Engineering > EXAM > STS 322 Midterm Exam | Questions and Answers (All)
STS 322 Midterm Exam | Questions and Answers
Document Content and Description Below
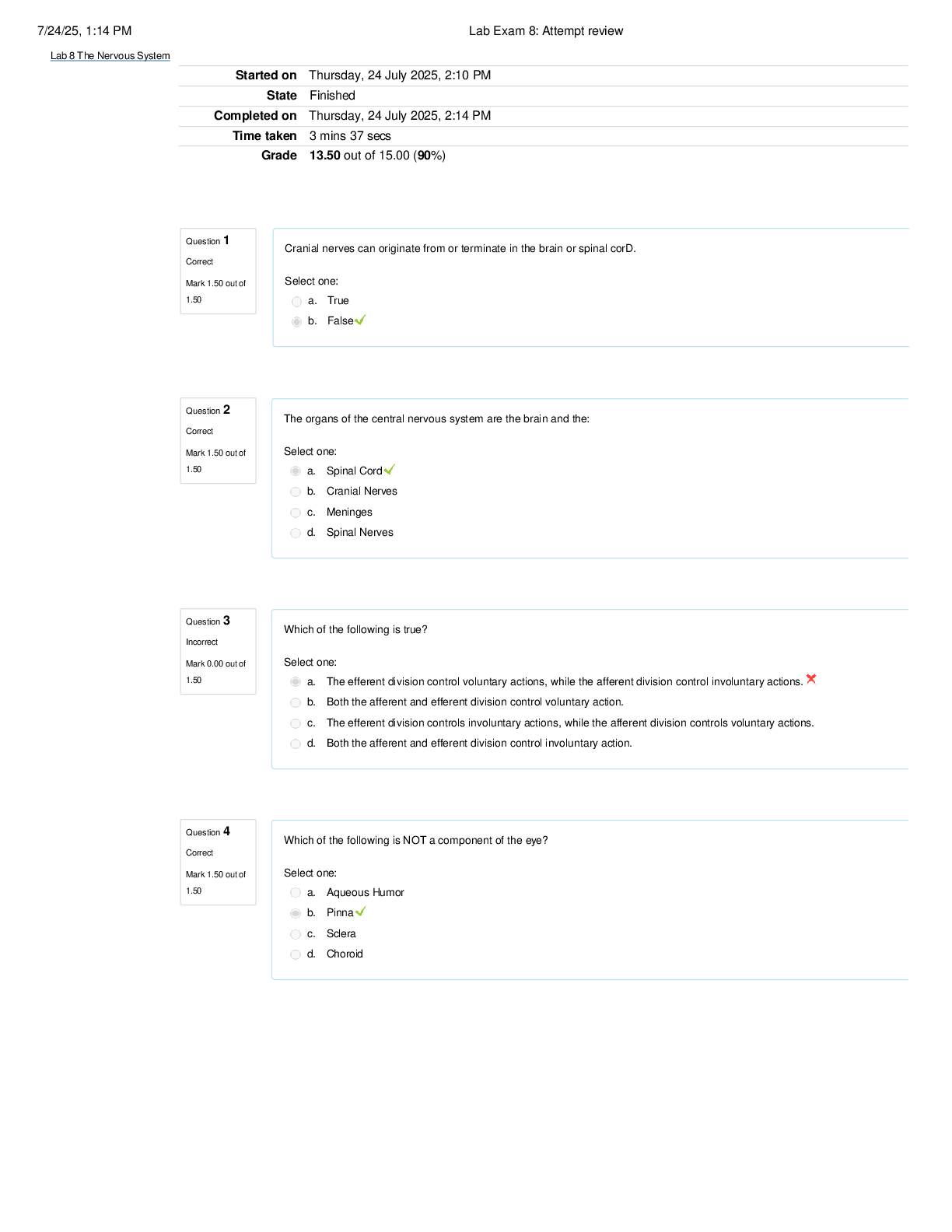
STS 322 Midterm Exam | Questions and Answers What was the first in a series of events that contributed to the Three Mile Island (TMI) nuclear power plant accident? a) a routine maintenance operation ... , the changing of water in a system of pipes b) production of radioactive waste c) an order from an official with the Tennessee Valley Authority d) clouds of radioactive material e) none of the above Was the cause of TMI human or mechanical error? a) human b) mechanical c) both human and mechanical d) human agents of a hostile foreign country e) none of the above What was a major contributing factor or what were major contributing factors to the radioactive waste spill from the Tsuruga nuclear power plant in Fukui, Japan? a) plan worker failed to notice open valve b) faulty valve-closure indicator light c) both a and b d) neither a nor b e) none of the above Japan changed the role of nuclear power in its energy equation as a result of the Tsuruga spill True False What uncommon type of nuclear reactor, which has been described as inherently risky to operate as a commercial power source, was a major contributing factor to the seriousness of the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant? a) RBMK b) PWR c) PPK d) IAEA e) none of the above What was a positive outcome of the Chernobyl accident in Russia? a) reactor modification b) country abandoned nuclear power c) OSHA d) NRC e) none of the above ________ ________ ________ was ________ during the Bhopal accident? methyl, isocyanate, vapor, released What was a positive outcome of the Bhopal vapor leak? a. Improved concrete b. Inquiry into accident's causes c. Special chemical compounds d. All of the above e. None of the above What was a contributing factor or what were contributing factors in the sinking of the Titanic and the seriousness of the event? a. April is one of the worst months for icebergs b. Lookouts were working without binoculars, which were supposed to be standard c. There were only enough lifeboats and jackets for roughly half the passengers d. All of the above e. None of the above ________ was a major contributing factor or to the Andrea Doria-Stockholm collision off the coast of Massachusetts. Fog What was the most likely cause of the sinking of the submarine Thresher? a. Enemy attack at depth b. Failure to reduce speed to avoid collision with seamount c. Cracked fitting or faulty joint in a cooling pipe d. All of the above e. None of the above What was a positive outcome of the sinking of the submarine Squalus? a. Double-hulled retrofit b. Proven viability of McCann rescue chamber c. Improved rudder design d. Proven viability of the Nautilus e. None of the above The ________ ________ ________ was the safety organization that was formed as a result of the Titanic sinking International Ice Patrol What were some of the regulations that were adopted as a result of the Titanic sinking? a. Ships encountering ice fields had to come about and return to the port of embarkation b. Ships' crew members had to hide below deck c. Ships approaching ice fields were required to slow down or alter their course d. Ships crew members were required to hang warning signs off the sterns e. None of the above What was the definitive cause of the sinking of the submarine Scorpion? a. Could not be ascertained from the evidence then available b. Single- hulled design c. Steering system failure d. All of the above e. None of the above What rescue craft was developed, in part, due to the sinking