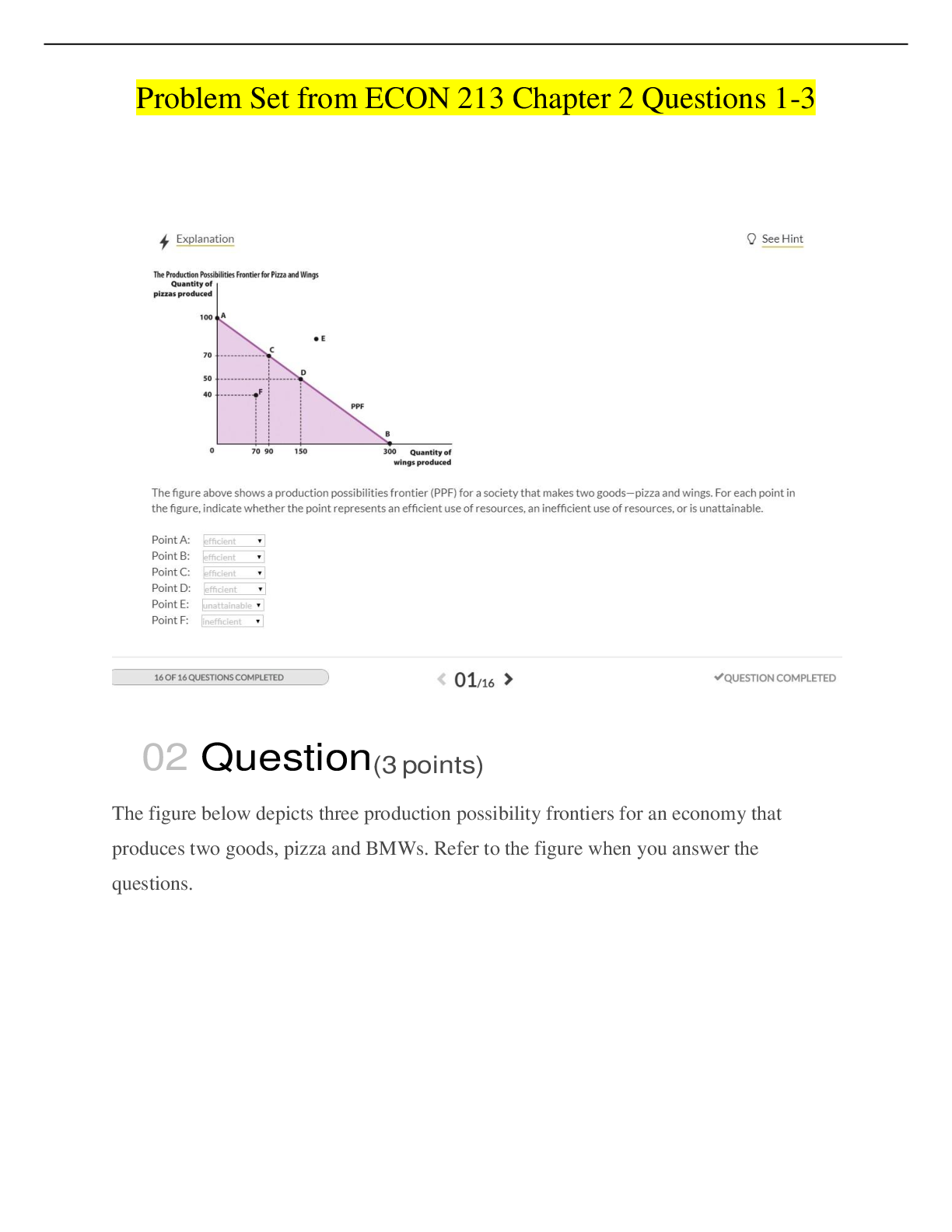
1. A 46-year-old woman complains of abrupt onset of her chest pounding.She is diagnosed with Bigeminy PVCs. Which of the following Class I agent listed below is the most effective agent for converting ventricular tachyca
...
1. A 46-year-old woman complains of abrupt onset of her chest pounding.She is diagnosed with Bigeminy PVCs. Which of the following Class I agent listed below is the most effective agent for converting ventricular tachycardia to normal sinus rhythm?
A. Lidocaine
B. Digoxin
C. Amiodarone
D. Flecainide
E. Adenosine
2. Which of the following characteristics is more associated with first generation (typical) antipsychotics, versus second generation (atypical) antipsychotics?
