SEJPME I and II QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ( LATEST ) | 100% A Grade guaranteed
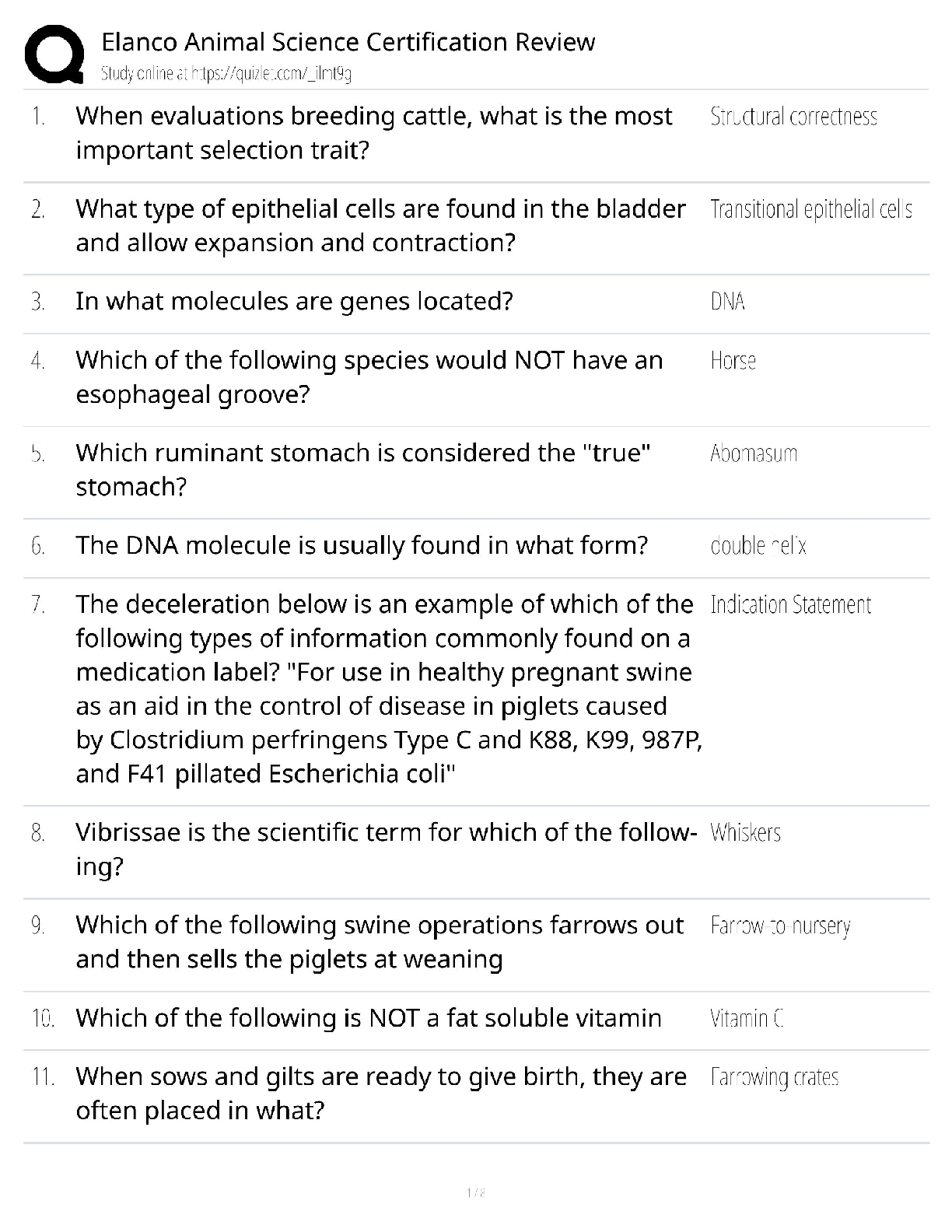
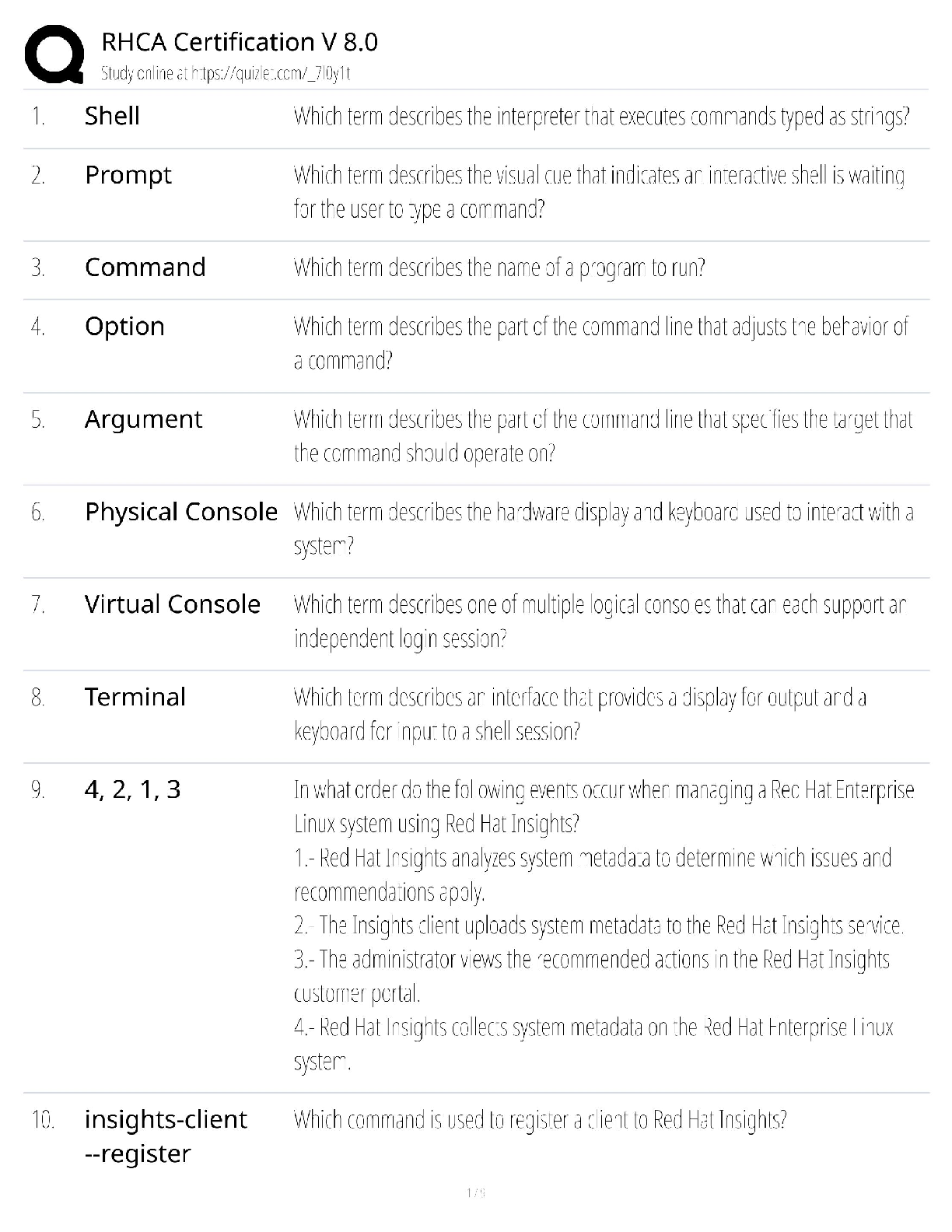
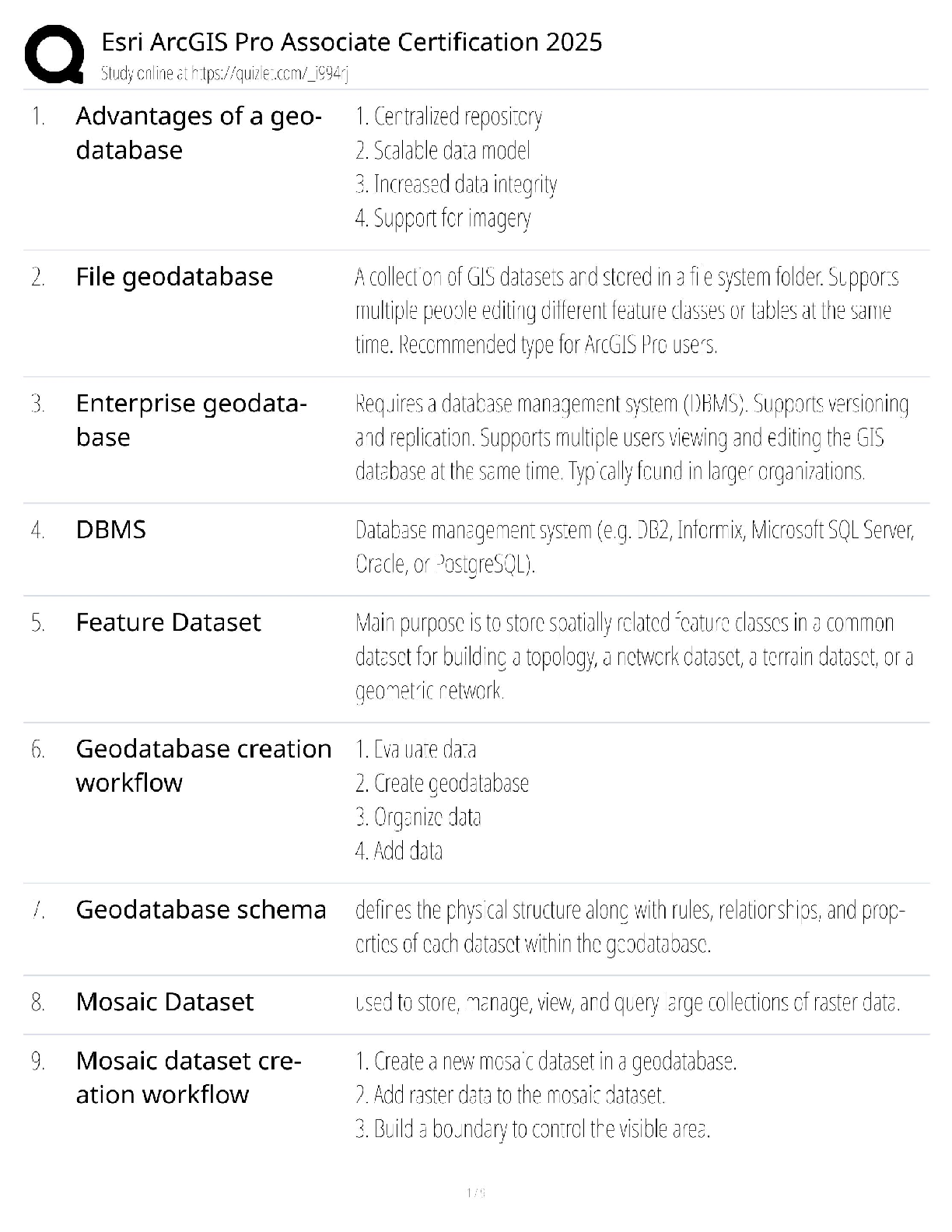
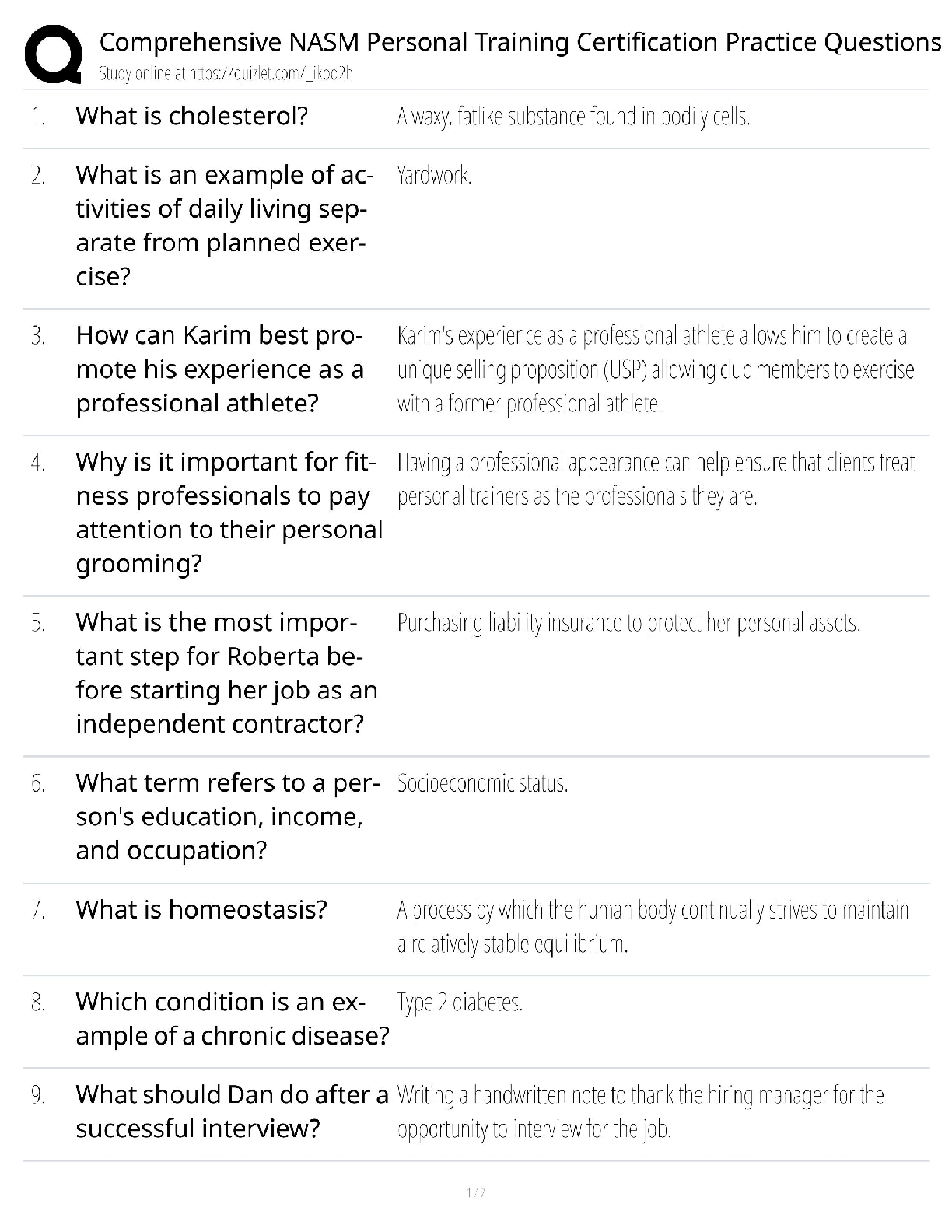
Document Content and Description Below
1) The Missile Defense Agency (MDA) works with the combatant commanders (CCDRs) of the _____.
(Select all that apply.) b, c, d
a) None of the answers are correct
b) United States Strategic Command
...
(USSTRATCOM)
c) United States Northern Command (USNORTHCOM)
d) United States Pacifc Command (USPACOM)
2) The main difference between Dining-In and Dining-Out for members of the Air Force is that spouses
and other non-military guests may atend a Dining-In. b
a) True
b) False
3) Which of the following are keys to success in joint assignments? (Select all that apply.) b, c, d
a) Checking the work of members from other Services
b) Knowing the people around you
c) Having competence in your area of the Service
d) Knowing how to solve problems
4) Today, the U.S. and its partners fnd themselves in an era in which they are unlikely to be fully at war
or fully at peace. a
a) True
b) False
5) If something of an ethical nature is ever in doubt, commanders should contact their legal counsel for
advice. a
a) True
b) False
6) There are a total of how many Reserve Components in the Armed Forces of the United States? d
1. 8
2. 5
3. 6
4. 7
7) The ______ is an interagency staff group that establishes or enhances regular, tmely, and
collaboratve working relatonships between other government agency (e.g., CIA, DOS, FBI)
representatves and military operatonal planners at the combatant commands. c
a) JIACG
b) HAST
c) CMOC
d) POLAD
8) Which of the following are consideratons when hostng a formal dinner? a
a) all of the answers are correct
b) identfy unique cultural consideratons in a foreign country
c) begin planning months in advance with the proposed guest list
d) print and mail invitatons four to six weeks in advance
e) plan the menu and walk through the upcoming evening's sequence of events9) The cornerstone of ARSOAC, the _____, is organized into four like batalions and provides nightme,
all-weather, medium range inserton, extracton, and resupply capability in hostle or denied areas. c
a) 106th Special Operatons Helicopter Regiment
b) 101st Airborne Division (Air Assault)
c) 160th Special Operatons Aviaton Regiment
d) 3rd Combat Aviaton Brigade
10) The Natonal Security Council comprises of which three levels of formal interagency commitees for
coordinaton and making decision on natonal security issues? c
a) executve, deputes, and interagency coordinaton
b) principals, deputes, and interagency policy
c) strategic, operatonal, and tactcal
d) principals, deputes, and interagency working group
11) In a traditonal cake-cutng ceremony the frst piece of cake is given to the youngest Marine present,
and the second piece of cake is given to the oldest Marine present. a
a) True
b) False
12) During the early 1990s, what event shifed the focus of the Army's actvites toward the stopping
old rivalries and conflicts? c
a) the collapse of the Warsaw Pact
b) the rise of global terrorism
c) the end of the Cold War
d) the breakup of the Soviet Union into smaller states
13) The U.S. contnues to become more dependent on the global domain within the informaton
environment consistng of the interdependent network of informaton technology infrastructures,
including the Internet, telecommunicatons networks, computer systems, and embedded processors and
controllers. It is imperatve that we safeguard this domain known as _____. d
a) space
b) networks
c) informaton
d) cyberspace
14) In 1798, the U.S. Navy and U.S. Marine Corps were created. a
a) True
b) False
15) Receiving realistc training, understanding the types of situatons encountered in war, eatng well,
getng enough rest, and having meaningful relatonships and friendships are all helpful in building _____
to the challenges and strains of military service. a
a) resilience
b) oppositon
c) vulnerability
d) indifference
16) Which of the following represent highlights of Air Force history? aa) Thall of the answers are correct
b) expansion into space
c) design of a doctrine of strategic bombing and one of organizatonal independence
d) development of the Strategic Air Command
17) Under the U.S. Consttuton, the Congress has the power to _____. d
a) close the U.S. borders
b) declare war, raise and support Armies, provide and support a Navy, make rules for the
government and regulaton of the land and naval forces
c) provide tanks and other equipment of war for Canada and Mexico
d) declare war, support allied armies, and provide ships for allied navies
18) Devised to survive on a potentally atomic batlefeld, vertcal envelopment enabled Marines to
achieve which of the following? b
a) night missions
b) speed and dispersion
c) beachhead assaults
19) Successful teamwork in the joint environment requires trust, confdence and _____. d
a) close supervision
b) tme to develop
c) clear rules of engagement
d) cooperaton
20) The Joint Task Force commander facilitates unifed acton and gains a greater understanding of the
roles of IGOs and NGOs and how they influence mission accomplishment by establishing a _____. d
a) Civil-Military Operatons Center (CMOC)
b) Joint Interagency Coordinaton Group (JIACG)
c) Humanitarian Assistance Coordinaton Center (HACC)
d) Interagency Policy Commitee (IPC)
21) During joint operaton planning, joint force commanders should begin to coordinate their actvites
with other agencies _____. c
a) when the combatant commander authorizes the plan
b) afer the operaton plan has been fnalized
c) as early as possible
d) afer the ambassador reviews the operaton plan
22) Reserve Component leaders agree that they receive adequate funding to support all levels of
operatonal use identfed by Service and Department of Defense plans. b
a) True
b) False
23) The primary functon of the Air Force is to provide prompt and sustained offensive and defensive air
operaton. a
a) True
b) False
24) _____ is a hostle environment that ofen presents complex emotonal and ethical dilemmas. c
a) Major combat operatonsb) Irregular warfare environment
c) Support for civil authorites
d) Humanitarian assistance operatons
25) _____ and _____ are two key structural enhancements that should improve the coordinaton of
multnatonal forces. d
a) Interoperability, liaison network
b) Ratonalizaton, training
c) Training, interoperability
d) Liaison network, coordinaton centers
26) During the Total Force Fitness ((TFF) Program secton of the course, we discussed the importance of
leader involvement. Leaders must identfy the metrics that will set the right conditons to promote total
ftness. In order to accurately assess the TFF program's effectveness, metrics must be _____ . c
a) challenging
b) feasible
c) quanttatve
d) observable
27) To reach the natonal strategic end state and conclude an operaton successfully, commanders must
integrate and synchronize stability operatons with offensive and defensive operatons. Planning for
stability operatons should begin _____. a
a) when major combat operatons have concluded
b) upon declaraton of a cease-fre
c) when Phase IV - Stabilize begins
d) when joint operaton planning is initated
28) Which of the following examples embodies Navy traditons and core values of honor, courage, and
commitment? a
a) "Don't give up the ship!"
b) all of the answers are correct
c) "Can you go and do likewise?"
d) "Surrender? I have not yet begun to fght!"
