Nutrition > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Quiz: Basic Concepts of Cellular Transport and Signaling: NUTR641: Nutritional Biochemistry I (D01) (All)
Quiz: Basic Concepts of Cellular Transport and Signaling: NUTR641: Nutritional Biochemistry I (D01)
Document Content and Description Below
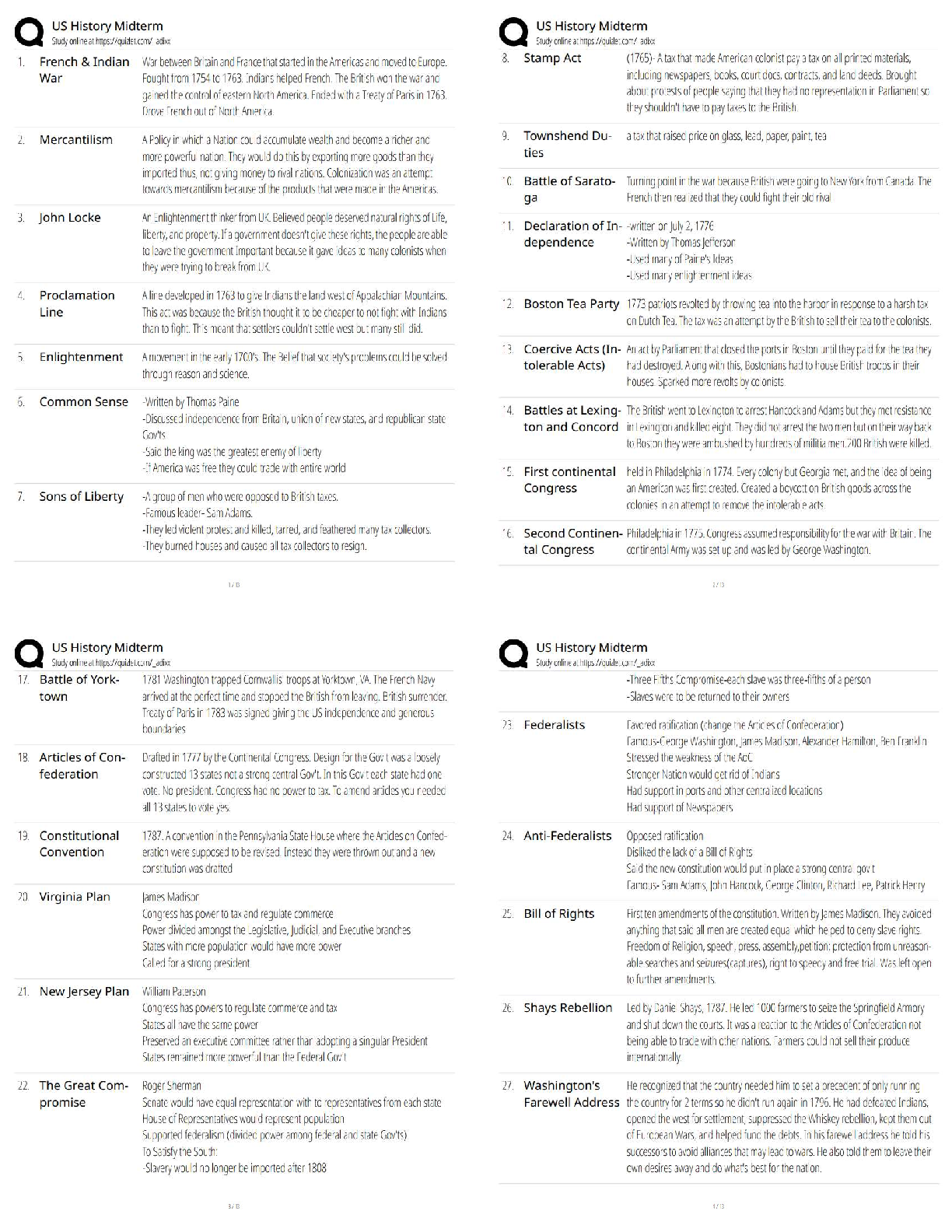
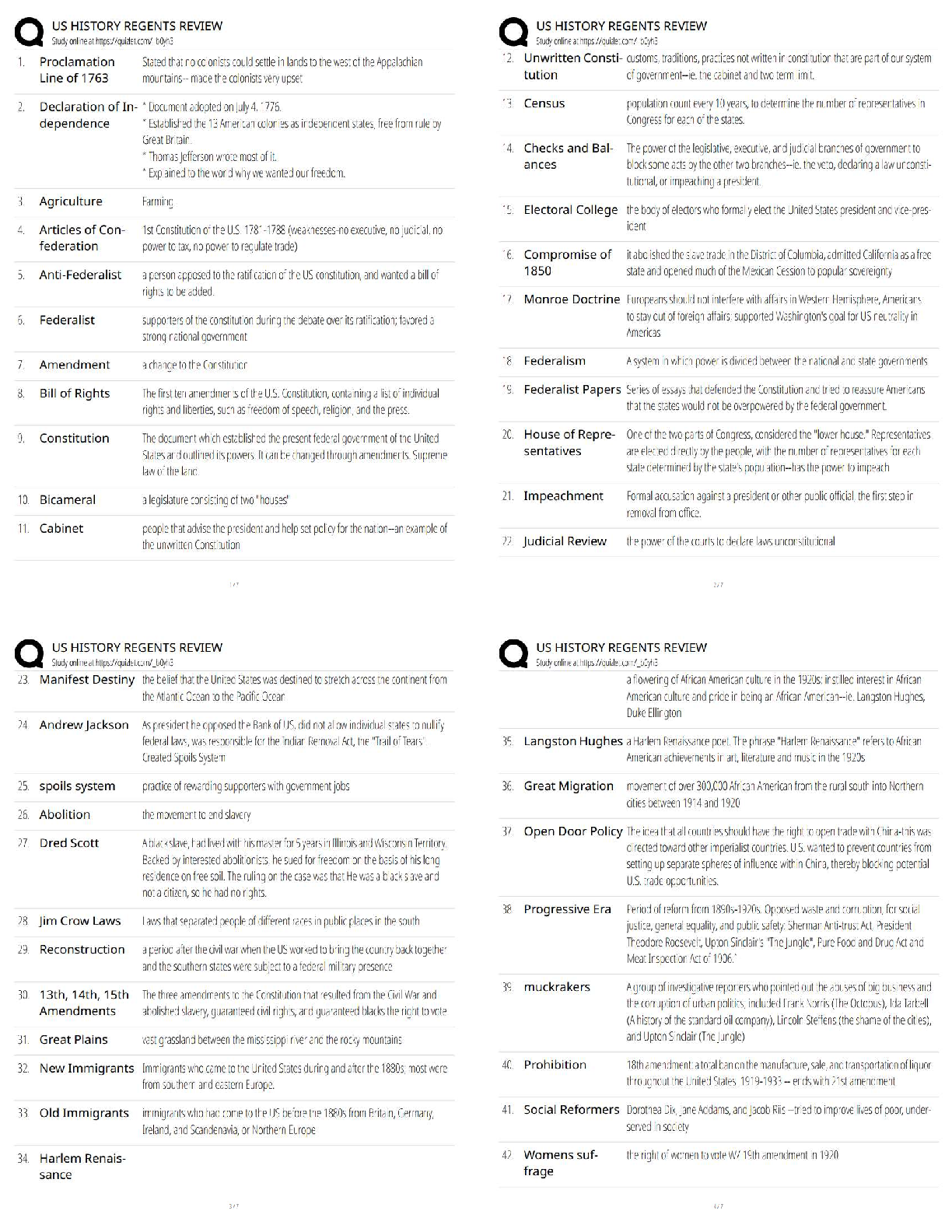
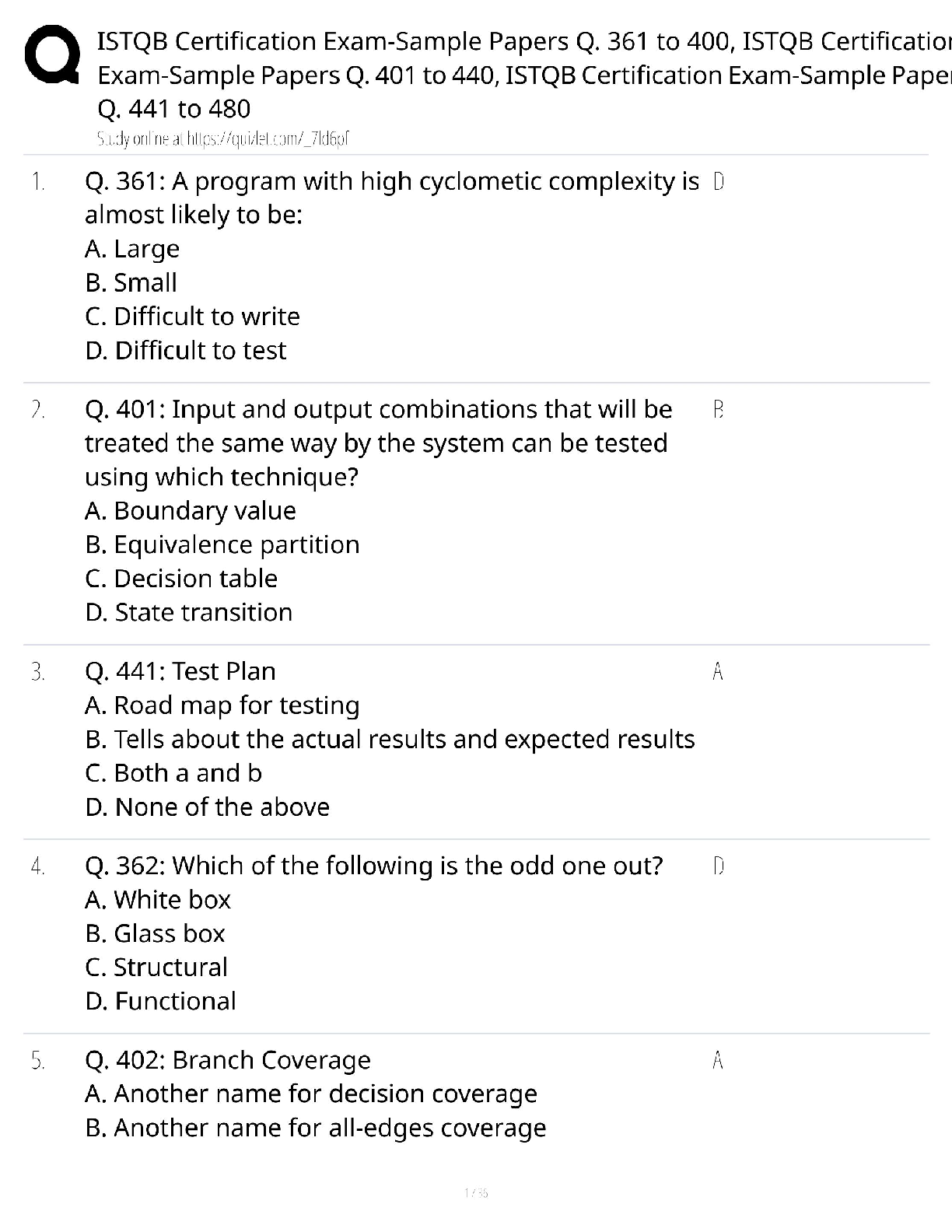
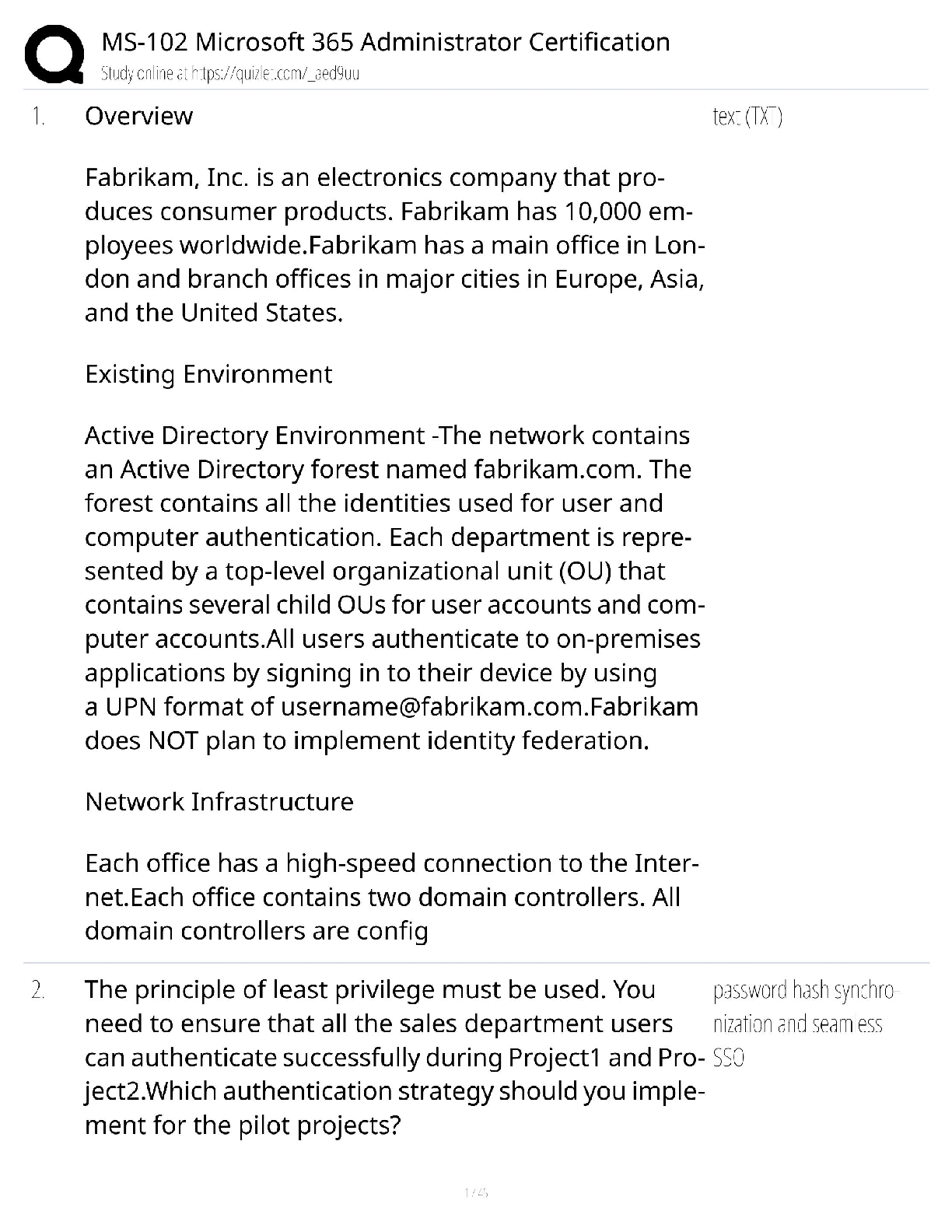
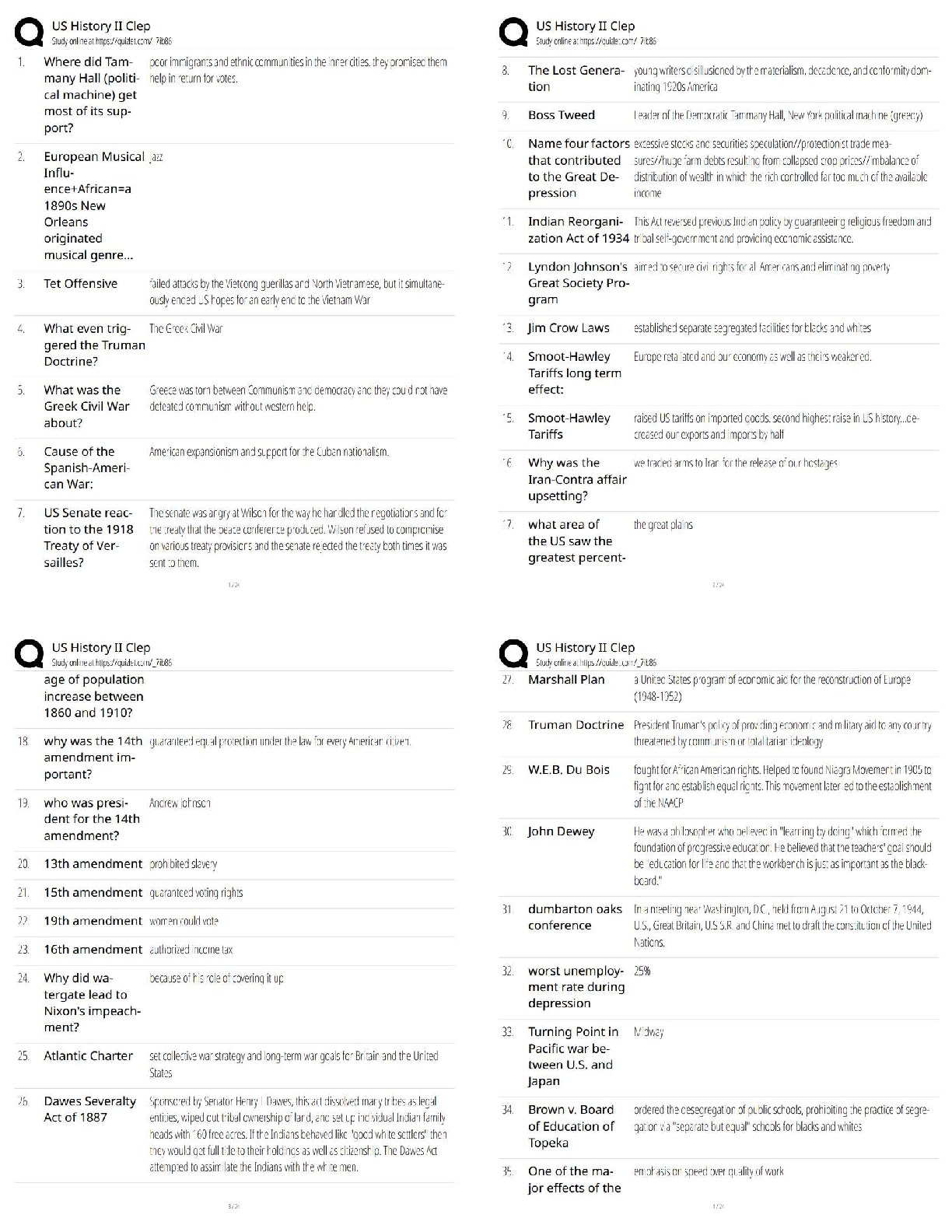
Quiz: Basic Concepts of Cellular Transport and Signaling: NUTR641: Nutritional Biochemistry I (D01) Quiz: Basic Concepts of Cellular Transport and Signaling Score for this attempt: 80 out of 80 ... Q uestion 1 2 / 2 pts regulatory subunits; two active monomers and two inactive monomers active subunits; two active monomers and an inactive dimer regulatory subunits; an active dimer and two inactive monomers active subunits; an active dimer and two inactive monomers regulatory subunits; two active monomers and an inactive dimer Q uestion 2 2 / 2 pts α1-adrenergic calmodulin β2-adrenergic insulin cortisol Q uestion 3 2 / 2 pts The quiz: Covers the Textbook material from Module 8: Week 8. Contains 35 multiple-choice and 2 short answer questions. Is limited to 1 hour and 30 minutes. Allows 2 attempts. Is worth 80 points. Submit this assignment by 11:59 p.m. (ET) on Friday of Module 8: Week 8. TAKE THE QUIZ AGAIN cAMP binds to the ________ subunits of protein kinase A allowing the tetramer to dissociate into ________. The ________ receptor is a receptor tyrosine kinase. Ile Leu Phe Val Asn Q uestion 4 2 / 2 pts III only I, II, III, IV II, III, IV II, III I, II Q uestion 5 2 / 2 pts selective removal of acyl chains from