*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Introduction to Medical Microbiology Exam #2 Study Guide[ CORRECT QUESTION AND ANSWERS GRADED A+] (All)
Introduction to Medical Microbiology Exam #2 Study Guide[ CORRECT QUESTION AND ANSWERS GRADED A+]
Document Content and Description Below
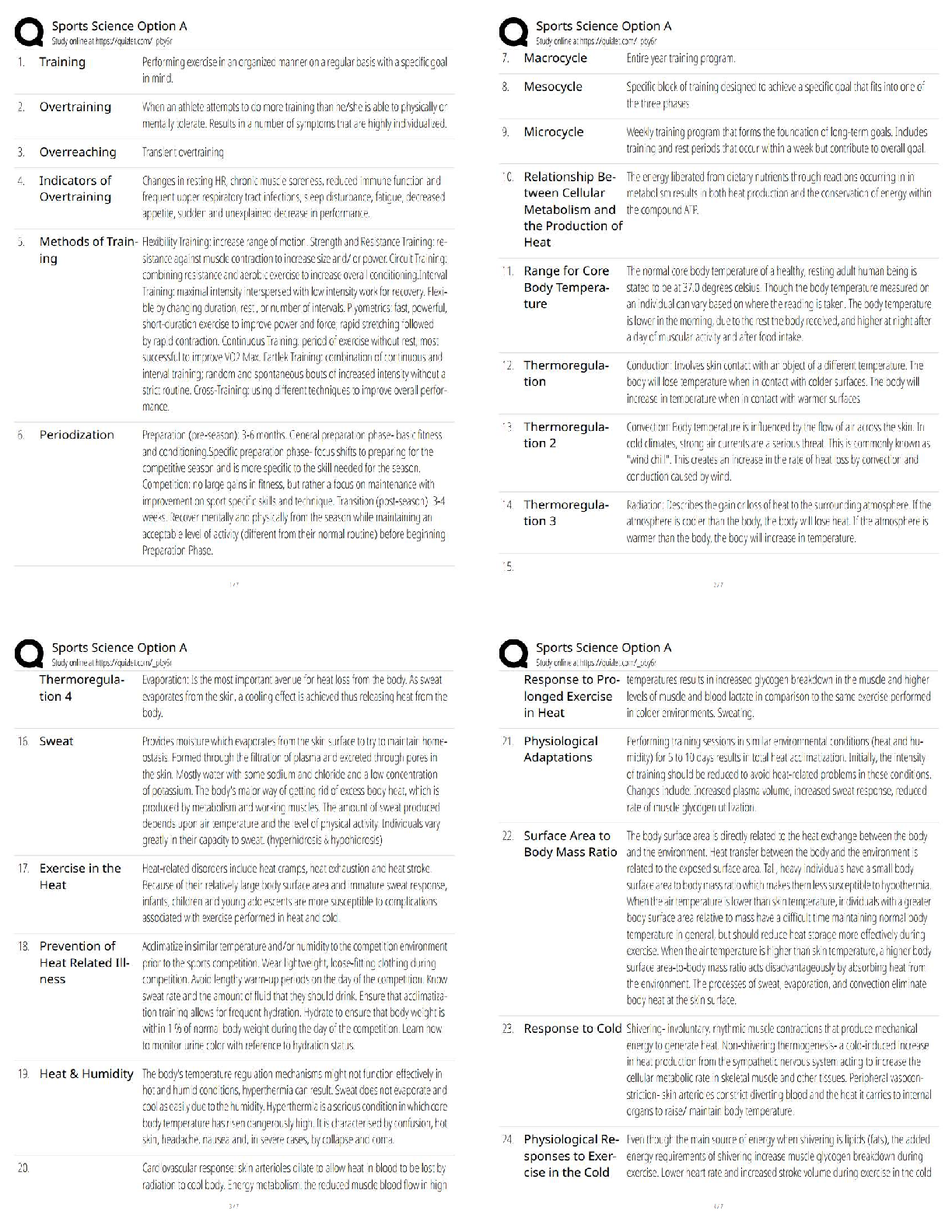
Introduction to Medical Microbiology Exam #2 Study Guide Chapter 6 – Acellular Pathogens 1. Know the basic characteristics and components of Viruses and the definition of Virion Obligate int ... racellular parasites - non-living, infectious agents, can’t live w/o host work by: invading, taking over cell functions & directing it to produce more viruses use structures & enzymes of cells to support own reproduction Can infect all forms of life: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya Considered ultramicroscopic- electron microscope 2000 viruses could fit into an average bacterial cell Viruses have nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protective protein coat (capsid) or called nucleocapsid Virion – fully formed virus that can establish an infection in a host cell 2. Know the basic structure of the viral Capsid and be able to distinguish between the 3 common shapes Outer protein shell made of repeating protein subunits known as capsomeres. 3 Common shapes: Helical - composed of rod-shaped capsomeres arranged into hollow discs Icosahedral - flat and rounded capsomeres arranged into a 20-sided figure Complex - have an icosahedral head, helical tail, and attachment fibers 3. Know the basic structure of the viral Envelope, including the definition of Naked Viruses and Spikes Double layer of lipid that surrounds the capsid Found on mostly animal viruses Naked viruses - viruses lacking an envelope Created from portions of the host cell membrane Spikes - viral proteins that protrude from the surface and help virus attach to host cell 4. Know the makeup and possible arrangements of viral Nucleic Acid Can be DNA or RNA but not both DNA may be linear/circular or double-stranded/single-stranded RNA can be double-stranded/single-stranded 5. Know the steps of Bacteriophage and Animal virus multiplication, be able to describe what happens during each step, and be able to identify differences between the two types Viral Multiplication: Bacteriophage (virus that infect bacteria) Viral Model Viral Multiplication: Animal Virus Model Attachment - virus & host cell come together - use tail fibers Penetration - bacteriophage injects nucleic acid into the host o protein coat remains on the outside Biosynthesis - virus shuts down host cell machinery and directs the host to produce new viral components Maturation - viral components assemble into new bacteriophages Release o Lytic cycle - viral enzyme digests the host cell wall resulting in cell lysis(rupture) and virus release o Lysogeny – viral DNA inserts into bacterial chromosome and enters inactive prophage state