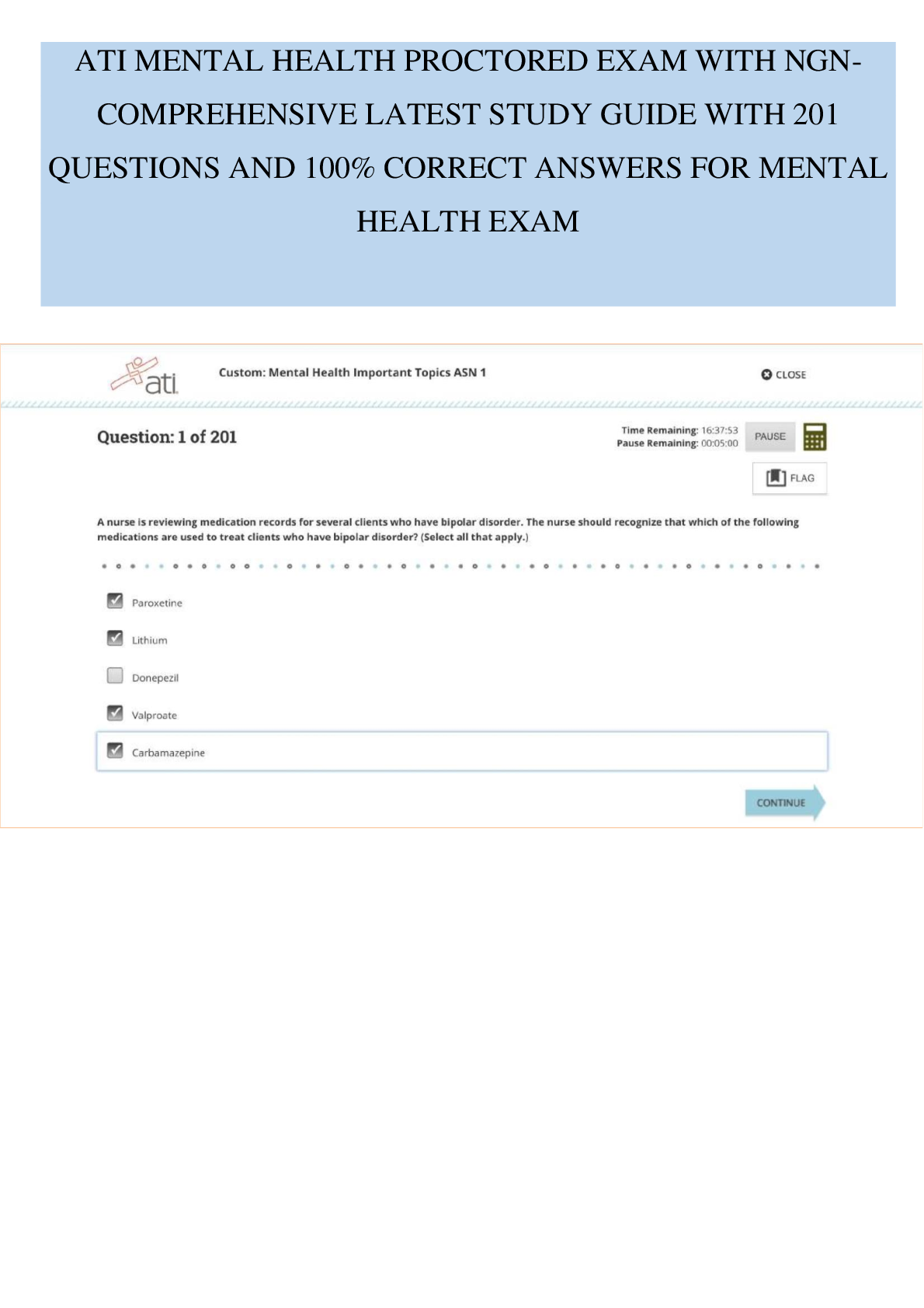
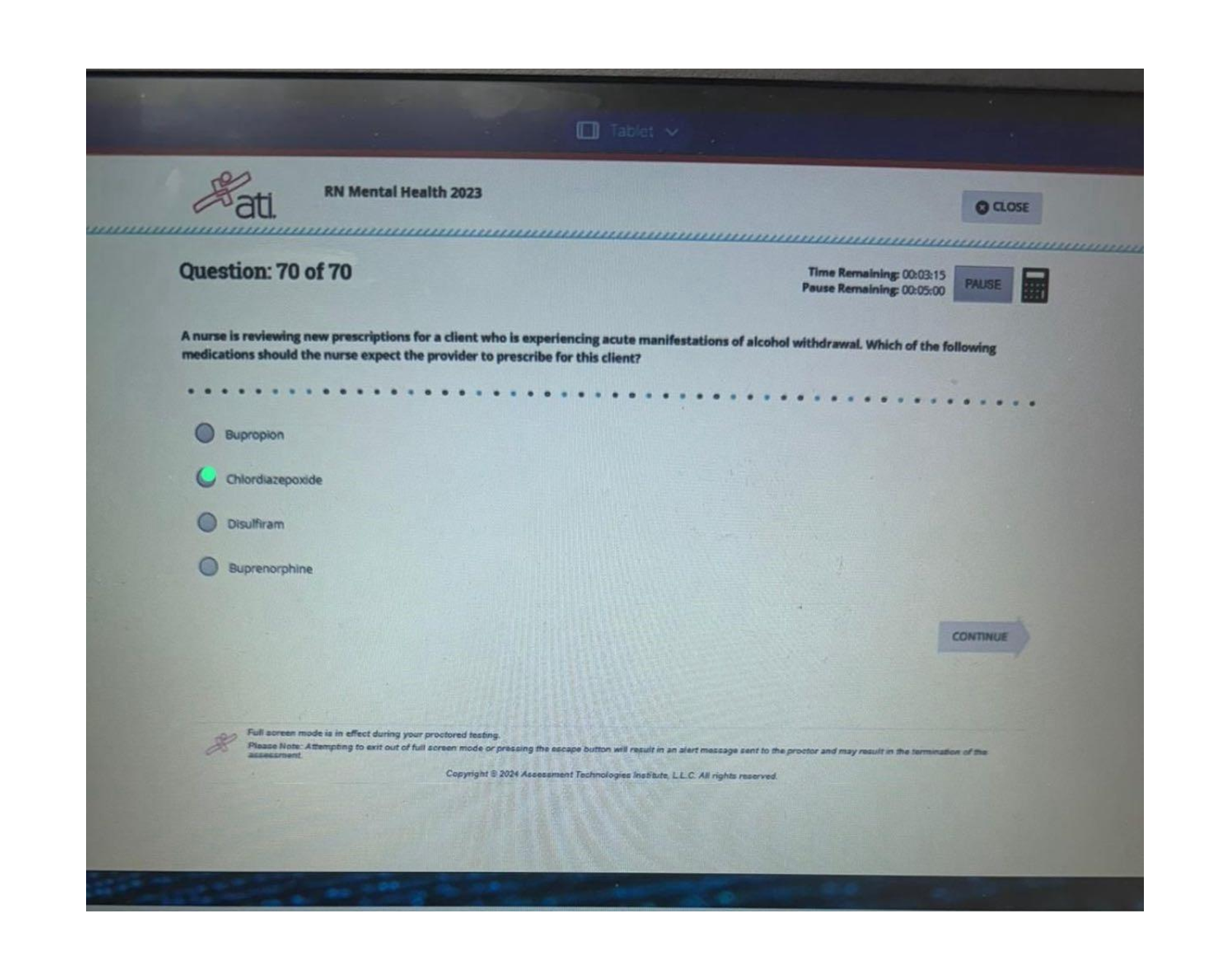
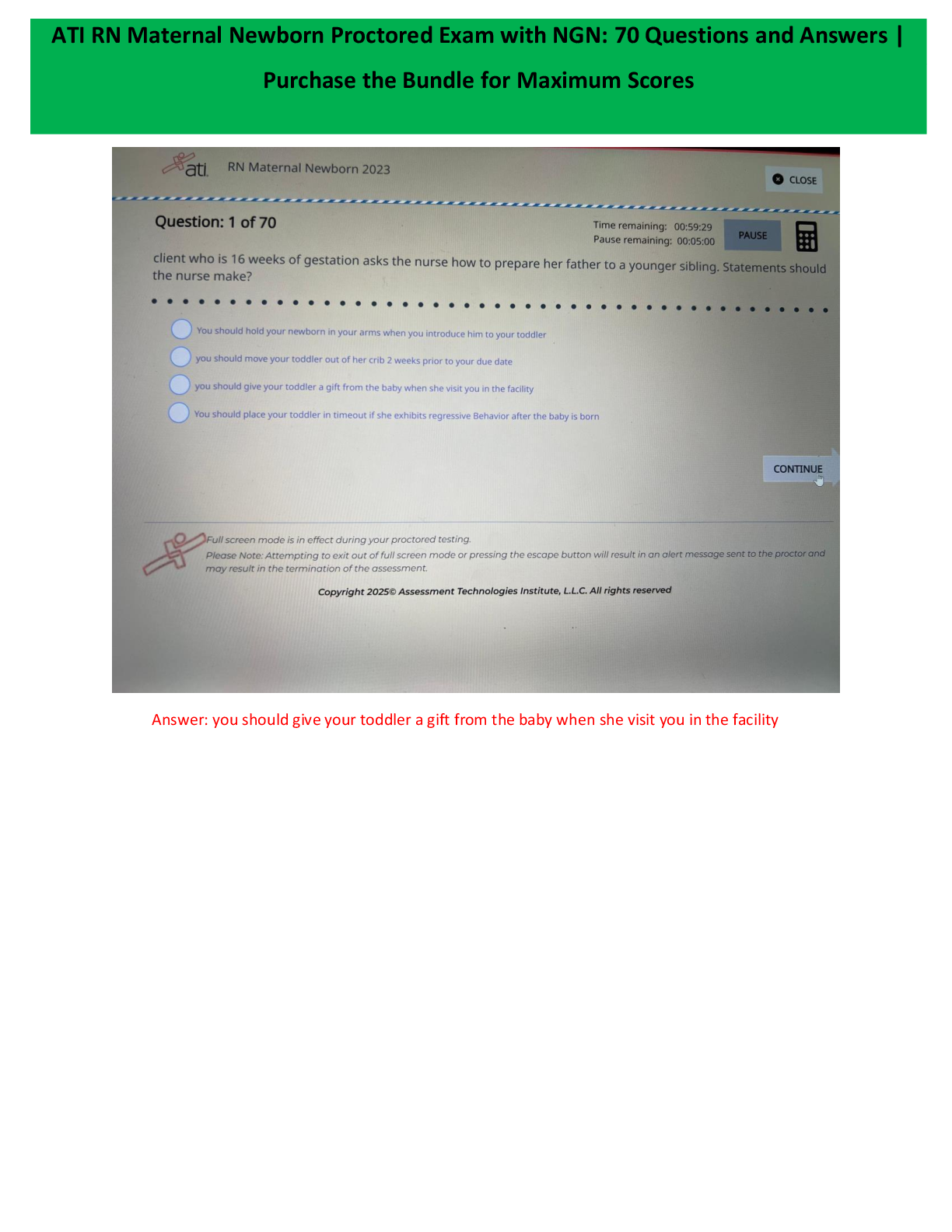
MCA II Exam 4 | Complete Solutions (Verified) Which clinical manifestation are found in the client diagnosed with stage 3 Parkinson Disease? Select all that apply A. Akinesia B. Mask-like face C. Postural Instability
...
MCA II Exam 4 | Complete Solutions (Verified) Which clinical manifestation are found in the client diagnosed with stage 3 Parkinson Disease? Select all that apply A. Akinesia B. Mask-like face C. Postural Instability D. Unilateral limb involvement E. Increased gait disturbances Parkinson disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that is one of the most common neurological disorders of older adults. stage 3 of Parkinson disease is characterized by postural instability and increased gait disturbances. the "masklike" face begins in stage 2 and continues in stage 3. akinesia is manifested in stage 4 of the disease. in stage 1 of Parkinson disease, only unilateral limb involvement is seen, but it progresses to bilateral in later stages. Which client statement indicates that the instructions to a client with a seizure disorder receiving phenytoin and phenoabarbital are understood? A. I will not have any seizures on this medication B. These medicines must be continued to prevent falls and injury C. Stopping the medications can cause continuous seizures and I may die D. By staying on the medications I will prevent post seizure confusion combination therapy suggests that this client has seizures that are difficult to control. sudden withdrawal of any antiepileptic medication can cause onset of frequent seizures or even status epilepticus. death can occur if seizures are continuous due to a lack of adequate oxygenation and cardiac irregularities. it is important to take medication as prescribed to lessen the frequency of seizures; there is no guarantee that seizures will stop. antiepileptic medications are not prescribed to prevent falls and injury and the added central nervous system (CNS) depression increases fall risk. although seizures may occur while the client is taking the medications, the medications do not stop post-seizure confusion. Which information would the nurse include in the teaching plan for a client diagnosed with epilepsy? a. the client will take anticonvulsant medications for life b. individuals taking phenytoin must floss their teeth regularly c. a diagnosis of epilepsy prevents individuals from ever obtaining a driver's license d. loss of consciousness during a seizure requires emergency evaluation gingival hyperplasia is a common side effect of phenytoin. clients may decrease or delay development of gingival hyperplasia by regular brushing and flossing of their teeth. although lifelong treatment with antiseizure medication is often required, some people are able to wean from antiseizure medication after they have been seizure free for a period of several years (generally 3 to 5) and have a normal electroencephalogram and neurological examination. driving laws for people with epilepsy vary from state to state. for example, some states require a seizure-free period of up to a year