29) Many external factors impact the psychological health of individuals. The culture of the military and
its expectatons and the _____ cycles require frequent change and adjustment. b
a) weather
b) deployment/redeployment
c) training
d) promoton
30) In the Chairman's White Paper, "Mission Command" (2012), the Joint Force of the future will fnd
themselves operatng in a security environment that is _____. b
a) predictable
b) dynamic
c) ill-prepared
d) segregated
31) What Services were established as precursors to the Coast Guard? (Select all that apply.) a, b, d
a) Steamboat Inspecton Service
b) Life Saving Service
c) Transportaton Security Administratond) Lighthouse and Revenue Cuter Service
e) Bureau of Navigaton
32) Frequently a decisive element, the _____ principle of joint operatons is based on the legality,
morality, and rightness of the actons undertaken. b
a) patence
b) objectve
c) restraint
d) legitmacy
33) Developing and maintaining professional relatonships with multnatonal partner's means _____. a
a) recognizing that their training and educaton may differ, but it does not mean they are less
dedicated or professional
b) contnually reinforcing our standards upon them
c) contnuously demonstratng our superiority over them
d) treatng them as professionals with limited skills
34) The multnatonal force commander must resolve or mitgate sovereignty through which of the
following? (Select all that apply.) a, c
a) coordinaton
b) compromise
c) communicaton
d) consensus
35) The complexity and challenges associated with planning for and executng an operaton includes:
(Select all that apply). a, b, c, d
a) intergovernmental
b) interagency
c) military
d) multnatonal partners
36) Deliberatons involving the possible use of force must include the Reserve Component at what
point in the planning process? d
a) late in the planning process
b) afer all of the planning is completed
c) somewhere - early, mid, or later - as long as they are included
d) early in the planning process
37) The end strength of the U.S. Coast Guard Reserve is _____ percent of the total Coast Guard. a
a) 50
b) 30
c) 20
d) 10
38) The aspect of PME that focuses on impartng joint knowledge and attudes is joint _____. d
a) doctrine
b) educaton
c) concepts
d) training39) The seizure and defense of naval bases is provided by which branch of the Armed Services? b
a) Coast Guard
b) Marines
c) Army
d) Navy
e) Air Force
40) The term joint force commander refers exclusively to the following three types of commanders: c
a) joint task force commander, functonal component commander, and subunifed commander
b) combatant commander, Service component commander, and functonal component commander
c) Service component commander, combatant commander, and joint task force commander
d) combatant commander, subordinate unifed commander, and joint task force commander
41) Ice Operatons and Marine Environmental Protecton fall under which role of the Coast Guard? a
a) maritme stewardship
b) maritme safety
c) maritme security
42) The _____ organize, train, equip, and provide combat-ready forces to conduct operatons as
directed by the President and Secretary of Defense. a
a) Joint Chiefs of Staff
b) combatant commands
c) joint task forces
d) military departments
43) Flexibility in aerospace power allows forces to exploit mass and maneuver simultaneously to a far
greater extent than surface forces can. a
a) True
b) False
44) The most well-known Coast Guard mascot during World War II, who provided a morale boost to his
crew, was named? a
a) Skipper
b) Sinbad
c) Aladdin
d) Smoky
45) Each geographic combatant command has a _____ to plan and control special operatons and other
Special Operatons Forces actvites. c
a) Joint Special Operatons Task Force (JSOTF)
b) Regional Special Warfare Command (RSWC)
c) Joint Special Operatons Command (JSOC)
d) Theater Special Operatons Command (TSOC)
46) Army Special Operatons missions can include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) b, c, d
a) major combat operatons
b) cyberspace operatons
c) training of foreign militaries
d) humanitarian assistance
47) _____ is the process used to mitgate operatonal risks. Although created with military operatons in
mind, these procedures can be used to plan other actvites. ba) Operatonal resource management
b) Operatonal risk management
c) Risk assurance
d) Risk avoidance
48) Military-politcal consideratons frequently cast special operatons into clandestne or covert
environments; therefore, their actvites normally involve oversight at the _____ level. c
a) tactcal
b) natonal
c) joint task force
d) operatonal
49) Under what circumstances may the Coast Guard be transferred to and operate as a service of the
Navy? (Select all that apply.) a, b, c
a) upon a declaraton of war
b) when directed by the President
c) when ordered by the Secretary of Defense
50) In the Chairman's White Paper, "America's Military - A Profession of Arms," this aspect of the Armed
Forces is identfed as the foundaton of our profession. d
a) Values
b) Legal Authority
c) Leadership
d) Honor
51. What WWII conference established the Joint Chiefs of Staff?
a) U.S.-Britsh Staff Conference (ABC-1)
b) First Moscow Conference (RIVIERA)
c) Casablanca Conference (SYMBOL)
d) First Washington Conference (ARCADIA)
52. The 1986 Goldwater-Nicholas Act____.
a) Added the Commandant of the Marine Corps as a permanent and partcipatng member of the
Joint Chiefs of Staff
b) Clarifed the chain of command and civilian control of the U.S. Military
c) Provided the Chief of the Natonal Guard Bureau full membership of the Joint chiefs of Staff
53. The Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff provides a channel of communicaton between the
President/SECDEF and the Combatant Commander.
a) True
b) False
54. Natonal Security Agency (NSA) provides which of the following support: (Select all the apply)
a) Solutons, products, and services
b) Timely, relevant, and accurate geospatal intelligence
c) Informaton systems security
d) Signals intelligence
55. The North American Aerospace Defense Command(NORAD) is operated by which countries? (Select
all that apply.)
a) Canada
b) Mexicoc) United States
d) Great Britain
56. The Missile Defense Agency (MDA) works with the Combatant Commanders (CCDRs) of which
commands? (Select all that apply)
a) United States Northern Command (USNNORTHCON)
b) United States Pacifc Command (USPACOM)
c) United States Strategic Command(USSTRATCOM)
57. ______ is a violent struggle among state and non-state actors for legitmacy over the relevant
populaton(s). It favors indirect and asymmetric approaches, though it may employ the full range of
military and other capabilites, in order to erode an adversary’s power, influence, and will.
a) Asymmetric Warfare
b) Traditonal Warfare
c) Joint Warfare
d) Irregular Warfare
58. The ability of the U.S. to achieve its natonal strategic objectves is dependent on the effectveness is
the U.S. Government in employing the instruments of natonal power, which are_____.
a) Diplomatc, Informatonal, Military, and Economic
b) Diplomacy, Defense, and Development
c) Politcal, Military, Economic, Social, Informatonal, and Infrastructure
d) Culture, Industry, Technology, and Geography
59. The President of the United States provides guidance for developing, applying, and coordinatng the
instruments of natonal power to achieve objectves that contribute to natonal security in the ____.
a) Natonal Defense Strategy
b) Natonal Security Strategy
c) Unifed Command Plan
d) Natonal Military Strategy
60. The _____, signed by the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, provides guidance for distributng and
applying military power to atain natonal strategic objectves. It describes the Armed Forces’ plan to
achieve military objectves in the near term and provides the vision for ensuring they remain decisive in
the future.
a) Joint Strategic Capabilites Plan
b) Natonal Security Strategy
c) Natonal Defense Strategy
d) Natonal Military Strategy
61. The statutory members of the Natonal Security Council are ____.
a) President, Vice President, Secretary of State, Secretary of Defense, and Secretary of Energy
b) President, Vice President, Secretary of Defense, and Secretary of State
c) President, Vice President, Secretary of State, Secretary of Defense, and Secretary of Treasury
d) President, Vice President, Secretary of Defense, and Security of Homeland Security
62. The _____ is the President’s principle forum for considering natonal security policy maters with his
senior natonal security advisors and cabinet ofcials.
a) Secretary of Homeland Security
b) Secretary of Defense
c) Natonal Security Council
d) Joint Chiefs of Staff63. The operatonal chain of command runs directly from the President to the Secretary of Defense and
then to the ____.
a) Chairmen of the Joint Chief of Staff
b) Chairmen of the Joint Chiefs of Staff and then to the Combatant Commanders
c) Combatant Commanders
d) Services Chiefs
64. The non-operatonal chain of command runs directly from the President to the Secretary of Defense
and then to the.
a) Service Chiefs via the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
b) Secretaries of the Military Departments and then to the Combatant Commanders
c) Combatant Commanders via the Service Chiefs
d) Secretaries of the Military Departments and then to the Service Chiefs
65. The _____ outranks all other ofces of the Armed Forces, but may not exercise military command
over any of the Armed Forces. This ofcer is the principle military advisor to the President, the Natonal
Security Council, and the Secretary of Defense.
a) Chairmen of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
b) Supreme Allied Commander
c) Combatant Commander
d) War Czar
66. A unifed or Specifed Command with a broad contnuing mission under a single commander
established and so designated by the President, through the Secretary of Defense and with the advice
and assistance of the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is called a _____.
a) Joint Task Force
b) Subordinate Unifed Command
c) Combatant Command
d) Component Command
67. A _____ is a joint force that is consttuted and so designated by the SecDef, a Combatant
Commander, a Subordinate Unifed Commander, or an existng JTF Commander to accomplish missions
with specifc, limited objectves and which do not require overall centralized control of logistcs. It is
dissolved when the purpose for which it was created had been achieved or when it is no longer required.
a) Combatant Command
b) Subordinate Unifed Command
c) Joint Task Force
d) Service Component Command
68. The term Joint Force Commander refers exclusively to the following three (3) types of commanders:
a) Combatant Commander, Subordinate Unifed Commander, and Joint Task Force Commander
b) Combatant Commander, Service Component Commander, and Functonal Component
Commander
c) Joint Task Force Commander, Functonal Component Commander, And Subunifed Commander
d) Service Component Commander, Combatant Commander, and Joint Task Force Commander69. Joint Force Air Component (JFACC), Joint Force Land Component Commander (JFLCC), and Joint Force
Maritme Component Commander (JFMCC) are all examples of _____.
a) Joint Task Force Commanders
b) Subunifed Commanders
c) Service Component Commanders
d) Functonal Component Commanders
70. These commands are established by Combatant Commanders when authorized by the SecDef
through the CJCS to conduct operatons on a contnuing basis in accordance with the criteria set forth for
Unifed Commands. They may be established on a geographic area basis such as the United States Forces
Japan or on a functonal basis such as Special Operatons Command, Pacifc.
a) Combatant Commands
b) Subordinate Unifed Commands
c) Joint Task Forces
d) Functonal Component Commands
71. Combatant Commanders exercise _____ (command authority)) over assigned forces. This is the
broadest command authority and may NOT be delegated or transferred.
a) Administratve Control (ADCON)
b) Operatonal Control (OPCON)
c) Tactcal Control (TACON)
d) Combatant Command (COCOM)
72. _____ is the authority to perform those functons of command over subordinate forces involving
organizing and employing commands and forces, assigned tasks, designatng objectves, and giving
authoritatve directon necessary to accomplish the mission. It includes authoritatve directon over all
aspects of military operatons and joint training necessary to accomplish missions assigned to the
command.
a) Combatant Command
b) Operatonal Control (OPCON)
c) Tactcal Control (TACON)
d) Administratve Control (ADCON)
73. The four categories of support are _____.
a) General, tactcal, operatonal, and strategic
b) Tactcal, operatonal, direct, and common
c) General, mutual, direct, and close
d) Reinforcing, mutual, complementary, and close
74. Which of the following are instruments of natonal power? (Select all that apply.)
a) Economics
b) Informaton
c) The Military
d) Diplomacy
75. The relevance of the interagency process at the strategic level to the Combatant Commander and the
U.S. military is that the process yields America’s major natonal security policy decisions.
a) True
b) False
76. Provides commanders with an increased capability to coordinate with other U.S. Government
agencies?a) Interagency Coordinaton
b) DIME
c) Annex V
d) Joint Interagency Group (JIACG)
e) Foreign Policy Advisor (POLAD)
77. The part of the CCRD’s Operaton Plan that specifes not only the capabilites that military planners
have determined the military may need, but also the interagency partners’ shared understanding of the
situaton, as well as the common objectves required to resolve the situaton?
a) Interagency Coordinaton
b) DIME
c) Annex V
d) Joint Interagency Group (JIACG)
e) Foreign Policy Advisor (POLAD)
78. The four most basic elements of natonal power?
a) Interagency Coordinaton
b) DIME
c) Annex V
d) Joint Interagency Group (JIACG)
e) Foreign Policy Advisor (POLAD)
79. Providing U.S. Government foreign policy perspectves and diplomatc consideratons, establishes
linkages with U.S. embassies and State Department?
a) Interagency Coordinaton
b) DIME
c) Annex V
d) Joint Interagency Group (JIACG)
e) Foreign Policy Advisor (POLAD)
80. The interacton that occurs between agencies of the U’S’ Government, including the Department of
Defense (DoD), for the purpose of accomplishing the objectve?
a) Interagency Coordinaton
b) DIME
c) Annex V
d) Joint Interagency Group (JIACG)
e) Foreign Policy Advisor (POLAD)
81. Which organizaton is the principle policy-making forum responsible for the naton’s security
strategy?
a) Natonal Security Council (NSC)
b) Department of Defense (DoD)
c) Department of Homeland Security (DHS)
d) U.S. Congress
82. What are the key critcisms of the interagency process? (Select all that apply)
a) It is ofen tme-consuming
b) It can be cumbersome
c) No one is in charge, except the President
d) Rarely is it effectve83. Which of the following optons represent the Statutory Advisors of the Natonal Security Council?
a) President, Vice President, Secretary of State, and Security of Defense
b) Secretary of the Treasury and Secretary of Homeland Security
c) Chief of Staff to the President, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and the Director of Natonal
Intelligence
d) Chairmen of the Joint Chiefs of Staff and Director of Natonal Intelligence
84. The Natonal Security Council compromises these three levels of formal commitees for coordinatng
and making decisions on natonal security issues.
a) Principles, Deputes, and Interagency Policy
b) Executve, Deputes, and Interagency Coordinaton
c) Principles, Deputes, and Interagency Working Group
d) Strategic, Operatonal, and Tactcal
85. The ____________ is the principle military advisor to the President, the Natonal Security Council,
and the Security of Defense.
a) Natonal Security Advisor
b) Combatant Commander
c) Director of the Joint Staff
d) Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
86. The ________ is the principle forum to advise the President with respect to the integraton of
domestc, foreign, and military policies relatng to natonal security and for coordinatng these policies
among various government agencies.
a) Homeland Security Council
b) Natonal Security Council
c) Foreign Affairs Council
d) Natonal Economic Council
87. The concept of _____ highlights the synergistc applicaton of all the instruments of natonal power
and includes the actons of non-military organizatons as well as military forces.
a) Interagency cooperaton
b) Unifed acton
c) Unity of command
d) civil military operatons
88. U.S, military forces are authorized under certain conditons to provide assistance to U.S. civil
authorites for disasters, catastrophes, infrastructure protecton, and other emergencies. This assistance
is known as _____ within the defense community because the assistance will always be in the support of
a lead federal agency.
a) Consequence management
b) Civil defense
c) Civil support
d) Crisis management
89. It is imperatve that the Combatant Commander or JTF Commander coordinate closely with the
_____ on military actvites in a partcular country because, while not authorized to command military
forces, he or she can deny military actons.
a) Ambassador
b) Natonal Security Advisor
c) Secretary Of State
d) Foreign Policy Advisor90. The Country Team provides for rapid interagency consolaton and acton on recommendatons from
the feld. DoD is normally represented on the Country Team by which of the following?
a) Marine Security Detachment, Security Assistance Organizaton
b) Politcal Advisor, Joint Interagency Coordinaton Group
c) Defense Ataché, Foreign Policy Advisor
d) Defense Ataché, Security Cooperaton Organizaton
91. _____ are independent, diverse, flexible, grassroots focused, primary relief providers that are
frequently on the scene before U.S. military and will most likely remain long afer military forces have
departed.
