General Science > EXAM > BSCI 2300 Exam 1 | Verified with 100% Correct Answers (All)
BSCI 2300 Exam 1 | Verified with 100% Correct Answers
Document Content and Description Below
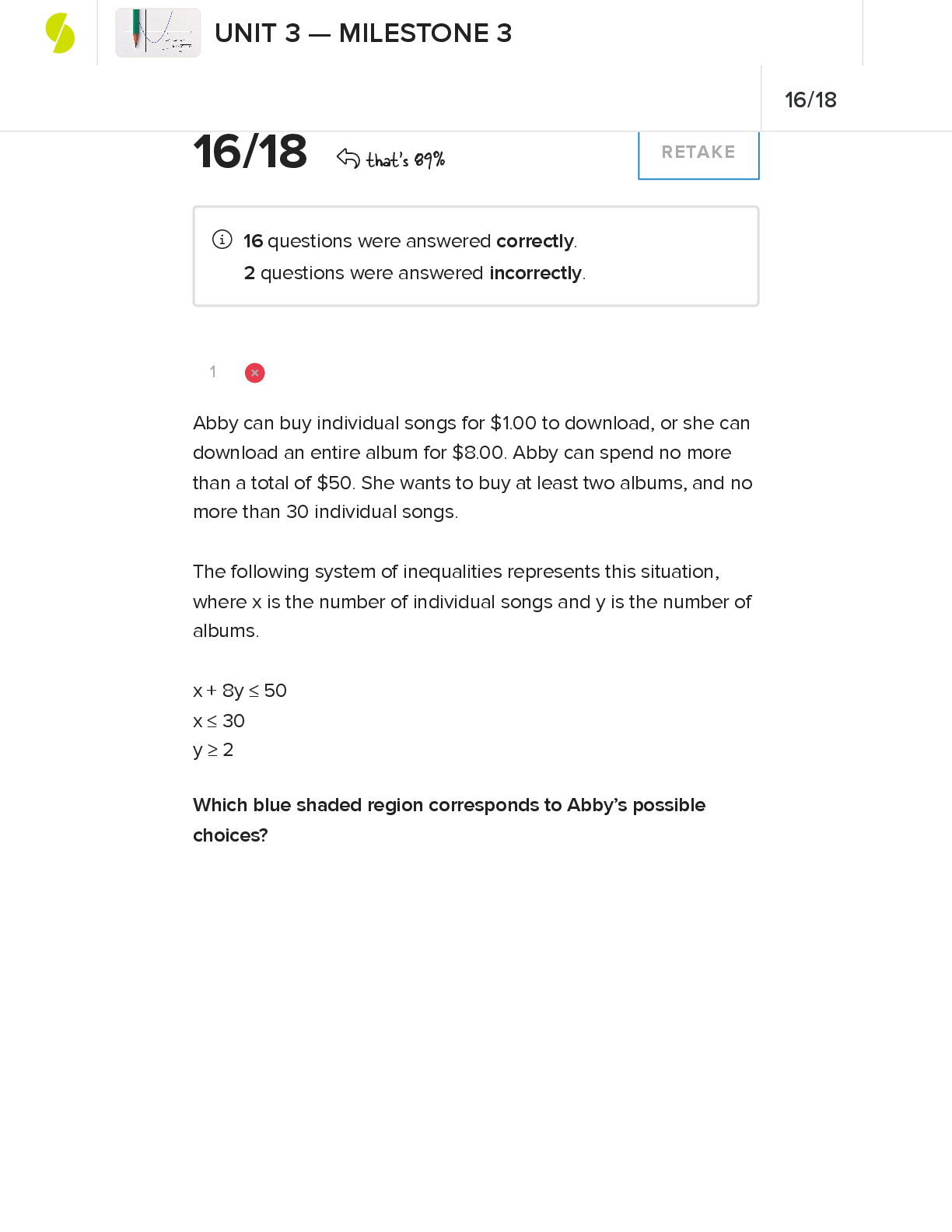
BSCI 2300 Exam 1 | Verified with 100% Correct Answers What are the components of pre development? who idea generation site assessment access govt restraints define building program financial feasib... ility What are the steps of the project delivery process? pre development, design and engineering, construction, operations Who are involved in the construction process? GC, Subcontractors, design consultant, suppliers, fabricators, vendors, inspectors What are the goals of a construction project? safety/quality, on time., under budget (can only have 2 of the 3) What are some project delivery methods? Design bid build design build Construction management at fee CM@Risk Integrate project design Describe Design bid build standard jobs for public money Design happens before bidding which happens before construction Longer timeline Describe Design Build Can be designed and built at the same time More expensive Better quality Faster delivery Describe CM@Risk Useful for alrge projects with multiple phases or lots of coordination CM sometimes part of the owners team CM controls the subcontractors Describe Integrated project delivery Owner, CM, and SE form partnership Money to design and build is put into partnership and partnership benefits from any cost/time saving measures What is a fixed fee? - Owner pays an agreed fixed amount - GC assumes most of the risk - best for projects where the scope of work is well defined before construction starts What is cost plus? - owner pays GC direcrt costs plus an addedd fee - owner assumes more cost risk but has potential savings - suites projects where score is not fully defined - adding a guaranteed max adds some risk back to the GC What is master format? - used for organizing info in construction specifications and docs - improves organization and communication What is a zoning ordinance? - affects the pre development phase - enforced by the city planning department - controls all parts of a project What are building codes? - affects building phase What are 3 examples of international residential codes? - one and two family homes - townhouses - 3 stories max What are IBC occupancy groups? International building code - types 1-5 - 1 being the most resistant (high rise office building) - 5 being the least resistant (single family home) What does IBC stand for? International Building Code What does ICS stand for? Incident Command System What is something ICS decides? determines the max allowable building size (greater risk, smaller building) List some standard setting agencies ASTM international ANSI OSHA What are strategies for project sustainability? - location and transport - sustainable sites water efficiency - energy and atmosphere - material and resources - indoor environmental quality What is site survey? - initial clearing layout- environmental features, limits of construction, BMPs - cut/fill staking Why is the soil type important? soil controls... - drainage - excavation time and cost - structural support - settling What is the classification of soils? - Boulders- >12 inches- 2 hands to lift - Cobbles- 3-12 inches- 1 hand to lift - Gravel- .187- 3 inches- single particle in between fingers - Sand- .003-.187 inches- too small to pick up only 1 particle at a time - Silt and Clay- <.003 inches- cant see individual particles Is larger or smaller soil particles better for holding structures? Smaller What is cohesionless soil? solid that has little bumps that get caught together, falls apart when you pick it up What is cohesive soil? example is clay, doesn't fall apart when picked up What is graded soil? lots of different sized particles What is non graded soil? all the same size particle Why is site excavation important? you might not be the first to dig there What color is electrical when excavating a site? Red What color is communication when excavating a site? Orange What color is sanitary/storm sewer when excavating a site? Green What color is water when excavating a site? Blue What color is gray water when excavating a site? Violet What color is neutral when excavating a site? White What is the site excavation process? - clearing - stripping - grubbing - stockpiling Why remove topsoil? - organic soil is made of material that gets smaller as fungi and animal eat them - doesn't hold weight well - holds water