BIO 228 Lab Final - Questions with 100% Correct Answers
Document Content and Description Below
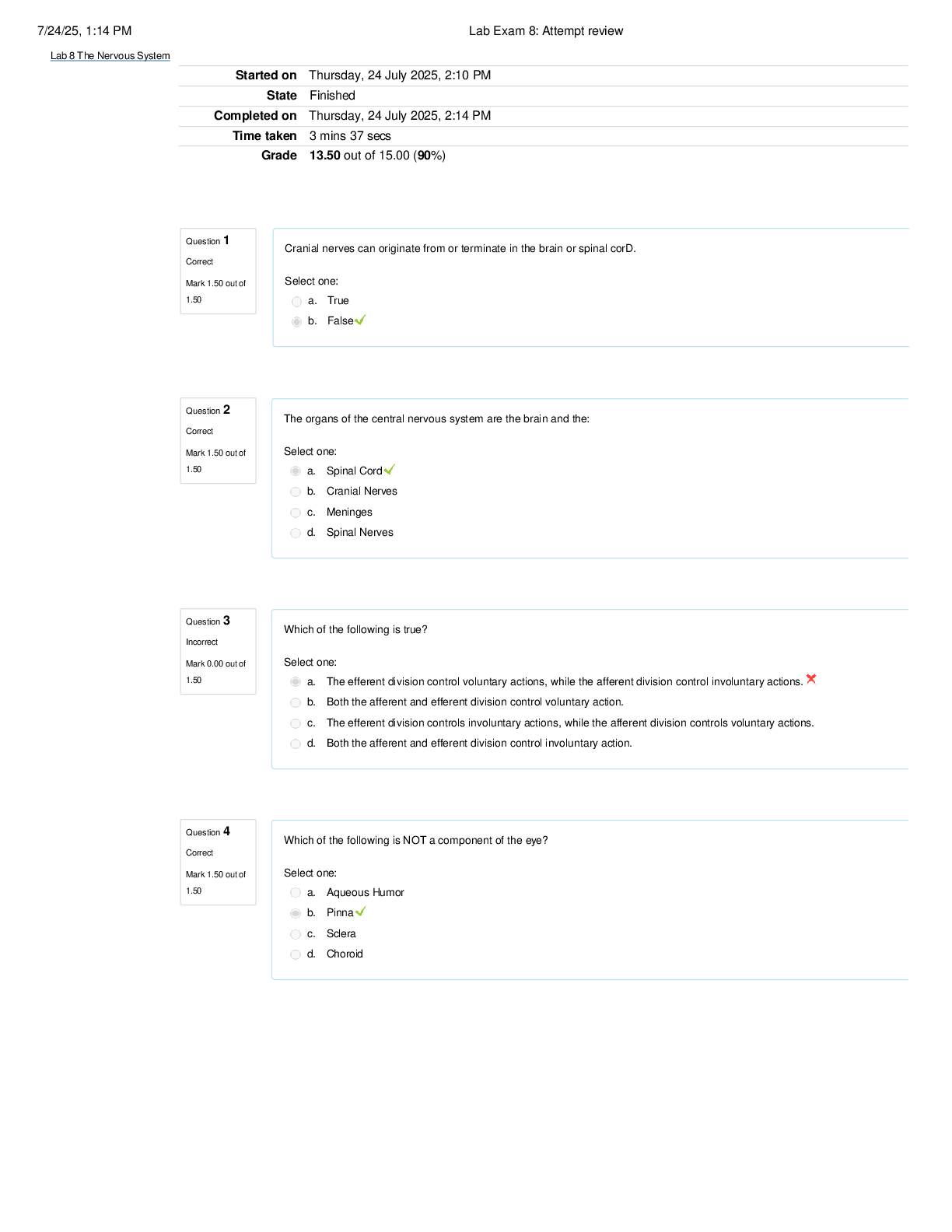
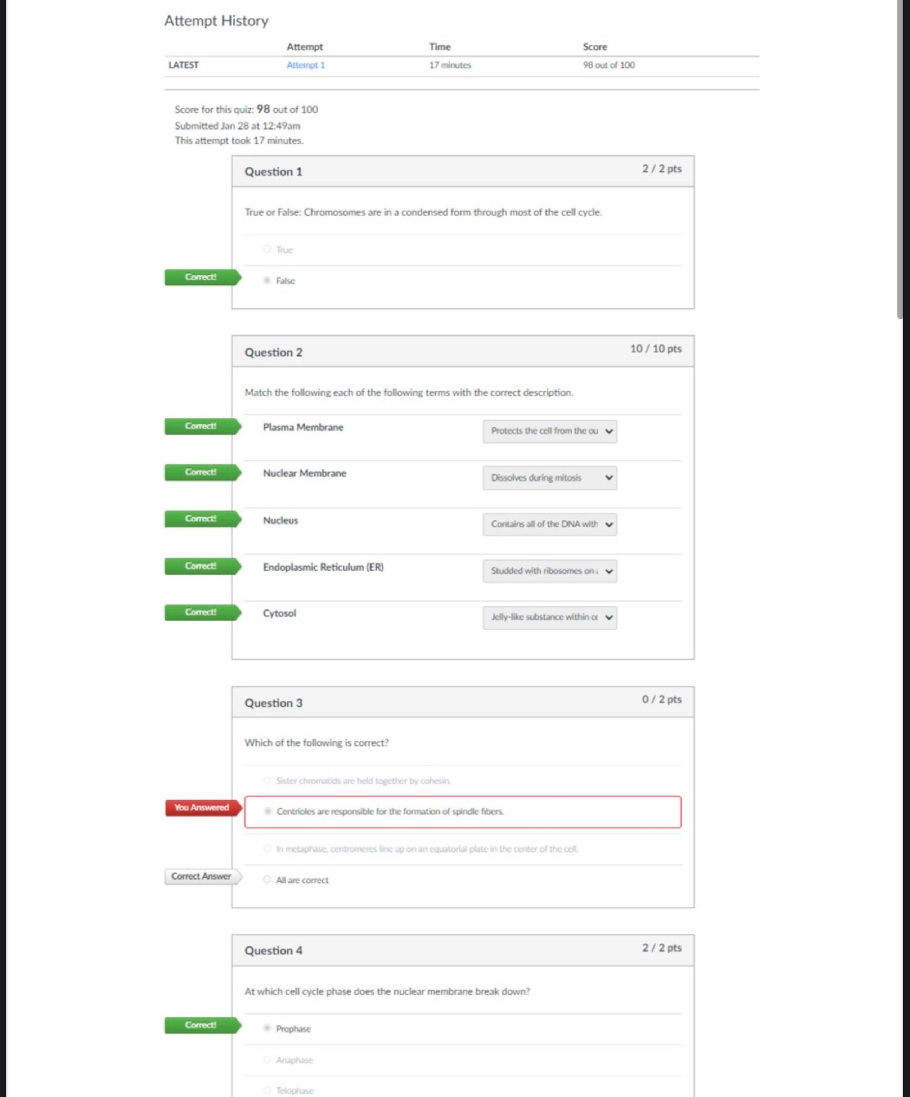
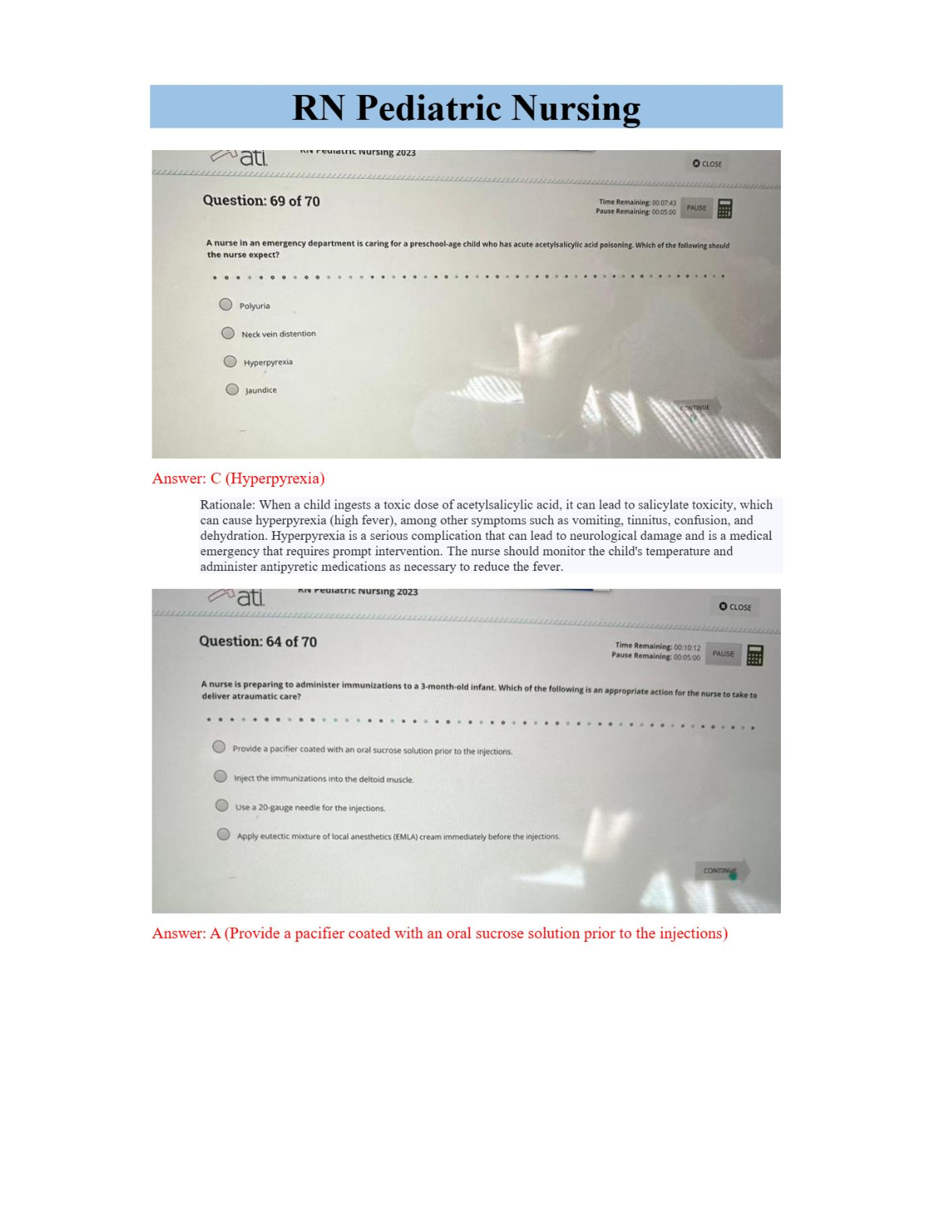
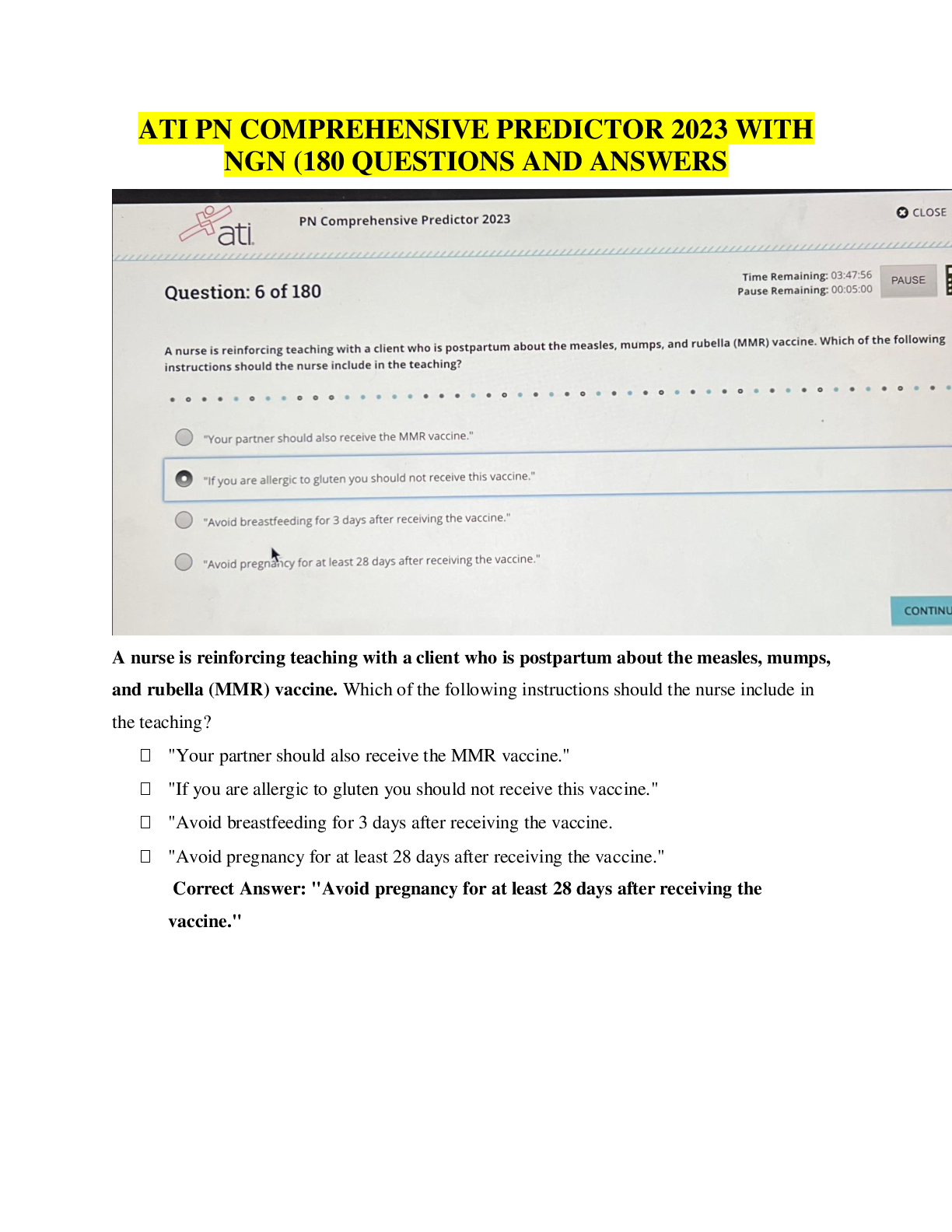
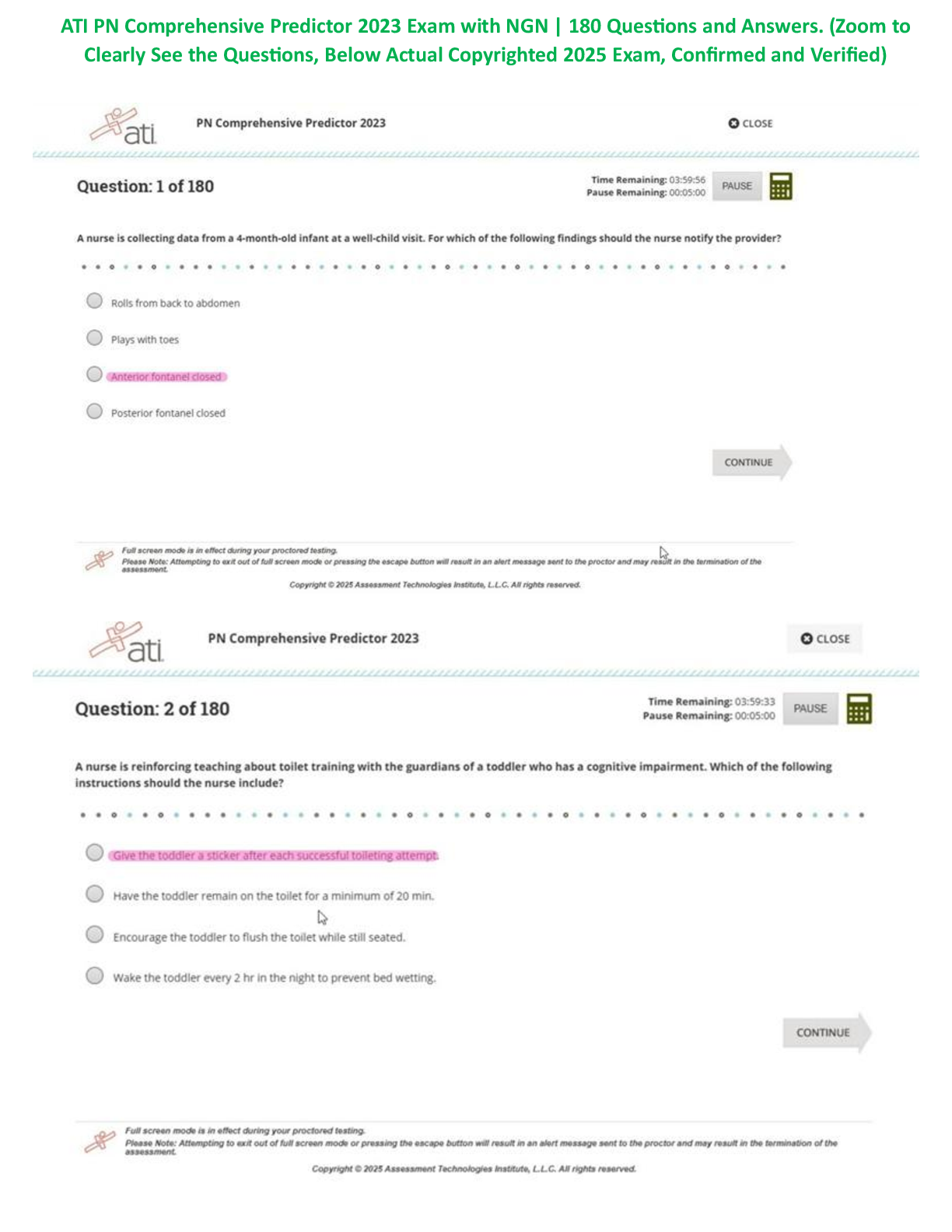
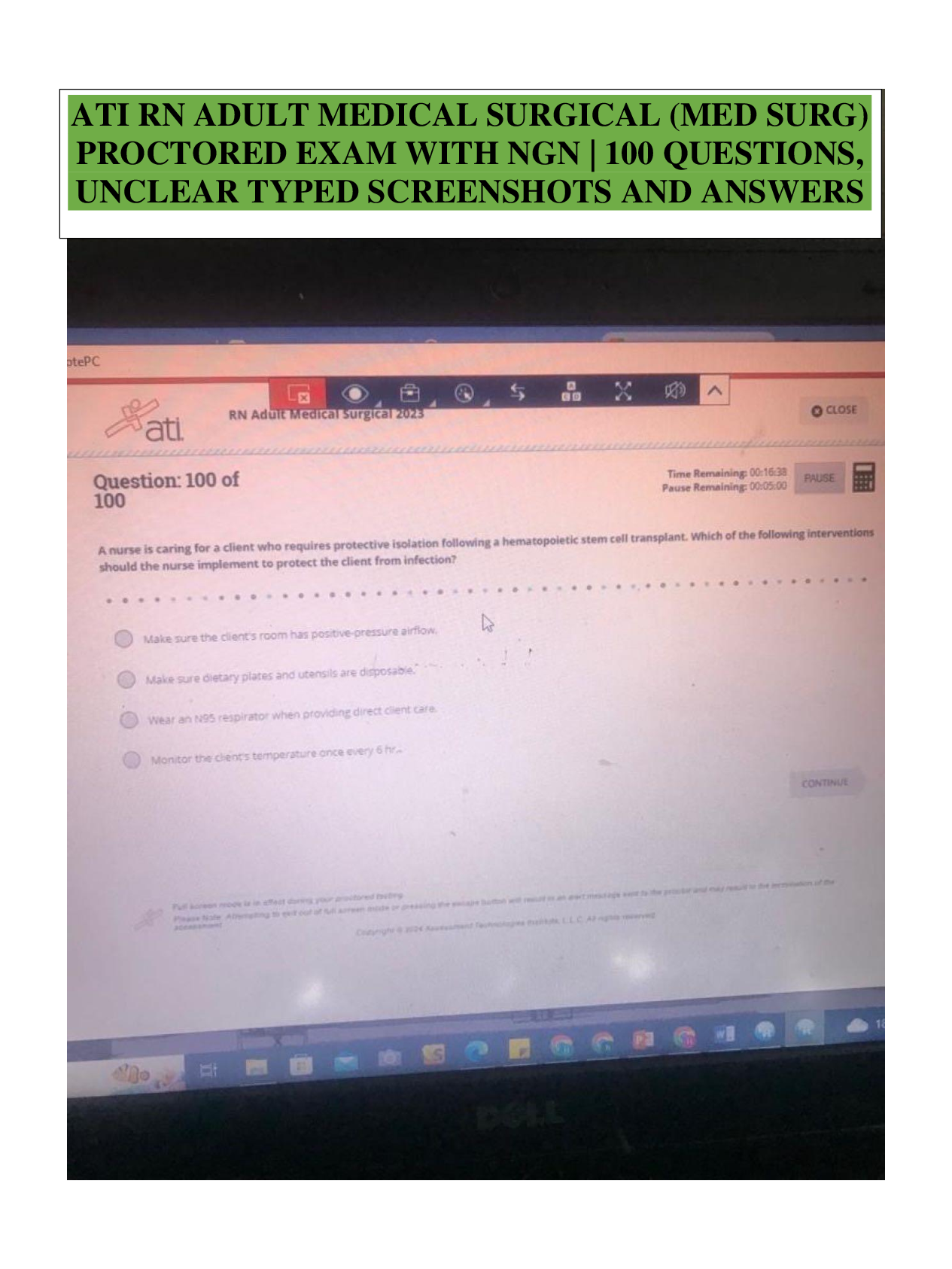
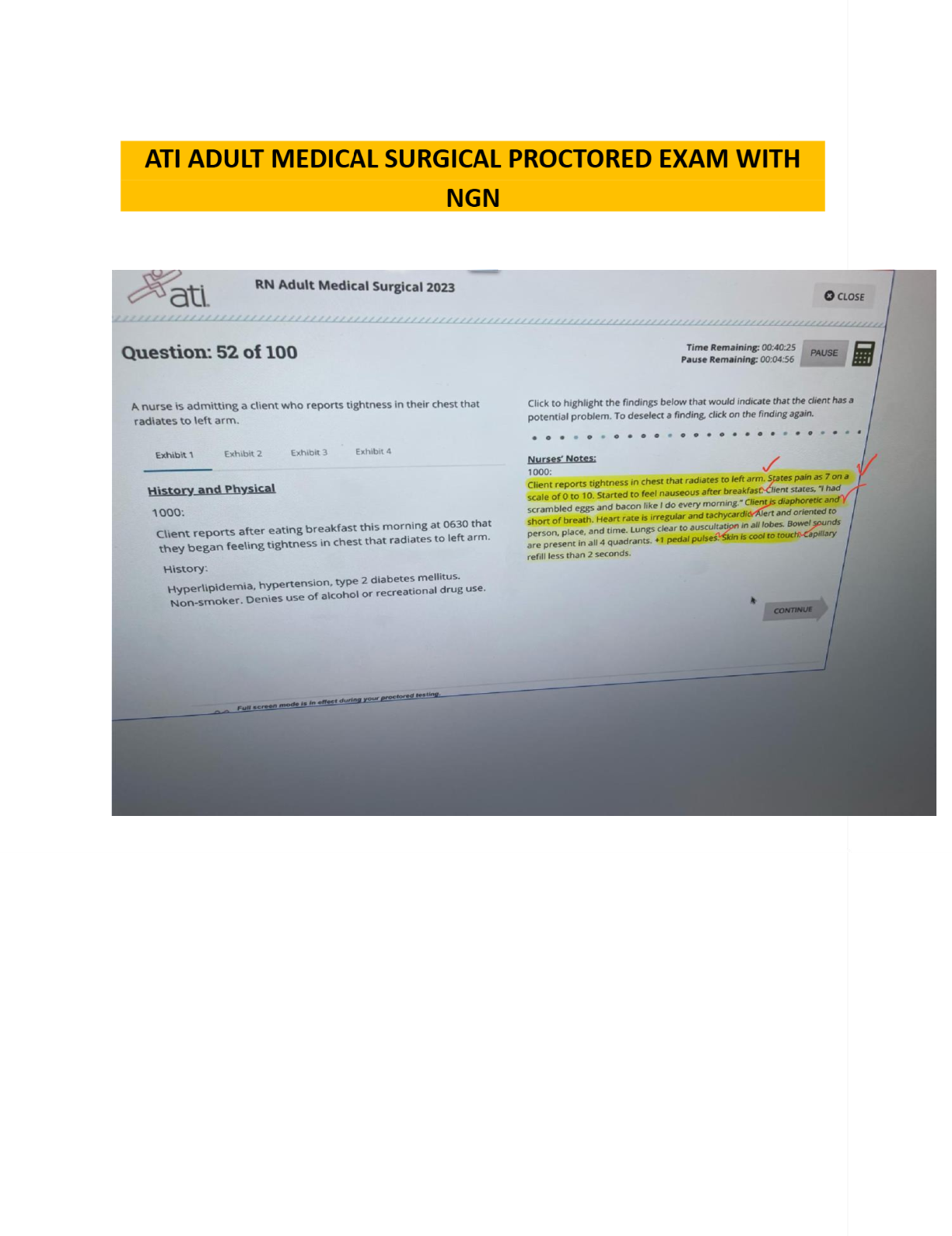
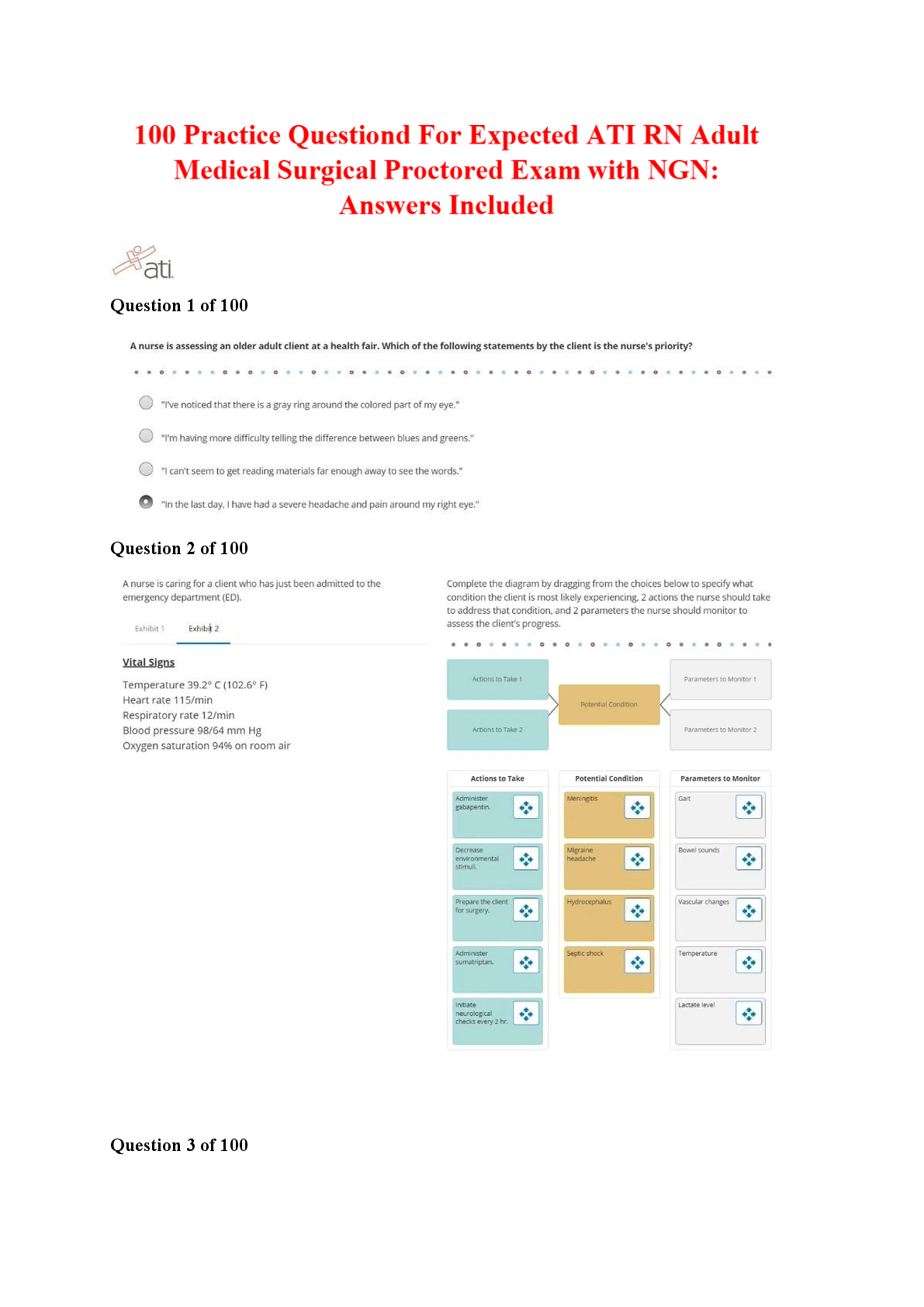
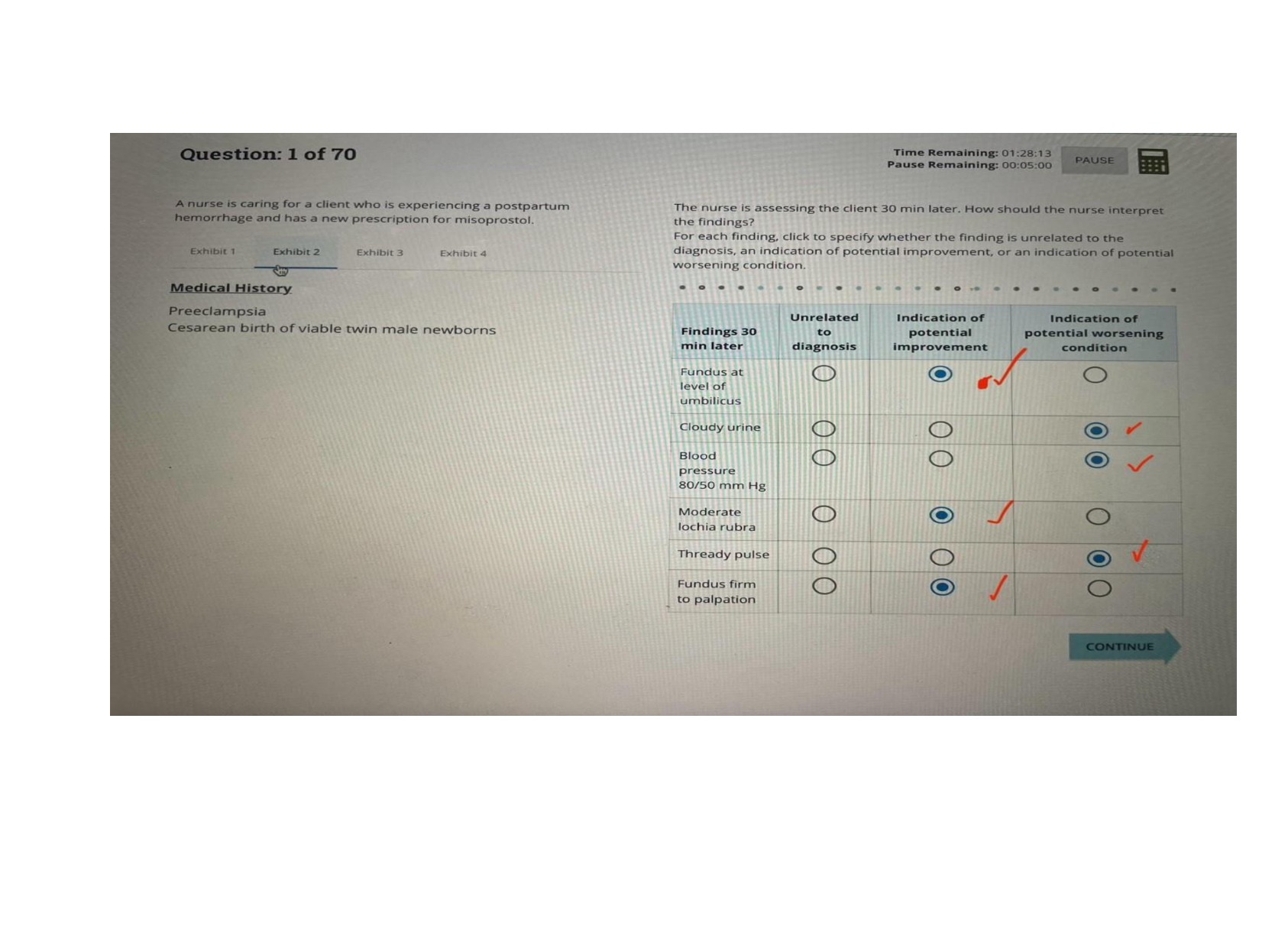
BIO 228 Lab Final - Questions with 100% Correct Answers Which of the following structures is lined with simple cuboidal epithelium with microvilli? (Check all that apply.) - distal convoluted tubule ... - proximal convoluted tubule The glomerulus of the kidney consists of _______ capillaries Fenestrated Which of the following is considered an abnormal constituent of urine? (Check all that apply.) - erythrocytes - glucose - ketone bodies Which of the following structures are located in the renal cortex? - renal corpuscle - proximal