a) IGOs
b) OGAs
c) NGOs
d) FAOs
92. In most situatons, IGOs and NGOs need which of these military capabilites?
a) Threat assessment, force protecton, and airlif
b) Logistcs, communicatons, and security
c) Airlif, sealif, and intelligence
d) Security, transportaton, and explosive ordnance disposal
93. The JTF Commander facilitates unifed acton and gains a greater understanding of the roles of IGOs
and NGOs and how they influence mission accomplishment by establishing a _____.
a) Humanitarian Assistance Coordinaton Center (HACC)
b) Joint Interagency Coordinaton Group (JIACG)
c) Interagency Policy Commitee (IPC)
d) Civil-Military Operatons Center (CMOC)
94. A partcular type of operaton is not doctrinally fxed and could shif within the range of military
operatons, for example a counterinsurgency operaton escalatng from a security cooperaton actvity
into a major operaton or campaign.
a) True
b) False
95. The range of military operatons includes these three categories of operatons: (1) military
engagement, security cooperaton, and deterrence: (2) crisis response and limited-contngency
operatons: and ______.
a) Major batles and engagements
b) Contngency and crisis operatons
c) Major operatons and campaigns
d) Traditonal and irregular warfare
96. These operatons are typically limited in scope and scale and conducted to achieve a very specifc
objectve in an operatonal area. They include noncombatant evacuaton operatons, recovery
operatons, consequence management, strikes, raids, homeland defense, and defense support of civil
authorites.
a) Military engagementb) Crisis response and limited-contngency operatons
c) Security cooperaton and deterrence actvites
d) Major combat operatons and campaigns
97. Various joint operatons such as a show of force or sanctons enforcement support _____ by
demonstratng natonal resolve and willingness to use force when necessary.
a) Joint operaton planning
b) Prepositoning assets
c) Deterrence
d) Interagency coordinaton
98. The purpose of specifying the _____ is to direct every military operaton toward a clearly defned,
decisive, and achievable goal.
a) Center of gravity
b) Critcal vulnerability
c) Objectve
d) Decisive point
99. The purpose of _____ is to concentrate the effects of combat power at the most advantageous place
and tme to produce decisive results.
a) Maneuver
b) Mass
c) Objectve
d) Offensive
100. Combatant Commanders and subordinate joint force commanders must work with U.S ambassadors
(or diplomatc missions), Department of State, and other agencies to best integrate the military actons
with the diplomatc, economic, and informatonal instruments of natonal power to promote_____.
a) Unity of command
b) Joint operatons
c) Economy of force
d) Unity of effort
101. The purpose of _____ is to maintain legal and moral authority in the conduct of operatons. It is
based on the actual and perceived legality, morality, and rightness of the acions from the various
perspectves of interested audiences.
a) Perseverance
b) Legitmacy
c) Restraint
d) Security
102. _____ helps prevent adversary acton through the presentaton of a credible threat is counteracton.
It stems from the belief of a potental aggressor that a credible threat of retaliaton exists, the
contemplated acton cannot succeed, or the costs outweigh any possible gains.
a) Military engagement
b) Security cooperaton
c) Deterrence
d) Decepton
103. At the strategic level, _____ encompasses those planning actvites , such as contnuity of
operatons and contnuity of government, undertaken to ensure DoD processes, procedures, and
resources are in place to support the President and SECDEF in a designated natonal security emergency.a) Military engagement
b) Emergency preparedness
c) Security cooperaton
d) Crisis acton planning
104. Combatng terrorism involves actons taken to oppose terrorism from wherever the threat exists,
and encompasses _____ -defensive measures taken to reduce vulnerability to terrorist acts-and _____-
offensive measures taken to prevent, deter, preempt, and respond to terrorism.
a) Consequence management, emergency preparedness
b) Counterterrorism, antterrorism
c) Force protecton, counterinsurgency
d) Antterrorism, counterterrorism
105. An operaton that employs coercive measures to interdict the movement of certain types of
designated items into or out of a naton or specifed area is known as _____.
a) Antterrorism
b) Arms control
c) Enforcement of sanctons
d) Show of force
106. The DoD contributon to a unifed acton effort to support and augment the development of the
capacity and capability of foreign security forces and their supportng insttutons to facilitate the
achievement of specifc objectves shared by the USG is called _____.
a) Enforcing exclusion zones
b) Show of force
c) Security force assistance
d) Sanctons enforcement
107. Operatons designed to demonstrate U.S. resolve, and involve the appearance of a credible military
force in an atempt to defuse a situaton that, if allowed to contnue, may be detrimental to U.S. interests
are known as _____ operatons.
a) Economy of force
b) Show of force
c) Enforcement
d) Naton assistance
108. Joint force commanders must integrate and synchronize offensive, defensive, and stability
operatons that compromise major operatons and campaigns. Planning for stability operatons should
begin _____.
a) Near the end of joint operaton planning
b) Only afer planning for offensive and defensive operatons is complete
c) At the start of Phase IV Stabilize
d) When joint operaton planning is initated
109. Although _____ may be the stronger posture, it is the _____ that is normally decisive in combat.
Therefore, commanders will normally seek to transiton to the decisive operatons et the earliest
opportunity.
a) Joint, single-Service
b) Offense, defense
c) Defense, offense
d) Atriton, maneuver110. Major operaton and campaign plans must feature a (n)_____ offensive, defensive, and stability
operatons in all phases.
a) Equal proporton of
b) Similar degree of
c) Appropriate balance between
d) Effectve sequencing of
111. Joint force commanders strive to isolate enemies by denying them _____. The intent is to strip away
as much enemy support or freedom of acton as possible, while limitng the enemy’s potental for
horizontal or vertcal escalaton.
a) Movement and maneuver
b) Allies and sanctuary
c) Airfelds and seaports
d) Command and control
112.Preplanned, deterrence-oriented actons carefully tailored to bring an issue to early resoluton
without armed conflict are known as _____.
a) Peacekeeping
b) Flexible deterrent optons
c) Diplomatc efforts
d) Smart power
113. A joint military operaton conducted either as a major operaton or a part of a larger campaign to
seize and hold a military lodgment in the face of armed oppositon for the contnuous landing of forces is
called ____. These operatons may include amphibious, airborne, and air assault operatons, or any
combinaton thereof.
a) Joint recepton, staging, onward-movement, and integraton
b) Forcible entry
c) Full spectrum superiority
d) Force protecton
114. The ultmate measure of success in peace building is _____. Therefore, joint force commanders seek
a clear understanding of the natonal and coaliton strategic end state and how military operatons
support that end state.
a) Politcal, not military
b) Adversary military culminaton
c) Economic sufciency
d) Security sector reform
115. The responsibility to plan and coordinate U.S. government efforts in stabilizaton and reconstructon
has been assigned to _____.
a) Department of State
b) Department of Defense
c) Geographic Combatant Command
d) U.S. Agency for Internatonal Development
116. Pursuant to Executve Order 12656, the _____ is responsible for the protecton and evacuaton of
American citzens abroad and for safeguarding their property.a) Department of Defense
b) Department of Homeland Security
c) Geographic Combatant Command
d) Department of State
117. Military operatons that apply military force or threaten its use, normally pursuant to internatonal
authorizaton, to compel compliance with resolutons or sanctons designed to maintain or restore peace
and order are known as _____ operatons.
a) Peacekeeping
b) Peace enforcement
c) Peace building
d) Peace making
118. In foreign humanitarian assistance operatons, commanders usually establish a _____ because it is
critcal to working with the partcipatng intergovernmental organizatons (IGOs) and nongovernmental
organizatons (NGOs).
a) Joint operatons center (JOC)
b) Joint intelligence center (JIOC)
c) Civil-military operatons center (CMOC)
d) Media operatons center (MOC)
119. Operatons conducted to search for, locate, identfy, recover, and return isolated personnel,
sensitve equipment, items critcal to natonal security, or human remains are known as _____.
a) Noncombatant evacuaton operatons
b) Recovery operatons
c) Foreign humanitarian assistance
d) Consequence management
120. A military operaton to temporarily seize an area, usually through forcible entry, in order to secure
informaton, confuse an adversary, capture personnel or equipment, or destroy an objectve or capability
is called a _____. It ends with a planned withdrawal upon competton of the assigned mission.
a) Peace operaton
b) Raid
c) Recovery operaton
d) Noncombatant evacuaton operaton
121. The North Atlantc Treaty Organizaton (NATO) is an example od a(n) _____.
a) Multnatonal force
b) Alliance
c) Unifed command
d) Coaliton
122. Key consideratons involved in planning and conductng multnatonal operatons are affected by.
a) Financial resources constraints
b) Motves and values of the organizaton’s members
c) Media influence
d) Non-military organizatons
123. Factors that enhance interoperability are _____.a) Lack of coaliton security teams
b) Conflictng personalites
c) Varying levels of experience among coaliton partners
d) A command atmosphere that permits positve critcism and rewards the sharing of informaton
124. Developing and maintaining professional relatonships with multnatonal partners means _____.
a) We must treat them as professionals with limited skills
b) We must contnually reinforce our standards upon them
c) Recognizing that their training and educaton may differ, but does not mean they are less
dedicated or professional
d) Contnuously demonstratng our superiority over them
125. The vetng process for partcipaton in multnatonal operatons serves as a mechanism to _____.
a) Support and enhance individual efforts
b) Increase perceived legitmacy of operatons domestcally and internatonally
c) Minimize clashes that may occur between intergovernmental agencies
d) Force all partcipants to authorize full range of employment of their forces
126. Factors affectng military capabilites of natons include_____.
a) Leader development and natonal interest
b) Religion and culture
c) North Atlantc Treaty Organizaton (NATO)
d) Non-governmental organizatons (NGOs)
127. When employing local natonal support, appropriate security measures should be taken to _____.
a) Ensure that contracted linguists promote only U.S. interests
b) Ensure that contracted linguists do not jeopardize operatons through espionage
c) Utlize contracted linguists with general knowledge of some areas but no specifc knowledge of
any one locaton
d) Only validate cross-cultural communicatons skills of select coaliton partners
128. During the conduct of military operatons, multnatonal personnel must be able to _____.
a) Develop guidance for detainee operatons in a joint environment according to their respectve
laws
b) Target only a small percentage of individuals who fall into different categories under the law of
war
c) Enforce local Rules of Engagement (ROE) without regard to approved coaliton ROE
d) Properly control, maintain, protect, and account for all detainees according to applicable
domestc law, regardless of their category
129. Main role is deterrence. Should hostlites arise, provides forces for prompt and sustained combat
primarily on land.
a) United States Department of Army
b) United States Department of the Navy
c) United States Department of the Marine Corps
d) United States Department of the Air Force
e) United States Coast Guard
f) United States Special Operatons Command
130. Fills the three main roles: Strategic nuclear deterrence, Deployment of forces overseas, Security of
the Sea Lines of Communicaton (SLOCs).a) United States Department of Army
b) United States Department of the Navy
c) United States Department of the Marine Corps
d) United States Department of the Air Force
e) United States Coast Guard
f) United States Special Operatons Command
131. Provides fleet marine forces of combined arms, together with supportng air components, for two
purposes: Service with the fleet in the seizure or defense of advanced naval bases, Conduct land
operatons essental to the prosecuton of a naval campaign.
a) United States Department of Army
b) United States Department of the Navy
c) United States Department of the Marine Corps
d) United States Department of the Air Force
e) United States Coast Guard
f) United States Special Operatons Command
132. Primary role is to provide prompt and sustained offensive and defensive air operatons.
a) United States Department of Army
b) United States Department of the Navy
c) United States Department of the Marine Corps
d) United States Department of the Air Force
e) United States Coast Guard
f) United States Special Operatons Command
133. Protect the public, the environment, and U.S. economic interests in any maritme region offering
service on fve areas: Maritme Safety, Natonal Defense, Maritme Security, Mobility, Protecton of
Natonal Resources.
a) United States Department of Army
b) United States Department of the Navy
c) United States Department of the Marine Corps
d) United States Department of the Air Force
e) United States Coast Guard
f) United States Special Operatons Command
134. Organize, train, and equip Special Operatons Forces (SOFs) for actvites or missions for all the
Services.
a) United States Department of Army
b) United States Department of the Navy
c) United States Department of the Marine Corps
d) United States Department of the Air Force
e) United States Coast Guard
f) United States Special Operatons Command
135. The primary functon of the Services and Special Operatons Command is to provide forces, each of
which is organized, trained, and equipped to perform specifc roles.
a) True
b) False
136. What is the Army’s primary role?a) To train and equip itself for the overwhelming and synchronized applicaton of land combat
power
b) To support the other Services
c) To train and equip itself for the overwhelming and synchronized applicaton of both land and air
combat power
d) All of the above
137. Army Special Operatons missions can include which of the following? (Select all that apply.)
a) Humanitarian assistance
b) Cyberspace operatons
c) Training of foreign militaries
d) Major combat operatons
138. What are the fundamental roles of the U.S. Navy, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard in the
implementaton of the Natonal Security Strategy (NSS)? (Select all that apply.)
a) Secure the United States from direct atack
b) Secure strategic access and retain global freedom of acton
c) Strengthen existng and emerging alliances and partnerships
d) Establish favorable security conditons
139. These capabilites compromise the core of the U.S. maritme power and reflect an increase in
emphasis on those actvites that prevent was and build partnerships.
a) Readiness, preparedness, technical prowess, and training
b) Peacekeeping and contngency operatons
c) Forward presence, deterrence, sea and area control
d) Forward presence, deterrence, sea and area control, power projecton, maritme security, and
humanitarian assistance and disaster response (HS/DR)
140. Marine Corps forces exploit the Total Force Concept, employing combinatons of Actve Duty and
Reserve Marines to ensure that missions are effectvely and efciently executed.
a) True
b) False
141. Which of the following are roles of the U.S. Marine Corps according to Title 10 U.S. Code?
a) Visit, board, search, and seizure (VBSS) training for embargo or intercepton operatons
b) Develop tactcs, techniques, and equipment-use phases of amphibious operatons by landing
c) Narcotcs/drug interdicton and illegal alien interdicton
d) All of the above
142. Which of the following best defne the benefts of versatlity in aerospace power? (Select all that
apply.)
a) Versality allows aerospace forces to be employed at the strategic, operatonal, and tactcal levels
equally effectvely.
b) Versality allows air operatons to shif quickly and decisively from one campaign objectve to
another
c) Versatlity allows aerospace forces to achieve objectves simultaneously at all three levels of war
in parallel operatons.
143. Aerospace Forces produce synergistc effects that are designed not to exceed separately employed
individual forces.
a) True
b) False144. Which of the following are among the Coast Guard’s roles? (Select all that apply.)
Being transferred by Presidental order to the U.S. Navy for operatonal purposes
a) Law enforcement
b) Environmental enforcement
c) Environmental protecton
d) Ice Operatons
e) Search and Rescue
145. The Army can trace its origins to colonial America.
a) True
b) False
146. Which of the following describes the Army’s regulatons, including every detail of the Soldier’s life?
a) Blue Book of the Regulatons for the Order and Discipline of the Troops of the United States
b) The Army Regulatons of 1821
c) The Consttuton
d) All of the above
147. During the early 1990s, what event shifed the focus of the Army’s actvites toward stopping old
rivalries and conflicts?
a) The end of the Cold War
b) The collapse of the Warsaw Pact
c) The rise of global terrorism
d) The breakup of the Soviet Union into smaller states
148. Which of the lessons learned during the Mexican War did the Union Navy use?
a) Move forward from the sea and seize ports
b) Embargo trade and blockade
c) Extract without foundering and unload troops while maintaining stern to the surf
d) Choices 2 and 3
e) Choices 1 and 2
149. Which technological advancements turned the tde on the U-boats? (Select all that apply.)
a) Long-range reconnaissance planes
b) Escort carriers
c) Destroyers equipped with advanced sonars
d) Directon-fnding equipment
e) Ant-submarine weapons
150. Through which of the following strategies has the U.S. Navy retained its traditonal roles while
expanding into expeditonary warfare?
a) Sea power concept
b) “From the Sea” and later “Forward from the Sea
c) U.S. Containment Policy151. Why was the partcipaton of the Montord Point Marines in the amphibious assault at Saipan such
a historic event?
a) No Higgins boats were available
b) It represented the fnal trial and full integraton of the Armed Forces
c) The marines were well-trained
152. Which of the following are examples of how the Marine Corps has adapted and evolved as an
expeditonary force? (Select all that apply.)
a) Amphibious operatons
b) MPFs and MAGTFs
c) Close air support
d) Helicopter-borne vertcal envelopment tactcs
153. In the name of strategic mobility, the Marine Corps adopted prepositoning for which of the
following purposes?
a) For speed and dispersion
b) To provide material needed to sustain a brigade for 30 days in a potental combat zone
c) For amphibious assault
154. During the 1930s, which two essental building blocks for an effectve air force fell into place?
(Select all that apply.)
a) A vision of a long-range, four-engine bomber that became reality with the frst B-17
b) A comprehensive doctrine of air warfare
c) Clear tactcs, techniques, and organizaton for air-ground cooperaton
155. Which of the following problems faced the newly created Air Force in 1947? (Select all that apply.)
a) Establishing an organizaton adapted to air operatons
b) Transitoning from propeller-driven aircraf to jet aircraf
c) Modifying doctrine, strategy, and tactcs to accommodate nuclear weapons
d) Frequent incoming ballistc missiles
e) Arranging for support services
156. Which of the following represent highlights of U.S. Air Force history?
a) Design of a doctrine of strategic bombing and one of organizatonal independence
b) Development of the Strategic Air Command
c) Expansion into space
d) All of the above
157. What Services were established as precursors to the U.S. Coast Guard? (Select all that apply.)
a) Lighthouse Service and Revenue Cuter Service
b) Bureau of Navigaton
c) Life Saving Service
d) Steamboat Inspecton Service
e) Transportaton Security Administraton
158. USCG has always served under the Security of the Treasury, reflectng its early historical mission.
a) True
b) False159. The offering of ceremonial toasts is a traditonal Army custom at a formal Dining-In, which includes
passing the wine “over the water,” a historical reference to James I, who was exiled by Oliver Cromwell.