before reinstating or issuing a driver's license. The person who has experienced a single seizure may not need to go to the hospital, unless the event is a first-time seizure, the seizure is prolonged or the seizure results in bodily harm. Which instruction about phenytoin will the nurse provide during discharge teaching to a client with epilepsy who is prescribed phenytoin for seizure control? a. antiseizure medications will probably be continued for life b. phenytoin prevents any further occurrence of seizures c. this medication needs to be taken during periods of emotional stress d. your antiseizure medication usually can be stopped after a year's absence of seizures seizure disorders usually are associated with marked changes in the electrical activity of the cerebral cortex, requiring prolonged or lifelong therapy. seizures may occur despite medication therapy; the dosage may need to be adjusted. a therapeutic blood level must be maintained through consistent administration of the medication irrespective of emotional stress. absence of seizures will probably result from medication effectiveness rather than from correction of the pathophysiological condition. A client asks the nurse what causes the sudden loss of vision common in persons with multiple sclerosis. which factor would the nurse include in the explanation? a. virus-induced iritis b. intracranial pressure c. closed-angle glaucoma d. optic nerve inflammation optic nerve inflammation is a common early effect of multiple sclerosis caused by lesions in the optic nerves or their connections (demyelization). this effect may resolve during periods of remission. at present, there is no evidence of viral infection of the eyes in multiple sclerosis. tumors of the brain and cerebral edema, not multiple sclerosis, cause increased intracranial pressure because the skull cannot expand. closed-angle glaucoma causes blindness as a result of increased intraocular pressure, not inflammation of the optic nerve, which is commonly associated with multiple sclerosis. closed-angle glaucoma is unrelated to multiple sclerosis. Which finding would the nurse expect when assessing a client who is in an early stage of multiple sclerosis? select all that apply. a. headache b. nystagmus c. skin infection d. scanning speech e. intention tremors involuntary, rhythmic movements of the eyes (nystagmus) and other visual disturbances, such as diplopia and blurred vision, are common initial symptoms of optic nerve lesions. some common initial signs of multiple sclerosis are scanning speech, intention tremors and nystagmus. these adaptations are associated with disseminated demyelination of nerve fivers of the brain and spinal cord. although this is a neuromuscular disorder, headaches are not a common symptom. pressure ulcers may occur late, not early, in the progression of the illness because of immobility, and these pressure ulcers may become infected. Which immunomodulatory is beneficial for the treatment of clients with multiple sclerosis? a. Interleukin 2 b. Interleukin 11 c. Beta interferon d. Alpha interferon beta interferon is an immunomodulator administered in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. IL-2 