A. Mesolimbic area dopamine blockade
B. Low prolactin elevations
C. Improvement in executive functioning and cognition
D. Little to no risk of EPS
E. Treatment of negative symptoms
3. RB is a premenopausal caucasian female with a diagnosis of early stage invasive ductal carcinoma. Biopsy indicates the primary tumor is ER/PR(+) and negative for HER2 overexpression.Which of the following would be most appropriate therapy to initiate in RB?
A. Lapatinib 1000 mg PO daily
B. Letrozole 2.5 mg PO daily
C. Pertuzumab 840 mg IV every 3 weeks
D. Tamoxifen 20 mg PO daily
4. JT is a 58 year old female with a diagnosis of triple negative metastatic breast cancer. Her cancer is ER/PR(-) and negative for HER2 overexpression. Which of the following medications would be most appropriate to initiate in JT?
A. Docetaxel
B. Letrozole
C. Tamoxifen
D. Trastuzumab
5. Angela is a 54 year old African American female who presents to the diabetes management clinic with complaints of intermittent episodes of sudden onset fatigue and lightheadedness. She was diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes 12 years ago. She reports some problems with medication compliance because some of them make her feel really strange and sometimes even sick. She has an extreme fear of needles and absolutely refuses injecting herself. Her PCP feels like she is running out of options and elicits your help. She is 5’4 and weighs 223 Ibs.
Current medications: Metformin 1,000 mg BID, Januvia 100 mg daily, Farxiga 10 mg daily, amlodipine 10 mg daily
Labs
HbA1c
10.7% SCr
1.91
BG 245 Urinalysis
Glucose
(+)
Ketones
(-)
Albumin
(+)
BUN 41 GFR
26
BP
91/59 CrCl
21
Which antihyperglycemic medication may be contributing to Angela’s hypotension?
A. Farxiga
B. Metformin
C. Januvia
D. Insulin
6. Which of the following diluents can be used when preparing a phenytoing injection?
A. Normal Saline
B. D5W
C. Lactated ringers
D. D20W
E. Hypertonic saline
7. Which of the following are appropriate monitoring recommendations for people with diabetes?
A. Dilated eye exam annually
B. Comprehensive foot exam annually
C. Urine albumin test annually
D. A and B
E. A,B, and C
8. Which of the following are warnings associated with the use of erythropoietin stimulating agents? (Select all that apply)
A. Acute chest syndrome
B. MI
C. Stroke
D. Recurrence of tumors
E. VTE
9. How often should a person with diabetes have an HbA1C test?
A. Twice a year if her diabetes remains uncontrolled
B. Quarterly if her diabetes remains uncontrolled
C. Monthly if her diabetes remains uncontrolled
D. Annually if her diabetes is controlled
E. Every office visit
10. In the ER, a hispanic 39 year old male patient, DT continues to experience chest pain on exertion and with an increased heart rate. The following results are obtained: fasting lipid profile: total cholesterol 246 mg/dL, HDL 27 mg/dL, LDL=160, triglycerides 150 mg/dL fasting glucose 198 mg/dL; HbA1c: 8.5, Na=138, K=4.1, Hb=14, Hct=40, PLTs=320
Exercise treadmill test: positive for ischemic angina, HR=80, BP=165/99, Troponin negative, CK MB negative
EKG= ST-segment elevation DT is evaluated in the heart cath lab for any blockages. After the procedure, he is placed on an antiplatelet regimen for 6 months.
Which of the agents listed below inhibit platelet aggregation through the inhibition of P2Y12 receptor antagonists.
A. Eliquis
B. Abcixamab
C. Brilenta
D. Kcentra
E. Dabigatran
11. In the ER, a hispanic 39 year old male patient, DT continues to experience chest pain on exertion and with an increased heart rate. The following results are obtained: fasting lipid profile: total cholesterol 246 mg/dL, HDL 27 mg/dL, LDL=160, triglycerides 150 mg/dL fasting glucose 198 mg/dL; HbA1c: 8.5, Na=138, K=4.1, Hb=14, Hct=40, PLTs=320
Exercise treadmill test: positive for ischemic angina, HR=80, BP=165/99, Troponin negative, CK MB negative
EKG= ST-segment elevation DT is evaluated in the heart cath lab for any blockages. After the procedure, he is placed on an antiplatelet regimen for 6 months.