a) True
b) False
160. Which of the following are consideratons when hostng a formal dinner?
a) Begin planning months in advance with the proposed guest list
b) Printng and mailing invitatons four to six weeks in advance
c) Planning the menu and walking through the upcoming evening’s sequence of events
d) Identfying unique cultural consideratons in a foreign country
e) All of the above
161. A group or person is honor-bound to do which of the following upon receiving a limerick at mess?
a) Ignore it as any self-generated entertainment
b) Refute the remark prior to the close of the dinner hour
c) Return the embarrassment in kind
162. Who are the caretakers of naval customs, traditons, honors, and ceremonies?
a) Admirals
b) Commanders
c) Chief pety ofcers
d) None of the above
163. Which core value does the following tenet represent: make decisions in the best interest of the
Navy and the naton, without regard to personal consequences?
a) Honor
b) Commitment
c) Courage
d) None of the above
164. Which of the following are among Marine Corps customs, courtesies and traditons? (Select all that
apply.)
a) Dining-in and Mess Night
b) Addressing Enlisted Marines
c) Hail and Farewell
d) Marine Corps Birthday Ball
165. Which of the following represents Marine core values?
a) Competence
b) Resoluton
c) Courage
d) No wounded or dead Marine will ever be lef on the feld or unatended, regardless of the cost
of bringing him in.
e) All of the above
166. While it is appropriate and strongly recommended to greet a person by name and grade, if you are
unsure of an enlisted Marin’s name and grade, “Marine” is as appropriate as “Good morning, Sir,” in the
case of an ofcer.
a) True
b) False167. Promotons and Re-enlistments are ceremonies requiring formaton in this order: (a) Personal
awards presented frst, (b) Promoton second, and (c) Re-enlistments third.
a) True
b) False
168. The fallen comrade’s toast at a mess night is the last toast to be given.
a) True
b) False
169. The newest and lest formal of the dinning traditons, requiring combat dress.
a) Dining-Out
b) Dining-In
c) Combat Dining-In
170. A newer custom than Dining-In, which includes spouses and other guests.
a) Dining-Out
b) Dining-In
c) Combat Dining-In
180. Formal dinner for the members of the military.
a) Dining-Out
b) Dining-In
c) Combat Dining-In
181. Which of the following ceremonies afrms a “Leader among Leaders” in the USAF, using a symbol of
truth, justce, and power rightly used?
a) Top 3 Inducton
b) The order of the Sword
c) Grog Bowl
d) None of the above
182. Which of the following is the USCG moto?
1. “Semper Fidelis”
2. “Anchors Aweigh”
3. “Semper Paratus”
4. None of the above
183. The United States Coast Guard’s moto is Semper Paratus, meaning “always ready.”
1. True
2. False
184. Reserve Components now comprise almost what percent of the Total Force and are an integral part
of the Armed Forces of the United States?
a) 30%
b) 40%
c) 50%
d) 60%
185. which of the following is NOT one of the major levels of mobilizaton?a) Full mobilizaton
b) Limited reserve call-up
c) Partal mobilizaton
d) Presidental reserve call-up
186. Which mobilizaton authority provides the President a means to actvate, without a declaraton of
natonal emergency, not more than 200,000 reservists for not more than 365 days to meet the support
requirements of any operatonal mission?
a) Partal mobilizaton (PM)
b) SecDef call-up (SCU)
c) Presidental reserve call-up (PRC)
d) Selectve mobilizaton (SM)
187. Which type of mobilizaton entails mobilizing all Reserve Component units in the existng approved
force structure, as well as all individual reservists, retred military personnel, and the resources needed
to meet requirements of a war or other natonal emergency involving an external threat to the natonal
security, and is for the duraton of the emergency plus six months?
a) Full mobilizaton (FM)
b) Partal mobilizaton (PM)
c) Selectve mobilizaton (SM)
d) Total mobilizaton (TM)
189. _____ is key to successful employment, readiness, and use of Reserve Component forces.
a) Adaptability
b) Predictability
c) Transformaton
d) Training
190. With over half of its forces in the Reserve Components, the Army relies heavily on the _____.
a) Army Natonal Guard
b) Army Reserve
c) Both the Army Natonal Guard and Army Reserve
d) None of the answers are correct
191. Reserve Component units train to a lesser standard than Actve Component units.
a) True
b) False
192. The primary responsibilites of the Air Force Reserve Components, the Air Force Reserve and the Air
Natonal Guard, include airlif and air refueling.
a) True
b) False
193. The following Reserve Components have both a Federal (Title 10) mission and a State (Title 32)
mission, and therefore can be used to enforce State laws.
a) Army Reserve and Army Natonal Guard
b) Air Reserve and Air Natonal Guard
c) Navy Reserve and Maritme Corps Reserve
d) Air Natonal Guard and Army Natonal Guard
194. Which of the following Reserve Component is NOT part of the Department of Defense?
a) Army Natonal Guardb) Coast Guard Reserve
c) Marine Corps Reserve
d) Navy Reserve
195. Special Operatons involve the use of small units of specially trained personnel using specialized
tactcs and equipment to achieve _____objectves.
a) Tactcal
b) Strategic or operatonal
c) Insignifcant
d) Intermediate
196. Most special operatons forces are _____oriented. This allows them to maintain a cultural
awareness and a language capability for their assigned areas.
a) Politcally
b) Mission
c) Regionally
d) Special tactcs
197. Short-duraton strikes and other small-scale offensive actons conducted with specialized military
capabilites to seize, destroy, capture, exploit, recover, or damage designated targets in hostles, denied,
or diplomatcally and/or politcally sensitve environments is called _____. It differs from other offensive
actons in the level of diplomatc or politcal risk, the operatonal techniques employed, and the degree
of discriminate and precise use of force to achieve specifc objectves.
a) Special reconnaissance
b) Counterterrorism
c) Direct acton
d) Unconventonal warfare
198. Reconnaissance and surveillance actons normally conducted in a clandestne or covert manner to
collect or verify informaton of strategic or operatonal signifcance, employing military capabilites not
normally found in conventonal forces are called _____. These actons acquire informaton concerning
the capabilites, intentons and actvites of an enemy.
a) Strategic reportng
b) Foreign internal defense
c) Special reconnaissance
d) Unconventonal warfare
199. Operatons and actvites that are conducted to enable a resistance movement or insurgency to
coerce, disrupt, or overthrow a government or occupying power by operatng through or with an
underground, auxiliary, and guerrilla force in a denied are known as _____. It is a core actvity is special
operatons forces.
a) Unconventonal warfare
b) Civil affairs operatons
c) Special reconnaissance
d) Direct acton
200. Special operatons forces are organized under the _____, a functonal unifed command responsible
for providing mission capable operatons forces to the geographic combatant commanders.
a) United States Northern Command (USNORTHCOM)
b) United States Strategic Command (USSSTRATCOM)
c) United States Special operatons (USSOCOM)d) United States Transportaton Command (USTRANSCOM)
201. Afer the atacks if 9/11, USSCOM assumed an operatonal role in synchronizing the DoD effort in
_____.
a) Support of the U.S. government response to pandemic influenza
b) Global operatons against terrorist networks
c) Cyberspace operatons
d) Combatng weapons of mass destructon
202. The cornerstone of the Special Forces Group’s capability is the _____. A highly trained team of 12 SF
Green Berets.
a) Army Special Operatons Aviaton (ARSOA)
b) Military Informaton Support Operatons Command (MISOC)
c) Operatonal Detachment-Alpha (ODA)
d) Ranger Regiment
203. The _____ is a lethal, agile, and flexible, capable of executng a myriad of complex, joint special
operatons missions in support of U.S. policy and objectves.
a) 101st Airborne Division (Air Assault)
b) 160th Special Operatons Aviaton Regiment
c) 82nd Airborne Division
d) 75th Ranger Regiment
204. These units support military commanders by working with civil authorites and civilian populatons
in the commander’s area of operatons during peace, contngency operatons, and war and are known as
_____ teams.
a) Foreign are ofcers
b) Politcal advisors
c) Civil affairs
d) Special forces
205. The units manned by Special Warfare Combatant-craf Crewmen who operate and maintain a
variety of combatant and other craf for maritme special operatons are known as _____.
a) SEAL Platoons
b) Special Boat Teams
c) SEAL Delivery Teams
d) Special Tactcs Groups
206. The 193rd Special Operatons Wing of the Pennsylvania Air Natonal Guard provides the holy _____
platorm in the Department of Defense with the EC-130 Commando Solo.
a) Airborne early warning
b) Airborne psychological operatons
c) Electronic warfare
d) Combat aviaton advisor
207. The Air Force's Batlefeld Airmen or _____ Teams frequently operate with Navy Seals, Army
Rangers, and Special Forces in direct acton, airfeld seizure, and personnel recovery missions in hostle
territory.
a) Air commando
b) Special tactcs
c) Aero Scout
d) Special Warfare208. This MARSOC element trains, advises, and assists friendly host naton forces – including naval and
maritme military and paramilitary forces – to enable them to support their governments’ internal
security and stability, to counter subversion, and to reduce the risk of violence from internal and external
threats. It has the capability to form the nucleus of a Joint Special Operatons Task Force.
a) Marine Special Operatons Regiment (MSOR)
b) Marine Air-Ground Task Force (MAGTF)
c) Marine Expeditonary Brigade (MEB)
d) Marine Special Operatons Support Group (MSOSG)
209. A special operatons command-forward can transiton to a _____.
a) Theater Special Operatons Command (TSOC)
b) Joint Special Operatons Task Force (JSOTF)
c) Civil-Military Operatons Center (CMOC)
d) Joint Special Operatons Command (JSCO)
210. Special Operatons Forces are a valuable asset for the joint planner, however, they comprise only a
small part of the total force – a litle over ____ percent of the total force.
a) 10
b) 5
c) 2
d) 15
211. In joint SOF mission planning, a demanding fll-up, real-tme _____ can mitgate much of the
inherent risks of many SOF missions. It is key to the success of complex joint SOF missions.
a) Batle rhythm
b) Rehearsal
c) Training exercise
d) Firing course
212. Which of the following is NOT one of the SOF Truths?
a) Humans are more important than hardware
b) Quality always beats quantty
c) SOF cannot be mass produced
d) Competent SOF cannot be created afer emergencies occur
213. Regardless of when or where employed, the Armed Forces of the United States abide by U.S. vlues,
the standards for the profession of arms, and _____.
a) Geneva conventon
b) Consttutonal principles
c) Military law
d) Uniformed code of military justce
214. This term refers to the aggregate of features and trails that form the individual nature of a person.
In the context of the profession of arms, it entails moral and ethical adherence to our values. It is at the
heart of the relatonship of the profession with the American people, and to each other.
a) Competence
b) Character
c) Justce
d) Leadership
215. The purposeful reliance by one Service on another Service’s capabilites to maximize
complementary and reinforcing effects on both (i.e., synergy) is known as _____.a) Mutual trust
b) Bilateral agreement
c) Joint interdependence
d) Joint requirement
216. The concept of "jointness" must be advanced through contnual joint force development efforst.
What does that statement imply?
a) Joint staff leaders do not endorse joint development
b) “Jointness” is not an automatc Service state of being
c) Service members naturally embrace “jointness”
d) Joint force development is a “one tme” occurrence on one’s career
217. _____ prepares individuals, joint forces, or joint staffs to respond to strategic, operatonal, or
tactcal requirements considered necessary by the Combatant Commanders to esecute their assigned or
antcipated missions.
a) Joint doctrine
b) Joint educaton
c) Joint training
d) Joint concepts
218. Successful mission command demands that subordinate leaders at all echelons exercise disciplined
initatve, actng aggressively and independently to accomplish the mission.
a) True
b) False
219. Successful mission command demands that subordinate leaders at all echelons exercise _____.
a) Regularly
b) Cautous power
c) Risk supervision
d) Disciplined initatve
220. Successful teamwork requires _____ commensurate with responsibility.
a) Rank
b) Delegaton of authority
c) Maturity
d) Experience
221. Taking steps and precautons to reduce the likelihood of something negatve or hazardous
happening, or reducing the extent of the exposure to a risk, is called risk modifcaton.
a) True
b) False
222. This hostle environment ofen presents complex emotonal and ethical dilemmas.
a) Irregular warfare environment
b) Major combat operatons
c) Humanitarian assistance operatons
d) Support for civil authorites
223. Which of the following is a technical or personal risk when using social media?a) Network security intrusions
b) Espionage
c) Personal identty thef and impersonaton
d) All of the above
224. Military members are expected to maintain a higher standard of conduct than might be accepted in
the larger society and are subject to the rules and regulatons of the Uniform Code of Military Justce.
a) True
b) False
225. A state of well-being in which one is aware of personal abilites and limits, copes well with life
stresses, works productvely and effectvely, and contributes [positvely to his or her communites is
known as _____. It describes a healthy body, mind, and spirit which can be seen in a person’s ability to
deal with typical stressors.
a) Physical ftness
b) Psychological health
c) Post-traumatc stress disorder
d) Personal awareness
276. Exposure to stressful situatons, trauma, and combat will cause a response and resultng change.
These responses and changes will all be negatve.
a) True
b) False
277. Symptoms of _____ include depression, substance abuse, problems of memory and cogniton, and
other physical and mental health problems. It is also associated with difcultes in social or family life,
including occupatonal instability, marital problems, family discord, and difcultes in parentng.
a) Post-traumatc stress disorder
b) psychiatric disorder syndrome
c) Psychological trauma dysfuncton
d) Traumatc brain injury
278. Symptoms of _____ include headaches, memory gaps, confusion, atenton problems, irritability,
ringing in the ears, dizziness, nausea, fatgue, slowed reacton tme, sleep difculty, and performance
difcultes.
a) Post-traumatc stress disorder
b) Psychiatric disorder syndrome
c) Phycological trauma dysfuncton
d) Traumatc brain injury
279. is an integratve and holistc framework to beter understand, assess, and maintain the ftness of the
joint force.
a) Wounded Warrior Program
b) Total Force Fitness (TFF) Program
c) Physical Fitness Testng (PTF) Program
d) Performance Evaluaton Program280. 1) “The Noncommissioned Ofcer and Pety Ofcer: Backbone of the Armed Forces (2013)" states
that, "To be successful in building and sustaining [a solid and trustworthy] relatonship with ofcers,
NCOs/POs must be _____."
a) educated and empowered
b) properly trained and equipped
c) competent, credible, and capable
d) provided with intent and closely supervised
281. Which of the following is NOT a member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff?
a) Chief of Naval Operatons
b) Commandant of the Coast Guard
c) Commandant of the Marine Corps
d) Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
282. What are the Army's primary missions? (Select all that apply.)
a) Secure the United States from direct atack
b) Preparing now for an uncertain future
c) Responding to crisis
d) Shaping the internatonal environment
283. Exposure to stressful situatons trauma, and combat will cause a response and resultng change.
These responses and changes will all be negatve.
a) True
b) False
284. The _____ is a lethal, agile, and flexible force, capable of executng a myriad of complex, joint
special operatons missions in support of U.S. policy and objectves.
a) 82nd Airborne Division
b) 75th Ranger Regiment
c) 160th Special Operatons Aviaton Regiment
d) 101st Airborne Division (Air Assault)
285. The pinning ceremony signifes which of the following?
a) transiton from the role of a follower to that of a leader
b) completon of a successful mission
c) retrement of a sailor
286. The main idea of the Chairman's White Paper, "America's Military - A Profession of Arms" is to:
a) open an debate on whether the Armed Forces is a profession
b) establish a new way of thinking about the profession of arms
c) renew our commitment to the Profession of Arms
d) identfy the reasons why the Armed Forces is considered a profession
287. Between 1777 and 1778, Baron Friedrich Willhelm von Steuben taught the Contnental Army what
aspects of war? (Select all that apply.)
a) bayonet usage
b) rifle cartridges loading
c) drill formatonsd) proper care of equipment
288. Because not every naton will agree with proposed coaliton actons, what is an acceptable workarounds to accomplish the mission without offending other natons?
a) Rotatng coaliton partners through lead roles to promote their own politcal agendas
b) Establish a basis for coaliton members to easily accept and advocate preferred coaliton optons
c) Openly show favoritsm towards one naton over another naton
d) Establish temporary consensus through personal and professional relatonships
289. _____ are operatons require independent actons involving a high degree of professionalism, selfdiscipline, flexibility, patence, and tact.
a) Support for civil authorites
b) Major combat operatons
c) Humanitarian assistance operatons
d) Peacekeeping operatons
290. Nongovernmental organizatons are usually willing to quickly align themselves with intervening
military forces in order to ensure their ability to achieve their objectves and for their physical security.
a) True
b) False
291. Which of the following would be initated into the "Top 3"?
a) Sgt. Maj.
b) Master Sgt.
c) Col.