treats metastatic renal cell carcinoma and metastatic melanoma. interleukin 11 (IL-11) prevents development of thrombocytopenia after chemotherapy. alpha interferon treats hairy cell leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, and malignant melanoma. Which symptom would the nurse expect to decrease in response to corticosteroid therapy prescribed for a client with multiple sclerosis? a. emotional lability b. muscular contractions c. pain in the extremities d. visual impairment corticosteroids decrease the inflammatory process around the optic nerve, thus improving vision; visual impairment is the most common physiological manifestation of multiple sclerosis. steroids are associated with increased emotional lability. steroids are not effective in easing muscle contractions. pain in the extremities is not common unless spasms are present; steroids do not relieve spasms. A registered nurse teaches a nursing student about cluster headaches. Which statement made by the nursing student indicates a need for further teaching? a. "Each episode of a cluster headache may last up to 3 hours." b. "Pupillary constriction occurs during the period of cluster headaches." c. "Pulsating pain is the characteristic type of pain that occurs in cluster headaches." d. "Cluster headaches occur for weeks to months followed by a period of remission." sharp stabbing pain is the characteristic type of pain that occurs in cluster headaches. each episode of a cluster headache may last from a few minutes to 3 hours. constriction of the pupil, swelling around the eye, and facial flushing occur during the period of cluster headaches. a period of remission after a few weeks or months of headaches is characteristic of cluster headaches. Which information does the nurse include in the teaching plan for the client who is prescribed sumatriptan for migraine headache? a. it should be administered when headache is at its peak b. it should be administered by deep Intramuscular injection c. is contraindicated in people with coronary artery disease d. injectable sumatriptan may be administered every 6 hours as needed in addition to promoting therapeutic cerebral vasoconstriction, sumatriptan promotes undesirable coronary artery vasoconstriction. coronary vasoconstriction may cause harm to the client with coronary artery disease. for maximum effectiveness, sumatriptan should be administered at the onset of migraine headache. sumatriptan may be given orally, subcutaneously, or as a nasal spray. the maximum adult dose of sumatriptan may be given orally, subcuntenously, or as a nasal spray. the maximum adult dose of sumatriptan is two 6-mg doses in a 24-hour period for a total of 12 milligrams. the two doses must be separated by at least an hour. the second dose should not be administered unless some response was observed with the first dose. A patient receiving sumatriptan for migraine headaches is experiencing adverse effects after taking the drug. Which adverse effect is of greatest concern to the nurse? Triptan drugs are contraindicated in patients with coronary artery disease because they can cause arterial narrowing. Patients taking triptan drugs should report angina