Pathophysiology > EXAM > HTHRHSC 5500 Concepts Assessment 1 Exam | Questions and Answers (All)
HTHRHSC 5500 Concepts Assessment 1 Exam | Questions and Answers
Document Content and Description Below
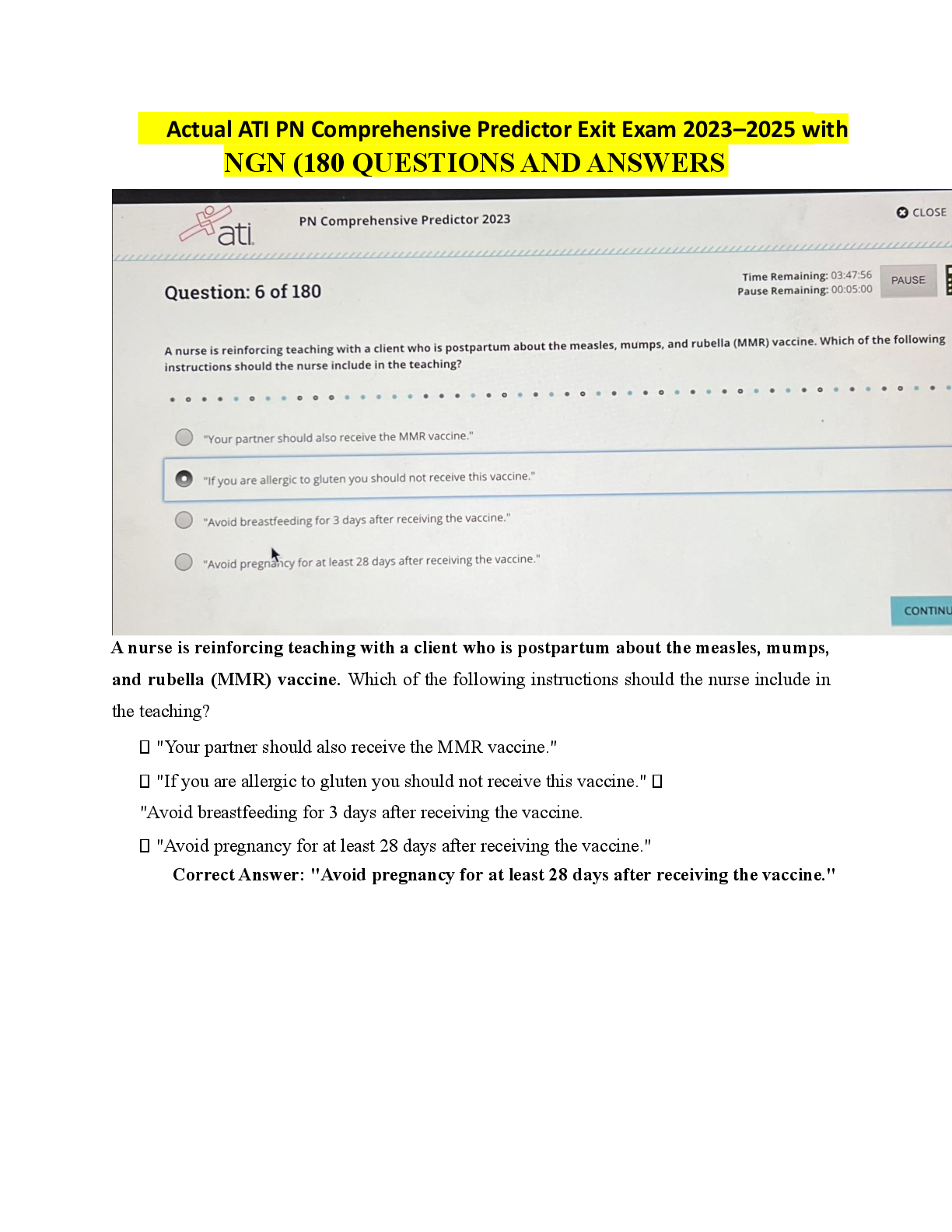
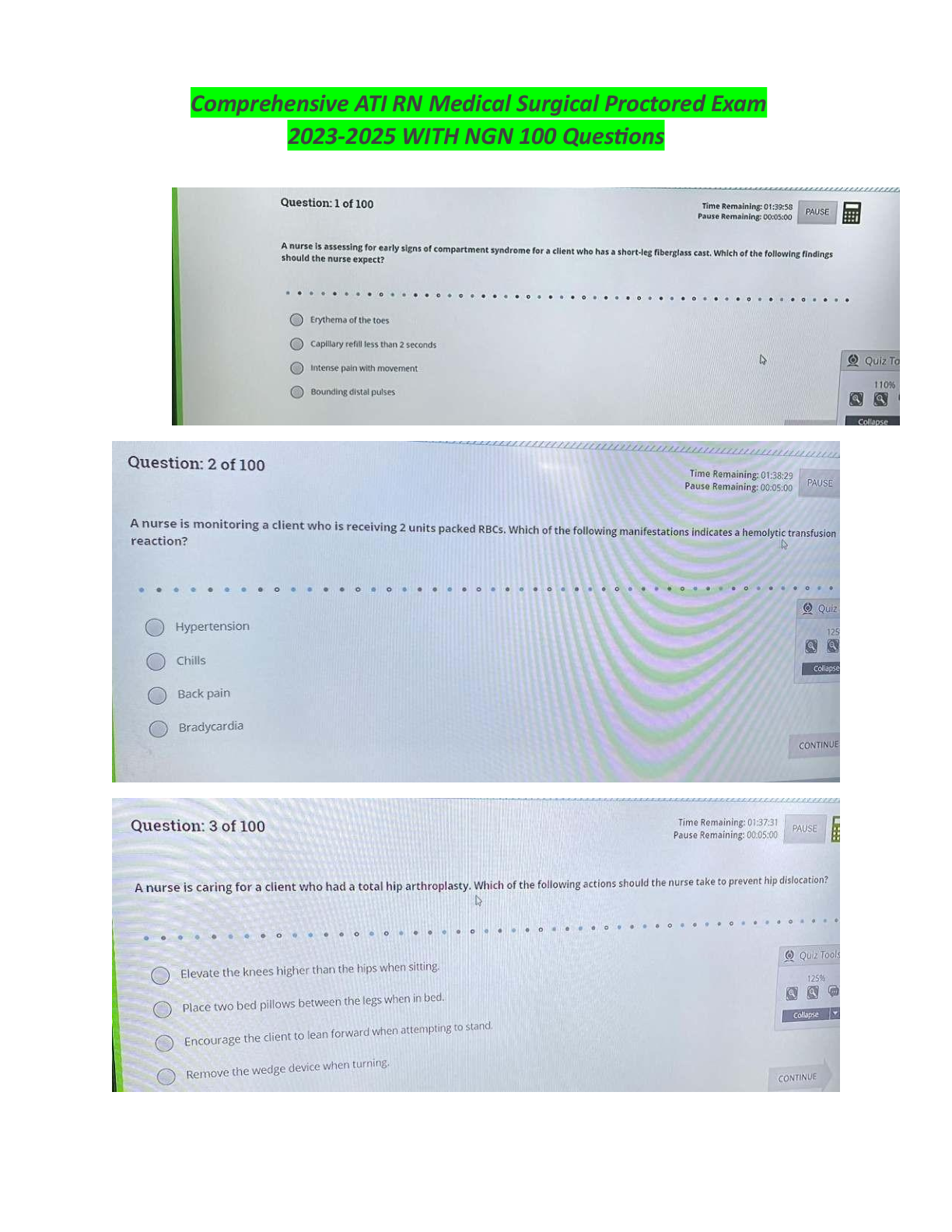
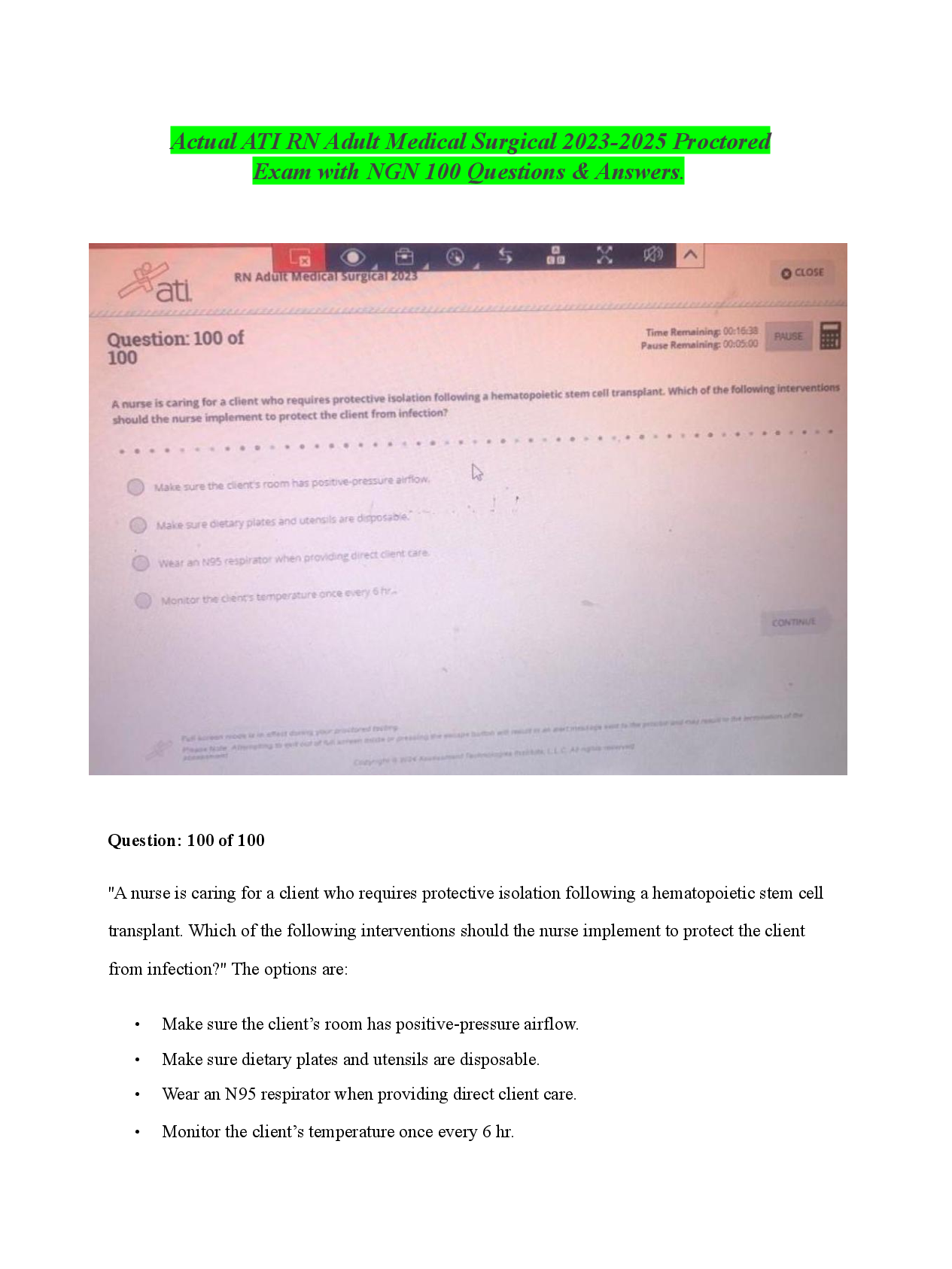
HTHRHSC 5500 Concepts Assessment 1 Exam | Questions and Answers Darrell Johnson is a 30 year-old man, who sustained a fracture of his left tibia 2 months ago. The cast has just been removed, and he ... is amazed at the degree to which the muscles in his leg have shrunk. What are the reasons for this muscle cell atrophy? Select all correct responses. This muscle cell atrophy is adaptive and reversible. This muscle cell atrophy is a pathological response due to denervation. This muscle cell atrophy is a physiological response due to disuse. About 50% of males over age 60 develop benign prostatic hyperplasia as a result of the excessive release of androgens. The hyperplasia may increase to such an extent that the prostate, which encircles the urethra, can cause urethral narrowing resulting in a slow or weak urine stream, hesitancy in starting urine flow, and frequent urge to urinate. What are the characteristics of hyperplasia? Select all correct responses. Cellular hyperplasia occurs when there is activation of the genes controlling cell proliferation and the intracellular messengers that control cell replication and growth. Physiologic hyperplasia occurs in response to a stimulus and ends after the stimulus is removed; i.e., removal of the stimulating hormone. Hyperplasia can only occur in cells capable of mitotic division. Cellular hyperplasia is an increase in number of cells in a tissue or organ. Sylvia Lewis is a 62-year-old woman, who has smoked cigarettes most of her adult life. She notices that she is more prone to respiratory tract infections. What type of cellular changes occur in the pulmonary airways when the ciliated columnar epithelial cells that are exposed to the chronic irritation of cigarette smoke are replaced by stratified squamous epithelial cells? Metaplasia What are the causes of intracellular accumulations? Select all that apply. environmental agents that cannot be metabolized and removed from the cell inability of cell to metabolize an endogenous product due to blockage of a metabolic