EDIS 2310 Final Exam | Complete Solutions (Verified)
Document Content and Description Below
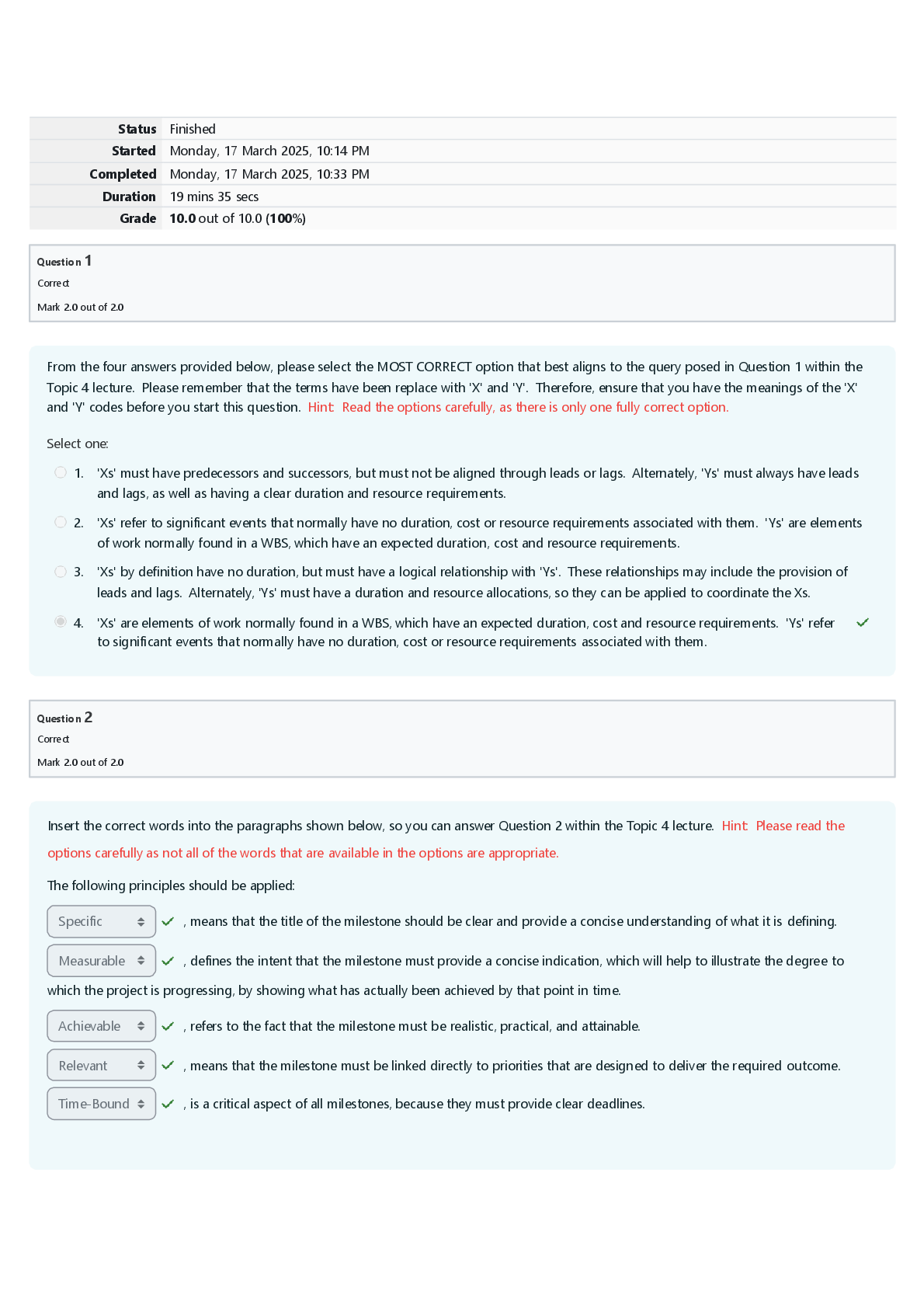
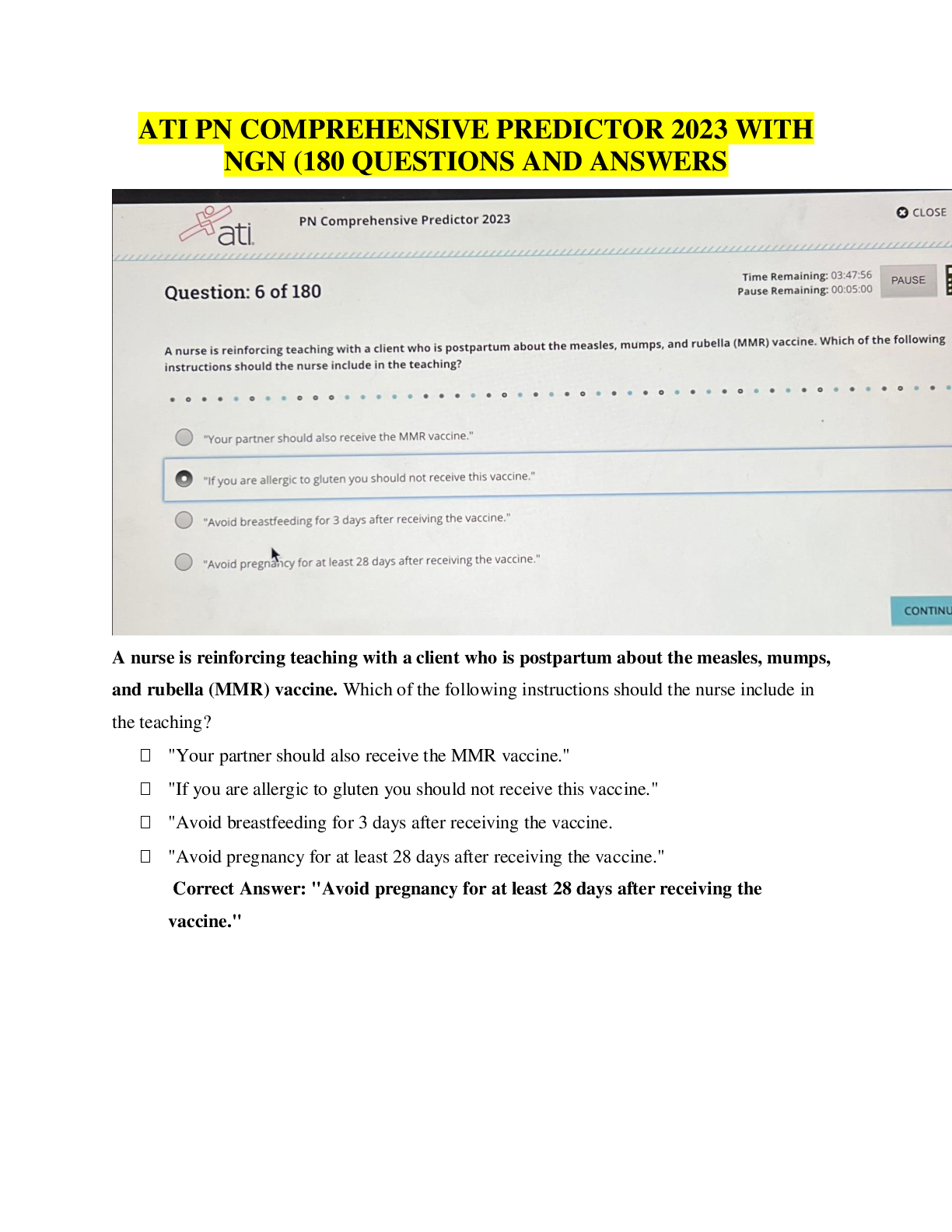
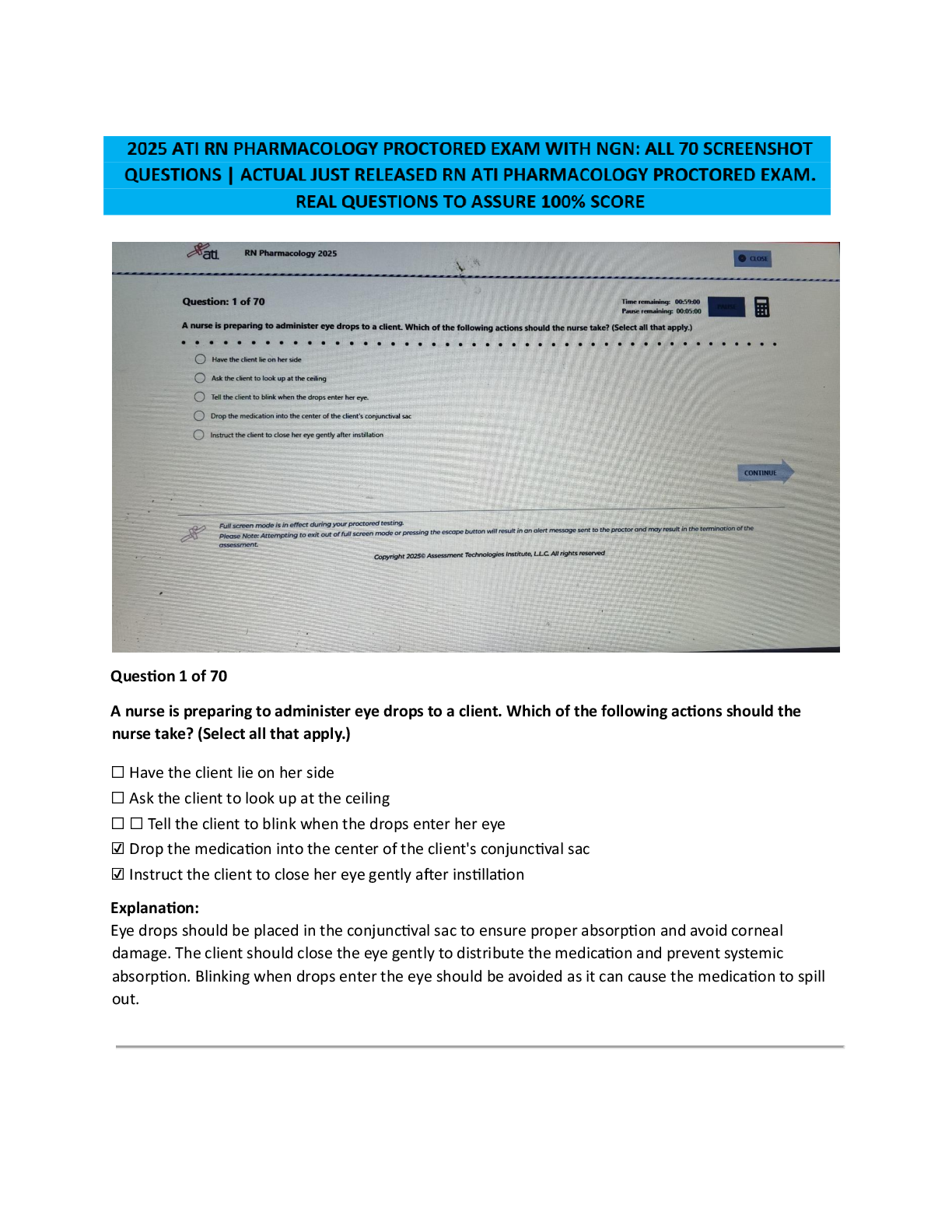
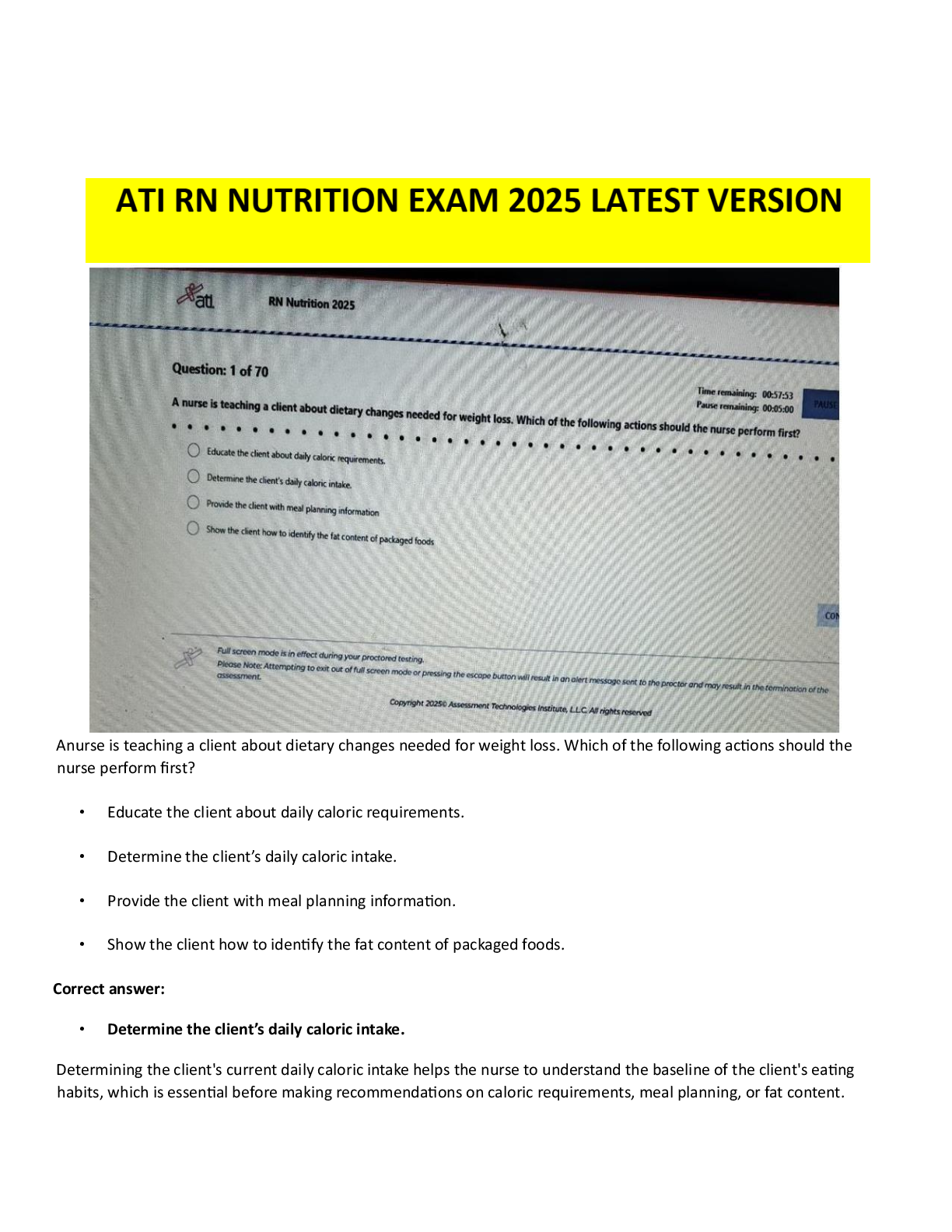
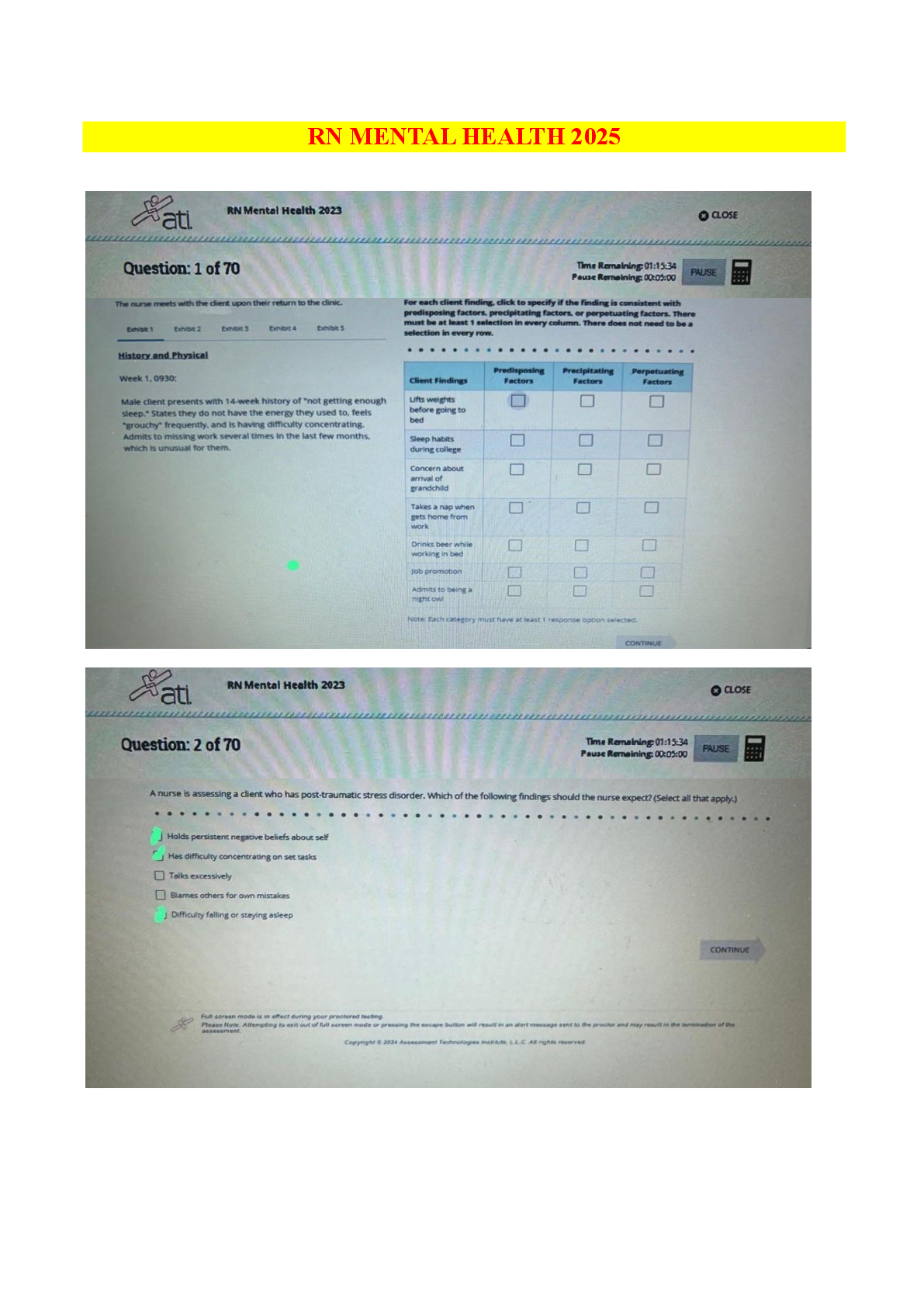
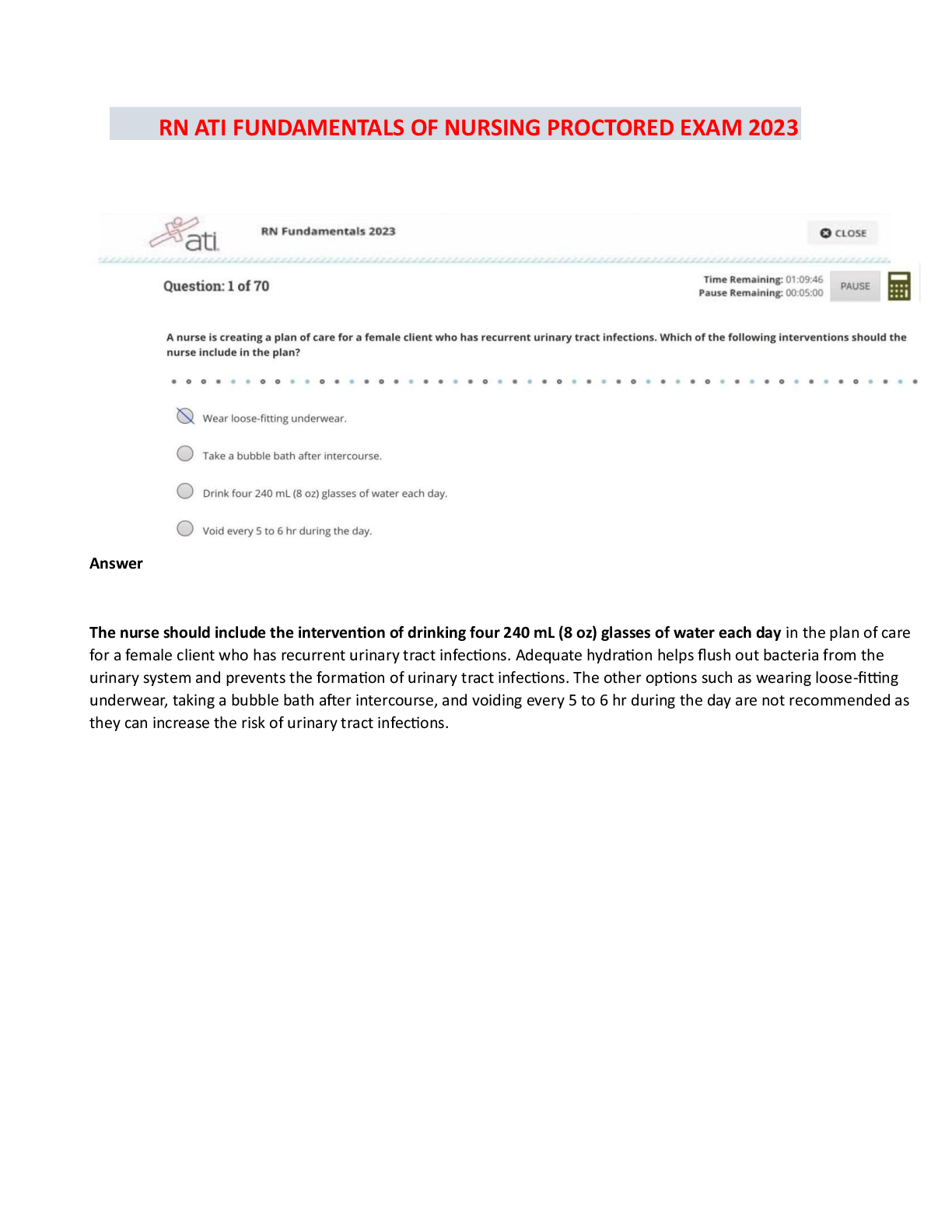
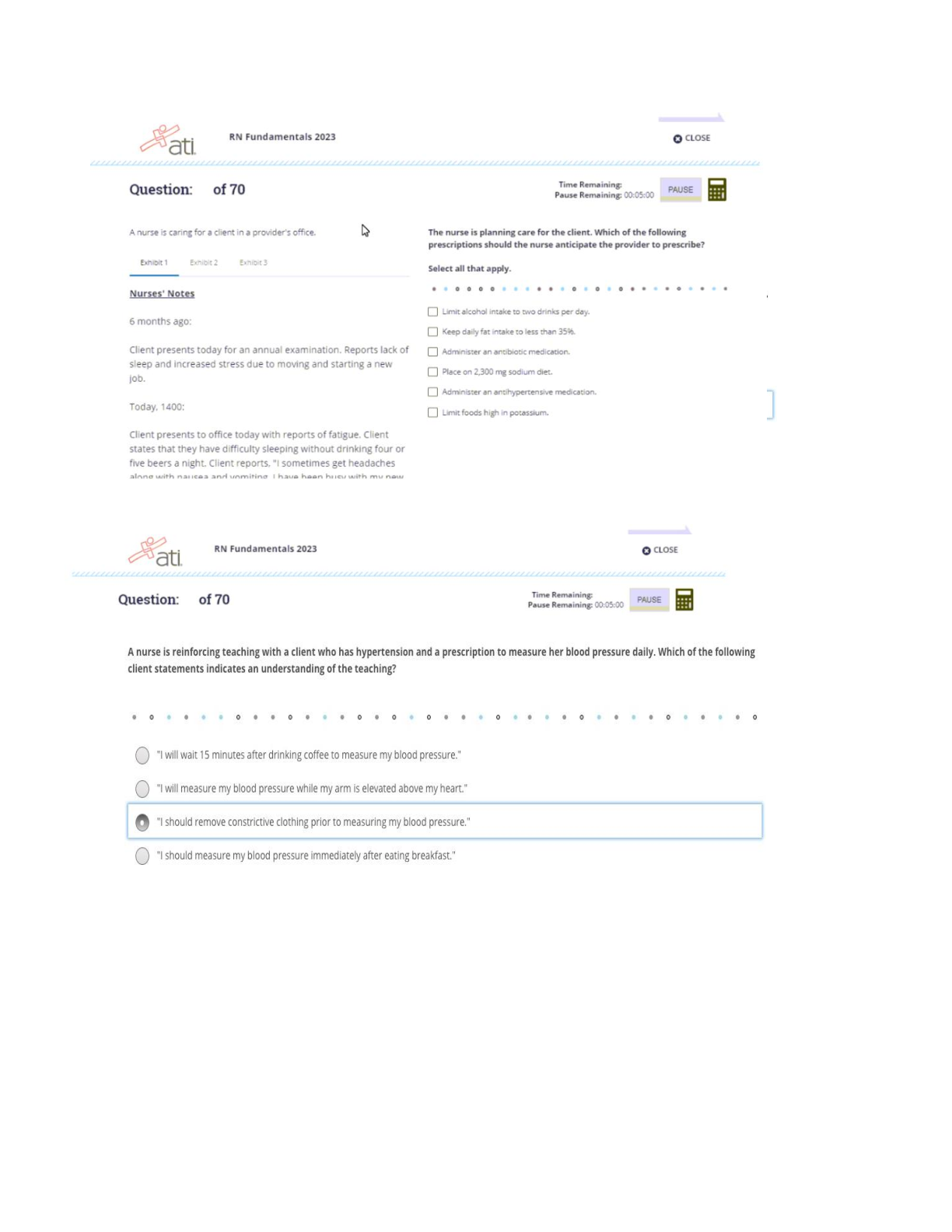
EDIS 2310 Final Exam | Complete Solutions (Verified) Five strategies that are essential for providing effective education for young children with autism in inclusive classrooms are teaching commun ... ication and social competence; using instructional strategies that maintain the class's natural flow; teaching and providing opportunities for independence; building a classroom community that includes all children; and which of the following? A. The use of applied behavior analysis B. The use of discrete trial training C. The use of visual cues and supports D. Promoting generalization and maintenance of skills Providing systematic instruction in imitation skills and planning opportunities for students with disabilities to interact directly with typically developing peers are strategies for which of the following? A. Teaching and providing opportunities for independence B. Using instructional strategies that maintain the natural flow of the class C. Teaching communication and social competence to students with autism D. Promoting generalization and maintenance of skills Using naturalistic teaching procedures and using different cues and prompts to ensure that each child receives adequate support are two ways of doing which of the following? A. Teaching communication and social competence B. Using instructional strategies that maintain the child's natural flow C. Teaching and providing opportunities for independence D. Promoting generalization and maintenance of skills Using activities that will engage children with a large range of abilities and allowing every child to have a turn and play a role are ways to do which of the following? A. Build a classroom community that includes all children B. Promote generalization and maintenance of skills C. Teach communication and social competence D. Teach and provide opportunities for independence What