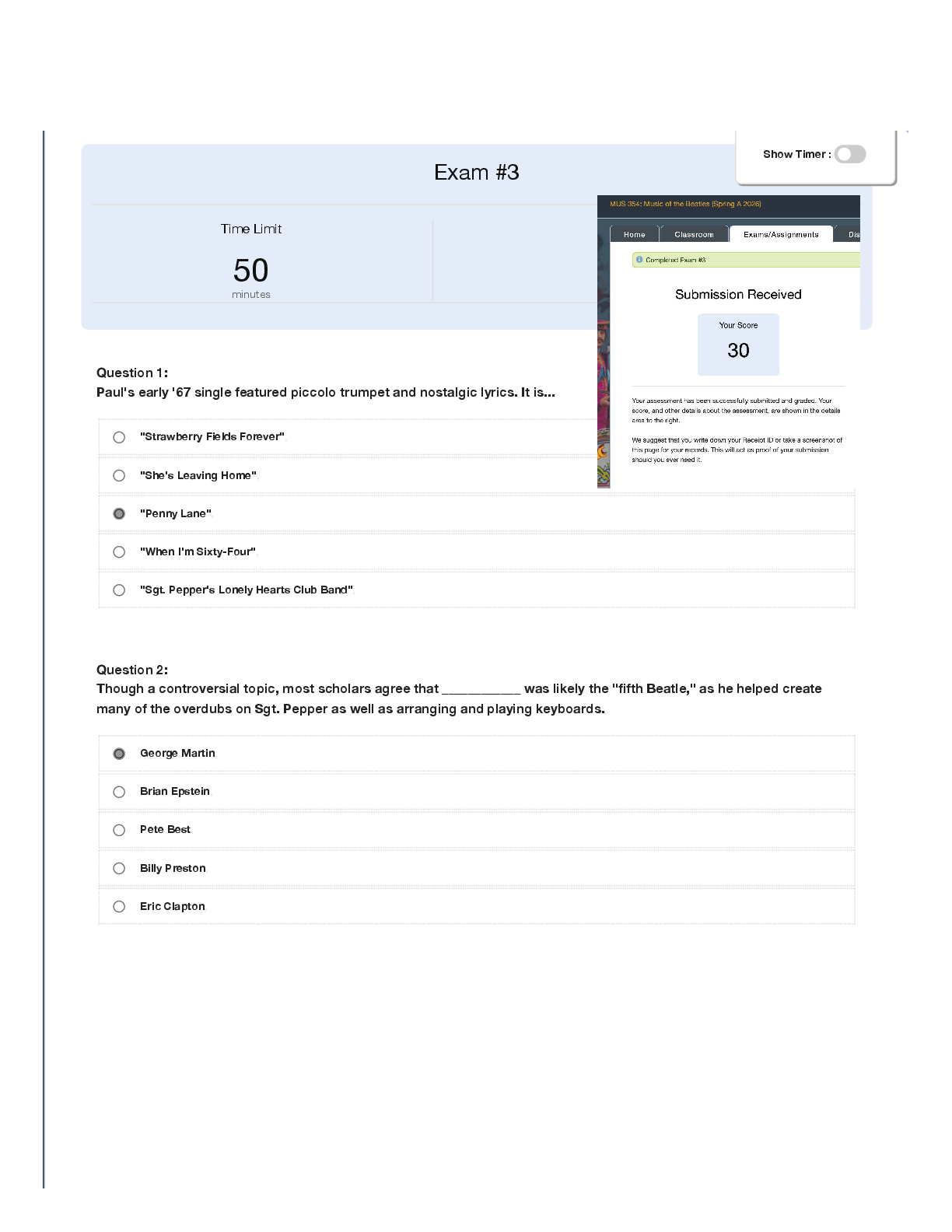
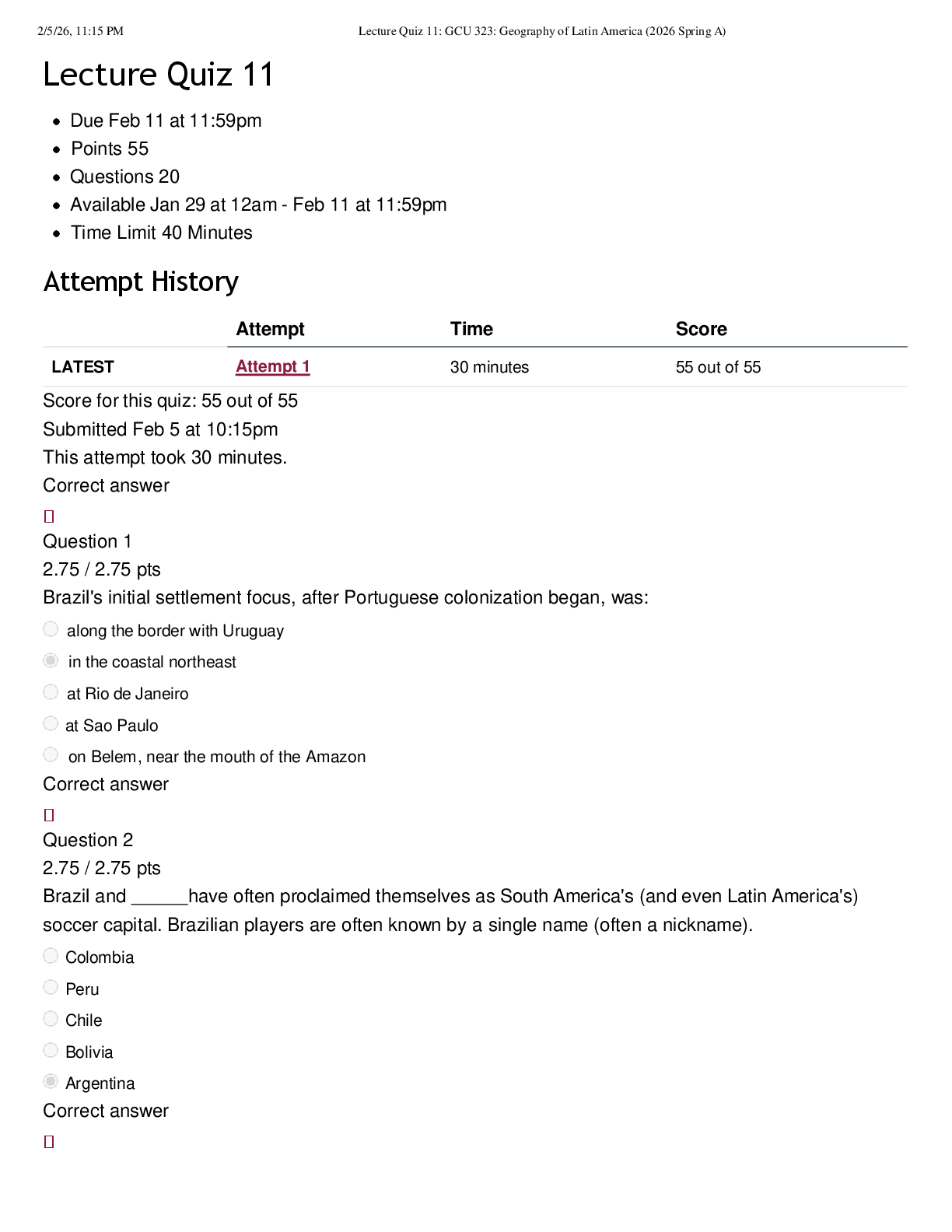
GENB 4350 Final Assignments | Complete Solutions (Verified) Which of the following methods of international expansion offers the lowest source of risk? a. Outsourcing b. Sales agent c. Joint venture d. Merger A repres
...