Which of the agents listed below have the ability to convert plasminogen to plasmin thus treating pts with STEMI or Acute MI in which clots form in the coronary arteries?
A. Argatroban
B. Bivalirudin
C. Dabigatran
D. Tenectaplase
E. Fondaparinux
12. JB is a 9-year-old who has been diagnosed with pneumonia. Which of the following are common in this age group?
A. Bordetella pertussis, Chlamydia pneumoniae
B. Streptococcus pneumoniae, mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia pneumoniae
C. E.Coli, GBS, Listeria monocytogenes
D. E.Coli, Streptococcus pneumoniae, mycoplasma pneumoniae
E. CMV, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Listeria monocytogenes
13. Which formulation contains 20% elemental Iron?
A. Ferrous Sulfate
B. Ferrous Fumarate
C. Ferrous Gluconate
D. Ferrous sulfate
E. Carbonyl Iron
14. Match the agents listed below with the most appropriate counseling tip. __1__Nexplanon __2__FC2 __3__Caya __4__Xulane __5__Mifepristone
A. Irregular menstrual bleeding (>10%)
B. Twist the outside ring before removal
C. Must remain in place for 6 hours after intercourse
D. Reapply if detached less than 24 hours and still sticky
E. Can disrupt an existing pregnancy
15. Match the following agents with their appropriate mechanism of action. __1__Teriparatide __2__Risedronate __3__Denosumab __4__Duavee
A. Stimulates osteoblast activity and calcium absorption/reabsorption similarly to parathyroid hormone
B. Inhibits the activity of osteoclasts, resulting in decreased bone resorption
C. Inhibits activation and formation of osteoclasts by blocking the activation of RANK by RANK-L
D. Estrogen agonist/antagonist on select tissue to maintain bone mineral density
16. K.S. is a 63-year-old Asian American male with a past medical history of depression, hypertension, and systemic lupus erythematosus. He has taken prednisone 20 mg daily for nine months, which has been monitored by a rheumatologist. However, his primary care physician is concerned about his bone health based on recent laboratory findings. Which of the following options is appropriate for the treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis?
A. Alendronate 5 mg tablet by mouth daily
B. Ibandronate 150 mg by mouth once monthly
C. Zoledronic acid 5 mg IV once yearly
D. Risedronate 35 mg by mouth once weekly
E. Teriparatide 20 mcg SQ once daily
17. You are on your community pharmacy APPE and a patient presents to the pharmacy requesting a Flu shot in the month of October. The patient has COPD and is 65 years old. The patient has never received a pneumonia shot. The patient should receive the PPSV 23 now, in addition to a high dose flu vaccine.
True
False
18. TJ is a 67-year-old man with COPD who is presenting to the family medicine clinic today to have a follow-up appointment. His last COPD exacerbation is the second hospital admission in the last 6 months related to TJ ‘s COPD instability. After TJ s hospitalization, his discharge COPD regimen was changed to include tiotropium, 1 inhalation daily in addition to salmeterol 50 mcg, 1 inhalation Q 12 h, and an albuterol MDI as needed. The patient states that his respiratory symptoms are better than when he was admitted 1 month ago, but he still has shortness of breath every day and a decreased exercise capacity (e.g., he becomes very short of breath after walking a couple of blocks). He states that he is adherent to the new medication regimen that was changed on discharge from the hospital. No other medications were changed at that time that he can recall. Which of the following is appropriate per the GOLD Guidelines?
A. Continue tiotropium, STOP salmeterol 50mcg BID, START Advair 500/50 mcg BID
B. Continue tiotropium, STOP salmeterol 50mcg BID, START Advair 250/50 mcg BID
C. Continue tiotropium, STOP salmeterol 50mcg BID, START Flovent 200 mcg BID
D. Continue tiotropium, STOP salmeterol 50mcg BID, START Symbicort 160/4.5 mcg BID
E. Continue tiotropium, STOP salmeterol 50mcg BID, START QVar 80mcg once daily
19. FF is a 41 year old Caucasian female that presents to an outpatient clinic for PCP follow up. She is recently in remission for papillary carcinoma of the breast. Her physician wants to begin management of her vasomotor symptoms associated with pre-menopause as well as prevent osteoporosis. Her physician cannot contact her OBGYN or her oncologist today. Her physician asks you, the clinical pharmacist, for recommendations to manage her severe vasomotor symptom relief and promotion of bone health. Choose all that apply:
A. FF is a candidate for Duavee®. A SERM (Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator) does not have progesterone or an estrogen in its formulations. This hormonal property allows Duavee® to remain efficacious for treating her severe vasomotor symptoms and osteoporosis prevention.