292. Resilience-based training contributes to the overall mission readiness of the Armed Forces.
a) True
b) False
293. The U.S. Army and U.S. Navy are under the same jurisdicton.
a) True
b) False
294. Leaders in a joint environment have no reason to be familiar with the rules and regulatons
concerning maintaining good order and discipline within their commands including the punitve artcles
of the Uniform Code of Military Justce.
a) True
b) False
295. Factors that inhibit interoperability are _____.
a) constant efforts to eliminate sources of confusion
b) visits to assess multnatonal capabilites
c) multnatonal training exercises
d) refusal to cooperate with partners; restricted access to natonal proprietary defense informaton
296. While its missions might include forcible entry operatons and peace enforcement, humanitarian
assistance is not within the Marine Corps' purview.
a) True
b) False297. The comprehensive doctrine of air warfare supported the conclusion that high-alttude, daylight
bombing of an enemy's war-supportng industries and transportaton systems could win a war.
a) True
b) False
298. There are eight distnct domains within the Total Force Fitness (TFF) Program. Which one of the
following IS NOT one of the eight domains?
a) Psychological Fitness
b) Spiritual Fitness
c) Environmental Fitness
d) Organizatonal Fitness
299. Which of the following are expected of every Marine in batle? (Select all that apply.)
a) Courage
b) no wounded or dead Marine will ever be lef on the feld or unatended, regardless of the cost of
bringing him in
c) resoluton
d) competence
300. The directon or exercise of authority over subordinate or other organizatons with respect to
administraton and support, including organizaton of Service forces, control of resources and
equipment, personnel management, unit logistcs, individual and unit training, readiness, mobilizaton,
demobilizaton, discipline, and other maters not included in the operatonal missions of the subordinate
or other organizatons is known as _____.
a) Combatant Command (COCOM)
b) Administratve Control (ADCON)
c) Operatonal Control (OPCON)
d) Tactcal Control (TACON)
301. Who is considered the "Father of the Coast Guard?"
a) Douglas Munro
b) Ida Lewis
c) Sumner Kimball
d) Alexander Hamilton
302. The frst step in solving a problem is to _____.
a) gather multple perspectves on the problem
b) report the problem to the commanding ofcer
c) defne the problem
d) draf an acton plan
303. The frst-ever Natonal Defense Strategy (NDS) was initated by Secretary of Defense (SECDEF)
Rumsfeld in 2005, and then updated in 2008 by SECDEF Gates. However in 2012, SECDEF Paneta
released Sustaining U.S. Global Leadership: Priorites for 21st Century Defense, sometmes referred to as
the _____, and widely understood to be the replacement for the NDS. This strategic document was
writen to identfy defense priorites in the face of budget cuts.
a) Natonal Military Strategyb) Defense Strategic Guidance (correct)
c) Joint Strategic Capabilites Plan
d) Natonal Security Strategy
305. Joint _____ provides the fundamental principles that guide the employment of U.S. military forces
in coordinated acton toward a common objectve.
a) doctrine
306. What are the Army's primary missions? (Select all that apply.)
b) responding to crises
c) shaping the international environment
d) preparing now for an uncertain future
307. The principle of joint operatons designed to ensure the commitment necessary to atain the
natonal strategic end state is _____.
a) Perseverance
SEJPME II
308) Which of the following actons may help overcome the staff organizaton challenge of integratng
communicaton-related actvites?
a) ensure these tasks are led only by the J3 or J5
b) ensure there is no divide between primary agency "inform" role and "influence" actvites
c) establish some form of communicaton directorate or cell
d) creatng a passive communicaton posture
309) Which of the following statements concerning operatonal-level branch and sequel planning is
TRUE?
a) Much of the informaton precipitatng operatonal commanders' major decisions across all
event horizons will likely come off the JOC floor, rather than through other venues.
b) Some branch and sequel planning at the operatonal level may not result in precise, detailed
predictve decision points with associated CCIRs.
c) Branch and sequel planning, at the operatonal level, results in precise, predictve decision
points with associated CCIRs
d) Decision points supportng branch and sequel executon are normally extremely well defned
and quanttatve requiring minimal commander interface for decision.
310) This critcal path involves the use of a joint targetng working group (JTWG) that enables selectng
and prioritzing targets and matching the appropriate lethal and supportng nonlethal responses.
a) lethal actons
b) inform and influence
c) stability
d) steering
311) Planning for communicaton strategy involves the careful alignment of themes and messages with
interagency organizatons and other stakeholders.a) True
b) False
312) The directon or exercise of authority over subordinate or other organizatons with respect to
administraton and support, including organizaton of Service forces, control of resources and
equipment, personnel management, unit logistcs, individual and unit training, readiness, mobilizaton,
demobilizaton, discipline, and other maters not included in the operatonal missions of the
subordinate or other organizatons is known as _____.
a) combatant command
b) operatonal control
c) tactcal control
d) administratve control
313) Force protecton is a required actvity throughout each joint operaton or campaign phase. This
type of operaton is a(n) _____ operaton.
a) planning
b) offensive
c) defensive
d) stability
314) The joint communicatons system includes synchronizaton of war fghtng functons, such as
locatng and identfying friendly forces, and supports the conduct of operatons. This contributes to
_____.
a) tactcal flexibility
b) strategic agility
c) network-enabled operatons
d) operatonal reach
315) Which of the following are challenges commanders face in identfying key audiences? (Select all
that apply.)
a) Key audiences may overlap local, regional, and global arenas.
b) Key audiences may be adversarial, neutral, or friendly.
c) Key audiences do not include groups of people who are hostle to the mission.
d) Key audiences will all have the same reactons to words, actons, and images.
e) Key audiences could be any group of people who may impact the joint task force's operatons.
316) What effect(s) can occur when commanders retain tactcal level decision-oriented CCIRs at the
operatonal level in lieu of decentralizing CCIRs associated with decentralized decision approval levels?
a) slows subordinates' agility
b) adds unnecessary reportng requirements
c) shifs HQ's focus away from setng conditons
d) All of the answers are correct
317) Which of the following provides the necessary upfront directon for the synchronizaton of staff
planning efforts for both lethal and nonlethal actvites?
a) objectves, priorites, and commander's critcal informaton requirements (CCIR)
b) planning guidance, commander's intent, and an operatonal frameworkc) targetng data, diplomatc informaton military and economic (DIME) data, and planning
guidance
d) objectves, priorites, and an operatonal framework
318) The principles of personnel support are defned as having a _____ that is _____.
a) command emphasis; responsive, and responsible
b) staff emphasis; responsive and responsible
c) command emphasis; synchronized, unifed, and flexible
d) staff emphasis; synchronized, unifed, and flexible
319) The operatonal chain of command runs directly from the President to the Secretary of Defense
and then to the _____.
a) Service Chiefs
b) Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
c) Combatant Commanders
d) Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff and then to the Combatant Commanders
320) Commanders have recognized the need for some form of staff organizaton that can _____ to
inform or influence the audiences in support of desired outcomes. (Select all that apply.)
a) craf the themes and messages
b) synchronize actons, words, and images
c) direct communicaton strategy through a stove-piped process
d) remain passive in the informaton environment
321) A key functon of the J2 is to integrate outside stakeholders into intelligence planning and
operatons. The J2 can support the Joint Force Commander by integratng _____.
a) state and local militas
b) nongovernmental organizatons
c) partner naton intelligence capabilites and assessments
d) interested UN countries
322) Automaton technology can be used to reduce the burden of sortng through large amounts of
_____ to enable an analyst to correlate various sets of _____ to make an assessment.
a) data, informaton
b) informaton, intelligence
c) intelligence, data
d) data, intelligence
333) Which of the following joint recepton, staging, onward movement, and integraton (JRSOI )
elements are defned as "enabling"? (Select all that apply.)
a) Contract support
b) Multnatonal support
c) Force protecton
d) Legal support
334) What is a target?
a) All enemy enttes or objects
b) An offensive of defensive enemy weapon considered for engagement or actonc) An entty or object considered for lethal fres
d) An entty or object considered for possible engagement or acton
335) Which of the following is a technical or personal risk when using social media?
a) network security intrusions
b) espionage
c) all of the answers are correct
d) none of the answers are correct
e) personal identty thef and impersonaton
336) The _____ serves as the diplomatcally accredited defense ataché (DATT) and chief of the security
assistance organizaton (SAO).
a) U.S. Defense Ataché Ofce
b) chief of mission
c) joint task force liaison ofcer
d) senior defense ofcial
337) Which of the following statements BEST defnes the purpose of joint headquarters batle
rhythms?
a) The joint headquarters batle rhythm is a deliberate daily cycle of command, staff, and unit
actvites intended to provide the commander with a method to track current operatonal
events.
b) The joint headquarters batle rhythm is a deliberate daily cycle of command and staff actvites
intended to control the flow of future operatons.
c) The joint headquarters batle rhythm is a deliberate daily cycle of command, staff, and unit
actvites intended to synchronize current and future operatons.
d) The joint headquarters batle rhythm is a deliberate daily cycle of command and staff actvites
that enable the commander to accomplish mission objectves.
338) Which of the following statement(s) describes the beneft of the adaptve planning process?
(Select all that apply.)
a) centers on a strategic-level "Capstone" plan that provides the framework for other plans that
address contngencies that could happen in the geographic combatant command's areas of
responsibility
b) allows for contnual update and shared awareness of the plans
c) ensures each of the contngency plans take into account natonal interests so that actons
addressing one contngency do not inadvertently impact U.S. natonal interests in another area
339) Which of the following can be described as the most powerful command relatonship in terms of
gaining access to additonal capabilites?
a) support
b) tactcal control (TACON)
c) operatonal control (OPCON)340) Which of the following Natonal Intelligence leadership positons advises the Secretary of Defense
and Deputy Secretary of Defense, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, combatant commanders
(CCDRs), and USD(I) on all maters concerning military and military-related intelligence.
a) Director of the Defense Intelligence Agency
b) Under Secretary of Defense for Intelligence
c) Director of Natonal Intelligence
d) Joint Staff Directorate for Intelligence, J2
341) _____ is the routne contact and interacton between U.S. Armed Forces and another naton's
armed forces, foreign and domestc civilian authorites, and agencies to build trust and confdence.
a) Security
b) Large-scale combat
c) Relief and reconstructon
d) Military engagement
342) During _____, the Joint Force Commander will identfy the operatonal problems to solve and
determine where to focus the staff's efforts.
a) Mission Analysis
b) Course of Acton Development
c) Planning Initaton
d) Plan or Order Development
343) How can the sustainment community provide beter support to the components and the
commander's decision-making?
a) The sustainment community provides beter support when it comes together as a team that is
fully integrated across the staff.
b) The sustainment community provides beter support when its numbers of available staff
personnel are commensurate with the size of the tactcal force it is designated to support.
c) The sustainment community provides beter support when it focuses closer on the tactcal
fght.
344) Which of the following statements is true regarding organizing the various staff sectons as a
sustainment team?
a) The sustainment team should always be organized under the oversight of a deputy
commanding general - support (DCG-S).
b) The primary JFC staff sectons that would make up the sustainment team include the J1, J4, J8,
Engineer, Surgeon, Legal, and Chaplain.
c) Organizing the staff as a sustainment team is never effectve at the component level and below.
345) The J2 has overall staff responsibility for consolidatng and recommending _____.
a) priority intelligence requirements (PIRs)
b) host naton informaton requirements (HNIRs)
c) specifc informaton requirements (SIRs)
d) friendly force informaton requirements (FFIRs)346) Which of the following is a criterion in conductng assessments using measures of performance
(MOP)?
a) straight forward and are drawn directly from assigned tasks in the plan
b) upfront correct determinaton of measures-of-effectveness planning
c) enable an accurate visualizaton of progress toward mission accomplishment
d) used to assess changes in system behavior, capability, or operatonal environment
347) For the executon of a successful communicaton strategy, staff synchronizaton _____. (Select all
that apply.)
a) requires cross-talk and cross-representaton
b) integrates products
c) breaks down staff planning into clearly defned major subsets
d) does not impact actons, words, and images
e) relies on informed commander's guidance
f) begins at the executon phase of operatons
348) Which of the following statements concerning staff assessment products is FALSE?
a) Recommendatons are normally not developed by the assessment cell, but rather by the
affected/responsible staff focused on specifc lines of operaton.
b) Staff assessments products do not necessarily have to support the commander's requirements,
as long as the products provide meaningful informaton.
c) Staff assessments should provide recommendatons to the commander based upon the
assessment.
349) Which of the following statements describes characteristcs of a well-writen problem statement
that can help focus the staff and subsequent planning process?
a) The problem statement should mirror the mission statement to avoid any ambiguity as to what
the end state should be.
b) The problem statement should not allow external stakeholders to gain a shared, common
understanding, but should lead the commander and planners to quickly narrow the focus.
c) The problem statement should not pose a soluton, accounts for current circumstances, and
does not predict what future actons may occur.
d) The problem statement should focus on solving the problem and should directly, or implicitly,
propose solutons.
350) What is the primary goal of operatonal design?
a) Conceive and construct and the framework that underpins a campaign or major operaton plan
b) Understand the ends, ways, and means
c) Link tactcal acton to strategic objectves
d) Visualize the ultmate operatonal approach
351) The _____ is the principal assistant to the President in all maters relatng to the DoD.
a) SecDef
b) Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
c) Inspector General of the DoD
d) JCS Vice Chairman352) The purpose of feld maintenance operatons is to repair, modify, rebuild, and overhaul both
entre systems and components and is directly linked to life cycle systems readiness.
a) True
b) False
353) Which of the following are some of the key elements of the shape phase of joint operatons?
(Select all that apply.)
a) organizing and training
b) balance and simultaneity
c) stability operatons
d) conduct of rehearsals
354) What informaton management (IM) actvity is normally a theater-level decision because of its
signifcant second order effects, such as interoperability within the joint force, felding and pre-mission
training?
a) batle rhythm development maintenance procedures
b) determinaton of the networks, databases, and sofware applicatons
c) use of commander's critcal informaton requirements (CCIR) to guide and prioritze informaton
flow
d) development of procedures into a formalized, authoritatve document
355) Which of the following are key elements of a communicaton strategy?
a) narratve, theme, and message
b) words, actons, and audience
c) conditon, opportunity, and audience
d) stability, peace, and prosperity
356) Which statement best describes what is meant by the term "batle for the narratve?"
a) ongoing "informaton war" between competng natons, enttes, and/or ideologies to gain
superiority over the adversary's narratve and align communicaton efforts
b) race to exploit and change the perceptons of our internatonal partners in order to forward the
goals and intentons of the U.S. Government and its allies
c) challenge of constructng similar strategic narratves distributed throughout multple networks
to reinforce the beliefs, perceptons, attudes, and behaviors of our coaliton partners and host
naton governments
d) struggle to be frst to control the messages that only the adversaries will hear in order to inform
and/or influence their beliefs and perspectves
357) Knowledge management (KM) and informaton management (IM) are two distnct actvites that
are necessary aspects in today's headquarters decision-making. Which two overarching insights clearly
delineate their distnctons?
a) KM is people-centric. IM is informaton technology-centric.
b) KM is technology-centric. IM is people-centric.
c) KM focuses on the rules, procedures, applicatons, and tools. IM focuses on the players gaining
and sharing knowledge to aid decision making.
d) KM balances the need-to-share with the need-to-know. IM leverages the different perspectves
of the myriad of players.358) _____ focus on the enemy or adversary and the operatonal environment and drive intelligence
collecton and producton requirements.
a) Priority intelligence requirements
b) Friendly force informaton requirements
c) Tactcal informaton requirements
d) Commander's critcal informaton requirements
359) The use of capabilites oriented functonal task forces, such as special operatons and counter
improvised explosive device (IED) task forces, is a signifcant evoluton in joint task force organizaton.
a) True
b) False
360) How can headquarters staff personnel effectvely deal with the challenge of unplanned demands
from higher headquarters that may affect the batle rhythm?
a) The batle rhythm must be sufciently flexible to provide the support to the commander in
dealing with the event, and stll be able to functon in the commander's absence.
b) Headquarters staff personnel should maintain constant communicaton with higher
headquarters in an effort to prevent unplanned events which may affect the batle rhythm.
c) The batle rhythm should be managed by a J-code director or deputy when necessary, so that
the commander can deal with the unplanned event.
d) The batle rhythm should be packed with events that ensure all demands from higher
headquarters are being met, thereby minimizing unplanned events.
361) _____ is an operaton that encompasses comprehensive civilian and military efforts taken to
defeat an insurgency and to address any core grievances.
a) Counterinsurgency
b) Counterterrorism
c) Foreign internal defense
d) Stability
362) When framing the interorganizatonal coordinaton process, the frst queston to be asked will
usually be:
a) Who are the appropriate mission partners?
b) How are you sharing interorganizatonal perspectves within your organizaton to enrich the
Commander's decision making?
c) How are you coordinatng with your mission partners?
d) How will you share informaton with mission partners?
363) Communicaton strategy is not a separate or parallel effort, but an integral part of the
commander's overall strategy that ensures a shared understanding of the commander's vision, mission,
and objectves.
a) True
b) False
364) During Crisis Acton Planning, COA _____ is an objectve process where the staff considers COAs
independently of one another, against a set of criteria established by the Joint Force Commander and
staff.a) analysis
b) eliminaton
c) comparison
d) development
365) The mayor of San Antonio has asked the 502 Wing Commander for security forces and military
police from Fort Sam Houston to assist the local police during the annual festa events. The mayor
wants the military to assist with trafc and crowd control. Can Title 10 military personnel conduct this
type of support?
a) yes, because this type of support is permissible under the provisions of the Posse Comitatus Act
b) yes, because the mayor requested the support only for trafc and crowd control
c) yes, but only for Army and Air Force personnel; Marines and Navy personnel cannot provide
support
d) no, trafc control and crowd control is a violaton of the Posse Comitatus Act
366) The authority to protect the resilience and redundancy of critcal civilian infrastructure resides
with the Natonal Security Agency (NSA) under which U.S. Code?
a) Title 22
b) Title 14
c) Title 50
d) Title 10
367) Risk assessment, risk management, and recommending mitgatng measures to the commander
or others, are all steps that must be taken in order to properly mitgate risk.
a) True
b) False
368. _____ is a violent struggle among state and non-state actors for legitmacy and influence over the
relevant populaton(s). If favors indirect and asymmetric approaches, though it may employ the full
range of military and other capacites, in order to erode an adversary’s power, influence, and will.
a) Asymmetric Warfare
b) Traditonal War
c) Joint Warfare
d) Irregular Warfare
369. The ability of the U.S. to achieve its natonal strategic objectves is dependent on the effectveness
of the U.S. Government in employing the instruments of natonal power, which are _____.
a) Diplomatc, Informatonal, Military, and Economic
b) Diplomacy, Defense, and Development
c) Politcal, Military, Economic, Social, Informatonal, and Infrastructure
d) Culture, Industry, Technology, and Geography
370. The President of the United States provides guidance for developing, applying, and coordinatng the
instruments of natonal power to achieve objectves that contribute to natonal security in the _____.
a) Natonal Defense Strategy
b) Natonal Security Strategy
c) Unifed Command Plan
d) Natonal Military Strategy371. The _____, signed by the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, provides guidance for distributon
and applying military power to atain natonal strategic objectves. It describes the Armed Forces’ plan to
achieve military objectves in the near term and provides the vision for ensuring they remain decisive in
the future.
a) Joint Strategic Capabilites Plan
b) Natonal Security Strategy
c) Natonal Defense Strategy
d) Natonal Military Strategy
372. The statutory members of the Natonal Security Council are _____.
a) President, Vice President, Secretary of State, Secretary of Defense, and Secretary of Energy
b) President, Vice President, Secretary of Defense, and Secretary of State
c) President, Vice President, Secretary od State, Secretary of Defense, and Secretary of Treasury
d) President, Vice President, Secretary of Defense, and Secretary of Homeland Security
373. The _____ is the President's principle forum for considering natonal security maters with his senior
natonal security advisors and cabinet ofcials.