of the Scorpion? a. AZ-2 b. LL-CJ c. A-1 d. NR-1 e. None of the above Clear- cutting timber was an action in the open-roast smelting process that negatively affected the ecosystem in Sudbury, Ontario. True False What was a positive outcome of the Sudbury ecological disaster? a. Mining companies compelled to clean exhaust from smelters b. Mining industry apologized c. Mining industry fined d. Recovery of toxic meteorite e. None of the above What was a toxic gas released during the open roasts at Sudbury? a. Methyl isocyanate b. Sodium hexametaphosphate c. Thiamine mononitrate d. Ammonium bicarbonate e. Sulfur dioxide What was a major contributing factor to the Love Canal contamination incident in Niagara Falls, New York? a. Community built on a toxic waste dump b. Contaminated meteorite c. Naturally occurring chemical compounds d. Military munitions e. None of the above What was a positive outcome of the Love Canal contamination incident in Niagara Falls, New York? a. Chemical industry personally apologized to each individual involved b. Chemical industry accepted complete liability c. Chemical industry donated billions of dollars to the Sierra Club d. Chemical industry began recycling much of its waste e. None of the above What was the direct cause of the mercury poisoning that came to be known as Minamata disease? a. A large mercury-laden meteorite that crashed in Japan during the 1940s b. Naturally occurring mercury deposits c. Leftover contamination from military weapons testing d. Eating raw fish and shellfish that had absorbed organic mercury e. None of the above Agent Orange is what type of agent? a. Herbicide b. Insecticide c. Pesticide d. Fungiside e. None of the above What was an improper management decision or what were improper management decisions concerning Agent Orange use in Vietnam? a. Military personnel did not read the labels on barrels of the agent concerning spraying b. Concentration was much higher than recommended by military's own manual c. Areas were sprayed too frequently, dramatically increasing exposure risk d. Both b and c e. None of the above What was the cause of methylmercury poisoning of the seed grain in Iraq? a. A large methylmercury-laden meteorite that crashed in Iraq in the 1960s b. Fungicide treatment c. Herbicide treatment d. Pesticide treatment e. None of the above What was a positive outcome of the Iraq methylmercury poisoning in the United States? a. All alkylmercury seed dressings banned b. Methylmercury seed dressing production increased c. Special chemical treatments developed to neutralize methylmercury d. All of the above e. None of the above What was a positive outcome or what were positive outcomes of the Exxon Valdez oil spill? a. Oil Pollution Protection Act b. Petroleum Industry Response Organization c. Breath alcohol tests for tanker captains d. All of the above e. None of the above In addition to significant evidence that the captain of the Valdez, Joseph Hazelwood, was allegedly intoxicated and lacked sleep, what was a major technological failure that greatly contributed to the amount of oil spilled? a. Faulty sextants b. Single-hulled design c. Rudder failure d. Electrical problems e. Hydraulic failure Including the Valdez spill, how many oil spills of more than ten million gallons were there worldwide from 1978 to 1990? a. 26 b. 2 c. 5 d. 12 e. None of the above [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 4 out of 11 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$13.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 19, 2024
Number of pages
11
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 19, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
30