or chest discomfort to prevent cardiac injury associated with myocardial ischemia. Skin flushing, tingling feelings, and a warm sensation are common adverse effects with triptan medications and are not indications to avoid using this group of drugs. Which instruction will the nurse give a client with migraine headaches who is starting triptan medication therapy? a. "check your pulse before and after administration" b. "report any chest discomfort to the health care provider" c. "wait for 1 hour after symptom onset to administer the medication" d. "stop taking the medication if you experience warm, flushing sensations" clients need to be instructed to report chest discomfort to the health care provider immediately. clients taking triptan medications who experience chest discomfort must be investigated for myocardial ischemia. clients on beta-blocker therapy for migraines, not triptan therapy, will be instructed to monitor pulse. triptan medications are taken as soon as symptoms appear. warm, flushing sensations are a common experience in clients taking triptan medication; the side effect generally subsides with continued use and does not indicate a need to stop the medication. A client develops iron-deficiency anemia. Which of the client's laboratory test results should the nurse expect to be decreased? a. Ferritin level b. Platelet count c. White blood cell count d. Total iron-binding capacity Ferritin, a form of stored iron, is reduced with iron-deficiency anemia. Platelets will be within the expected range or increased with iron-deficiency anemia. Red, not white, blood cells are decreased with iron-deficiency anemia. Total iron-binding capacity will be increased with iron-deficiency anemia.) A 60-year-old client with gastric cancer has a shiny tongue, paresthesias of the limbs, and ataxia. The laboratory results show cobalamin levels of 125 pg/mL. Which medication would the nurse consider to be a high priority for the client? a. Oral hydroxyurea b. Vitamin B 12 injections c. Oral iron supplements d. Erythropoietin injections A shiny tongue, paresthesias of the limbs, ataxia, and cobalamin of 125 pg/mL (normal: 200- 835 pg/mL) are the manifestations of pernicious anemia. The client has pernicious anemia due to a vitamin B 12 deficiency and should be given vitamin B 12 injections. Vitamin B 12 cannot be given orally to a client with pernicious anemia because the client does not produce the intrinsic factors needed to absorb Vitamin B 12. Hydroxyurea is administered orally to clients with hemochromatosis. Oral iron supplements are given to clients with iron deficiency anemia. Erythropoietin injections are given to clients who have low red blood cells, hemoglobin, and hematocrit. Which prescribed treatment would the nurse question when a client who has sickle cell anemia has been admitted with acute chest syndrome? a. oxygen administration b. daily folic acid tablet c. daily iron supplement d. morphine sulfate prn the nurse would question the use of iron supplements in sickle cell anemia because sickle cell disease is not caused by iron deficiency. in addition, many clients with sickle cell anemia receive blood transfusions and iron toxicity can