membrane phospholipids allows the bilayer to bow outward the composition of the two membranes has no effect upon the rate of fusion addition of triacylglycerols to the membrane allows the bilayer to bow inward SNARE complexes dissociate to allow membrane fusion to occur none of the above Q uestion 6 2 / 2 pts II only I, II, and III III only I only I and II Q uestion 7 2 / 2 pts adenosine Which amino acid in the aquaporin channel hydrogen bonds with water to prevent the movement of protons? Which of the following is (are) an advantage(s) of protein phosphorylation regarding biochemical signaling? I. Phosphorylation is rapid and specific. II. Phosphorylation is enzymatically reversible. III. Phosphorylation can be amplified by cascade systems. IV. Phosphorylation results in covalent modification of enzymes and proteins. Which of the following occurs during the fusion of a synaptic vesicle and cell membrane? The activity of protein kinase A is affected by which of the following? I. activated adenylate cyclase II. levels of cAMP III. phosphodiesterases Which of the following is a ligand of the β2-adrenergic receptor? tyrosine norepinephrine serotonin caffeine Q uestion 8 2 / 2 pts polypeptides steroids amino acid derivatives eicosanoids all of the above Q uestion 9 2 / 2 pts saturated transduced specific desensitized none of the above Q uestion 10 2 / 2 pts phospholipase C adenosine receptor cAMP phosphodiesterase the G protein γ subunit arrestin Q uestion 11 2 / 2 pts autophosphorylation antagonism cross-talk desensitization poor receptor-ligand specificity Q uestion 12 2 / 2 pts Which of the following can be a hormone? When a receptor loses its ability to transmit a signal following continuous exposure to a ligand, the