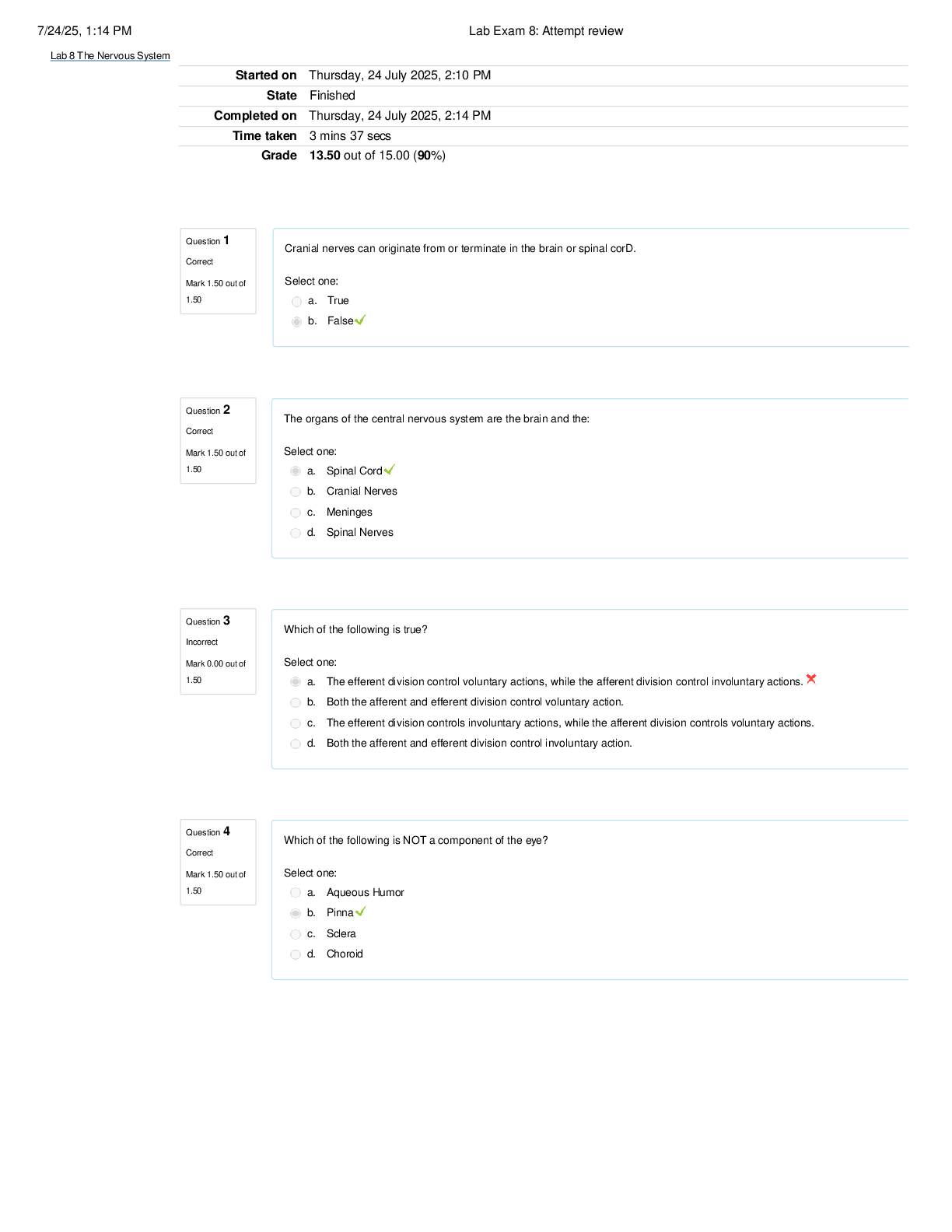
Supply Chain Exam 2 (Chapter 9) | Q & A with 100% Correct Answers The objective of layout strategy is to develop an effective and efficient layout that will meet the firm's competitive requirements. ... TRUE Which of the following is NOT one of McDonald's "seven major innovations"? A) the Happy Meal B) drive-through windows C) breakfast menus D) play areas E) self-service kiosks The objective of layout strategy is to: A) minimize cost. B) develop an effective and efficient layout that will meet the firm's competitive requirements. C) maximize flexibility. D) minimize space used. E) maximize worker satisfaction. The layout approach that addresses trade-offs between space and material handling is called the fixed-position layout. FALSE The ________ layout's main objective is to equalize the task time for each station. A) work cell B) fixed position C) office D) job shop E) product oriented A hospital's layout most closely resembles which of the following? A) product oriented B) work cell C) job shop D) project E) retail What layout strategy deals with low-volume, high-variety production? A) fixed-position layout B) retail layout C) warehouse layout D) office layout E) process-oriented layout "A special arrangement of machinery and equipment to focus on production of a single product or group of related products" describes what layout type? A) fixed-position layout B) intermittent production C) job shop D) work cell E) warehouse layout A good layout requires determining: A) material handling equipment. B) capacity and space requirements. C) environment and aesthetics. D) cost of moving between various work areas. E) all of the above Which of the statements below best describes office layout? A) positions workers, their equipment, and spaces/offices to provide for movement of information B) addresses the layout requirements of large, bulky projects such as ships and buildings C) seeks the best personnel and machine utilization in repetitive or continuous production D) allocates shelf space and responds to customer behavior E) deals with low-volume, high-variety production Utilization of the total "cube" is the dominant consideration in office layout. FALSE Deloitte & Touche solved the empty desk problem by: A) assigning permanent desks. B) implementing a "hoteling" program. C) creating open offices. D) no longer allowing employees to work from home. E) reducing the number of allowable sick days per employee. In the office relationship chart, which rating reflects the highest importance for two departments' closeness to each other? A) A B) E C) I D) O E) X Which of the following constitutes a major trend influencing office layouts? A) downsizing B) globalization C) environmental issues D) off-site employees E) health issues Workspace can inspire informal and productive encounters if it balances what three physical and social aspects? A) proximity, privacy, and persuasion B) privacy, persuasion, and permission C) proximity, privacy, and permission D) proximity, persuasion, and permission E) proximity, persuasion, and passion One guideline for a retail layout is to locate high-draw items around the periphery of the store. TRUE Category management is the use of computer software to evaluate the profitability of various merchandising plans for hundreds of categories. TRUE Servicescape refers to the physical surrounding in which the service is delivered. TRUE One guideline for determining the arrangement and space allocation of a retail store is to place high-impulse and high-margin items