develop secondary to frequent transfusions. oxygen administration would be appropriate for a client with a pulmonary complication such as acute chest syndrome. folic acid supplements are recommended for clients with sickle cell disease because folic acid is needed in the production of new red blood cells to replace cells lost to hemolysis. morphine sulfate is frequently prescribed to treat ischemic pain caused by sickled cells. Which action would the nurse anticipate when admitting a client having a sickle cell crisis to the nursing unit? select all that apply, a. place on strict isolation b. administer hydroxyurea c. administer aspirin 325 mg daily d. apply oxygen via nasal cannula e. avoid opirate-type analgesics hydroxyurea can reduce the number of sickling and pain episodes by stimulating fetal hemoglobin production. providing oxygen via nasal cannula provides additional oxygen, which decreases red blood cell sickling and improves tissue oxygenation. intravenous hydration will decrease the clumping of sickled cells and decrease obstruction of blood flow. strict isolation is not needed for clients in sickle cell crisis. aspirin is not helpful because the obstruction of blood flow is caused by obstruction of blood flow by sickled cells is very painful, and opiate analgesics are frequently needed for pain management. When both parents have sickle cell trait, what is the chance that a child will gave sickle cell disease? a. 25% b. 50% c. 75% d. 100% sickle cell is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder. if both individuals have sickle cell traits, there is a 25% chance they will produce a child with the disease. children will have a 50% chance of having sickle cell trait. a 75% chance of having offspring sickle cell trait or disease is not mathematically possible. a child born of parents who both have sickle cell disease will have 100% chance of having the disease. Which statement by an adolescent about sickle cell anemia would cause the nurse to conclude that the teaching has been understood? a. "I'll start to have symptoms when I drink less fluid." b. "I'll start to have symptoms when I have fewer platelets." c. "I'll start to have symptoms when I decrease the iron in my diet." d. "I'll start to have symptoms when I have fewer white blood cells." dehydration precipitates sickling of red blood cells and is a major causative factor for painful episodes associated with sickle cell anemia. an inadequate number of platelets (thombocytes) is unrelated to painful episodes associated with sickle cell anemia. iron intake is unrelated to the sickling phenomenon. an inadequate number of white blood cells is unrelated to painful episodes associated with sickle cell anemia. Which information will the nurse provide to minimize the risk for complications of pancytopenia as a result of chemotherapy? a. Avoid traumatic injury and exposure to infection. b. perform frequent mouth care with a firm toothbrush c. Increase oral fluid intake to at least 3 L/day. d. Report unusual muscle cramps or tingling sensations in the extremities. reduced platelets increase the likelihood of uncontrolled bleeding; reduced lymphocytes increase susceptibility to