convoluted tubule - distal convoluted tubule T or F: Blood pH of 7.1 with elevated partial pressure of carbon dioxide and normal bicarbonate levels is indicative of respiratory acidosis. true T or F: The internal urethral sphincter is composed of smooth muscle, whereas the external urethral sphincter is composed of skeletal muscle. True T or F: Increased sodium in the diet has been demonstrated to cause increases in systemic blood pressure due to the increase in blood viscosity. False T or F: Patients with kidney failure experience systemic edema as a result of increased solutes in the blood. Higher levels of plasma proteins drive fluid from the blood to the tissues. False In severe cases of hypertension, an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor may be prescribed for a patient. The enzyme ACE converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II. One target of angtiotensin II is the adrenal cortex, where angeotensin II stimulates the release of the hormone______________, which increases sodium retention and, as a result, increases water retention. aldosterone Patients with chronic hypertension are at risk of kidney damage. Which of the following structures is most susceptible to damage due to hypertension? gomerular membrane Which of the following is an abnormal constituent of urine? Glucose T or F: Urine should normally test negative for the presence of glucose. True T or F: Urine flows from the kidney to the bladder due to the hydrostatic pressure generated at the glomerular membrane. False A greater concentration of substances in urine (e.g., glucose or protein) would cause the urine to have a _____________ specific gravity than water. Higher T or F: Human somatic cells contain twenty-two pairs of autosomal chromosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. True Vesicular (Graafian) follicles contain a ________ oocyte. Secondary Which of the following is the male gonad? Testis Which of the following are germ layers present in an embryo? ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm A woman who is trying to conceive may purchase ovulation kits in order to test for the release of the secondary ooctye. An ovulation kit requires placing a dipstick in a collected urine sample. A positive test indicates that ovulation will happen typically within 48 hours. For which hormone is this test sensitive? luteinizing hormone T or F: Sustentacular cells, located within seminiferous tubules, produced testosterone, whereas interstitial (Leydig) cells, located between seminiferous tubules, produce androgen-binding protein. False The germinal epithelium is composed of which of the following types of epithelial tissue? simple cuboidal epithelium T or F: Spermatogonia are located near the basement membrane of the seminiferous tubules. True T or F: The product of mitosis is two diploid daughter cells, whereas the product of meiosis is four diploid daughter cells. False Name the structural and functional unit of the kidney Nephron Coiled balls of capillaries, found in the cortex of the kidneys, from which comes the filtrate, are referred to as Glomeruli What does urine flow through in order to exit the kidneys? Ureters The glomerulus of the kidney consists of what type of capillaries? Fenestrated endothelium Which of the following structures are located in the renal medulla? - collecting ducts - loop of henle/ nephron loop The thick limbs of the nephron loop are composed of simple cuboidal epithelium The thin limbs of the nephron loop are composed of simple squamous epithelium The capillary region that is specialized for filtration Glomerulus The capillary region that is specialized for reabsorption pertubular capillaries The primary site of tubular reabsorption proximal convoluted tubule The location of the macula densa distal convoluted tubule Receives urine from many nephrons and gives the medullary pyramids their striated appearance collecting duct Vessel entering into the glomerulus. afferent arteriole Type of nephron