pathway rate of cellular metabolism inadequate to remove excess of normal cell products Identify each of the following examples as either a reversible or an irreversible cellular accumulation. A woman is diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus with fatty accumulations in the liver cells. She institutes the prescribed oral antidiabetic drug and diet and exercise changes. At the most recent doctor visit, both her weight and blood sugar level are within normal ranges. reversible cellular accumulation Identify each of the following examples as either a reversible or an irreversible cellular accumulation. A man has a heart attack with necrosis of a portion of the myocardium due to prolonged anoxia. irreversible cellular accumulation Identify each of the following examples as either a reversible or an irreversible cellular accumulation. A man has atherosclerosis with >1.5 mm blockage in a coronary artery. A stent is placed in the artery to relieve the blockage. He follows his doctor's instructions for a diet and exercise regimen and takes a cholesterol-lowering drug. reversible cellular accumulation Identify each of the following examples as either a reversible or an irreversible cellular accumulation. An infant has a genetic disorder causing gangliosidosis - build up of glycolipids in the central nervous system neurons. There is progressive destruction of the neurons in the CNS. irreversible cellular accumulation Identify each of the following examples as either a reversible or an irreversible cellular accumulation. An infant with erythroblastosis fetalis develops kernicterus resulting in severe central nervous system injury. irreversible cellular accumulation Identify each of the following examples as either a reversible or an irreversible cellular accumulation. A woman develops a blockage of the common bile duct and she develops jaundice - noted first in the white of the eyes (sclera). The blockage is relieved with removal of the gallbladder and gallstones. reversible cellular accumulation Children >6 years of age that are exposed to lead in the environment may develop growth and intellectual retardation. Lead poisoning results from ______. exposure to lead over a period of time causing an abnormal accumulation of this exogenous substance in the body cells including nerve cells, which affects nerve transmission