in prominent locations. TRUE The main goal of retail layout is: A) minimizing material handling cost. B) minimizing customer confusion regarding location of items. C) minimizing storage costs. D) minimizing space required. E) maximizing profitability per square foot of floor space. Retail layouts are based on the notion that: A) handling costs should be minimized. B) storage costs should be minimized. C) average customer visit duration should be maximized. D) space used should be minimized. E) maximizing customer exposure rate maximizes sales and profit. Slotting fees: A) are charged by retailers to stock a product. B) can amount to as much as $25,000. C) are not a part of Walmart's business practices. D) can reduce the ability of small businesses to introduce new products. E) all of the above Which of the following is NOT a retail layout practice? A) Locate the high-draw items around the periphery of the store. B) Distribute power items throughout the store. C) Use end-aisle locations to maximize product exposure. D) Use prominent locations for high-impulse and high-margin items. E) All of the above are retail layout practices. What is the primary reason why retailers tend to locate high-draw items around the periphery of the store? A) More shelf space for those popular items is available around the periphery. B) There will be less congestion of customers than there would be in the middle. C) This arrangement will help to maximize customer exposure to other items in the store. D) It is easier to put large advertisement signs on the outside walls right next to the items. E) This arrangement allows customers to travel through the store as quickly as possible. Which of the following does NOT support the retail layout objective of maximizing customer exposure to products? A) Locate high-draw items around the periphery of the store. B) Use prominent locations for high-impulse and high-margin items. C) Maximize exposure to expensive items. D) Use end-aisle locations. E) Convey the store's mission with the careful positioning of the lead-off department. Ambient conditions; spatial layout and functionality; and signs, symbols, and artifacts are all: A) indicators of imbalance on an assembly line. B) indicators that cross-docking has been successful. C) elements of customization in a warehouse layout. D) elements of servicescapes. E) elements of successful office layouts. Cross-docking processes items as they are received, rather than placing them in storage. TRUE Balancing low-cost storage with low-cost material handling is important in which of the following? A) fixed-position layout B) process-oriented layout C) office layout D) repetitive and product-oriented layout E) warehouse layout Which of the following reduces product handling, inventory, and facility costs, but requires both (1) tight scheduling and (2) accurate inbound product information? A) phantom-docking B) random stocking C) ASRS D) customizing E) cross-docking The major problem addressed by the warehouse layout strategy is: A) minimizing difficulties caused by material flow varying with each product. B) requiring frequent close contact between forklift drivers and item pickers. C) addressing trade-offs between space and material handling. D) balancing product flow from one work station to the next. E) locating the docks near a convenient access point to the closest highway. The concept of customizing in a warehouse layout: A) is possible, but it causes serious loss of oversight of the quality function. B) cannot be considered seriously in today's high efficiency