B. FF is a candidate for Duavee®. A SERM (Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator) does have an estrogen in its formulations but does not have a progesterone. This hormonal property allows Duavee® to remain efficacious for treating her severe vasomotor symptoms and osteoporosis prevention.
C. FF is a candidate for Premarin® Vaginal Cream. Since there is only one hormone in this formulation along with its topical properties being favorable for this patient, it would be an excellent option for FF.
D. FF is not a candidate for Duavee®. Due to its hormonal properties it would not be a safe option for FF.
E. FF is not a candidate for any SERM or conjugated estrogens.
20. Women with a uterus need to always add estrogen to their regimen. Estrogen prevents hyperplasia in the
Uterus.
True
False
21. Which of the following statements are true about Kadecylo? Select ALL that apply.
A. Indicated for those who are homozygous for the F508 del mutation
B. Indicated for those who have the CFTR genotype G551D
C. Can be used as sprinkles
D. Is a combination of Ivacaftor and lumacaftor
E. Is a combination of Tezacaftor and Ivacaftor
22. In the ER, a hispanic 39 year old male patient, DT continues to experience chest pain on exertionand with an increased heart rate. The following results are obtained: Fasting lipid profile, total cholesterol 246 mg/dL, HDL 27 mg/dL, LDL=160, triglycerides 150mg, fasting glucose 198 mg/dL; HbA1c=8.5, Na=138, K=4.1, Hb=14, Hct=40, PLTs=320
Exercise treadmill test= Positive for ischemic angina, HR=80, BP=165/99, Troponin negative, CK MB negative
EKG= ST elevation DT is evaluated in the heart cath lab for a PCI to determine any blockages. After the procedure, he is placed on an oral anticoagulant agent to prevent future clotting events in the coronary arteries.
Which of the agents listed below inhibit platelet aggregration through the direct inhibition of Factor II.
A.Rivaroxaban
B.Apixaban
C.Arixtra
D.Cangrelor
E.Bivalirudin
23. Adam is a 72 year old man admitted to the hospital for HF decompensation (acute HF). Adam notes progressively increased dyspnea when walking (now 10ft, previously 30 ft.) and orthopnea (now 4 pillows, previously 2 pillows), increased bilateral lower extremity swelling 3+, a 13-kg weight gain in the past 3 weeks, and dietary non-adherance.Pertinent labatory values are as follows: BNP 2300 pg/mL (0-50 pg/mL), K+ 4.9 mEq/L, BUN 32 mg/dL, SCr 2mg/dL, BP 108/62 mmHg, and HR 82 beats/min. Medications: Caarvedilol 12.5 mg BID, Lisinopril 40 mg/day, furosemide 120 mg IV BID, Spironolactone 25 mg/day, and digoxin 125 mg/day. After initial appropriate therapy was initiated, Adam is transferred to the coronary care unit for further management of diuretic -refactory decompensated HF, His O2 is now 87% on 4-L nasal cannula, and an arterial blood gas is being obtained. His blood pressure is 110/75 mmHg and heart rate is 75 beats/min.
Adam’s SCr and K+ concentrations have begun to rise and are now 2.2 mg/dl and 5.4 mEq/L respectively
In addition to a one-time dose of intravenous chlorothiazide, which one of the following best represents way in which Adam’s decompensated HF should be treated?
A. Nitroglycerin 20 mcg/min
B. Milirinone 0.5 mcg/kg/min
C. Dobutamine 5 mcg/kg/min
D. Sodium nitroprusside 1.0 mg/kg/min
24.Angela is a 54 year old African American female who presents to the diabetes management clinic with complaints of intermittent episodes of sudden onset fatigue and lightheadedness. She was diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes 12 years ago. She reports some problems with medication compliance because some of them make her feel really strange and sometimes even sick. She has an extreme fear of needles and absolutely refuses injecting herself. Her PCP feels like she is running out of options and elicits your help. She is 5’4 and weighs 223 Ibs.