and brain development Match the following examples of cell injury to the causative agent. Infection with a virus biological agent Match the following examples of cell injury to the causative agent. Allergic reaction to penicillin chemical agent Match the following examples of cell injury to the causative agent. Frostbite physical agent Match the following examples of cell injury to the causative agent. Disruption of intracellular bonds causing increased risk of skin cancer radiation injury Match the following examples of cell injury to the causative agent. Electrical shock physical agent Match the following examples of cell injury to the causative agent. Adverse drug reaction chemical agent Match the following examples of cell injury to the causative agent. Congenital malformation due to chromosomal abnormality genetic derangement Match the following examples of cell injury to the causative agent. Protein-calorie starvation nutritional imbalance Injurious agents (e.g., heat, genetic-causing metabolic disturbances, or altered immune responses) exert negative effects on the cell. What are the mechanisms that can result in cell injury or death? Mark all that apply. hypoxia or ischemia impaired calcium homeostasis free radical formation Jane Doe is a 45 y/o woman, who has been receiving radiation therapy for breast cancer. Check all true statements. Ionizing radiation is used in destruction of cancer cells causing ionization of molecules and atoms in cells by either directly hitting target molecules in the cell or by producing free radicals that interact with critical cell components. Endothelial cells in blood vessels are particularly sensitive to irradiation, therefore, immediately after irradiation, the initial erythema of the skin results from vessel dilatation. Ionizing radiation can immediately kill cells, interrupt cell replication, or cause genetic mutations. Because the injurious effects of ionizing radiation vary with the dose, fractionated doses given at intervals reduce the exposed tissues to irreversible radiation injury. There are 2 apoptotic pathways: extrinsic and intrinsic. Match the processes to the correct pathway. extracellular signaling proteins, TNF and Fas ligand, trigger apoptosis apoptosis extrinsic pathway There are 2 apoptotic pathways: extrinsic and intrinsic. Match the processes to the correct