receptor is said to be ________. Desensitization of a G protein-coupled receptor is caused by phosphorylation of the receptor by a specific kinase. What protein recognizes the phosphorylated receptor? The ability for some receptor tyrosine kinases to ultimately activate phospholipase C is an example of ________. Sos protein phosphoprotein phosphatase receptor tyrosine kinase guanine nucleotide exchange factor heterotrimeric G protein phosphorylase Q uestion 13 2 / 2 pts nuclear localization sequences transcription factors hormone response elements DNA-binding domains none of the above Q uestion 14 2 / 2 pts endoplasmic reticulum cytoplasm nucleus cell membrane mitochondria Q uestion 15 2 / 2 pts Na,K-ATPase; viral infections ABC transporter; cancer ABC transporter; bacterial infections Na,K-ATPase; parasitic infections none of the above Q uestion 16 2 / 2 pts uniporters peripheral membrane proteins signal transduction receptors integral membrane proteins none of the above is correct Which of the following functions as a regulatory protein by dephosphorylating activated enzymes? The complex formed between a lipid hormone and its receptor binds to ________ which are specific DNA sequences. Where are the ultimate targets of the Ras-dependent signaling cascade located within the cell? The P-glycoprotein is an example of a(n) ________ which has been linked to drug resistance in the treatment of ________. Integrins and aquaporins are examples of ________. Question 17 2 / 2 pts phosphorylation ligand binding voltage change pH change all of the above Q uestion 18 2 / 2 pts H+ Na+ ClK+ Ca2+ Q uestion 19 2 / 2 pts protein kinase G protein kinase A cAMP phosphodiesterase adenylate cyclase all of the above Q uestion 20 2 / 2 pts Binding of a hormone to a receptor must signal the exchange of GDP for GTP. Binding of GTP to the receptor protein must induce a change in conformation of the receptor. Binding of cAMP to the α subunit of the G protein must initiate translocation of the subunit. A cascade of events must occur that ultimately activates protein kinase C. All of the above are correct. Q uestion 21 2 / 2 pts antiporter uniporter symporter diporter none of the above Which of the following will cause the opening or closing of a gated ion channel? A sudden increase in the concentration of ________ causes the release of acetylcholine from the axon of a nerve cell. What enzyme is activated by association with an active G protein? Which of the following correctly states an essential step in the function of heterotrimeric G protein function? What is a transporter that moves two different molecules or ions in the same direction? Q uestion 22 2 / 2 pts G protein γ subunit calmodulin G protein β subunit G protein α subunit all of the above Q uestion 23 2 / 2 pts symporter; primary active transport uniporter; passive transport symporter; secondary active transport antiporter; secondary active transport uniporter; primary active transport Q uestion 24 2 / 2 pts antagonist agonist inside messenger second messenger G protein Q uestion 25 2 / 2 pts prior to membrane association, SNARE proteins are in an unfolded state formation of the SNARE complex is thermodynamically favorable, as is membrane fusion two proteins of the SNARE complex come from the membrane and one from the synaptic vesicle formation of a four-helix complex is critical for membrane association of the vesicle all of the above Q uestion 26 2 / 2 pts fever blood coagulation blood