GENB 4350 Final Assignments | Complete Solutions (Verified) Which of the following methods of international expansion offers the lowest source of risk? a. Outsourcing b. Sales agent c. Joint venture d. Merger A representative office: a. Offers a minimal business presence b. Is often the simplest overseas presence to set up c. Usually cannot conduct commercial business activity d. All of these are correct. Subject to any limitations of foreign ownership, the main choice(s) of entity for an overseas operation comprise(s): a. A liaison or representative office b. A branch c. A subsidiary d. All of these are correct. A branch is: a. A local office of the U.S. parent company b. Not a separate legal entity c. A local office of the U.S. parent company and not a separate legal entity d. None of these are correct. Before hiring workers abroad, the U.S. parent must consider whether having workers in a given country will trigger: a. The need for a branch registration b. The need to incorporate a subsidiary under local law c. A permanent establishment for tax purposes d. All of these are correct. Which of the following methods of international expansion offers the highest source of risk? a. Outsourcing b. Sales agent c. Joint venture d. Merger If a U.S. company is deemed to have a ________ in another country, it will be liable for corporate taxes under the domestic tax regime of the relevant country. a. Value added tax b. Permanent establishment c. Net operating loss d. None of these are correct. The initial set up costs for establishing an overseas branch or subsidiary include: a. Registration fees b. Notary fees c. Contribution of the initial equity d. All of these are correct Which of the following must a U.S. business consider when terminating employees overseas: a. Notice requirements b. Consultation with employees c. Severance payments d. All of these are correct. A subsidiary is: a. A separate legal entity b. A signal that the U.S. parent has made a long-term commitment to that country c. An entity that offers limited liability d. All of these are correct. Company X is planning to set up a foreign subsidiary. The laws of that foreign nation require multiple shareholders. Ideally, the additional shareholders in the subsidiary will include: a. Company employees b. Company board of directors c. Companies within the U.S. company's group d. All of these are correct Company F wants to establish a minimal overseas presence solely to conduct market research and a feasibility study. Company F should establish a: a. Representative Office b. Branch c. Subsidiary d. Hybrid approach Company B wants to ensure that its foreign subsidiary will keep the U.S. parent company apprised of factors affecting the local market, including new opportunities and threats, competitor actions, and educate the local team in the ways and culture of the U.S. business. Company B should: a. Appoint one of its own senior managers to head up the overseas subsidiary b. Appoint a local manager to head up the overseas subsidiary c. Hire a foreign consultant to head up the overseas subsidiary d. None of these are correct Company B is establishing a subsidiary in Europe and wants to comply with local employment regulations. These regulations stipulate that Company B would have to provide each employee with written information, including: a. Start date b. Job title c. Salary and benefits d. All of these are correct Company F wants to set up an overseas business operation. The overseas business is expected to grow and Company F wants the overseas operation to offer limited liability and signal their commitment to the overseas market. Company F should establish a: a. Representative office b. Branch c. Subsidiary d. Hybrid approach Company F wants to open a local office overseas that is fully owned and controlled by the parent company in the U.S. Company F should establish a: a. Representative office b. Branch c. Subsidiary d. Hybrid approach Company Z is setting up a foreign subsidiary. To avoid the dual employment problem, Company Z should: a. Set up the foreign subsidiary before employment offers are made b. Employment offers should be made only by duly authorized officers of the foreign subsidiary c. Set up the foreign subsidiary before employment offers are made and employment offers should be made only by duly authorized officers of the foreign subsidiary d. Make employment offers by the U.S.-based company Company X wants a fast and cost-effective way to establish a subsidiary in Ireland. Advisors have recommended purchasing a private company set up in advance and reserved for future use. This type of entity is called a: a. Shelf company subsidiary b. Branch c. Joint venture d. Representative office Company A plans to move its tax residence to a country with a lower corporate tax rate without actually relocating the company's operations by merging the company with a foreign entity. This plan is called a: a. Joint venture b. Reorganization c. Corporate inversion d. None of these are correct Company F wants to open multiple overseas offices that engage in marketing, business development and other pre-sales activities. The number of employees working in these foreign operations will be fairly small. Company F also wants to limit the exposure of