role has intensive, behaviorally-based early intervention played in educating students with autism? A. It has helped some children with autism learn communication, language, and social skills so that they have been able to succeed in general education classrooms. B. It has helped decrease the symptoms of autism. C. It has caused an increase in behavior problems when the students reach school age. D. It has helped students with autism decrease self-injurious behavior What is applied behavior analysis? A. One-on-one sessions during which a routinized sequence of contrived learning trials is presented as the teacher and child sit at a table B. Intensive, behaviorally-based early intervention C. A scientific approach to designing, conducting, and evaluating instruction based on empirically verified principles describing functional relationships between events in the environment and learning D. Visual cues and prompts that help students to perform skills with greater independence and accuracy What is discrete trial training? A. Intensive, behaviorally-based early intervention B. Visual cues and prompts that help students to perform skills with greater independence and accuracy C. One-on-one sessions during which a routinized sequence of contrived learning trials is presented as the teacher and child sit at a table D. A scientific approach to designing, conducting, and evaluating instruction based on empirically verified principles describing functional relationships between events in the environment and learning A wide variety of interventions that involve visual cues and prompts are called which of the following? A. Visual supports B. Applied behavior analysis C. Instructional accommodation D. Discrete trial training Characteristics of autism spectrum disorders may include impaired social relationships, communication and language deficits, intellectual functioning, and which of the following? A. Low IQ scores B. Low achievement level C. Reading difficulty D. Unusual responsiveness to sensory stimuli What is joint attention? A. The ability to hyper focus B. An early-developing social communication skill in which two people use gestures and gazes to share attention with respect to interesting objects or events C. The