pathway. death cell receptor independent apoptosis intrinsic pathway There are 2 apoptotic pathways: extrinsic and intrinsic. Match the processes to the correct pathway. death cell receptor dependent apoptosis extrinsic pathway There are 2 apoptotic pathways: extrinsic and intrinsic. Match the processes to the correct pathway. triggered by DNA damage with activation of p53 protein, ROS, hypoxia, decreased ATP, or cellular senescence apoptosis intrinsic pathway There are 2 apoptotic pathways: extrinsic and intrinsic. Match the processes to the correct pathway. Fas ligand binds to its receptor forming the death-initiating complex by converting procaspase-8 to caspase-8 and activating endonucleases that cause DNA fragmentation apoptosis extrinsic pathway There are 2 apoptotic pathways: extrinsic and intrinsic. Match the processes to the correct pathway. Bc12 protein regulators insert into the mitochondrial membrane opening channels for protein release into the cytoplasm apoptosis intrinsic pathway There are 2 apoptotic pathways: extrinsic and intrinsic. Match the processes to the correct pathway. mitochondria releases cytochrome c into the cytoplasm resulting in binding to caspace-3 allowing for bridging of the pathways and activation of caspase-8 apoptosis intrinsic pathway Oxidative stress resulting from exposure to high levels of ROS has been implicated as the causative agent in numerous disease states as well as the cause of physiological aging. Select all true responses that describe how oxidative stress affects cells. causes oxidation of cellular components resulting in cell injury and tissue damage changes gene expression; e.g. mutations in the gene for SOD that is associated with ALS causes endolthelial dysfunction resulting in cardiovascular disease Match the pathologic term to its correct descriptor. occurs in normal tissues as the result of increased serum calcium levels metastatic calcification Match the pathologic term to its correct descriptor. oxygen-containing molecules that are highly reactive reactive oxygen species (ROS) Match the pathologic term to its correct descriptor. natural and synthetic molecules that inhibit the reactions of ROS with biological structures Antioxidants Match the pathologic term to its correct descriptor. programmed cell death Apoptosis Match the pathologic term to its correct