Computer Architecture > EXAM > CECS 341 Exam 2 | Questions with Verified Answers (All)
CECS 341 Exam 2 | Questions with Verified Answers
Document Content and Description Below
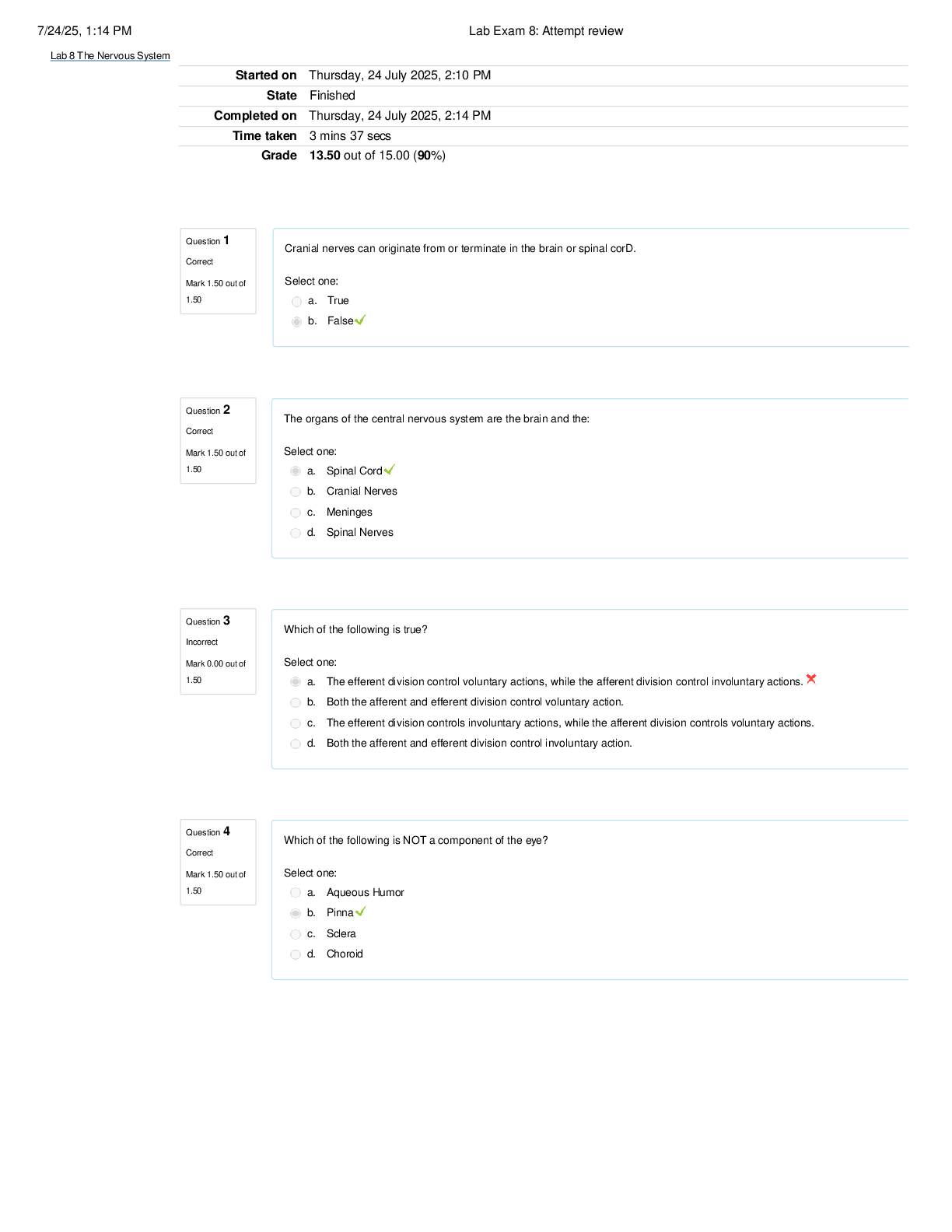
CECS 341 Exam 2 | Questions with Verified Answers The following code has a control hazard beq $t1, $t1, label2 label 1: add $s0, $s1, $s2 label2: sub $s3, $s4, $s5 True or false? True A control haz ... ard can be resolved via a stall True or False True To reduce stall due to branches, branch prediction involves executing a next instruction even if the processor is not sure that instruction should be next True or False True i1:lw $t0, 0($t0) i2:add $t1, $t0, $t0 a. must stall b. can avoid stalls using only forwarding c. execute without stall or forwarding i1: add $t1, $t0, $t0 i2: addi $t2, $t0, #5 i3: addi $t4, $t1, #5 a. must stall b. can avoid stalls using only forwarding c. execute without stall or forwarding i1: addi $t1, $t0, #1 i2: addi $t2, $t0, #2 i3: addi $t3, $t1, #2 i4: addi $t3, $t0, #4 i5: addi $t5, $t0, #5 a. must stall b. can avoid stalls using only forwarding c. execute without stall or forwarding In CC 2, Instr1 and Instr2 are both in stage IM true or false False the figure indicates that three ALUs are needed. true or false False two instructions could possibly need to use the ALU simultaneously true or false false Assuming a program has hundreds of instrustion( rather than just three as shown above), how many instructions might possibly be executing during one clock cycle A. 3 b. 5 Which is NOT part of stage 1L IF(instruction fetch) A. instruction memory is read B. the register file is written C. the IF/ID register is written Which is NOT part of stage 2: ID(instruction decode) a. pc is incremented b. register file is read c. sign extension d. control signals are generate for the current instruction e. the IF/ID register is read, and the ID/EX register is written Which is NOT part of stage 3: EX(execution) a. the ALU operates b. data memory is written c. the ID/EX register is read, and the EX/MEM register is written Which is NOT part of stage 4: MEM(memory) a. instruction memory is read b. Data memory is read c. The EX/MEM register is read, and the MEM/WB register is written Which is NOT part of stage 5: WB a. the register file is written b. the MEM/WB register is read, and the IF/ID register is written The store and load instruction behave similarly in stage 1(IF: instruction fetch) True or False True The store and load instructions behave similarly in stage 2 (ID:instruction decode). True or False True The store and load instructions behave similarly in stage 3:(EX: execute) true or false False the store and load instructions both write the data memory in stage 4: (MEM: memory) true or false false the store and load instructions differ in stage 5L (WB: write back) in that load writes to the register file whereas store reads the register file true or false. False Instr5 ( add $14..) a. being fetched b. being decoded c. executing on the ALU Instr3 ( add $12..) a. being fetched b. being decoded c. executing on the ALU Instr1(lw$10) a. being fetched b. writing back c. Nothing, already done Consider CC 6(clock cycle 6) What is Instr1(lw$10) doing? a.writing back b.Nothing, already done Consider CC 6(clock cycle 6). Assume Instr1 to Instr10 exist with no branches. What instruction is being fetched? a. Instr1 b. Instr5 c. Instr6 In what CC will Instr5 