ability to pay attention to two speakers at the same time D. The ability to multitask What is echolalia? A. Selective mutism B. Another name for stuttering C. Speaking in simple utterances, not words D. Verbatim repetitions of what people around the speaker have said Autistic savant means which of the following? A. Severe communication problems B. A person with extraordinary ability in the areas of memorization, mathematical calculations, or musical ability while functioning at the mental retardation level in all other areas C. Severe mental retardation in all areas D. Severe deficits in adaptive behavior skills A related group of conditions that has also been known as a pervasive developmental disorder (PDD) is which of the following? A. Childhood disintegrative disorder B. Autism spectrum disorders C. Asperger syndrome D. Rett Syndrome Autistic disorder is marked by three defining features with onset before age three: a qualitative impairment of social interaction, a qualitative impairment of communication, and which of the following? A. Reading difficulty B. Low achievement level C. Low IQ scores D. Restricted, repetitive, and stereotyped patterns of behavior Asperger syndrome is which of the following? A. An autism spectrum disorder that is at the mild end of the spectrum and is characterized by impairments in the social areas, particularly an inability to understand how to interact socially B. A qualitative impairment of social interaction, a qualitative impairment of communication, and restricted, repetitive, and stereotyped patterns of behavior C. A related group of conditions that has also been known as pervasive developmental disorder (PDD) D. An intellectual disability What is intermittent direct service by a speech-language pathologist also called? A. Special classroom approach B. Pull-out approach C. Inclusive approach D. General education classroom approach Communication disorder specialists also serve as what for regular and special education teachers? A. Pathologists B. Teachers C. Consultants D. Assistants Increasingly, speech-language pathologists are working as educational partners in what settings? A. The classroom B. Homes C. The resource room D. Community buildings Goals of therapy for articulation