Hematology > EXAMs > Hematology Quiz | Questions and Answers (Complete Solutions) (All)
Hematology Quiz | Questions and Answers (Complete Solutions)
Document Content and Description Below
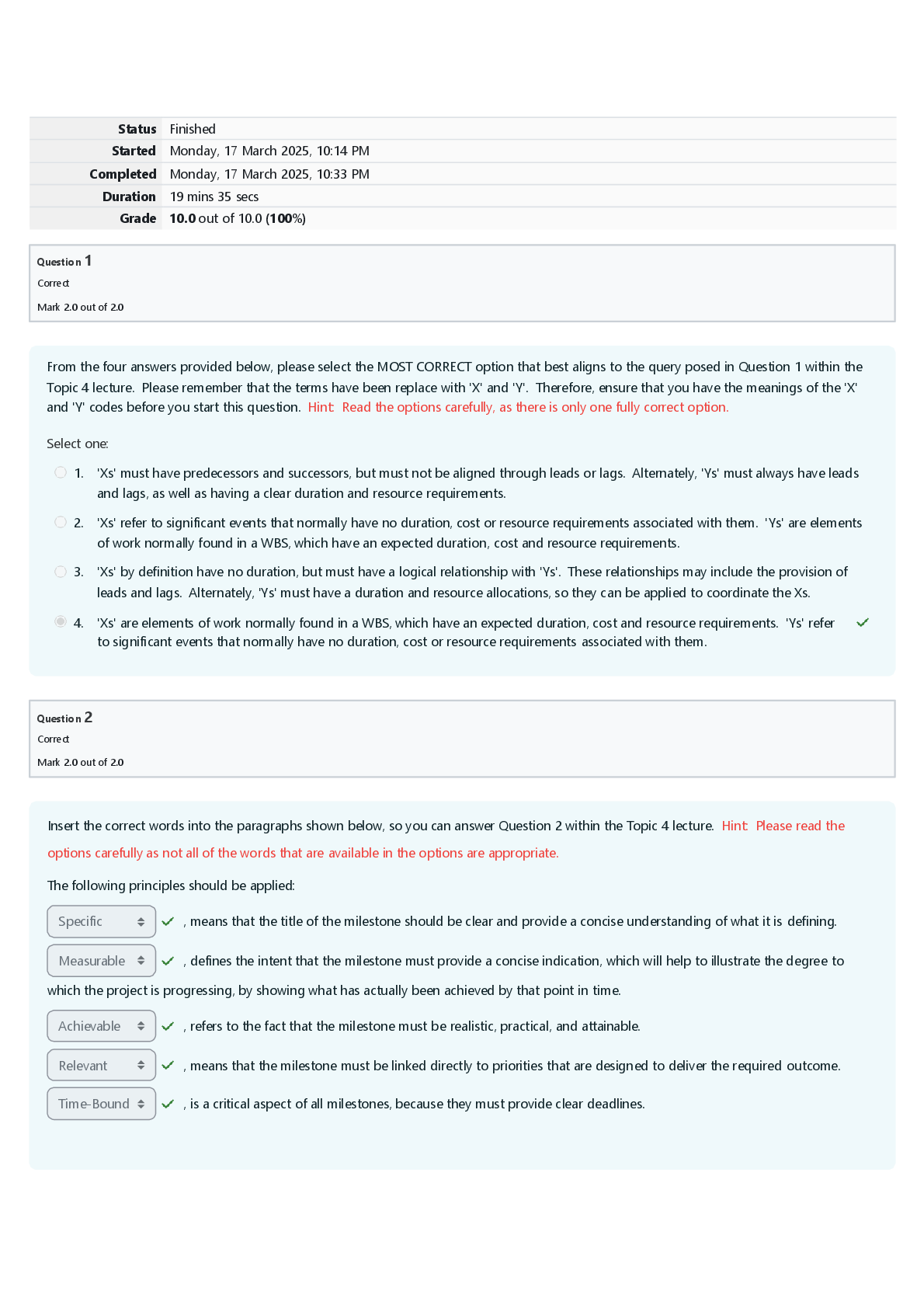
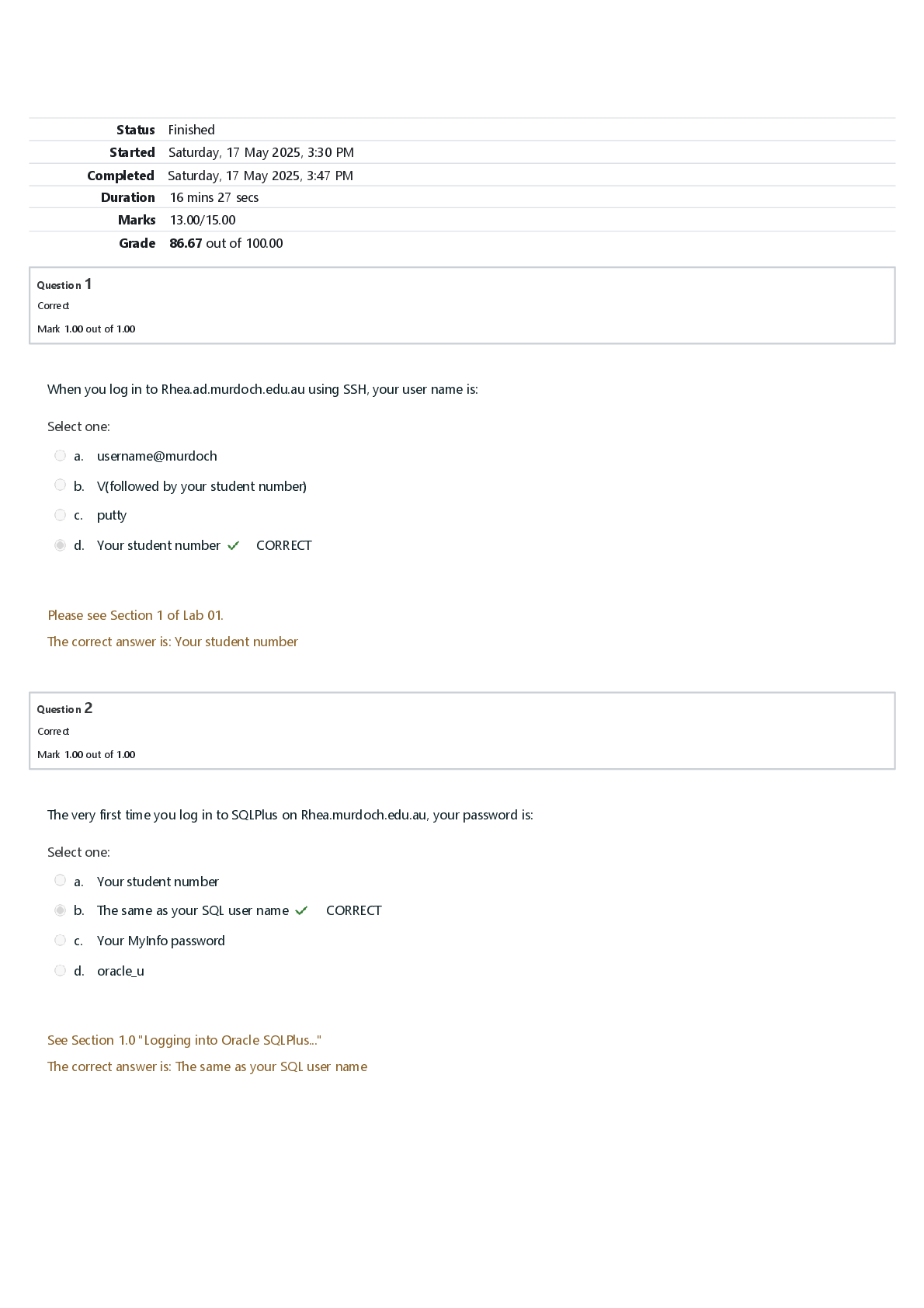
Hematology Quiz | Questions and Answers (Complete Solutions) A client with cirrhosis of the liver has a prolonged prothrombin time and a low platelet count. A regular diet is prescribed. What should ... the nurse instruct the client to do considering the client's condition? A) Avoid foods high in phytonadione. B) Check the pulse several times a day. C) Drink a glass of milk when taking aspirin. D) Report signs of bleeding no matter how slight. An adolescent who has sickle cell anemia is recovering from a painful episode. What does the nurse see as the priority issue for this adolescent? A) Restriction of movement during periods of arthralgia B) Separation from family during periods of hospitalization C) Alteration in body image resulting from skeletal deformities D) Interruption of education as a result of multiple hospitalizations The mother of a 13-year-old child with sickle cell anemia tells the nurse that the family is going camping by a lake this summer. She asks what activities are appropriate for her child. Which activity should the nurse suggest? A) Swimming in the lake B) Soccer with the family C) Climbing the mountain trails D) Motorboat rides around the lake A 13-year-old child with sickle cell anemia is experiencing a painful episode (vaso-occlusive crisis). The nurse assesses the child, obtains the child's vital signs, and reviews the child's laboratory test results. What is the priority nursing intervention? A) Providing oxygen therapy B) Administering an analgesic C) Initiating a blood transfusion D) Monitoring intravenous fluids (The pain experienced by the vaso-occlusive crisis is caused by sickle-shaped red blood cells that block blood flow through tiny blood vessels to the chest, abdomen, joints, and bones. Pain management is priority. If the client has evidence of hypoxia, then oxygen should be administered. Although a blood transfusion may be needed to treat the anemia and intravenous fluid reduce the viscosity of the sickled blood, it will not immediately relieve the pain.) An adolescent is admitted with an acute hemophilia episode. For what are rest, ice, compression, and elevation most helpful? A) Encouraging immobilization B) Decreasing swelling and inflammation C) Providing pain relief and reducing anxiety D) Controlling bleeding and retaining joint function (Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) therapy is implemented to support joints and prevent bleeding into joints. Reducing inflammation is not the goal of treatment for the hemophiliac process. Total immobilization is not required. Pain may be relieved to some degree but is not assured.) During a yearly physical examination a complete blood count (CBC) is performed to determine a client's hematologic status. Which laboratory result will the nurse check? A) Blood glucose B) Hemoglobin (Hb) C) C-reactive protein D) Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) (A CBC includes red blood cell (RBC) count and RBC indices, white blood cell (WBC) count and WBC differential count, Hb, hematocrit (Hct), and platelet count. A blood glucose level is not part of a CBC. The C-reactive protein level is not part of a CBC. BUN is not part of a CBC.) A client is admitted with thrombocytopenia. Which specific nursing actions are appropriate to include in the plan