pressure inflammation Activity of the Ras protein is analogous to the ________ in terms of its ability to bind GTP. Transport of glucose from the intestine into the intestinal cells is accomplished by a(n) ________. This is an example of ________. A small molecule produced inside a cell in response to a hormone binding to its receptor is called a(n) ________. Which of the following is true regarding SNARE complex formation? Which of the following can be regulated by eicosanoids? all of the above Q uestion 27 2 / 2 pts epinephrine glucagon insulin cortisol platelet derived growth factor Q uestion 28 2 / 2 pts cGMP cAMP diacylglycerol inositol trisphosphate nitric oxide Q uestion 29 2 / 2 pts stearic acid α-linolenic acid linoleic acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) arachidonic acid Q uestion 30 2 / 2 pts GDP; β GTP; α GDP; α GTP; β GDP; γ Q uestion 31 2 / 2 pts reuptake of acetylcholine by the nerve cell Which of the following hormones is able to cross biological membranes and thus the receptor is found inside the cell, not on the cell surface? The second messenger ________ opens Ca2+ channels in the endoplasmic reticulum. The eicosanoids are derived from the membrane fatty acid ________. Activation of a G protein in response to hormone binding requires binding of ________ to the ________ subunit. Which of the following would be the first to occur following opening of Ca2+ channels during acetylcholine-mediated neurotransmission to a muscle cell? binding of acetylcholine to muscle cell receptors hydrolysis of acetylcholine by acetylcholinesterase release of acetylcholine by the nerve cell binding of SNARE complex to synaptic vesicles and pre-synaptic membrane Q uestion 32 2 / 2 pts acylation; activates