descriptor. macroscopic deposition of calcium salts in injured tissue dystrophic calcification Match the pathologic term to its correct descriptor. ice crystal formation in cytosol temperature-induced injury Match the pathologic term to its correct descriptor. impaired oxygen delivery Ischemia Match the pathologic term to its correct descriptor. dead cells persist indefinitely as soft cheese like debris caseous necrosis Match the pathologic term to its correct descriptor. causes injury by changes in electron stability ionizing radiation Match the pathologic term to its correct descriptor. term applied to a large mass of tissue that undergoes necrosis Gangrene The cardinal signs of inflammation result from the physiologic process of the inflammatory cells and protein systems. Match the sign to its causative explanation. increased permeability of blood vessels due to histamine and other long-term vasoactive mediators causing accumulation of blood in the extravascular space swelling (tumor) The cardinal signs of inflammation result from the physiologic process of the inflammatory cells and protein systems. Match the sign to its causative explanation. fluid accumulation into the tissues and the release of bradykinin, prostaglandins, and histamine stimulating the sensory nerve endings pain (dolor) The cardinal signs of inflammation result from the physiologic process of the inflammatory cells and protein systems. Match the sign to its causative explanation. increased blood flow due to histamine release causing dilation of small blood vessels in area redness (rubor) The cardinal signs of inflammation result from the physiologic process of the inflammatory cells and protein systems. Match the sign to its causative explanation. increased perfusion in peripheral tissues due to vasodilation at the wound site and flow of warm blood into the area heat (calor) There are several cell types involved in the inflammatory process. Match the cell type to its descriptor(s) - there may be more than one match per descriptor. produce antiplatelet and antithrombotic agents to regulate vessel patency and blood flow endothelial cells [Show More]
Last updated: 11 months ago
Preview 4 out of 11 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 14, 2025
Number of pages
11
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 14, 2025
Downloads
0
Views
15