Current medications: Metformin 1,000 mg BID, Januvia 100 mg daily, Farxiga 10 mg daily, amlodipine 10 mg daily
Labs
HbA1c
10.7% SCr
1.91
BG 245 Urinalysis
Glucose
(+)
Ketones
(-)
Albumin
(+)
BUN 41 GFR
26
BP
91/59 CrCl
21
The drug appropriately matched to the action that should be taken in Angela’s case.
A. Metformin: reduce dose by 50% due to renal insufficiency
B. Metformin: d/c because medication as it is contraindicated for use in Angela’s case
C.Farxiga: reduce dose by 50% due to renal insufficiency
D. Januvia: d/c because medication as it is contraindicated for use in Angela’s case
E. Farxiga: Increase dose to 20 mg daily
25.Angela is a 54 year old African American female who presents to the diabetes management clinic with complaints of intermittent episodes of sudden onset fatigue and lightheadedness. She was diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes 12 years ago. She reports some problems with medication compliance because some of them make her feel really strange and sometimes even sick. She has an extreme fear of needles and absolutely refuses injecting herself. Her PCP feels like she is running out of options and elicits your help. She is 5’4 and weighs 223 Ibs.
Current medications: Metformin 1,000 mg BID, Januvia 100 mg daily, Farxiga 10 mg daily, amlodipine 10 mg daily
Labs
HbA1c
10.7% SCr
1.91
BG 245 Urinalysis
Glucose
(+)
Ketones
(-)
Albumin
(+)
BUN 41 GFR
26
BP
91/59 CrCl
21
Which of Angela’s medications require renal dosing?
A.Januvia
B. Metformin
C. Farxiga
D. B and C
E. A,B,and C
26. Angela is a 54 year old African American female who presents to the diabetes management clinic with complaints of intermittent episodes of sudden onset fatigue and lightheadedness. She was diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes 12 years ago. She reports some problems with medication compliance because some of them make her feel really strange and sometimes even sick. She has an extreme fear of needles and absolutely refuses injecting herself. Her PCP feels like she is running out of options and elicits your help. She is 5’4 and weighs 223 Ibs.
Current medications: Metformin 1,000 mg BID, Januvia 100 mg daily, Farxiga 10 mg daily, amlodipine 10 mg daily
Labs
HbA1c
10.7% SCr
1.91
BG 245 Urinalysis
Glucose
(+)
Ketones
(-)
Albumin
(+)
BUN 41 GFR
26
BP
91/59 CrCl
21
Which of the following is NOT a mechanism of action of one of her current medications?
A. Decrease hepatic glucose production
B. Lowers renal threshold for glucose resulting in increased output of excess glucose in urine
C. Inhibits the enzyme that inactivates incretin hormones
D. Stimulates glucose production from pancreatic beta cells
E. Slows absorption of glucose from the GI tract
27.Angela is a 54 year old African American female who presents to the diabetes management clinic with complaints of intermittent episodes of sudden onset fatigue and lightheadedness. She was diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes 12 years ago. She reports some problems with medication compliance because some of them make her feel really strange and sometimes even sick. She has an extreme fear of needles and absolutely refuses injecting herself. Her PCP feels like she is running out of options and elicits your help. She is 5’4 and weighs 223 Ibs.
Current medications: Metformin 1,000 mg BID, Januvia 100 mg daily, Farxiga 10 mg daily, amlodipine 10 mg daily
Labs
HbA1c
10.7% SCr
1.91
BG 245 Urinalysis
Glucose
(+)
Ketones
(-)
Albumin
(+)
BUN 41 GFR
26
BP
91/59 CrCl
21
Angela medication regimen requires changes for various reasons. Which of the following represents the best new regimen for Angela to achieve her ADA recommended HbA1C goal safely?
A. metformin 500 mg BID + Amaryl 2 mg daily
B. metformin 500 mg BID + liraglutide 0.6 mg daily x 1 week then increase to 1.2 mg daily
C. Continue her current regimen and add lantus 10 units QHS
D. Januvia 25 mg daily + Amaryl 2 mg daily
E. Actos 15 mg daily + Byetta 5 mg BID
28. Find the appropriately matched brand/generic combination
A. Rosiglitazone/Invokana
B. Metformin/Avandaryl
C. Insulin Aspart/Humulin N
D. Miglitol/Glycet
E. Liraglutide/Symlin
29. Which agent may worsen a patient’s lipid profile?
A. Byetta
B. Invokana
C. Fortamet
D. Actos
E. Amaryl
30.Which agent may improve a patient’s lipid profile?