of care for this client? Select all that apply. A) Avoid intramuscular injections B) Institute neutropenic precautions C) Monitor the white blood cell count D) Administer prescribed anticoagulants E) Examine the skin for ecchymotic areas (Intramuscular injections should be avoided because of the increased risk of bleeding and possible hematoma formation. Decreased platelets increase the risk of bleeding, which leads to ecchymoses. Neutropenic precautions are for clients with decreased white blood cells (WBCs), not platelets. Thrombocytopenia refers to decreased platelets, not WBCs. Anticoagulants are contraindicated because of the increased bleeding risk.) A client is seen in the clinic with sickle cell crisis. Which hemoglobin range will the nurse expect to find? A) 6-8 g/100 mL (60-80 mmol/L) B) 10-12 g/100 mL (100-120 mmol/L) C) 12-14 g/100 mL (120-140 mmol/L) D) 16-18 g/100 mL (160-180 mmol/L) (In sickle cell crisis, hemoglobin values are low, usually in the 6-8 g/100 mL (60-80 mmol/L) range showing many sickle-shaped cells, and the client also will have a low oxygen level. A level of 10-12 g/100 mL (100-120 mmol/L) is too high. A range of 12-14 g/100 mL (120-140 mmol/L) is a normal finding. 16-18 g/100 mL (160-180 mmol/L) may be indicative of dehydration rather than anemia.) A client is seen in the clinic with sickle cell anemia. A nurse teaches the client about sickle cell anemia. Which information from the client indicates a correct understanding of the condition? A) "I have abnormal platelets." B) "I have abnormal hemoglobin." C) "I have abnormal hematocrit." D) "I have abnormal white blood cells." (The client with sickle cell anemia has abnormal hemoglobin, hemoglobin S, causing the red blood cells to stiffen and elongate into a sickle. While it can affect hematocrit, it is really a result of the abnormal hemoglobin. The disorder affects hemoglobin rather than platelets or white blood cells.) A client has been experiencing extreme fatigue lately. The nurse suspects anemia and examines the client to identify additional clinical manifestations to support this inference. Which locations on the client's body should the nurse assess? Select all that apply. A) Sclera B) Nail beds C) Conjunctivae D) Palms of hands E) Bony prominences (Nail beds lose their pink coloration because of reduced hemoglobin. A reduced amount of hemoglobin decreases pink color of the lining of the eyelids (conjunctiva). Palms of the hands will become pale because of the decreased hemoglobin. Sclera is observed for signs of jaundice, not anemia, when they become pale yellow to orange. Bony prominences are not assessed when a client has anemia. Bony prominences are examined for redness caused by pressure that, if prolonged, can lead to a break in the skin and development of pressure ulcers.) A 78-year-old client comes to the health clinic presenting with fatigue. The client's laboratory results indicate a hematocrit of 32.1% and a hemoglobin of 10.5 g/dL (105 mmol/L). Which is the most appropriate nursing intervention in response to these laboratory results? A) Conduct a complete nutritional assessment of the client B) Nothing, because these are expected values for this client's age C) Advise the client to come back to the clinic to have the test repeated in three months D) Investigate the cause of the anemia while understanding that mild anemia is an expected response to the aging process (A nutritional assessment starts the investigation for a cause of the client's anemia and is an independent function of the nurse. These are not expected