a) Secretary of Homeland Security
b) Secretary of Defense
c) Natonal Security Council
d) Joint Chiefs of Staff
374. The non-operatonal chain of command runs directly from the President to the Secretary of Defense
and then to the _____.
a) Service Chiefs via the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
b) Secretaries of the Military Departments and then to the Combatant Commanders
c) Combatant Commanders via the Service Chiefs
d) Secretaries of the Military Departments and then to the Service Chiefs
375. The _____ outranks all other ofcers of the Armed Forces, but may not exercise military command
over any of the Armed Forces. This ofcer is the principle military advisor to the President, the Natonal
Security Council, and the Secretary of Defense.
a) Chairman of he Joint Chiefs of Staff
b) Supreme Allied Commander
c) Combatant Commander
d) War Council
376. A Unifed or Specifed Command with a broad contnuing mission under a single commander
established and so designated by the President, through the Secretary of Defense and with the advice
and assistance of the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is called a _____.
a) Joint Task Force
b) Subordinate Unifed Command
c) Combatant Command
d) Component Command377. A _____ is a joint force that is consttuted and so designated by the SecDef, a Combatant
Commander, a Subordinate Commander, or an existng JTF Commander to accomplish missions with
specifc, limited objectves and which do not require overall centralized control of logistcs. It is dissolved
when the purpose for which it was created has been achieved or when it is no longer required.
a) Combatant Command
b) Subordinate Unifed Command
c) Joint Task Force
d) Service Component Command
378. The term Joint Force Commander refers exclusively to the following three (3) types of commanders:
a) Combatant Commander, Subordinate Unifed Commander, and Joint Task Force Commander
b) Combatant Commander, Service Component Commander, and Functonal Component
Commander
c) Joint Task Force Commander, Functonal Component Commander, and Subunifed Commander
d) Service Component Commander, Combatant Commander, and Joint Task Force Commander
379. Joint Force Air Component Commander (JFACC) Joint Force Land Component Commander (JFLCC),
and Joint Force Maritme Component Commander (JFMCC) are all examples of _____.
a) Joint Task Force Commanders
b) Subunifed Commanders
c) Service Component Commanders
d) Functonal Component Commanders
380. These commands are established by Combatant Commanders when authorized by the SecDef
through the CJCS to conduct operatons on a contnuing basis in accordance with the criteria set forth for
Unifed Commands. They may be established on a geographic area basis such as United States Forces
Japan or a functonal basis such as Special Operatons Command, Pacifc.
a) Combatant Commands
b) Subordinate Unifed Commands
c) Joint Task Forces
d) Functonal Component Commands
381. Combatant Commanders exercise _____ (command authority) over assigned forces. This is the
broadest command authority and may NOT be delegated or transferred.
a) Administratve Control (ADCON)
b) Operatonal Control (OPCON)
c) Tactcal Control (TACON)
d) Combatant Command (COCOM)
382. _____ is the authority to perform those functons of command over subordinate forces involving
organizing and employing commands and forces, assigned tasks, designatng objectves, and giving
authorizaton directon necessary to accomplish the mission. It includes authoritatve directon over all
aspects of military operatons and joint training necessary to accomplish missions assigned to the
command.
a) Combatant Command
b) Operatonal Control (OPCON)
c) Tactcal Control (TACON)
d) Administratve Control (ADCON)
383. The four categories of support are _____.
a) General, tactcal, operatonal, and strategic
b) Tactcal, operatonal, direct, and commonc) General, mutual, direct, and close
d) Reinforcing, mutual, complementary, and close
384. Command authority over assigned or atached forces or commands, or military capability of forces
made available for tasking, that is limited to the detailed directon and control of movements or
maneuvers within the operatonal area necessary to accomplish missions or tasks assigned is known as
_____.
a) Administratve Control (ADCON)
b) Operatonal Control (OPCON)
c) Tactcal Control (TACON)
d) Combatant Command (COCOM)
385. The command authority established by a superior commander between subordinate commanders
when one organizaton should aid, protect, complement, or sustain another force is called _____.
a) Combatant Command
b) Administratve Control
c) Operatonal Control
d) Support
386. The _____, signed by the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, provides guidance for distributng
and applying military power to atain natonal strategic objectves. It describes the Armed Forces' plan to
achieve military objectves in the near term and provides the vision for ensuring they remain decisive in
the future.
a) Natonal Defense Strategy
b) Natonal Military Strategy
c) Joint Strategic Capabilites Plan
d) Natonal Security Strategy
387. The statutory advisers to the Natonal Security Council are the _____.
a) Director of Natonal Intelligence and the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
b) Director of Central Intelligence and the Atorney General
c) Natonal Security Advisor and the Economic Advisor
d) Secretary of Homeland Security and the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
388. The document, approved by the President, which delineates the general geographical area of
responsibility for geographic combatant commanders and specifes functonal responsibilites for
functonal combatant commanders, is called the _____.
a) Joint Strategic Capabilites Plan
b) Natonal Security Strategy
c) Unifed Command Plan
d) Guidance for Employment of the Force
389. The Joint Staff is under exclusive authority, directon, and control of the _____.
a) Joint Chiefs of Staff
b) Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
c) Combatant Commanders
d) Service Chiefs
390. Regardless of when or where employed, the Armed Forces of the United States abide by U.S. values,
the standards for the profession of arms, and _____.
a) Geneva conventon
b) Consttutonal principlesc) Military law
d) Uniformed code of military justce
391. This term refers to the aggregate of features and trails that form the individual nature of a person.
In the context of the profession of arms, it entails moral and ethical adherence to our values. It is at the
heart of the relatonship of the profession with the American people, and to each other.
a) Competence
b) Character
c) Justce
d) Leadership
392. The purposeful reliance by one Service on another Service’s capabilites to maximize
complementary and reinforcing effects of both (i.e., synergy) is known as _____.
a) Mutual trust
b) Bilateral agreement
c) Joint interdependence
d) Joint requirement
393. The concept of “jointness” must be advanced through contnual joint force development efforts.
What does that statement imply?
a) Joint Staff Leaders do not endorse joint force development
b) “Jointness” is not an automatc Service state of being
c) Service members naturally embrace “jointness”
d) Joint force development is a “one-tme” occurrence in one’s career
394. _____ prepares individuals, joint forces, or joint staffs to respond to strategic, operatonal, o tactcal
requirements considered necessary by the Combatant Commanders to execute their assigned or
antcipated missions.
a) Joint doctrine
b) Joint educaton
c) Joint training
d) Joint concepts
395. Successful mission command demands that subordinate leaders at all echelons exercise disciplined
initatve, actng aggressively and independently to accomplish the mission.
a) True
b) False
396. Successful mission command demands that subordinate leaders at all echelons exercise _____.
a) Regularly
b) Cautous power
c) Risk supervision
d) Disciplined initatve
397. Successful teamwork requires _____ commensurate with responsibility.
a) Rank
b) Delegaton of authority
c) Maturity
d) Experience398. Taking steps and precautons to reduce the likelihood of something negatve or hazardous
happening, or reducing the extent of the exposure to a risk, is called risk modifcaton?
a) True
b) False
399. This hostle environment ofen presents complex emotonal and ethical dilemmas.
a) Irregular warfare environment
b) Major combat operatons
c) Humanitarian operatons
d) Support for civil authorites
400. If something of an ethical nature is ever in doubt, commanders should contact their legal counsel
for advice.
a) True
b) False
401. Military member to maintain a higher standard of conduct than might be accepted in the larger
society and are subject to the rules and regulatons of the Uniform Code of Military Justce.
a) True
b) False
402. A state of well-being in which one is aware of personal abilites and limits, copes well with life
stresses, works productvely and effectvely, and contributes positvely to his or her communites is
known as _____. It describes a healthy body, mind, and spirit which can be seen in a person’s ability to
deal with typical stressors.
a) Physical ftness
b) Psychological health
c) Post-traumatc stress disorder
d) Personal awareness
403. Exposure to stressful situatons, trauma, and combat will cause a response and resultng change.
These responses and changes will all be negatve.
a) True
b) False
404. Symptoms of _____ include depression, substance abuse, problems of memory and cogniton, and
other physical and mental health problems. It is also associated with difcultes in social or family life,
including occupatonal instability, mental problems, family discord, and difcultes in parentng.
a) Post-traumatc stress disorder
b) Psychiatric disorder syndrome
c) Psychological trauma dysfuncton
d) Traumatc brain injury
405. Typical signs of _____ include headaches, memory gaps, confusion, atenton problems, irritability,
ringing in the ears, dizziness, nausea, fatgue, slowed reacton tme, sleep difculty, and performance
difcultes.
a) Port-traumatc stress disorder
b) Psychiatric disorder syndrome
c) Psychological dysfuncton
d) Traumatc brain injury406. Receiving realistc training, understanding the types of situatons encountered in war, eatng well,
getng enough rest, and having meaningful relatonships and friendships are all helpful in building _____
to the challenges and strains of military service.
a) Teamwork
b) Tolerance
c) Resilience
d) Unity of effort
407. _____ is an integratve and holistc framework to beter understand, assess, and maintain the
ftness of the joint force.
a) Wounded Warrior Program
b) Total Force Fitness (TFF) Program
c) Physical Fitness Testng (PFT) Program
d) Performance Evaluaton Program
408. The joint force commander has the operatonal authority and responsibility to tailor forces for the
mission at hand, selectng those that most effectvely and efciently ensure success.
a) True
b) False
409. Within joint command organizatons, leadership and ethics consideratons require us to _____ and
consider not only personal experiences, but also the lessons learned from others' experiences - both
positve and negatve.
a) seek out professional assistance
b) know all of the facts
c) acknowledge our own prejudice
d) critcally think about
410. Concussion is a term many service members prefer to use instead of "brain injury" when discussing
head injuries (mild traumatc brain injuries or mTBI).
a) True
b) False
411. U.S. Law, Title 10, USC, Secton 153, gives the _____ authority regarding joint force development,
specifcally providing authority to develop doctrine for the joint employment of the Armed Forces, and
to formulate policies for the joint training of the Armed Forces to include policies for the military
educaton and training of members of the Armed Forces.
a) Joint Chiefs of Staff
b) Service Chiefs
c) Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
d) Secretary of Defense
412. U.S. military service is based on values that U.S. military experience has proven to be vital for
operatonal success. These values adhere to the most idealistc societal norms, are common to all the
Services, and represent the essence of military professionalism. The fve values we discussed that entail
"Joint Service" consist of: duty, honor, courage, integrity, and selfless service.
a) True
b) False
413. Recognizing potentally hazardous or negatve situatons in advance is crucial to being prepared to
prevent them from occurring to begin with. With experience and maturity, the ability to instnctually
recognize signs of potental trouble increases.a) True
b) False
414. The foremost value of joint force leaders is _____.
a) experience
b) integrity
c) competence
d) physical courage
415. The _____ focuses on planning and executon of operatons using operatonal art to develop
strategies, campaigns, and operatons and employ military forces by integratng ends, ways, and means.
a) Strategic level
b) Operatonal level
c) Tactcal level
d) Politcal level
416. Read the following scenario, and as you read it, think about the 12 Principles of Joint Operatons.
Each principle applies to the described situaton in some capacity, but consider their relatve importance
for this partcular scenario. In the boxes provided below, indicate whether the principle listed is MOST
RELEVANT or LEAST RELEVANT to the scenario by typing in your response.
A sometmes-ally of the United States requests U.S. support in maintaining stability during an insurgent
uprising. The U.S. agrees to lead a multnatonal peace-keeping force in the volatle country, since
supportng the legitmate government adds stability to a key strategic region. The insurgents comprise of
a number of radical groups that follow a shared politcal ideology and collectvely seek economic control
within the region. They appear to be funded by narcotcs cartels and organized crime syndicates in
Central and Northern South America. The insurgents use a variety of disruptve, irregular warfare tactcs
to exert their influence, including the use of Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs), ambushes on peacekeeping forces, civilian kidnapping, graf, and civilian extorton. U.S. forces have also detected numerous
cyber-atacks that appear to originate from insurgent sources; however, none of these have been
successful
a) Objectve
LEAST RELEVANT
b) Offensive
LEAST RELEVANT
c) Mass
LEAST RELEVANT
d) Economy of Force
MOST RELEVANT
e) Maneuver
LEAST RELEVANT
f) Unity of Command
MOST RELEVANT
g) Security
MOST RELEVANT
h) Surprise
LEAST RELEVANT
i) Simplicity
LEAST RELEVANT
j) Restraint
MOST RELEVANT
k) Perseverance
MOST RELEVANT
l) LegitmacyMOST RELEVANT
Which principles did you rank as among the most important? Explain why.
Restraint, perseverance, and legitmacy were ranked among the most important because these principles
directly support irregular warfare conditons, such as those described in the scenario. Security was also
ranked highly, because the scenario oppositon forces use irregular means, such as IEDs and ambush
atacks. Next, Economy of Force was ranked among the top principles because stability operatons must
be carried out with the upmost efciency, so that the U.S. achieves an optmal return on investment.
Finally, because the mission involves a multnatonal coaliton, Unity of Command takes on greater
priority; coordinaton among forces becomes more challenging as a greater number of units, agencies,
and countries become involved.
Which principles did you rank as among the least important? Explain why.
Having a clear objectve is vital. However, since the strategic objectve in this scenario is to maintain
stability in an ally's country, developing more detailed operatonal objectves takes on comparatvely less
signifcance. Similarly, since the mission involves stabilizaton, versus aggression, taking offensive acton
becomes less important, as is the element of surprise, the exploitaton of maneuver, and the
concentraton of a large mass of combat power. Finally, while simplicity is important (partcularly in
multnatonal operatons), it is less vital in the described scenario; given the complexity of the situaton,
simple responses may not be sufcient.
417. The following image is a concept map for you to review. Note that there are several empty boxes on
the map labeled "Queston 1" through "Queston 5". In the boxes provided below, choose the proper
concept for each of these empty boxes by typing in your response in the space provided.
Queston 1: Which of the following concepts best fts this box? (Directng, Operatons, Security,
Communicatons, or Financing): SecurityQueston 2: Which of the following concepts best fts this box? (Share informaton, Reportng an event,
Establishing mutual security, Communicatng with leaders in the area, or Counterinsurgency): Share
Informaton
Queston 3: Which of the following concepts best fts this box? (Joint Communicatons, Joint Maneuvers,
Joint Acton Planning, Joint Maters, or Joint Forces): Joint Maters vs Joint Force
Queston 4: This is the purposeful reliance by one Service on another Service's capabilites to maximize
complementary and reinforcing effects of both, with the degree of interdependence varying with specifc
circumstances. (Joint Agreement, Joint Independence, Joint Interdependence, Joint Dependence, or Joint
Cooperaton): Joint Interdependence
Queston 5: Which of the following concepts best fts this box? (Associate, Develop, Refne, Collaborate,
or Synchronize): Synchronize
418. The _____ system provides many things, including means by which the President and the SecDef
can receive warnings and intelligence so that accurate and tmely decisions can be made.
Nuclear Command and Control
Defense Contnuity
Natonal Military Command
Joint Force Commander’s Communicaton
419. Think about the module you just completed. What are three things you already knew about this
material, three things you learned, and three things you would like to learn more about. Record your
answers below:
I already knew
1.
2.
3.
I just learned
1.
2.
3.
I would like to learn more
1.
2.
3.420. As an example of General vs. Specialized Forces, Navy and Air Force Service members, accustomed
to working with enlisted personnel who are specialized technicians, may approach joint staff work from a
more _____ perspectve than that of their ground Service member counterparts.
a) Technical or managerial
b) Centralized
c) Statc
d) Assessing
421. A _____ is a series of related major operatons aimed at achieving strategic and operatonal
objectves within a given tme and space.
a) mission
b) campaign
c) functon
d) engagement
422. Select the answer that matches the following defniton. This purpose of joint operatons is to
defend natonal interests, not only in conflict but through preventatve measures to deter potental
adversaries who could threaten the vital interests of the U.S. or its partners.
a) Provide a stabilizing presence
b) Project power despite ant-access/area denial challenges
c) Maintain a safe, secure, and effectve nuclear deterrent
d) Deter and defeat aggression
423. Select the answer that matches the following defniton. This type of command is composed of
signifcant assigned components of two or more Military Departments.
a) Specifed Combatant Command
b) Unifed Combatant Command
c) Subordinate Unifed Command
d) Joint Task Force
424. _____ is the employment of available weapons and other systems to create a specifc lethal or
nonlethal effect on a target.
a) Movement and maneuver
b) Command and control
c) Joint fres
d) Sustainment
425. A functonal Component Command has many favorable factors associated with it, including
reduced span of control, integrated planning, unity of effort, and _____.
a) control over the scheme of maneuver
b) responsible for service-specifc functons
c) comprised of service forces
d) decreased combat efciency
426. Differences between the Services in career paths leading up to a joint assignment may surprise new
staff Service members in joint assignments. This demonstrates which key element to remember when
working with other services?
a) Prior experience working with senior ofcers vs. litle or none
b) Centralized vs. decentralized approach
c) Statc vs. dynamic mission setsd) General vs. specialized enlisted forces
427. _____ are the broad and enduring purposes for which the Services and the Combatant commands
(or CCMDs) were established by law.
a) Functons
b) Roles
c) Organizatons
d) Responsibilites
428. Select the answer that matches the following defniton. This purpose of joint operatons is to
conduct a sustainable pace of presence operatons abroad, including rotatonal deployments and
bilateral and multlateral training exercises.
a) Deter and defeat aggression
b) Maintain a safe, secure, and effectve nuclear deterrent
c) Project power despite ant-access/area denial challenges
d) Provide a stabilizing presence
430. Some services have an emphasis that vacillates between combat, law enforcement, and safety
patrols. This demonstrates which key element to remember when working with other services?
a) centralized vs. decentralized approach
b) base-centric vs. ship-centric
c) statc vs. dynamic mission sets
d) size and capacity vs. speed and flexibility
431. Select the answer that matches the following defniton. This type of command is established by
unifed combatant commanders, and conducts operatons on contnuing basis using specifed criteria.
a) Specifed Combatant Command
b) Unifed Combatant Command
c) Joint Task Force
d) Subordinate Unifed Command
432. Select the answer that matches the following defniton. This purpose of joint operatons is to
maintain an arsenal capable of deterring potental adversaries and to assure U.S. allies and other security
partners that they can count on America's security commitments.