disorders include acquisition of the correct speech sounds, generalization of the sounds to all speaking settings and contexts, and which of the following? A. A medical examination B. Application of behavioral principles C. Identifying the error patterns D. Maintenance of the correct sounds Goals of therapy for phonological errors include helping the child identify the error patterns and which of the following? A. Maintenance of the correct sounds B. Gradually produce more linguistically appropriate sound patterns C. Acquisition of the correct speech sounds D. Generalization of the sounds to all speaking settings and contexts Which of the following has strongly influenced the treatment of fluency disorders? A. Application of behavioral principles B. Complete medical examinations C. Intensive articulation therapy D. Intensive speech-sound therapy In some school districts, speech language pathologists screen the spoken language abilities of which children? A. Kindergarten children B. First grade students C. All elementary education students D. Students with special needs If a child fails a speech and language screening test, they are candidates for which of the following? A. A battery of tests B. A hearing test C. A language test D. A systematic, in-depth evaluation Why is an auditory discrimination test conducted? A. To determine what sounds are being missed B. To determine whether the child has good comprehension skills C. To determine whether the child is hearing sounds correctly D. To determine fluency rates Distortions, substitutions, omissions, and additions are types of which of the following? A. Speech-sound errors B. Phonological errors C. Language errors D. Articulation errors Articulation disorders are exhibited by which of the following? A. A child showing difficulty with distortions and additions to speech B. An interruption in the flow of speaking characterized by atypical rate and rhythm, and repetitions of sounds, syllables, words, and phrases C. A child who is not able to produce a given sound (i.e., who does not have the sound in his or her repertoire of sounds) D. A child produces a given sound correctly in one situation but not in others. When a child produces a given sound correctly in one