values; an intervention is indicated. Medical treatment should be initiated first, and then the test should be repeated to determine the client's response to therapy; it is not within the legal function of the nurse to give medical advice. Anemia is not an expected response to the aging process.) A client is receiving warfarin. The nurse explains the need for careful regulation of dietary intake of vitamin K. What is the rationale for the nurse's teaching? A) Vitamin K promotes platelet aggregation. B) Vitamin K promotes ionization of blood calcium. C) Vitamin K promotes fibrinogen formation by the liver. D) Vitamin K promotes prothrombin formation by the liver. (Vitamin K promotes the liver's synthesis of prothrombin, an important blood clotting factor, and will reverse the effects of warfarin. Platelet aggregation and fibrinogen formation by the liver are not promoted by vitamin K. Vitamin K does not affect calcium ionization.) The student nurse demonstrates correct understanding of anemia related to chronic disease with which statement? A) "Red blood cells appear normal in size and color; however, there is a decreased amount produced." B) "The red blood cells have an increased life span with a decrease in normal functioning." C) "Administration of vitamins B 12 and folate will help to treat this type of long-term anemia." D) "This is the mildest form of anemia and is easily corrected through administration of blood products." (Anemia of chronic disease results in a decrease in the production of red blood cells (RBCs) in response to chronic inflammation; the red blood cells are normal size, shape, and color. There is a decrease in the life span of the RBC, and the administration of folate or B 12 will not correct the anemia, as these levels are generally within normal limits. This form of anemia can be very severe, and treatment is directed at identification and management of the underlying cause.) A client is admitted with a higher than expected red blood cell (RBC) count. What physiologic alteration does the nurse expect will result from this clinical finding? A) Increased serum pH B) Decreased hematocrit C) Increased blood viscosity D) Decreased immune response (Viscosity, a measure of a fluid's internal resistance to flow, is increased as the number of red blood cells suspended in plasma increases. The number of cells does not affect the blood pH. The hematocrit will be higher. RBCs do not affect immunity.) The nurse is caring for a client with iron deficiency anemia that has decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit levels. The nurse expects to identify what other abnormal laboratory level? A) Macrocytic red blood cells (RBCs) B) Thrombocytopenia C) Decreased folate levels D) Increased total iron-binding capacity (TIBC) (TIBC may be elevated from 350 to 500 mcg/dL (82 μmol/L) (expected range is 250 to 460 mcg/dL [45-82 mcmol/L]) because the RBCs are compensating for the iron deficiency. The RBCs are microcytic, not macrocytic, because of their low iron content. A low platelet count is not associated with iron deficiency anemia. Decreased folate levels often are noted in vitamin B 12 anemias, such as occur with sprue and celiac diseases, as well as in folate deficiency anemia, but not in iron deficiency anemia.) A client is started on a continuous infusion of heparin. Which finding does the nurse use to conclude that the intervention is therapeutic? A) International normalized ratio (INR) is between 2 and 3 B) Prothrombin time (PT) is 2.5 times the control value C) Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) is double the control value D) Activated clotting time (ACT) is in the range of 70 to 120 (Activated partial thromboplastin time should be 1.5 to 2.5 for the control of heparin therapy. INR and PT are used to evaluate therapeutic levels of warfarin. The ACT increases to a range of 150 to 200 when heparin reaches therapeutic levels.) A child has been diagnosed with hemophilia type A after experiencing excessive bleeding from a minor trauma. The parents ask how this could happen in addition to many other questions. Hemophilia A is linked to a deficiency in what? A) Factor II B) Factor III C) Factor IX D) Factor VIII (Hemophilia type A, which is the most common type of hemophilia, is from a deficiency of Factor VIII. Factors II and III are distractors. Factor IX is associated with hemophilia type B.) The nurse is making rounds on a client who has developed severe bone marrow depression after receiving chemotherapy for cancer. Which of these actions by the nurse is appropriate? Select all that apply. A) Monitor for signs of alopecia. B) Encourage an increase in fluids. C) Wash hands before entering the client's room. D) Advise use of a soft toothbrush for oral hygiene. E) Report an elevation in temperature immediately. F) Encourage the client to eat raw, fresh fruits and vegetables. (It is essential to prevent infection in a client with severe bone marrow depression; thorough hand-washing before touching the client or client's belongings is important. Thrombocytopenia occurs with most chemotherapy treatment programs; using a soft toothbrush helps prevent bleeding gums. Any temperature elevation in a client with neutropenia must be reported to the primary healthcare provider immediately because it may be a sign of infection. Although alopecia does occur with chemotherapy, it is not related to bone marrow suppression. Increasing fluids will neither reverse bone marrow suppression nor stimulate hematopoiesis. This is not related to bone marrow suppression. Clients who have severe bone marrow depression must avoid eating raw fruits and vegetables and undercooked meat, eggs, and fish to prevent possible exposure to microbes.) A client who is in hypovolemic shock has a hematocrit value of 25%. What does the nurse anticipate that the primary healthcare provider will prescribe? A) Lactated Ringer solution B) Serum albumin C) Blood replacement D) High molecular dextran (Blood replacement is needed to increase the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood; the expected hematocrit for women is 37% to 47% and for men is 42% to 52%. Lactated Ringer solution does not increase the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. Serum albumin helps maintain volume but does not affect the hematocrit level. Although dextran does expand blood volume, it decreases the hematocrit because it does not replace red blood cells.) A client develops iron-deficiency anemia. Which of the client's laboratory test results should the nurse expect to be decreased? A) Ferritin level B) Platelet count C) White blood cell count D) Total iron-binding capacity (Ferritin, a form of stored iron, is reduced with iron-deficiency anemia. Platelets will be within the expected range or increased with iron-deficiency anemia. Red, not white, blood cells are decreased with iron-deficiency anemia. Total iron-binding capacity will be increased with iron-deficiency anemia.) A client is diagnosed with pancytopenia caused by chemotherapy. What should a nurse teach the client about this complication? A) Begin a program of