Precautions for drug administration
Confirm the patient’s identity Topical administration
Topical drugs To apply a paste, a cream, or an ointment
♦ To prevent skin irritation from accumulated drug, remove residue from
...
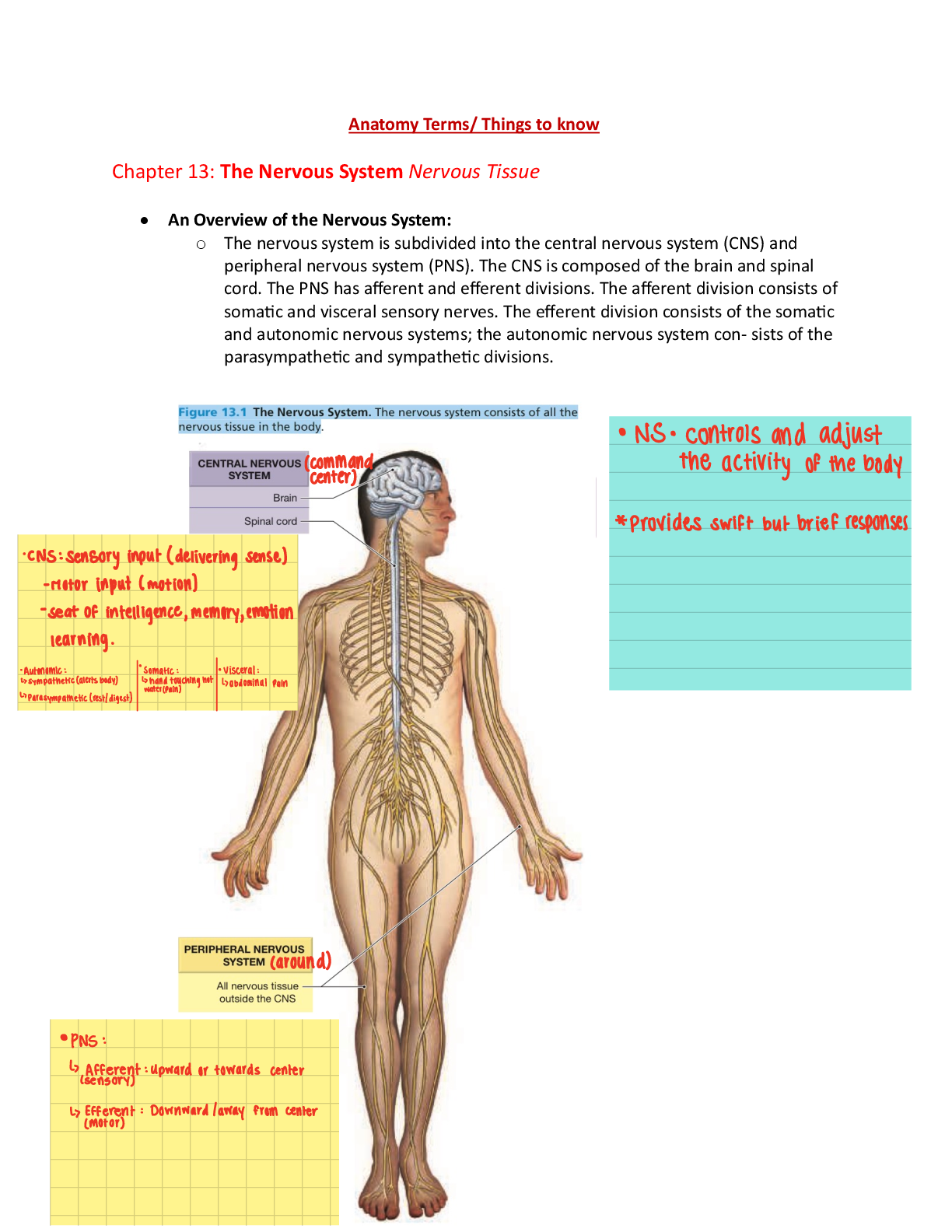
Precautions for drug administration
Confirm the patient’s identity Topical administration
Topical drugs To apply a paste, a cream, or an ointment
♦ To prevent skin irritation from accumulated drug, remove residue from previous applications before each new application.
♦ Always wear gloves to prevent your skin from absorbing the drug.
♦ Never apply ointment to the eyelids or ear canal unless ordered. The ointment may congeal and occlude the tear duct or ear canal.
♦ Inspect the treated area often for adverse or allergic reactions.
Equipment
For a transdermal patch For transdermal ointment
To apply a transdermal patch
To apply transdermal ointment
After applying transdermal drugs
Special considerations
To instill eyedrops
To apply eye ointment
After instilling eyedrops or applying ointment
Implementation
Equipment
Special considerations
Nasal drugs
To use a nasal spray
To use a nasal aerosol
Special consideration
To insert an ointment, a cream, or a gel
After vaginal drug insertion
Special considerations
Respiratory administration
Handheld oropharyngeal inhalers
Implementation
To use a metered-dose inhaler
To use a turbo-inhaler
To use a dry-powder, multidose inhaler
To use a holding chamber (InspirEase)
Special considerations Enteral administration
Oral drugs Implementation
Drugs given by nasogastric tube or gastrostomy tube
Giving a drug by NG tube
Giving a drug by gastrostomy tube
Buccal and sublingual drugs
Rectal suppositories or ointment
Special considerations
Inserting a rectal suppository
Parenteral administration
Subcutaneous injection
For single-dose or multidose vials
Giving the injection
Special considerations Intradermal injection Special considerations Intramuscular injection Drug precautions
Drug-tobacco interactions
ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
Possible effects
chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride, chlorpromazine hydrochloride, diazepam
Possible effects
hormonal contraceptives that contain estrogen and progestogen
Possible effects Nursing considerations
propoxyphene hydrochloride
Possible effects
propranolol hydrochloride
Possible effects
Nursing considerations theophylline
Possible effects
Drug-alcohol interactions Compatibility of drugs with tube feedings Drug-alcohol interactions Effects of mixing drugs and alcohol Analgesics Anxiolytics Antidepressants Antihistamines Antipsychotics Hypnotics
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
Oral antidiabetics
Cephalosporins metronidazole disulfiram DRUG
Aminoglycosides
amikacin
gentamicin
kanamycin
neomycin
netilmicin
streptomycin
tobramycin
Amphetamines
amphetamine
benzphetamine
dextroamphetamine
methamphetamine
Reporting adverse drug reactions
Monitoring patients using herbs aloe
capsicum
cat’s claw
chamomile (German, Roman)
echinacea
evening primrose
fennel
feverfew
flaxseed
garlic
ginger
ginkgo
ginseng (American, Panax, Siberian)
goldenseal
kava
milk thistle
nettle
passionflower
St. John’s wort
SAM-e
saw palmetto
valerian Taking medications safely at home
[Show More]









.png)