A. Byetta
B. Invokana
C. Fortamet
D. Actos
E. Amaryl
31. Which of the following are considered normocytic anemia. Select all that apply
A. Anemia of chronic disease
B. Acute blood loss anemia
C. Chronic blood loss anemia
D. Anemia due to bone marrow failure
E. Hemolytic anemia
32. The half life of epoetin alpha is about 3 times that of darbapoetin alpha.
True
False
33. JJ is a 49 year old man who experiences headache cycles two times a year, usually in the spring and fall. The headaches occur for 3 to 4 weeks and he may have 5 headaches daily. The headaches are an unbearable type of pain that comes suddenly, located in his left eye, and stops within 1 to 2 hours. He experiences severe ocular and nasal symptoms, such as nasal stuffiness or rhinorrhea, ocular lacrimation, and ptosis. Which of the following is an appropriate abortive treatment option for the patient?
A.Zomig tablets
B. Imitrex SC
C. Topiramate
D. Oxygen
E. Maxalt nasal spray
34.MS is a 30 year old female with well controlled partial seizures, but has migraine HA weekly, resulting in missed work and family activities. Which of the following anticonvulsants is used as a prophylatic treatment for migraine headaches? Select all that apply.
A.Keppra
B.Trileptal
C.Topamax
D.Valproate
E.Fycompa
35. Which of the following would be an absolute contraindication for receiving triptans as therapy? Select all that apply
A.Iron deficiency anemia
B.Uncontrolled hypertension
C. Ischemic heart disease
D.Diabetes
E. Depression
36. A patient presents a new prescription for zonisamide. About which of the following side effects should the pharmacist counsel the patient?
A.Weight gain
B.Hyponatremia
C. A change in urine color
D. Contraindicated in pts with a history of sulfa allergy
E.Peripheral edema
37.Which of the following is indicated for ALL stages of Alzheimer’s disease?
A. Memantine
B. Exelon
C. Razadyne
D. Namzaric
E. Namenda
38. A patient with metabolic alkalosis will likely have a bicarbonate (HCO3) of greater than 26. If the patient is saline unresponsive, which of the following therapy would benefit her?
A. NaCL
B. KCL
C. Sprionolactone
D. Acetazolamide
E. B, C, and D
39. Which of the following describes the role of Nuplazid in treating patients with Parkinson’s disease?
A. It is used as monotherapy in early PD
B. It is used to treat psychosis associated with PD
C. It is used during off episodes experienced during advanced PD
D. It is used to reduce the GI side effects of agents used to treat PD
E. It is used to delay the use of carbidopa/levodopa in PD
40. Which of the following would be MOST appropriate to initiate in a 55 yo patient to treat her Parkinson’s?
A.Cogentin 1mg po QID
B.Requip 0.25mg po TID
C. Mirapex 0.5mg po TID
D.Comtan 200mg po TID
E. Neupro transdermal 8mg/24 hours
41. Which of the following is true regarding buspirone?
A. It can be used for acute anxiety symptoms
B. Benefits can be seen in 2-4 weeks
C. There is no potential for abuse
D. Grapefruit juice should be avoided with use
E. It has best efficacy for patients who have had prior BZD treatment
42.Lawrence Smith, 62 year old man, was hospitalized today with increasing SOB and lower extremity edema. His reports his symptoms started approximately 1-1.5 weeks ago. He noted that he was gaining about 2lb daily and gained approximately 20lbs of weight over the week prior to admission. Patient reported that he has been compliant to all of the medications.Physical examination revealed evidence of cold extremities. Chest X-ray: PA and lateral view revealed evidence of congestive failure with cardiomegaly, interstitial edema, and some early alveolar edema.Vital signs: BP:90/70 mmHg, pulse 70 beats/minute Past Medical History CAD(s/p STEMI 6 years ago), COPDx 3 years HFx2 years Dyslipidemia x 10 years EF:30% Past medication history: Aspirin 325mg, Furosemide 40mg po daily, Losartan 25 mg po once daily; Isosorbid mononitrate ER 30 mg po QAM; Metformin 500 mg po BID; Rosuvastatin 10 mg po daily; Patient’s symptoms improved and ready to be discharged. At what dose of oral furosemide should Lawrence be discharged with?