can re- enter lytic cycle can carry toxins Attachment -virus attaches to specific host cell receptors o spikes instead of tail fibers Penetration –entire virion taken into cell o Endocytosis – engulfment by host cell o Membrane fusion – viral envelope fuses with host cell membrane Uncoating - the envelope (if present) & capsid are separated from nucleic acid o viral nucleic acid released into cytoplasm Biosynthesis and Maturation o Virus stops host function & makes duplication of DNA or RNA to produce the components for new viruses o New viruses assemble themselves Release o Enveloped viruses - released by budding & exocytosis o Naked viruses - released when the cell lyses o DNA viruses can integrate into the host chromosomes to form a provirus 6. Know the basic Nomenclature rules for viruses and be able to match the virus families with examples of virus members listed *only know disease it cause and not if RNA or DNA? Common DNA Viruses Common RNA Viruses Poxviridae – Smallpox virus Herpesviridae o Herpes simplex type I (HSV-1) o Herpes simplex type II (HSV-2) o Varicella-zoster virus o Epstein-Barr virus o Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Papillomaviridae – Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Hepadnaviridae – Hepatitis B virus Parvoviridae – Parvovirus B19 Adenoviridae - Adenovirus Picornaviridae – Poliovirus, Rhinovirus and Hepatitis A virus Togaviridae – Encephalitis viruses and Rubella virus Rhabdoviridae – Rabies virus Reoviridae – Rotavirus Retroviridae – Human Immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Filoviridae – Ebola, Marburg virus Orthomyxoviridae – Influenza virus 7. Know the difference between Acute versus Persistent infections and Latent versus Chronic infections Acute infections - short duration host may develop long-lasting immunity Persistent infections - persist for years, often without disease symptoms Latent infection - virus can remain silent in the host cell & reactivate o Ex. Herpes Simplex, Chicken Pox Chronic infection – recurrent symptoms over a long time o Ex. Hepatitis C, HIV 8. Be able to define Oncoviruses, Cytopathic Effects, and Syncytia Oncoviruses – cause the host cell to become cancerous o Virus don’t kill the host cell but causes it to change its properties (transformation) Cytopathic Effects (CPE) - virus-induced damage to the cell that alters its microscopic appearance Syncytia – fusion of multiple host cells into single large cells with multiple nuclei [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 18 pages
![Preview image of Introduction to Medical Microbiology Exam #2 Study Guide[ CORRECT QUESTION AND ANSWERS GRADED A+] document](https://scholarfriends.com/storage/Studyguide2_micro.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 22, 2021
Number of pages
18
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 22, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
132






.png)
.png)
.png)