easily What are some reasons for excavating soil? - getting to stable soil - basements- What are some shoring types? - piles - shotcrete - slurry walls - bracing - rakers (benched is stepped down) (shored is straight down) What are dewatering methods? - well point - watertight barrier What is soil mixing? columns of soil strengthened with Portland cement and eater are created prior to excavation What is the difference in a foundation and a basement? anything above soil is a foundation and anything below is a basement/substructure What are requirements of a foundation? - must transmit building loads to the rock - must not fall or collapse - must not settle or damage the structure - must be economically and technically feasible What decides the size of a building? - based on bearing capacity of soil - measured in lbs per square foot or kips per square foot - the higher the bearing capacity of soil the smaller the foundation size What is a dead load? acts continuously on foundation - weight of structure - permanent thing What are live loads? - furniture - people - snow What are wind loads? - exert an upward force on a flat low slope roofs - loads are resisted bu anchorage to foundation and wind bracing elements What are earthquake loads? - both horizontal and vertical - shaking and swaying do most damage - isolating building structure from foundation with flexible joints What is a shallow foundation? transfers load to the earth at he base of the column or wall of the structure What is spread footing? term used to describe the lowest part of the shallow foundation What is continuous footing? refined concrete footing extended to support a row of columns What is isolated footing? the individual spread footings supporting free standing columns What is mar/raft foundation? thick heavy reinforced concrete slab as a footing for a number of columns or an entire building What is geopier foundation? installed by drilling or augering a hole into the soft or weak soil and then filling with gravel or other aggregate material, then is often done with the help of specialized equipment What is a grade beam foundation? a reinforced concrete beam supporting a bearing wall or neat ground level and transferring load to isolated footing, piers, or piles When are deep foundations used? are used where the solid is directly below the building substructure are weak or unstable What are caissons? holes drilled in the soil What is the process of putting in a caisson? - casing installed - bell on tip enlarged - bottom inspected and tested - reinforced placed - concrete placement What are types of wooden piles? - creosote treated - limited load capacity What are types of steel piles? - H shaped - hollow pipe, filled with concrete after being driven - steel subject to corrosion details about concrete piles - precast, reinforced concrete solid sections - most expensive What is a friction pile? load transferred by friction resistance between the pile and the earth What is an end bearing pile point loading, pole that puts all the pressure at the end of the pile What is a pile driver whacks top of pile until pile won’t move any further Details about storm drainage - gravity driven - lay from the bottom up - typically first utility installed Storm drain types - Reinforced concrete pipe RCP (most expensive but most durable) - High density polyethylene HDPE - Corrugated Metal Pipe CMP Spigot and bell end of a pipe Details about a sanitary sewer - gravity driven - lay from bottom up What is a 2 pipe system uses separate pipes for sewage and water runoff What is a one pipe system uses the same pipe for sewage and slo excess water Details about water systems - pressurized so doesn't need to be sloped - depth doesn't matter - has to be flushed out before you can drink water out of it Details about gas systems - pressurized - tested to make sure there aren't leaks What is site prep - clearing vegetation and existing structures - grading creates a level surface for construction - soil stabilization prevent erosion and ensures a strong foundation What is soil stabilization - the process of modifying soil properties to enhance its engineering qualities - involves biological, chemical, or mechanical adjustments - improves permeability, strength, durability, compressibility, and plasticity [Show More]
Last updated: 6 months ago
Preview 4 out of 15 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 26, 2025
Number of pages
15
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 26, 2025
Downloads
0
Views
14