situation but not in others, he is exhibiting which of the following? A. Fluency disorder B. Speech-sound error C. Articulation disorder D. Phonological disorder Narrating, explaining or informing, requesting, and expressing are four important functions of which of the following? A. Questioning B. Classroom participation C. Reading D. Communication The function of communication that is most beneficial to reading is which of the following? A. Expressing B. Narrating C. Explaining D. Requesting Paralinguistic and nonlinguistic behaviors are which of the following? A. Other forms of communication B. Early reading skills C. Cues that play major roles in human communication D. Early language skills What two placement options are available in most areas of the United States for students who are deaf or hard of hearing? A. Private schools and residential school placement B. Inclusion and pull-out programs C. Public school programs and residential school placement D. General education classroom and general education classroom with supports Are most hearing-impaired students who are included in the general education classroom considered to be hard-of-hearing or deaf? A. Totally deaf B. Deaf or hard of hearing C. Neither deaf nor hard of hearing D. Hard-of-hearing The skill level of which educator plays a critical role in the success and appropriateness of a general education classroom placement for students who are deaf? A. Classroom teacher B. Educational interpreter C. Speech pathologist D. Paraeducator Auditory training is which of the following? A. It is the process of understanding a spoken message by observing a speaker's face. B. It teaches the child to learn, to listen, and to learn by listening instead of simply learning to hear. C. It supplements oral communication with a visual representation of spoken language in the form of hand signals that represent the 45 phonemes of spoken English. D. It clarifies the sound-symbol relationship between spoken English and print. What is cued speech? A. Teaches the child to learn, to listen, and to learn by listening instead of simply learning to hear B. Clarifies the sound-symbol relationship between spoken English and print C. A supplement to oral communication with a