liability towards the U.S. parent company and minimize costs. Company F should establish a a. Representative office b. Branch c. Subsidiary d. Hybrid approach Unless restricted by statute, deed, or otherwise, a landowner has a right to everything existing permanently below the surface of her or his property to______ the center of the earth A 200-year-old oak tree located on a piece of property is considered to be______ real property Certain personal property, known as fixtures, can become so closely associated with the real property to which it is attached that the law views it as real property. a. True b. False Fee simple absolute is: a. an interest in land that exists only for the life of the person and then reverts to the original owner. b. a future nonpossessory interest in real estate. c. an interest in land in which the owner has the greatest possible aggregation of rights and privileges. Joint Tenancy The joint ownership of property by two or more co-owners in which each co-owner owns an undivided portion of the property. On the death of one of the joint tenants, his or her interest automatically passes to the surviving joint tenants. Conveyance The transfer of a title to land from one person to another by deed, or a document (such as a deed) by which an interest in land is transferred from one person to another. Tenancy in common Co-ownership of property in which each party owns an undivided interest that passes to his or her heirs at death. Tenancy by the entirety A less common form of shared ownership of real property by married persons that restricts either party's ability to transfer ownership without consent. Life estate An interest in land that exists only for the duration of the life of some person, usually the holder of the estate. The two major types of concurrent ownership are (select two): a. joint tenancy. b. tenancy at sufferance. c. tenancy in common. d. tenancy at will. In ______ states, it is presumed that a co-tenancy is a tenancy in common. Most When a joint tenant transfers her or his rights to another without the consent of the other joint tenants, doing so ______ the joint tenancy. Terminates A joint tenancy differs from a tenancy in common primarily in that a joint tenancy has the: a. right of survivorship. b. right of ownership. c. right of development. Community property is a form of concurrent ownership found in _____ state(s). A limited number of Tenancy at sufferance A type of tenancy under which one who, after rightfully being in possession of leased premises, continues to wrongfully occupy the property after the lease has been terminated. The tenant has no rights to possess the property and occupies it only because the person entitled to evict the tenant has not yet done so. Leasehold estate An estate in realty held by a tenant under a lease. In every leasehold estate, the tenant has a qualified right to possess and/or use the land. Periodic tenancy A lease interest in land for an indefinite period involving payment of rent at fixed intervals, such as week-to-week, month-to-month, or year-to-year. Tenancy at Will A type of tenancy under which either party can terminate the tenancy without notice. This usually arises when a tenant who has been under a tenancy for years retains possession, with the landlord's consent, after the tenancy for years has terminated. Fixed-term tenancy A type of tenancy under which property is leased for a specified period of time, such as a month, a year, or a period of years. This is also called a tenancy for years. Interests in land that do not include any rights to possess the property are known as nonpossessory interests. a. True b. False In real property law, the right to enter onto and remove things from the property of another (for example, the right to enter onto a person's land and remove sand and gravel therefrom) is known as a Profit The difference between a profit in gross and profit appurtenant is that: a. a profit in gross is a future interest and a profit appurtenant is a present interest in land. b. a profit appurtenant is related to adjacent land and a profit in gross is related to nonadjacent land. c. a profit in gross involves the use of a quick claim deed, while the profit appurtenant does not. Most easements and profits are created by an express grant in a contract, a deed, or a will. a. True b. False A revocable right to enter onto another person's land is known as a: a. license. b. possession. c. trespass. d. tenancy. Ownership interests in real property are frequently transferred, or conveyed, by sale and the terms of the transfer are specified in a real estate sales contract. a. True b. False Which of the following is typically NOT the way in which real property ownership can be transferred? a. Sale b. Gift c. Conjecture d. Will e. Inheritance f. Adverse possession g. Eminent domain Real estate sales contracts are often contingent on the buyer's ability to obtain______ Financing In a sale for real estate, who is normally responsible for having the premises inspected for physical or mechanical defects and for insect infestation? a. The buyer b. The seller c. The real estate agent d. The state Title insurance Required by most lenders to ensure that the buyer does not suffer a loss if someone else claims ownership