infection. aggressive oral hygiene can precipitate bleeding from the gums. although fluids may be increased to flush out the toxic by-products of chemotherapy, this has no effect on pancytopenia. muscle cramps or tingling sensations in the extremities are adaptations to hypocalcemia; hypocalcemia is unrelated to pancytopenia. Ten minutes after the initiation of a blood transfusion, a client reports chills and flank pain. Which nursing action would be performed first? a. Stop the transfusion. b. Obtain the vital signs. c. Notify the health care provider. d. Maintain the flow with normal saline. This is a sign of an acute hemolytic transfusion reaction, indicating that the recipient's blood is incompatible with the transfused blood; pain is caused by hemolysis, agglutination, and capillary plugging in the kidneys. Obtaining the vital signs is important but must not precede stopping the transfusion because more incompatible blood will be infused, increasing the severity of the transfusion reaction. After the infusion is stopped, the provider should be notified and normal saline should be infused to keep the line patent. Which action would the nurse take next after the nurse immediately stops the infusion of a client demonstrating signs and symptoms of a transfusion reaction? a. Obtain blood pressure in both arms b. Send a urine specimen to the laboratory c. Hang a bag of normal saline with new tubing d. Monitor the intake and output every 15 minutes The tubing must be replaced to avoid infusing the blood left in the original tubing; the normal saline infusion will maintain an open line for any further intravenous (IV) treatment. All vital signs should be taken eventually; blood pressure may be taken on either arm, not necessarily both. A urine sample is collected after the blood transfusion is stopped, the tubing replaced, and a bag of normal saline hung. The specimen will be analyzed to determine kidney function. Although the intake, and especially the output, should be monitored to assess kidney function, this is not the priority. An adult male with chronic anemia is experiencing increased fatigue and occasional palpitations at rest. Which laboratory data would the nurse identify as consistent with these symptoms? a. RBC count of 4,500,000/uL b. Hematocrit (Hct) value of 38% c. Normal red blood cell (RBC) indices d. Hemoglobin (Hgb) of 8.6 g/dL (86 g/L) The patient's symptoms indicate moderate anemia, which is consistent with a Hgb of 6 to 10 g/dL. The other values are all within the range of normal. Which menu choice indicates that the patient understands the nurse's recommendations about dietary choices for iron-deficiency anemia? a. Omelet and whole wheat toast b. Cantaloupe and cottage cheese c. Strawberry and banana fruit plate d. Cornmeal muffin and orange juice Eggs and whole grain breads are high in iron. The other choices are appropriate for other nutritional deficiencies but are not the best choice for a patient with iron-deficiency anemia. A patient who is receiving methotrexate for severe rheumatoid arthritis develops a megaloblastic anemia. Which nutrient supplement should the nurse plan to explain to the patient? a. Iron b. Folic acid c. Cobalamin (vitamin B12) d. Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) Methotrexate use can lead to folic acid deficiency. Supplementation with oral folic acid supplements is the usual treatment. The other nutrients would not correct folic acid deficiency, although they would be used to treat other types of anemia. Which patient statement to the nurse indicates that the patient understands self-care for pernicious anemia? a. "I need to start eating more red meat and liver." b. "I will stop having a glass of wine with dinner." c. "I could choose nasal spray rather than injections of vitamin B12." d. "I will need to take a proton pump inhibitor such as omeprazole (Prilosec)." Because pernicious anemia prevents the absorption of vitamin B12, this patient requires injections or intranasal administration of cobalamin. Alcohol use does not cause cobalamin deficiency. Proton pump inhibitors decrease the absorption of vitamin B12. Eating more foods rich in vitamin B12 is not helpful because the lack of intrinsic factor prevents absorption of the vitamin. Which potential complication should the nurse identify as a high risk for a patient admitted to the hospital with idiopathic aplastic anemia? a. Seizures b. Infection c. Neurogenic shock d. Pulmonary edema Because the patient with aplastic anemia has pancytopenia, the patient is at risk for infection and bleeding. There is no increased risk for seizures, neurogenic shock, or pulmonary edema Which nursing intervention is important when providing care for a patient with sickle cell crisis? a. Limiting the patient's intake of oral and IV fluids b. Evaluating the effectiveness of opioid analgesics c. Encouraging the patient to ambulate as much as tolerated d. Teaching the patient about high-protein, high-calorie foods Pain is the most common clinical manifestation of a crisis and usually requires large doses of continuous opioids for control. Fluid intake should be increased to reduce blood viscosity and improve perfusion. Rest is usually ordered to decrease metabolic requirements. Patients are instructed about the need for dietary folic acid, but high-protein, high-calorie diets are not emphasized Which statement by a patient indicates good understanding of the nurse's teaching about preventing sickle cell crisis? a. "Home oxygen therapy is frequently used to decrease sickling." b. "There are no effective medications that can help prevent sickling." c. "Routine continuous dosage opioids are prescribed to prevent a crisis." d. "Risk for a crisis is decreased by having an annual influenza vaccination." Because infection is the most common cause of a sickle cell crisis, influenza, Haemophilus influenzae, pneumococcal pneumonia, and hepatitis immunizations should be administered. Although continuous dose opioids and oxygen may be administered during a crisis, patients do not receive these therapies to prevent crisis. Hydroxyurea (Hydrea) is a medication used to decrease the number of sickle cell crises What action is expected by the nurse caring for a patient who has an acute exacerbation of polycythemia vera? a. Place the patient on bed rest. b. Administer iron supplements. c. Avoid use of aspirin