visual representation of spoken language in the form of hand signals that represent the 45 phonemes of spoken English D. The process of understanding a spoken message by observing a speaker's face Which of the following clarifies the sound-symbol relationship between spoken English and print? A. Visual phonics B. Cued Speech C. Speech reading D. Auditory learning Which of the following descriptions defines a hearing aid? A. It is a microphone transmitter worn by the teacher and a receiver worn by the student. B. It makes sounds louder. C. It is a surgically implanted device placed under the skin behind the ear. D. It is a person who interprets for a hearing-impaired person. When a microphone transmitter worn by the teacher and a receiver worn by the student combine, they are a type of which of the following? A. Hearing aid B. Cochlear implant C. Sound interpreter D. Group listening device How does speech-to-text translation help students with hearing impairments? A. It increases access by deaf students to live presentations, such as public or classroom lectures. B. The printed text of all television shows appears on the bottom of the screen. C. It adds acoustic couplers to telephones to make it possible to send messages over conventional telephone lines in typed or digital form. D. It provides special signal devices to alert persons with hearing impairments to certain sounds or events, such as alarms. Acquisition of English literacy, speaking, academic functioning, and social functioning are which of the following? A. Four areas that are easy for children with hearing loss B. Four areas that are difficult for children with hearing loss C. Four causes of hearing loss D. Four precursors to hearing loss Smaller vocabulary, difficulty with function words, and omitting the endings of words are characteristics of which of the following for students with hearing loss? A. Difficulty with speaking B. Difficulty with social functioning C. Difficulty with acquisition of the English language D. Difficulty with academic achievement Feeling isolated, without friends, and unhappy in school are which of the following? A. Social difficulties of students who try to befriend students with hearing loss B. Signs of depression in students