a) Project power despite ant-access/area denial challenges
b) Maintain a safe, secure, and effectve nuclear deterrent
c) Deter and defeat aggression
d) Provide a stabilizing presence
433. The _____ exercise ADCON through their respectve Service Chiefs over the Service.
a) Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
b) Functonal Combatant Commanders
c) Secretaries of the Military Departments
d) Combatant Commanders
434. Technology is ofen applied against what common analyst concern?
a) Informaton overload
b) CCIR management
c) Subjectve assessments
d) Replacing cross staff collaboraton
435. Which of the following statements highlights the critcal features of intelligence?a) Allows antcipaton or predicton of future situatons and circumstances
b) Provides raw, factual informaton on a wide variety of subjects
c) Informs decisions by illuminatng the differences in available courses of acton
d) Contributes to or shapes the commander’s decision making process
436. Analysis is a synthesis of quanttate analysis and qualitatve judgement and therefore rarely subject
to competng interpretatons.
a) True
b) False
437. What is the primary role of the joint force J2?
a) To inform the commander
b) To analyze data
c) To collect data and relate data from a wide spectrum into usable informaton
d) To manage collecton assets to maximize data collecton across the operatonal environment
438. Commanders use intelligence to _____. (Select all that apply)
a) Support a predictve estmaton of the situaton
b) Understand adversary capabilites and intentons
c) Visualize and understand all dimensions of the OE
439. Which of the following are true when forming priority intelligence requirements (select all that
apply)
a) PIRs are subject for which there is a need to collect informaton or produce intelligence
b) Staff must be aware of intelligence requirements of higher, adjacent, subordinate and supportng
elements
c) The JFC’s PIRs should prioritze the most urgent intelligence requirements.
d) All of the above
440. Afer intelligence requirements are established, the staff reviews existng databases for answers to
requirements. Then, if the intelligence requirement does not exist, the _____.
a) Staff issues a request for informaton
b) Staff collects informaton themselves
c) Staff rejects JFC’s PIR
d) JFC refnes the PIR to match available intelligence
441. What is the defniton of collecton requirements management?
a) Matching intelligence collecton requirements with appropriate collecton capabilites
b) Analyzing the priority intelligence requirements against existng elements of essental
informaton]
c) Matching the commander’s critcal informaton requirements with the other intelligence
operatons
d) Synchronizes the tming of collecton with the operatonal scheme of maneuver and with other
intelligence operatons
442. Why does collecton planning require the ability to call on a variety of collecton sources?
a) To allow flexible tasking of assets
b) To minimize the effects of enemy decepton
c) To ensure subordinate units maintain situatonal awareness of PIRs
d) To provide spare assets on call in event of cancellatons
443. Doctrinal, manning, and organizatonal consideratons are what part of the joint intelligence
architecture planning process?a) Systems architecture planning
b) Operatonal architecture planning
c) Technical architecture planning
d) Logistcal architecture planning
444. Intelligence disseminaton requirements and procedures must be coordinated through the _____.
a) Communicatons directorate of the J6
b) Joint force command J3
c) Joint force command J2
d) Joint Collecton Management Board
445. What role(s) is responsible for providing maps, charts, digitzed products, and precise geodetc
coordinates?
a) The Intelligence Ofcer (J2)
b) The Geospatal Informaton and Service Ofcer
c) The Intelligence Analysts and Targeteers
d) The Collecton Managers
446. The joint intelligence preparaton of the environment (JPOE) consists of four steps.
Step 1 Analyze the adversary and other relevant aspects of the operatonal environment
Step 2 Describe the impact of the operatonal environment on the adversary and friendly courses of
actons (COAs)
Step 3 Evaluate the capabilites of adversary forces operatng in the operatonal environment
Step 4 Determine and describe potental adversary COAs and civilian actvites that might impact military
operatons
447. Disseminaton of informaton can sometmes be defned by a strategy called Push and Pull. Pull
refers to which of the following:
a) Involves direct electronic access to databases, intelligence fles, or other repositories by
intelligence organizatons at all levels
b) Refers to validatng informaton from multple sources
c) Allows the higher echelons to move intelligence down to satsfy existng lower echelon
requirements or to relay other relevant informaton to the lower level.
d) Indicates informaton that is pulled from raw data that cannot be validated
448. Intelligence defnitons:
g. Warning Intelligence – Focuses on the opportunites to counter and alter only those threats that have
detrimental effects for the U.S. (including U.S. military or politcal decision cycles, infrastructure, COA, or
loss of governance). Provides a distnct communicaton to a decision maker about threats against U.S.
security, interests, or citzens; carries a sense of urgency, implying the decision maker should take acton
to deter or mitgate the threat's impact.
a. Current Intelligence – Involves the integraton of tme-sensitve, all-source intelligence and
informaton into concise, objectve reportng on the current situaton in a partcular area. Involves the
integraton of tme-sensitve, all-source intelligence and informaton into concise, objectve reportng on
the current situaton in a partcular area.
h. General Military Intelligence – Supports the requirements to quickly respond to differing crisis
situatons with corresponding intelligence spanning the globe. Focuses on the military capabilites of
foreign countries and organizatons to include non-state actors, and other topics that could affect
potental US or multnatonal military operatons.f. Target Intelligence - Identfes and nominates specifc COGs and HVTs that, if exploited in a systematc
manner, will create the desired effects and support accomplishment of the commander’s objectves.
Portrays and locates the components of a target or target complex, networks, and support infrastructure,
and indicates its vulnerability and relatonship to the enemy Centers of Gravity (COG); consists of analysis
of physical and virtual atributes and signatures as well as Batle Damage Assessment (BDA) resultng
from the applicaton of lethal or non-lethal military force.
b. Scientfc and Technical Intelligence - Comprises characteristcs, capabilites, vulnerabilites, and
limitatons of all weapon systems, subsystems, and associated material, as well as related research and
development. Examines foreign developments in basic and applied sciences and technologies with
warfare potental, partcularly enhancements to weapon systems; addresses overall weapon systems,
tactcs analysis, and equipment effectveness.
d. Counterintelligence – Analyzes the threats posed by foreign intelligence and security services, and
the intelligence actvites if non-state actors such as organized crime, terrorist groups, and drug
trafckers. Informaton gathered and actvites conducted to identfy, deceive, exploit, disrupt, or protect
against espionage, other intelligence actvites, sabotage, or assassinatons conducted for or on behalf of
foreign powers, organizatons, or persons, or their agents, or internatonal terrorist organizatons or
actvites.
e. Estmatve Intelligence – Reaches beyond descriptons of adversary capabilites or reportng of enemy
actvity to forecast the unknown based on an analysis of known facts using patern analysis, inference,
and statstcal probability techniques. Forecasts of current or potental situatons with implicatons for
planning and executng military operatons; includes a descripton of relevant actors' capabilites, and
reportng of their actvites, and it analyzes known factors using techniques such as patern analysis,
inference, and statstcal probability to address unresolved variables.
c. Identty Intelligence – Results from the fusion of identty atributes (biologic, biographic, behavioral,
and individuals) and other informaton and intelligence associated with those atributes collected across
all intelligence disciplines. Results from the fusion of identty atributes (biologic, biographic, behavioral,
and reputatonal informaton related to individuals) and other informaton and intelligence associated
with those atributes collected across all intelligence disciplines.
449. What level of intelligence is produced for the President, Congress, Secretary of Defense, senior
military leaders, and combatant commanders?
a) Doctrinal
b) Natonal strategic
c) Natonal security
d) Theater strategic
450. An intelligence report is received by the JFC detailing the capabilites and safe houses of an
extremist group operatng in its area of regard. What type of intelligence does this represent?
a) Tactcal intelligence
b) Theater strategic intelligence
c) Operatonal intelligence
d) Human intelligence
451. To be successful, a joint force commander must be able to influence and coordinate a diverse
coaliton of joint and multnatonal forces as well as civilian agencies and groups. What are some of the
civilian groups the FRC must consider? Select all that apply.
a) Nongovernmental organizatons
b) State and local militas
c) Multnatonal forces
d) Host naton agencies452. Prior to planning for operatons in support of the JFC OPLAN, a briefng is presented to the planning
staff concerning the environmental conditons, layout of adversarial forces and their relatonship with
rural communites and leaders, as well as the history of relatonship between the local populaton and
foreigners. Which one of the ten principles of intelligence does this represent?
a) Prioritzaton
b) Collaboraton
c) Integrity
d) Synchronizaton
453. Assuming the truism that intelligence is imperfect, what is the best way to minimize the obstacles to
achieve a high degree of fdelity in the products of intelligence?
a) Antcipatng the changing operatonal environment and focusing collecton efforts to support
ongoing operatons54.
b) Collaboratng with allies and coaliton partners who posses niche expertse and alternatve
perspectves that compliment joint force intelligence environment
c) Stafng efforts to achieve a mix of skills and characteristcs that enable them to remain
responsive to a changing environment
d) Constantly strive to maintain the highest possible standards of excellence
454. Which of the following intelligence principles is described as the process of collectng and
examining informaton from available sources and intelligence disciplines to derive as complete an
assessment as possible.
a) Collaboratve
b) Unity of effort
c) Fusion
d) Synchronizaton
455. Principles of intelligence:
Synchronizaton – Requires that all intelligence sources and methods be applied in concert with the
operatons plan and operatons order.
Predicton – Vulnerable to incomplete informaton and adversary decepton, but should never be
avoided because it helps JFCs determine enemy intentons and capabilites.
Collaboraton – Relies on unhindered access to and sharing of all relevant informaton and can take
many forms such as compettve analysis, brain storming, and federaton.
Fusion - Relies in a fnished intelligence product that provides the most accurate and complete picture
possible of what is known about an actvity.
456. Identfy the natonal intelligence member that has overall responsibility for intelligence support to
the President and the day-to-day management of the intelligence community.
a) Director of the Central Intelligence Agency
b) Under Secretary of Defense for Intelligence
c) Director of Natonal Intelligence
d) Director of the Defense Intelligence Agency457. Which of the following natonal intelligence leadership positons advises the Secretary of Defense
and Deputy Secretary of Defense, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, combatant commanders (CCDRs),
and USD(I) on all maters concerning military and military-related intelligence?
a) Director of the Defense Intelligence Agency
b) Under Secretary of Defense for Intelligence
c) Director of Natonal Intelligence
d) Joint Staff Directorate for Intelligence, J2
458. Which of the following intelligence communites is responsible for providing intelligence support in
areas such as human factors analysis, counterterrorism, personal recovery, and noncombatant
evacuaton operatons?
a) Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA)
b) Natonal Security Agency (NSA)
c) Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)
d) Central Security Service (CSS)
459. Which of the following non-DoD intelligence communites supports HUMINT collecton, all source
analysis, and politcal, economic, and biographic intelligence?
a) Department od State (DOS) Bureau of Intelligence and Research
b) Department of Energy (DOE)
c) Federal Bureau Investgaton (FBI)
d) Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)
460. The _____ is the primary intelligence organizaton that provides support to the combatant
commands at the operatonal and tactcal levels.
a) Natonal Intelligence Support Team (NIST)
b) Joint Intelligence Operatons Center (JIOC)
c) Defense Joint Intelligence Operatons Center (DJOC)
d) Joint Intelligence Support Element (JISE)
461. The intelligence component of the Natonal Joint Operatons and Intelligence Center (NJIOC)
provides planning, management, and infrastructure for intelligence working groups and intelligence task
forces that provide direct intelligence support during major conflicts.
a) True
b) False
462. JIPOE Steps:
DIA – Intelligence support provided includes, but is not limited to, all-source military analysis, human
factors analysis, HUMINT, MASINT, MEDINT, CI, counterterrorism, chemical, biological, radiological, and
nuclear counterproliferaton, counterdrug operatons, and personnel recovery
NSA/CSS – A unifed organizaton that provides for the SIGNIT mission of the U.S. to ensure the
protecton of natonal security systems for all departments and agencies of the U.S. Government
NGA – Provides tmely, relevant and accurate GEOINT support to IMINT, geospatal informaton, natonal
imagery collecton management, commercial imagery, imagery-derived MSAINT, and some
meteorological and oceanographic data and informatonNRO – Responsible for integratng unique and innovatve space-based reconnaissance technologies and
the engineering, development, acquisiton, and operaton of space reconnaissance systems and related
intelligence actvites
463. Joint intelligence planning supports joint operaton planning and results in the producton of what
three products?
a) Dynamic Threat Assessment
b) Annex B: Intelligence
c) Contngency Plan
d) Natonal Intelligence Support Plan
464. Advance scouts report that a key bridge crossing is being defended by two tank platoons supported
by a reinforced infantry brigade. Which of the following type of intelligence does this represent?
a) Natonal
b) Operatonal
c) Tactcal
d) Theater strategic
465. What principle of intelligence is most susceptble to incomplete informaton and enemy decepton
efforts?
a) Synchronizaton
b) Predicton
c) Fusion
d) Agility
466. This intelligence product category forecasts current or potental situatons with implicatons for
planning and executng military operatons.
a) Target Intelligence
b) Current Intelligence
c) Estmatve Intelligence
d) Warning Intelligence
467. Which of the following are tasks that the J2 performs? (Select all that apply.)
a) Assesses the characteristcs of the adversary's decision-making process and identfes
weaknesses that may be exploited
b) Produces threat assessments on a contnuing basis to help the commander create or exploit
opportunites to accomplish friendly force objectves
c) Analyzes the adversary and other relevant aspects of the operatonal environment
d) Ensures that critcal intelligence is disseminated appropriately in a tmely manner to the joint
force commanders (JFCs), staff, and components
468. The JTF J2 should have personnel knowledgeable in foreign disclosure policy and procedures and
should obtain necessary foreign disclosure authorizaton from DIA as soon as possible.
a) True
b) False
469. Which of the following roles must be well versed with tmelines required to complete a required
product and able to obtain the aid of external resources in acquiring needed intelligence?
a) J2 Collecton Manager
b) Intelligence Analystsc) Targeteers
d) J2
470. Collecton actvites acquire and extract data from the operatonal environment such that Processing
and Exploitaton can convert that data into informaton to be used during Analysis and Producton to
refne into _____ to satsfy Requests for Informaton (RFI) or the commander's Priority Intelligence
Requirements (PIR).
a) intelligence
b) informaton
c) data fee
d) translaton
471. What two features distnguish intelligence from informaton?
a) Allows antcipaton or predicton of future situatons and circumstances
b) Contributes to or shapes the commander's decision making process
c) Consists of the synthesis of quanttatve analysis and qualitatve judgment with an assigned
degree of coincidence to the analytcal conclusion
d) Provides raw, factual informaton on a wide variety of subjects
472. The Commander's Critcal Informaton Requirements represent both Friendly Force Informaton
requirements and _____, which are derived from the intelligence organizaton and veted across staff.
a) identfed collecton gaps
b) mission analysis identfed requests for informaton
c) priority intelligence requirements (PIR)
d) threat assessments
473. Military operatons vary in scope, purpose, and _____ across a range that spans from military
engagement to major operatons and campaigns.
a) Conflict intensity
b) End state
c) Expected outcome
d) Contngencies
474. _____ is the protecton of U.S. sovereignty, territory, domestc populaton, and critcal defense
infrastructure against external threats and aggressive or other treats as directed by the President.
a) Civil support
b) Peace operatons
c) Homeland defense
d) Combatng terrorism
475. By arranging operatons and actvites into phases, the JFC can beter integrate and _____
subordinate operatons in tme, space, and purpose.
a) Visualize
b) Synchronize
c) Mitgate
d) Organize
476. Which of the following are effectve means to achieve deterrence? (Select all that apply.)
a) Foster a climate of peaceful cooperaton
b) Ensure joint operatons forces are ready to conduct decisive operatons
c) Develop a Security Cooperaton Plan
d) Remove forces from area477. _____prevents an adversarial acton by presentng a credible threat of counteracton. This actvity
can occur during both peace and war.
a) Diplomacy
b) Deterrence
c) Foreign humanitarian assistance
d) Security cooperaton
478. Which of the following statements accurately reflect crisis and limited contngency operatons?
(Select all that apply,)
a) Are part of the JFC’s OPLAN
b) Are used to restore stability in a naton where internal conflict threatens regional stability
c) Must achieve a very specifc or operatonal objectve
d) Are conducted to achieve tactcal objectves
479. Executve Order 12656, Assignment of Emergency Preparedness Responsibilites, delegates DoD to
advise and assist DOS in preparing and implementng plans for _____.
a) Non-combat evacuaton
b) Foreign internal defense
c) Foreign humanitarian assistance
d) Military support
480. A(n) _____, such as foreign humanitarian assistance, can be a major operaton if the combinaton of
size, scope, and duraton requires the commander to phase the operaton as a set of tasks, actvites, and
missions over tme.
a) Interdicton
b) Noncombat operaton
c) Campaign
d) Combat operaton
481. To achieve military strategic objectves quickly and at least cost, JFCs normally will seek the earliest
opportunity to conduct decisive _____ operatons.
a) Defensive
b) Offensive
c) Planning
d) Stability
482. Which of the following are some of the key elements of the shape phase of joint operatons? (Select
all that apply.)
a) Organizing and training
b) Conduct of rehearsals
c) Stability operatons
d) Balance and simultaneity
483. _____ contributons provide operatonal leverage by gathering critcal informaton, undermining a
potental adversary’s will or capacity to wage war, and enhancing the capabilites of conventonal U.S. or
multnatonal forces.
a) SOF
b) USSOCOM
c) CA
d) FDO484. The “Seize the Initatve” phase of joint operatons seeks decision advantage by using all available
elements of combat power to: (Select all that apply.)
a) Seize and maintain the initatve
b) Deny the enemy the opportunity to achieve its objectves
c) Generate in the enemy a sense of inevitable failure and defeat
d) Denounce enemy military by using propaganda to turn public against their military or leadership
485. When JFCs consider incorporatng combinatons of contguous and noncontguous AOs with linear
and nonlinear operatons, they chose the combinaton that fts the operatonal environment and the
purpose of the operaton. Which of the following combinatons describes a typical sustained offensive
and defensive operaton against powerful, echeloned, and symmetrically organized forces combat power
and protects sustainment functons?
a) Linear operatons in contguous AOs
b) Linear operatons in noncontguous AOs
c) Nonlinear operatons in contguous AOs
d) Nonlinear operatons in noncontguous AOs
486. During stability operatons, it is critcal to avoid inadvertently legitmizing an individual or
organizaton in a country where no government exists.
a) True
b) False
487. During the enable civil authority phase of operatons, the JFC may be required to transfer
responsibility of operatons to another as the terminaton criteria.
a) True
b) False
488. Using the following image of the Joint Operatons Phasing Model, provide a response (Deter,
Dominate, Enable, Seize, Shape, or Stabilize) for each of the phases below labeled "1" through "6".
a) Phase 1: Deter
b) Phase 2: Seize
c) Phase 3: Stabilize
d) Phase 4: Dominate
e) Phase 5: Enable
f) Phase 6: Shape
489. Identfy the term (Deter, Dominate, Enable, Seize, Shape, or Stabilize), that corresponds to each of
the defnitons below.
a) This phase, while preparatory in nature, may include mobilizaton and inital deployment into
a theater. Deter
b) This phase includes denying the enemy its inital objectves. Seize
c) This phase may require the joint force to perform limited local governance, and integrate the
efforts of other supportng inter-organizatonal partners untl legitmate local enttes are
functoning. Stabilize
d) This phase's success depends on overmatching enemy capabilites at the critcal tme and
place. Dominate
e) This phase is focused on helping the civil authority stabilize and begin to administer services to
the populace. Enable
f) This phase is executed contnuously, and may mitgate conditons that could lead to a crisis.