products. d. Monitor fluid intake and output. Monitoring hydration status is important during an acute exacerbation because the patient is at risk for fluid overload or underhydration. Aspirin therapy is used to decrease risk for thrombosis. The patient should be encouraged to ambulate to prevent deep vein thrombosis. Iron is contraindicated in patients with polycythemia vera. Which intervention will be included in the nursing care plan for a patient with immune thrombocytopenic purpura? a. Assign the patient to a private room. b. Avoid intramuscular (IM) injections. c. Use rinses rather than a soft toothbrush for oral care. d. Restrict activity to passive and active range of motion. IM or subcutaneous injections should be avoided because of the risk for bleeding. A soft toothbrush can be used for oral care. There is no need to restrict activity or place the patient in a private room. Which laboratory result will the nurse expect to show a decreased value if a patient develops heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)? a. Prothrombin time b. Erythrocyte count c. Fibrinogen degradation products d. Activated partial thromboplastin time Platelet aggregation in HIT causes neutralization of heparin, so the activated partial thromboplastin time will be shorter, and more heparin will be needed to maintain therapeutic levels. The other data will not be affected by HIT. A young adult who has von Willebrand disease is admitted to the hospital for minor knee surgery. Which laboratory value should the nurse monitor? a. Platelet count b. Bleeding time c. Thrombin time d. Prothrombin time The bleeding time is affected by von Willebrand disease. Platelet count, prothrombin time, and thrombin time are normal in von Willebrand disease A routine complete blood count for an active older man indicates possible myelodysplastic syndrome. What should the nurse plan to explain to the patient? a. Blood transfusion b. Bone marrow biopsy c. Filgrastim administration d. Erythropoietin administration Bone marrow biopsy is needed to make the diagnosis and determine the specific type of myelodysplastic syndrome. The other treatments may be necessary later if there is progression of the myelodysplastic syndrome, but the initial action for this asymptomatic patient will be a bone marrow biopsy., Which action will the admitting nurse include in the care plan for a patient who has neutropenia? a. Avoid intramuscular injections. b. Check temperature every 4 hours. c. Place a "No Visitors" sign on the door. d. Omit fruits and vegetables from the diet. The earliest sign of infection in a neutropenic patient is an elevation in temperature. While unpeeled fresh fruits and vegetables should be avoided, fruits and vegetables that are peeled or cooked are acceptable. Injections may be required for administration of medications such as filgrastim (Neupogen). The number of visitors may be limited and visitors with communicable diseases should be avoided, but a "no visitors" policy is not needed. Which laboratory test will the nurse use to determine whether filgrastim (Neupogen) is effective for a patient with acute lymphocytic leukemia who is receiving chemotherapy?
[Show More]