with hearing loss C. Difficulties experienced by siblings of children with hearing loss D. Social difficulties reported by students with severe or profound hearing loss What is deafness? A. A hearing impairment so severe that the child is impaired in processing linguistic information through hearing, with or without amplification, and adversely affects a child's educational performance B. Significant hearing loss that makes some special adaptations necessary C. An impairment in hearing, whether permanent or fluctuating, that adversely affects a child's education performance but is not included under the definition of deafness D. A person has sufficient hearing to understand speech. What is a hearing impairment? A. An impairment so severe that the child is impaired in processing linguistic information through hearing, with or without amplification, and adversely affects a child's educational performance B. Significant hearing loss that makes some special adaptations necessary C. A person has sufficient hearing to understand speech. D. An impairment in hearing, whether permanent or fluctuating, that adversely affects a child's educational performance but that is not included under the definition of deafness Residual hearing means which of the following? A. Hearing impairment, whether permanent or fluctuating, adversely affects a child's educational performance. B. Significant hearing loss that makes some special adaptations necessary C. A deaf person may perceive some sounds. D. A person has sufficient hearing to understand speech Approximately 88 percent of students with visual impairments are educated in which of the following settings? A. Public schools B. Special schools C. Private schools D. Home school Which of the following is not a factor that determines how a hearing loss affects language and communication? A. The language spoken in the home B. The attitudes of parents and siblings C. The degree of hearing loss D. The presence or absence of other disabilities Vision specialists provide supports to which of the following? A. Special education teachers B. General education teachers C. Students with visual impairments in the general education classroom D. Parents Approximately four percent of school-age