Shape490. A _______ may be appropriate when the contemplated military operatons exceed the scope of a
single major operaton.
a) coaliton
b) campaign
c) large-scale combat operaton
d) strategic objectve
491. Campaigns are _____.
a) the most extensive of joint operatons
b) service oriented
c) independently embarked on
d) low in resource requirements
492. Establishing and maintaining access to operatonal areas where joint forces are likely to operate is
an acton in the _____ phase.
a) dominate
b) seize
c) shape
d) deter
493. _____ generally are governed by various directves and agreements and do not require a joint
operaton plan (OPLAN) or operaton order (OPORD) for executon.
a) Advance measures
b) Contnuity of operatons
c) Commitment of forces
d) Engagement actvites
494. If the crisis is caused by a(n) _____ that threatens regional stability, U.S. forces may intervene to
restore or guarantee stability.
a) embargo
b) credible threat
c) internal conflict
d) external threat
495. Operaton RESTORE HOPE in Somalia was a crisis response operaton which required _____ to
protect U.S. forces while accomplishing the mission.
a) combat operatons
b) deterrence actvites
c) security cooperaton
d) major campaigns
496. _____ ensure(s) DoD processes, procedures, and resources are in place to support the President
and Secretary of Defense in a natonal security emergency.
a) Commitment of forces
b) Engagement actvites
c) Contnuity of operatons
d) Advance measures
497. _____ is DoD support to U.S. Government actons that plan for, prepare for, respond to, and
recover from the effects of domestc and foreign chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear incidents.
a) Civil support
b) Recovery operatonsc) Chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear consequence management
d) Homeland defense
498. _____ contain conflict, redress the peace, and shape the environment to support reconciliaton and
rebuilding and facilitate the transiton to legitmate governance.
a) Peace operatons
b) Recovery operatons
c) Stability operatons
d) Foreign humanitarian assistance
499. _____ is/are DoD's unifed effort to support and augment the development of the capacity and
capability of foreign security forces and their supportng insttutons to facilitate the achievement of
specifc objectves shared by the U.S. Government.
a) Foreign humanitarian assistance
b) Security force assistance
c) Civic assistance programs
d) Stability operatons
500. _____ operatons can include the provision of emergency infrastructure reconstructon.
a) Offensive
b) Defensive
c) Stability
d) Planning
501. The scope of a(n) _____ or limited contngency operaton is by its nature different in scope than a
full-scale operaton.
a) crisis response
b) peacekeeping operaton
c) antterrorism
d) interdicton
502. Executve Order 12656, Assignment of Emergency Preparedness Responsibilites, delegates DoD to
advise and assist DOS in preparing and implementng plans for _____.
a) foreign humanitarian assistance
b) non-combat evacuaton
c) foreign internal defense
d) military support
503. _____ is generally limited in scope and duraton because it is intended to supplement or
complement efforts of civil authorites or agencies with the primary responsibility for providing
assistance.
a) Civil defense
b) Foreign internal defense
c) Deterrence
d) Foreign humanitarian assistance
504. To achieve military strategic objectves quickly and at least cost, JFCs normally will seek the earliest
opportunity to conduct decisive _____ operatons.
a) planning
b) defensive
c) offensived) stability
505. _____ contributons provide operatonal leverage by gathering critcal informaton, undermining a
potental adversary's will or capacity to wage war, and enhancing the capabilites of conventonal U.S. or
multnatonal forces.
a) FDO
b) CA
c) SOF
d) USSOCOM
506. U. S. Forces may be required to engage in several types of joint operatons simultaneously, across a
range of military operatons. Commanders combine and sequence offensive, defensive, and _____
operatons to achieve objectves.
a) deterrence
b) crisis response
c) stability
d) contngency
507. Supportng the conditons for economic reconstructon is an acton in the _____ phase.
a) shape
b) stabilize
c) deter
d) enable
508. When JFCs consider incorporatng combinatons of contguous and noncontguous AOs with linear
and nonlinear operatons, they choose the combinaton that fts the operatonal environment and the
purpose of the operaton. Which of the following combinatons describe a typical sustained offensive
and defensive operaton against powerful, echeloned, and symmetrically organized forces and where the
forward line of own troops focus combat power and protect sustainment functons?
a) linear operatons in noncontguous AOs
b) nonlinear operatons in contguous AOs
c) nonlinear operatons in noncontguous AOs
d) linear operatons in contguous AOs
509. _____ are DoD actvites, normally in support of the United States Agency for Internatonal
Development or the Department of State, conducted outside the U.S., its territories, and possessions, to
relieve or reduce human suffering, disease, hunger, or privaton.
a) Stability operatons
b) Civil support
c) Foreign humanitarian assistance
d) Foreign internal defense
510. Military engagement occurs as part of _____, but also extends to interacton with domestc civilian
authorites.
a) civil defense
b) planning
c) security cooperaton
d) counterinsurgency511. If the crisis revolves around _____ to a regional partner, combat commanders employ joint forces to
deter aggression and signal U.S. commitment
a) internal conflict
b) credible threats
c) coup d'etat
d) external threats
512. Joint Logistcians coordinate sustained logistc readiness through the integratng functons of _____.
a) Translatng strategic guidance, developing operatonal concepts, and assessing logistc plans
b) Planning, executng, and controlling joint logistc operatons
c) Unity of effort, environment-wide visibility, and rapid and precise response
d) Organizing for executon, achieving situatonal awareness, and designatng lead Service
responsibilites
513. Which of the following key global providers is responsible for recruitng, organizing, supplying, and
maintaining ready forces for deployment?
a) Services
b) Defense Logistcs Agency (DLS) Service
c) Joint Staff
d) USTRANSCOM
514. Which of the following joint logistc imperatves links the mission, commander’s intent, and
operatonal objectves to core logistc capabilites, procedures, and organizatons?
a) Assessment
b) Executon
c) Planning
d) Control
515. Which of the following statements describes the “supply” functonal capability within joint logistcs?
a) The joint logistcian manages supplies and equipment, inventory, and supplier networks
b) The joint logistcian manages people, material, and transportaton
c) The join logistcian balances Commander’s Critcal Informaton Requirements (CCIRs) with risk,
force availability, and unit readiness.
d) The logistcian develops plans, studies, feasibility, and identfes who is responsible for executng
the plan.
516. The purpose if feld maintenance operatons is to repair, modify, rebuild, and overhaul both entre
systems and components and is directly linked to life cycle systems readiness.
a) True
b) False
517. Which statement describes the difference between the responsibilites of the supported combatant
commander (CCDR) and the supportng CCDR?
a) The supported CCDR establishes a collaboratve process, whereas the supportng CCDR
determines preemployment standards.
b) The supported CCDR regulates the transportaton flow of support personnel, whereas the
supportng CCDR regulates the force flow based on strategic, operatonal, and tactcal control.
c) The supported CCDR builds and validates force and movement requirements, whereas the
supportng CCDR reports force movement requirements data.
518. Match each core capability with the correct descripton.Use the following terms to answer questons 1 - 7 below: Logistcs Services; Operatonal contract
Support; Health Services Support; Deployment and Distributon; Supply; Maintenance Operatons; or
Engineering Operatons.
Queston 1: ______ provides managed materiel inventories that are determined through deliberate
collaboraton with maintenance and distributon providers to optmize the end effect of the supply chain
to the warfghter. Supply
Queston 2: ______ provides life cycle systems readiness capability that enables the requirements,
acquisiton and sustainment communites to provide systems with optmal availability and reliability to
the joint warfghter at best value to the Services. Maintenance Operatons
Queston 3: ______ supports the materiel movement during logistcal sustainment of operatons.
Deployment and Distributon
Queston 4: ______ promotes individual practces that prevent or correct any human conditon that
would impair or preclude the joint force from achieving its objectves. Health Services Support
Queston 5: ______ force multplier that helps commander integrate, synchronize and direct operatons.
Engineering Operatons
Queston 6: ______ comprised of disparate actvites that enable the global sustainment for military
forces. Logistcs Services
Queston 7: ______ensures that the Service is augmented by military and government sources of
support, that the support is orchestrated and manage and that visibility is maintained. Operatonal
Contract Support
519. Within the Personnel Services Division, which support organizaton is responsible for maintaining
personal data of Service members related to their employment?
a) Financial Management
b) Religious Ministry
c) Human Resources
d) Legal Support
520. Which two of the following describe J1 functons? (Select all that apply)
a) The J1 partcipates in all applicable planning and assessment process
b) The J1 advises joint logistc requirements and requires various nongovernmental organizatons
(NGOs) to support all of these
c) The J1 coordinates with higher, supportng, and subordinate manpower and personnel
directories
521. Once a Mission is defned by the SecDef, the joint task force (jt) headquarters identfes its
personnel requirements. These requirements are summarized in the _____.
a) Global Force Management Plan
b) Concept of Operatons (CONOPS)
c) Joint Manning Document
d) Operaton Plan (OPLAN)
522. The President and SecDef are responsible for assigning forces to specifed combatant commands.
a) Trueb) False
523. Who is responsible for the organizaton and employment of legal personnel assigned or atached to
a joint task force (JTF) headquarters?
a) Joint Force Commander
b) Staff Judge Advocate
c) SecDef
d) Geographic Combatant Commander
524. Staff Judge Advocates (SHAs) are responsible for _____/ (Select all that apply)
a) Developing the organizatonal structure for their sectons
b) Understanding the legal support requirements of the joint task force (JTF) to which they are
assigned
c) Identfying the personnel requirements for their sectons
d) Operatng on a sustained 24-hour batle rhythm
525. The responsible personnel for Global Force Management Process 1 – Assignment is:
a) SecDef
b) SecDef and Secretaries of Military Departments
c) Chairman of Joint Chiefs of Staff
526. The responsible personnel for Global Force Management Process 2 – Appointment is:
a) SecDef
b) SecDef and Secretaries of Military Departments
c) Chairman of Joint Chiefs of Staff
527. The responsible personnel for Global Force Management Process 3 – Allocaton is:
a) SecDef
b) SecDef and Secretaries of Military Departments
c) Chairman of Joint Chiefs of Staff
528. An environment in which operatons may or may not be opposed at any point during deployment
by forces or individuals not under the host government’s control in a/an _____environment.
a) Uncertain
b) Permissive
c) Hostle
d) Operatonal
529. Which stage of the protecton process assembles and organizes natonal resources to support
natonal objectves in tme of war or any other emergency?
a) Joint recepton, staging, onward movement, and integraton (JRSOI)
b) Deployment
c) Mobilizaton
d) Employment
530. Who is responsible for assigning forces and resources to combatant commands?
a) Supportng Combatant Commander
b) Commander, Joint Chief of Staff
c) Supported Combatant Commanderd) SecDef
531. Who is responsible for organizing, training, equipping, and providing administratve and logistc
support for forces?
a) SecDef
b) Military Departments
c) Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (CJCS)
d) Supported Combatant Commander (CCDR)
532. Which of the following are phases of the deployment process? (Select all that apply)
a) Deployment planning
b) Mobility
c) Redeployment actvites
d) Movement
533. Which of the following recepton, staging, onward movement, and integraton (JRSOI) elements are
defned as “enabling”? (Select all that apply.)
a) Force protecton
b) Multnatonal support
c) Contract support
d) Legal support
534. Redeployment encompasses which of the following phases? (Select all that apply.)
a) Planning
b) Redeployment actvites
c) Movement
d) Joint recepton, staging, onward movement, and integraton (JRSOI)
535. Which of the following are issues considered during redeployment planning? (Select all that apply.)
a) Intelligence preparaton
b) Protecton
c) Infrastructure assessment
d) Force health protecton
536. Which of the following is described as the quality or capability of military forces that permits them
to transiton from place to place while retaining their ability to fulfll their primary mission?
a) Deployment
b) Transportability
c) Flexibility
d) Mobility
537. The purpose of the personnel estmate is to _____. (Select all that apply.)
a) identfy the most appropriate forces that best meet the SecDef's requirements
b) apporton forces to the combatant commander
c) develop the most effectve soluton to a problem
d) collect and analyze relevant informaton538. The movement phase of deployment is comprised of which of the following three segments?
a) POE operatons
b) maintain, repair, or sustain equipment
c) POE to port of debarkaton (POD)
d) origin to air or sea ports of embarkaton (POE)
539. Which of the following is described as the ability to project the military instrument of natonal
power?
a) Global force management
b) Operaton plan (OPLAN)
c) Concept of operatons (CONOPS)
d) Global force projecton
540. Which of the following are phases of the deployment process? (Select all that apply.)
a) Deployment planning
b) Mobility
c) Predeployment actvites
d) Movement
541. Which of the segments of joint recepton, staging, onward movement, and integraton (JRSOI) is
defned as the process of ofoading, marshalling, and transportng personnel, equipment, and materiel?
a) Staging
b) Recepton
c) Integraton
d) Onward movement
542. During which phase of projecton are forces and materiel transferred to support another joint force
commander's operatonal requirements?
a) Sustainment
b) Joint recepton, staging, onward movement, and integraton (JRSOI)
c) Deployment
d) Redeployment
543. The operatonal environment is generally described by which of the following conditons?
a) tolerant, liberal, and autocratc
b) foreign, natve, and unrestricted
c) strategic, tactcal, and dictated
d) permissive, uncertain, and hostle
544. Which of the segments of joint recepton, staging, onward movement, and integraton (JRSOI) is
defned as the process of synchronizing the transfer of capabilites into an operatonal commander's
force?
a) Staging
b) Onward movement
c) Integraton
d) Recepton
545. When identfying support actvites during pre-redeployment, redeploying forces _____.a) perform all personnel, supply, and inspecton actvites
b) confrm readiness and available movement dates
c) must be supported with medical care, life support, supplies, and materiel
d) may move to a designated staging area to prepare
546.
16) The purpose of feld maintenance operatons is to repair, modify, rebuild, and overhaul both entre
systems and components and is directly linked to life cycle systems readiness.
a) True
b) False
17) Which of the following types of plans describes the most probable outcomes of a mission and
identfes force requirements?
a) Operaton plan (OPLAN)
b) Crisis Plan
c) Concept of operatons (CONOPS)
d) Contngency Plan
18) The joint logistcs environment (JLE) exists within the _____ environment and consists of _____ that
affect the employment of logistc capabilites.
a) strategic; authorites, logistc providers, and imperatves
b) strategic; operaton plans, service capabilites, and climates
c) operatonal; conditons, circumstances, and influences
d) tactcal; situatons, provisions, and restrictons
19) Who is responsible for the organizaton and employment of legal personnel assigned or atached to
a joint task force headquarters?
a) Joint Force Commander
b) Geographic Combatant Commander
c) Staff Judge Advocate
d) SecDef
20) While employed, the Staff Judge Advocate ensures that the joint force commander understands the
_____.
a) requirements from host natons for a transparent legal environment in which to conduct joint
operatons
b) laws, treates, and agreements that apply to U.S. relatons with the foreign governments and
their inhabitants
c) cultures and religious beliefs that impact U.S. relatonships with the foreign inhabitants
d) trafc laws and ports of entry requirements that impact transportaton of personnel and
materiel into the foreign naton
21) Which stage of the projecton process is identfed by the movement of forces within the
operatonal areas (OAs), the positoning of forces into a formaton for batle, or the relocaton of forces
and materiel to a different OA?
a) Sustainment
b) Mobilizaton
c) Deployment
d) Redeployment22) During the joint recepton, staging, onward movement, and integraton (JRSOI) phase of
redeployment, destnaton recepton refers to _____.
a) preparing the force for the next crisis
b) recovering the unit's assigned personnel and equipment
c) tracking the force to determine exact locaton of personnel, equipment, and materiel
d) transportng forces via a common user or commercial lif from a port of debarkaton (POD) to a
demobilizaton staton
23) Which of the following describe the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff's (CJCS's) responsibilites?
(Select all that apply.)
a) Monitors the capabilites of United States Transportaton Command (USTRANSCOM)
b) Prescribes a movement priority system to ensure responsiveness to meet the needs of the
combatant commander (CCDR)
c) Prepares joint logistc and mobility plans to support joint operaton plans (OPLANS)
d) Reviews the CCDR's plans and programs to determine adequacy, consistency, acceptability, and
feasibility to perform the assigned mission
24) Which statement describes the difference between the responsibilites of the supported combatant
commander (CCDR) and the supportng CCDR?
a) The supported CCDR establishes a collaboratve process, whereas the supportng CCDR must
prioritze mission, align forces, and consider planned theater distributon.
b) The supported CCDR ensures units retain visibility and mobility, whereas the supportng CCDR
determines predeployment standards.
c) The supported CCDR builds and validates force and movement requirements, whereas the
supportng CCDR reports force movement requirements data.
d) The supported CCDR regulates the transportaton flow of support personnel, whereas the
supportng CCDR regulates the force flow based on strategic, operatonal, and tactcal control.
25) Which three of the following when combined are some of the functons that comprise core
capabilites of joint logistcs?
a) batle rhythm
b) supply
c) situatonal awareness
d) maintenance operatons
e) health service support
26) Within the Personnel Services Division, which support organizaton is responsible for maintaining
personal data of Service members related to their employment?
a) Human Resources
b) Religious Ministry
c) Legal Support
d) Financial Management
[Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 73 pages












 (Diane Pacitti etc.png)