A. 20mg
B. 40mg
C. 80mg
D. 160mg
43. A 70 year old man with advanced prostate cancer and ischemic cardiomyopathy (left ventricular ejection fraction 18%) was brought to the ER after two episodes of near syncope. He is somnolent and falls asleep during the interview. He is on a very low doses of ACE inhibitors and did not tolerate a beta blocker an outpatient because of low blood pressure. His baseline creatinine is 2.1, heart rate is paced at 70 and blood pressure is lower than usual 72/55 ( Past medical history: CKD, HF). Based on the observation which of the following would you recommend?
A. Initiate nitroglycerin IV
B. Initiate nesiritide
C. Initiate dobutamine
D. Initiate milirinone
44. AW is a 67 year old man with type 2 DM, HTN, and stage 5 CKD. He receives hemodialysis 3 times a week with a high flux hemodialysis membrane. His wife brought him into the ED this morning after she noticed increased confusion and lethargy, worsening over the past 2-3 days. According to his wife, the patient missed his HD session 2 days ago. She reports no other new symptoms except for increased pain in his feet from his neuropathy for which his PCP increased his gabapentin dose last week. Labs reported: Na 140 mEq/L Hgb 11.2 g/dL Ca 9.8 mg/dL K 6.1 mEq/L Hct18 mEq/L WBC 7.8 x 103/mm3 AST 12 IU/L BUN 82 mg/dL ALT 8 IU/L SCr 8.2 mg/dL Oral therapy for ambulatory patients with metabolic acidosis include all the following EXCEPT:
A.Shol’s Solution
B.Baking Soda
C.NaHCO3
D.Acetazolamide
E.Polycitra K
45. Which patient with diabetes is the best candidate for more intensive therapy and stringent goals?
B. Tristan is a 51 yo male diagnosed with T2DM 3 months ago. He is retired from the Army as of 2 months ago and is very regimen and taking his medication. His endocrinologist started him on Metformin.
46. Which of the following therapies would be indicated to treat hypercalcemia associated with non-small cell lung cancer?
A.Zolendronate
B. Calcitonin
C.NaCl + Lasix IV
47. What is the patient’s corrected calcium level?
14.4
48. Which of the following fluids that could be given to her. Which one(s) are considered crystalloids? Select all that apply
Ringer’s Lactate
0.9% Sodium Chloride
D5W + ½ NaCl + 20 mEq of K
49. Which of the following fluids that could be given to her, Which one should NOT be considered at this time? Select All That Apply
Heparin
Albumin
50. Calcijex is used in patients with ESRD renal failure because because it can:
Decrease serum phosphate level
Control reabsorption of calcium from the kidneys
Control absorption of calcium in the intestines
51. Select abnormal lab values from the followin? Select all that apply
Potassium
Phosphorus
Albumin
Calcium
52. Which of the following is not a prodrug?
Morphine
53. Which of the following is contraindicated to patient receiving IV recombinant tissue plasminogen activator?
Rapidly resolving symptoms
54.If taken concomitantly with Donepezil, Which can cause a drug interaction?
Elavil
Diphendramine
Prachol
Allof the above
55. Will reduce in fractures in women.
True
False
56. Ketoralac is limited to 5 days of use because of _______________
GI ulcers
57.Local national and international guidelines for the treatment of schizophrenia are unified in the recommendation which antipsychotics as the 3rd step in treating patients who are not adequately treated with their antipsychotic ?
Clozapine
58. Which of the following drugs have a potential for being abused? Select all that apply
Dextromethmorphan
Diacetylmorphine
Phencyclidine
Pseudoephendrine
Gabapentin
59. Which of the following is an appropriate therapy for Jasmine for secondary prevention of stroke?
Rivaroxaban 20 mg po BID
60. Which of the following treatment would likely correct potassium abnormalites? Select
all that apply
Kayexalate
Insulin + Dextrose
NaHCO3
61. Which of the following agents listed below can blind and reverse the effects of Unfractionated Heparin?
Protamine
62. Which of the following agents is a GIIBIIIA receptor complex?
Tirofaban
63. Which significant drug complication is associated with the patient’s PCI?
Thrombocytopenia
[Show More]