to the property Marketable title Ownership that is free from any encumbrances except those appropriately disclosed Closing The date of performance of the real estate sales contract Escrow account A special location where deposits are held until the conditions of sale have been met Habitability An implied warranty promising that the premises are of sound construction and in working order In most jurisdictions, a seller who knows of a defect that is not obvious and that would affect the value of the property in a material way has: a. a duty to disclose the problem. b. no obligation to disclose the problem. c. no obligation because the rule of caveat emptor applies. Warranty Deed A deed in which the grantor guarantees to the grantee that the grantor has title to the property conveyed in the deed, that there are no encumbrances on the property other than what the grantor has represented, and that the grantee will enjoy quiet possession of the property. Special warranty deed A deed in which the grantor only covenants to warrant and defend the title against claims and demands of the grantor and all persons claiming by, through, and under the grantor. Deed A document by which title to property, usually real property, is passed. Metes and bounds A system of measuring boundary lines by the distance between two points, often using physical features of the local geography. Quitclaim deed A deed intended to pass any title, interest, or claim that the grantor may have in the property but not warranting that such title is valid. It offers the least amount of protection against defects in the title. To be valid, a deed must include: (1) the names of the [grantor] (the giver or seller) and the donee or buyer, (2) words evidencing the [intent] to convey, such as, "I hereby bargain, sell, grant, or give," (3) a legally [sufficient] description of the land, (4) the seller's [signature] , and (5) [delivery] of the deed. Ans in [ ] The type of deed that provides the buyer with the greatest legal protection is a_____ Warranty deed A statute that allows deeds, mortgages and other real property transactions to be recorded so as to provide notice to future purchasers or creditors of an existing claim on the property is known as a_____ Recording statute To obtain title of property by adverse possession, an individual's possession must be actual and [not consensual, try others maybe constant] ; it must be open, visible, and [notorious] (not secret or clandestine); it must be continuous and peaceable for the [required] period of time; and it must be [hostile] and adverse. Ans in [ ] There are many public policy reasons for the adverse possession doctrine. Select three. a. Resolving boundary disputes b. Resolving title concerns c. Assuring property is put to productive use d. Avoiding unnecessary paperwork e. Moving to electronic record keeping f. Assisting the poor in obtaining property Eminent Domain The power of a government to take land for public use from private citizens for just compensation. Inverse Condemnation The taking of private property by the government without payment of just compensation as required by the U.S. Constitution. The owner must sue the government to recover just compensation. Restrictive Covenant A private restriction on the use of land that is binding on the party that purchases the property originally, as well as on subsequent purchasers. If its benefit or obligation passes with the land's ownership it is said to, "run with the land." When the government uses its power of eminent domain to acquire land owned by a private person or company, it is called_____ A taking When a government takes private property without paying compensation, the landowner is forced to sue the government for compensation. a. True b. False A restrictive covenant is binding on the party who purchases the property originally, but not on subsequent purchasers. a. True b. False Zoning Laws The rules and regulations that collectively manage the development and use of land. Variance A form of a relief from zoning and other laws that is granted to a property owner; used to make up for any deficiency in real property so that it could prevent the property from complying with zoning regulations. Industrial Use Land use for light or heavy manufacturing, shipping, or heavy transportation. Special Use Permits A permit that allows for a specific exemption to zoning regulations for a particular piece of land in a location that has a particular zoning characteristic. Commercial Use Use of land for business activities only, sometimes called "business use". Residential Use Use of land for construction of buildings for human habitation only. The United States Supreme Court has held that zoning is a constitutional exercise of the government's police powers. a. True b. False Zoning restrictions _____ absolute. are not A property owner requesting a variance must demonstrate that the requested variance is [necessary] for reasonable development, is the [least intrusive] solution to the problem, and [will not] alter the essential character of the neighborhood. Ans in [ ] Generally, a person cannot buy property with zoning regulations in effect and then argue that a variance is needed for the property to be used for the owner's intended
[Show More]