methylation; hydrolyzes hydrolysis; inhibits phosphorylation; phosphorylates none of the above Q uestion 33 2 / 2 pts I, III, IV I, II, IV I only I, IV I, III Q uestion 34 2 / 2 pts II, III, IV I, II, III I, II, III, IV III, IV I, II Q uestion 35 2 / 2 pts cAMP; adenylate cyclase inositol diphosphate; phospholipase C Ligand binding to a receptor tyrosine kinase causes ________ of the receptor which then ________ the next protein in the signaling pathway. Heterotrimeric G proteins ________. I. consist of three subunits, Gα, Gβ, and Gγ II. function as an autoinhibtory segment III. can function as a mediator to adenylate cyclase activity IV. are anchored to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane Which of the following is (are) associated with cAMP binding to cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA)? I. cAMP binds to the regulatory subunits. II. PKA tetrameric regulatory subunits and catalytic subunits dissociate. III. Catalytic subunits phosphorylate multiple targets with specific serine and threonine residues. IV. cAMP is membrane bound via phosphoinositol attachment. The second messenger ________ is produced by the enzyme ________. cGMP; GTP cyclase triacylglycerol; phospholipase C nitric oxide; arginase Q uestion 36 5 / 5 pts Your Answer: Correct! Q uestion 37 5 / 5 pts Your Answer: Correct! Quiz Score: 80 out of 80 What are the principle features of the fluid mosaic model of membranes? Principle features of the fluid mosaic model of membrane: Fluidity: The lipid bilayer moves laterally within the layer, influenced by factors such as temperatures, types of lipids, and the presence of cholesterol. Lipid Bilayer: Mainly composed of phospholipids (hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails). Integral and Peripheral Protein: Integral proteins interact with the hydrophobic interior of the membrane. Peripheral proteins attach loosely to the membrane through interaction with integral proteins or lipid bilayer, and can also be involved in signaling pathways. Dynamic Nature: The dynamic movement is essential for membrane functions such as receptor-mediated endocytosis and cell signaling. What is an amphipathic compound? Explain how such compounds contribute to the structure of biological membranes. An amphipathic compound is a molecule that has hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions. Hydrophilic is (water-loving), hydrophobic (waterrepelling). The dual regions allow amphipathic compounds to interact with aqueous and nonpolar substances. This compound contributes to the formation of the lipid bilayer which is composed of phospholipids (hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails). The bilayer structure is when the phospholipids are arranged in a way that the hydrophilic heads are facing the water/polar side of the membrane, and the hydrophobic tails are facing inward, away from the water, forming the basic structure of the cell membrane. Integral Membrane proteins are also amphipathic and span the lipid bilayer. The lipid bilayer arrangement helps to anchor these proteins within the membrane, allowing them to perform transport, signaling, and enzymatic activity. Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 3 out of 9 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 20, 2024
Number of pages
9
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 20, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
45










 Summer 2022.png)