with a long loop of Henle (nephron loop) that dips way down into the medullary pyramid. juxtamedullary nephrons Generally the larger of the two vessels associated with the glomerulus afferent arteriole Artery that arches over the top (base) of each medullary pyramid arcuate arteries Type of epithelial tissue found in the PCT simple cuboidal epithelial cells which have a brush border Type of epithelial tissue found in the thin limb of the loop of Henle (nephron loop simple squamous epithelium Type of epithelial tissue lining the urinary bladder and ureter transitional epithelium Place the layers of the wall of the ureter in order, from innermost to outermost. mucosa, muscularis, adventitia. How many layers in the wall of the urinary bladder? 4 Which kidney is located more superiorly than the other? left is superior Place the following structures in order from innermost to outermost. paranephric fat, perinephric fat, renal capsule, renal fascia renal capsule, perinephric fat, renal fascia, paranephric fat Identify the three structures that form the boundaries of the urinary trigone right ureter left ureter urethra List the 3 sections of the male urethra in the correct order from proximal to distal. prostatic, membranous, spongy urethra Which usually has a larger diameter, the afferent arteriole or the efferent arteriole? afferent arteriole Glucose reabsorption in the nephron occurs in the proximal convoluted tubule Which of the following systems is/are employed to regulate acid-base balance in the blood? respiratory system urinary system What is the normal volume of urine excreted in a 24-hour period? 1.0 to 1.8 L What substance is responsible for the normal yellow color of urine? Urochrome Which has a greater specific gravity: 1 ml of urine or 1 ml of distilled water? 1 ml of Urine Name the three major nitrogenous wastes found in the urine. Urea Ureic acid Creatinine Normal urine is usually pale yellow to amber in color because of the presence of: urochrome The average pH value of urine is 6.0 ____________ like other blood proteins, is/are too large to pass through the glomerular filtration membrane and is/are normally not found in urine. albumin What is the normal specific gravity of urine? 1.001 - 1.030 List 4 abnormal urinary constituents: Hematuria (blood in urinary tract) Proteinuria (protein in the urine) Glycosuria (too much glucose in urine) Pyuria (leukocytes in urine, UTI) Why would your family physician at the turn of the twentieth century taste your urine? They would taste it to detect glucose and glucosuria for diabetes What happens to the concentration of glucose in the urinary bladder as the number of glucose carriers increases? [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 4 out of 11 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$13.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 25, 2024
Number of pages
11
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 25, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
42