meticulous mouth care. B) Avoid traumatic injury and exposure to infection. C) Increase oral fluid intake to at least 3 L/day. D) Report unusual muscle cramps or tingling sensations in the extremities. (Reduced platelets increase the likelihood of uncontrolled bleeding; reduced lymphocytes increase the susceptibility to infection. Beginning a program of meticulous mouth care is helpful for stomatitis, not pancytopenia; aggressive oral hygiene may precipitate bleeding from the gums. Although fluids may be increased to flush out the toxic byproducts of chemotherapy, this will have no effect on pancytopenia. Unusual muscle cramps or tingling sensations in the extremities are signs of hypocalcemia and do not apply to pancytopenia.) A child has been diagnosed with hemophilia type A after experiencing excessive bleeding from a minor trauma. The parents ask what symptoms of bleeding they should be looking for in the future. What symptoms should the nurse list? Select all that apply. A) Epistaxis B) Hematuria C) Hemarthrosis D) Easy bruising E) Frequent fevers F) Fast clotting of injuries G) Dark-colored tarry stools (Epistaxis, also known as nosebleeds, is a common symptom of a lack of clotting factor. Hematuria (blood in the urine) may be grossly apparent. The child may experience joint pain and deformities from bleeding into joints. Excessive bruising will occur from bleeding into tissue with seemingly minor injuries. Dark-colored tarry consistency stools are indicative of gastrointestinal bleeding. Frequent fevers are not associated with hemophilia. Prolonged clotting times occur with this condition.) The laboratory values of a client with a new diagnosis of cancer of the esophagus include a hemoglobin of 7 g/dL (70 mmol/L), hematocrit of 25%, and red blood cell (RBC) count of 2.5 million/mm 3 (2.5 X 10 12/L). Which priority goal should the nurse add to the plan of care? A) The client will be free of injury. B) The client will remain pain free. C) The client will demonstrate improved nutrition. D) The client will maintain effective airway clearance. (Based on the presented data, improving nutritional status is the priority at this time. The decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit levels and RBC count may be a result of malnutrition; also, cancer of the esophagus can cause dysphagia and anorexia. Although maintaining the client's safety is a goal, it is not as high a priority as another concern based on the data provided in the question. The data given do not relate to the presence of pain. The data given do not relate to airway obstruction.) A client had part of the ileum surgically removed. The nurse monitors the client closely for anemia. What is the rationale for the nurse's action? A) Folic acid is absorbed in the ileum. B) Cobalamin is absorbed in the ileum. C) Iron absorption is dependent on simultaneous bile salt absorption in the ileum. D) Copper, cobalt, and nickel are dependent on simultaneous bile salt absorption in the ileum. (Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) combines with intrinsic factor, a substance secreted by the parietal cells of the gastric mucosa, and is absorbed in the ileum. Cobalamin is needed to make red blood cells. Folic acid and iron are not absorbed. Copper, cobalt, and nickel are not absorbed in the ileum.) The nurse assesses a client for the development of pernicious anemia after reviewing the client's history. Which condition did the nurse most likely find in the history? A) Acute gastritis B) Diabetes mellitus C) Partial gastrectomy D) Unhealthy