children with visual impairments attend which of the following? A. Public schools B. Home school C. Residential schools D. This group is not formally educated What are expanded curriculum priorities for students with visual impairments? A. Braille, tactile aids, and manipulatives B. Functional vision and optical devices C. Speech-to-text software and optical scanners D. Orientation and mobility, listening skills, and functional life skills What are some examples of orientation and mobility aids for students with visual impairments? A. Braille and optical scanners B. Tactile-experience books and speech-to-text software C. Cane skills, guide dogs, and sighted guides D. Functional vision and optical devices The systematic development of listening skills is which of the following? A. An important component of the educational program of every child with visual impairments B. Essential for good reading skills C. Essential for learning speech D. Not important for students with visual impairments Effective vision requires proper functioning of what three anatomical systems? A. Optical system, muscular system, and nervous system B. Circulatory system, optical system, and muscular system C. Whole body system D. Communication system, circulatory system, visual system Causes of visual impairments are grouped into what three broad categories? A. Refractive errors, myopia, and hyperopia B. Refractive errors, structural impairments, and cortical visual impairments C. Cataract, glaucoma, and nystagmus D. Muscular issues, optical problems, and nervous system disorders Decreased vision or blindness due to known or suspected damage to or malfunction of parts of the brain that interpret visual information refers to what? A. Optical malfunction B. Muscle dysfunction C. Cortical Visual Impairments D. Visual impairments [Show More]
Last updated: 10 months ago
Preview 5 out of 21 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

EDIS 2310 QUIZZES (CH 1-4) AND FINAL EXAM BUNDLE
EDIS 2310 QUIZZES (CH 1-4) AND FINAL EXAM BUNDLE
By Ajay25 10 months ago
$18
2
Reviews( 0 )
$18.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 26, 2025
Number of pages
21
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 26, 2025
Downloads
0
Views
72