factories. C) is theoretically sound, but several years away in practice. D) incorporates value-added activities in warehouses. E) locates stock wherever there is an open location. ASRS stands for which of the following? A) automated storage and retrieval system B) automated storage and recovery system C) automated scan and recognize system D) automated scan and retail system E) automated scan and retrieval system Which of the following is TRUE of random stocking? A) Because items are stocked randomly, accurate inventory records are not necessary. B) Its results always minimize handling costs. C) Products have their own permanent storage spot. D) Each pick can be of only one product. E) None of the above is true. Cross-docking means which of the following? A) Avoid placing materials or supplies in storage by processing them as they are received. B) The same docks can be used either incoming or outbound shipments. C) The same dock is used to unload and then reload the same truck. D) Warehouse docks are designed in the shape of a cross. E) Docks are placed in the warehouse according to the direction (north, south, east, or west) from which the truck is arriving. The dominant problem associated with the fixed-position layout is that workers are fixed in position, and they cannot be reassigned. FALSE The fixed-position layout would be MOST appropriate in which of the following settings? A) a fast-food restaurant B) a doctor's office C) a casual dining restaurant D) a cruise ship assembly facility E) a washing machine assembly line For which of the following operations would a fixed-position layout be MOST appropriate? A) assembling automobiles B) producing TV sets C) constructing a highway tunnel D) refining of crude oil E) running an insurance agency Because problems with fixed-position layouts are so difficult to solve well onsite, operations managers: A) virtually never employ this layout strategy. B) utilize this approach only for construction projects such as bridges and office towers. C) increase the size of the site. D) often complete as much of the project as possible offsite. E) utilize this layout only for defense contractors. Which of the following is NOT one of the factors complicating the techniques for addressing the fixed-position layout? A) The volume of materials needed is dynamic. B) At different stages of a project, different materials are needed; therefore, different items become critical as the project develops. C) Takt times at workstations are dynamic. D) There is limited space at virtually all sites. E) All of the above are complicating factors. A process-oriented layout is the traditional way to support a product differentiation strategy. TRUE Job lots are groups or batches of parts processed together. TRUE Process-oriented layouts typically have low levels of work-in-process inventory. FALSE The most common tactic to arrange departments in a process-oriented layout is to minimize material handling costs. TRUE Which type of layout features departments or other functional groupings in which similar activities are performed? A) process-oriented B) product-oriented C) fixed-position D) mass production E) unit production One of the major advantages of process-oriented layouts is: A) high equipment utilization. B) large work-in-process inventories. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 4 out of 15 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 17, 2024
Number of pages
15
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 17, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
78