dietary habits (Removal of the fundus of the stomach (gastrectomy) destroys the parietal cells that secrete intrinsic factor (needed to combine with vitamin B 12 preliminary to its absorption in the ileum). Hemorrhaging may cause anemia; however, pernicious anemia occurs when the intrinsic factor is not produced. The beta cells of the pancreas are not involved in secretion of intrinsic factor. Dietary intake does not affect the production of intrinsic factor.) A client with cancer develops pancytopenia during the course of chemotherapy. The client asks the nurse why this has occurred. What explanation will the nurse provide? A) Steroid hormones have a depressant effect on the spleen and bone marrow. B) Lymph node activity is depressed by radiation therapy used before chemotherapy. C) Noncancerous cells also are susceptible to the effects of chemotherapeutic drugs. D) Dehydration caused by nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea results in hemoconcentration. (Chemotherapy destroys erythrocytes, white blood cells, and platelets indiscriminately along with the neoplastic cells because these are all rapidly dividing cells that are vulnerable to the effects of chemotherapy. Stating that steroid hormones have a depressant effect on the spleen and bone marrow is not a true description of the side effects of steroids. Depressed lymph node activity as a result of radiation therapy used before chemotherapy is not the cause for fewer erythrocytes, white blood cells, and platelets. Although it is true that dehydration caused by nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea results in hemoconcentration, this does not explain pancytopenia.) A nurse provides teaching regarding vitamin B 12 injections to a client with pernicious anemia. What statement by the client indicates that teaching was understood? A) "I must take this monthly for the rest of my life." B) "I should take this vitamin, as needed, when feeling fatigued." C) "Once my symptoms subside, I can stop taking this vitamin." D) "I need to have this available for use during exacerbations of anemia." (Because the intrinsic factor does not return to gastric secretions even with therapy, B 12 injections will be required for the remainder of the client's life. Vitamin B 12 must be taken on a regular basis for the rest of the client's life.) A client with a diagnosis of anemia is receiving packed red blood cells. What is the most important action by the nurse when administering the transfusion? A) Warning the client about the possibility of fluid overload B) Monitoring the client's response, particularly within the first 10 minutes C) Adjusting the client's transfusion flow rate so that it infuses at a consistent rate during the procedure D) Having the client tested for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) before administering the blood transfusion (Transfusion reactions usually occur early during the administration of a blood transfusion (first 30 mL of blood); early detection of a transfusion reaction will permit a quick termination of the infusion. The risk of fluid overload is unlikely, and this information can be frightening. The donor's, not the recipient's, blood is tested for HIV. The flow rate should be slower during the first 10 to 15 minutes of the infusion to limit [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 5 out of 21 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 07, 2024
Number of pages
21
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 07, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
46