NOT be in the pipeline a. CC5 b. CC8 c. CC 10 Allowing jump, branches, and ALU instructions to take fewer stages than the five required by the load instruction will increase pipeline performance under all Circumstances a. correct b. incorrect In the non-pipelined datapath, for an r-type instruction, all the needed values for control lines like ALUOp, ALUSrc, RegDst, and RegWrite, can be determined when the instruction appears from instruction memory True or False True In the non-pipelined datapath, for an r-type instruction, the control signals ALUOp and ALUSrc are used in the instruction's 3rd clock cycle, while RegDst and RegWrite are used in the instruction's 5th clock cycle true or false False In the pipelined datapath, for an r-type instruction, all the needed values for control lines like ALUOp, ALUSrc, RegDst, and RegWrite, can be determined when the instruction appears from instruction memory True or False True In the pipelined datapath, for a R-type instruction, the control signals ALUOp, and ALUSrc are used in the instruction's 3rd clock cylce, RegWrite is used in the instruction 5th clock cycle. true or false True The MIPS pipelined control approach determines all control line values during an instruction's 1st clock cycle, the instruction fetch stage true or false False The control line values are different in the pipelined datapath than in the non-pipelined datapath True or false False The sw instruction would read the old(wrong)value from $2 True or False False The or instruction would read the old(wrong) value from $2 True or false True Suppose a sixth instruction was sub $3 $13, $14. A pipeline data hazard would exist True or false True A new pipeline data hazard would be introduced if the second instruction was replaced with or $13, $6, $5 True or false False Two actions must be completed before a beq's branch can be taken, actions that take time. Obviously, one is determined whether the beq's two source registers' values are equal. the other is to compute____ a.The beq's target address b. the beq instruction's source registers' addresses c. the beq instruction's address The action of computing the beq's target address can be done earlier, in the ID stage rather than the EX stage. The action means the target address will be computed for all instructions, not just beq instruction. A problem that may occur with such computing for all instructions is A. branching to a wrong address B. longer flushing C. no problem exist For beq, determining if the two source registers' values are equal is done in an earlier stage than EX using A. XOR gates B. the existing ALU C. a second ALU A five stage pipeline(IF, ID, MEM, WB) executes the following instruction sequence add $1, $2, $1 xxx $1, $2, $1 sub $1, $2, $1 Which exception should be recognized first in the above sequence a. arithmetic overflow b. undefined instruction c. hardware error RegDst 0 or 1 0 Branch 0 or 1 0 MemRead 0 or 1 1 MemtoReg 0 or 1 1 ALUSrc 0 or 1 1 RegWrite 0 or 1 1 For a store word (SW) instruction, MemRead would be 0 or 1 0 For a store word (SW) instruction, RegWrite would be 0 or 1 0 the value for the ALUSrc control signal is 0 or 1 0 the value for the ALUOp control signal is 00 or 01 01 Assume the current instruction is beq $t1, $t2, offset, and $t1 is 90 while $t2 is 85. The value for the branch control signal is 0 or 1 1 Assume the current instruction is beq $t1, $t2, offset, and $t1 is 90 while $t2 is 85. the value for the Zero control signal is 0 or 1 0 Assume the current instruction is beq $t1, $t2 ,offset, and $t1 is 90 while $t2 is 85. How will the PC be updated next? a. PC+4 b. target address The datapath shown requires four cycles to execute a branch instruction true or false False During a branch on equal instruction, two register are read, those register's values are subtracted. If the result is 0, Zero becomes 1, causing a new target address to pass through the mux on the upper right and be waiting to enter the PC on the next rising clock edge. True or False True Consider the subtraction of base ten numbers 6 - 4 using 32-bit binary numbers, and achieved by adding 6 with the two's complement of 4. What is the value of dcba? a. 1011 b. 1100 c. 1010 d. 0010 Consider the subtraction of base ten numbers 6 - 4 using 32-bit binary numbers, and achieved by adding 6 with the two's complement of 4. What is the value of zyxw? a. 1011 b. 1100 c. 1010 d. 0010 The MIPS add, addi, and sub instructions may result in an exception. a. True b. False A multiplexor is also called a selector, where its output is one of the inputs that is selected by a control. a. True b. False A datapath element that has internal storage is called a _____ element. a. Combinational b. State A register is a _____ element. a. Combinational b. State An ALU is a _____ element. a. Combinational b. State An edge-triggered clocking methodology means that any values stored in a sequential logic element are updated on a clock edge either from low to high or vice versa. a. True b. False We can use the word asserted to indicate a signal that is logically high and assert to specify that a signal should be driven logically high. a. True b. False A rising clock edge refers to the clock changing from _____. a. 0 to 1 b. 1 to 0 c. Either 0 to 1, or 1 to 0 The design of register file can read from two registers and write to one register during the same clock cycle. a. True b. False The design of register file allows writes to a register during the same cycle that the same register is read. a. True b. False The inputs carrying the register number to the register file are all bits wide, whereas the lines carrying data values are 32 bits wide. a. 3 b. 4 c. 5 d. 6 e. 16 A register write must be explicitly indicated by asserting the write control signal. a. True b. False A register read must be explicitly indicated by asserting the read control signal. a. True b. False For R-type instruction with three register operands, we need to read data(s) word from the register file. a. One b. Two c. Three For R-type instruction with three register operands, we need to write data word(s) into the register file. a. One b. Two For R-type instruction with three register operands, to write a data word, we will need inputs for the register file. a. One b. Two For R-type instruction with three register operands, we will need a total of outputs for the register file. a. One b. Two For the load instruction lw $t1, offset_value($t2), the value read from memory must be written into the register file in the specified register, which is . a. $t1 b. $t2 For the store instruction sw $t1, offset_value($t2), the value to be stored must also be read from the register file where it resides in . a. $t1 b. $t2 For the data memory, the control signals should be for a store instruction. a. MemWrite = 0 and MemRead = 0 b. MemWrite = 0 and MemRead = 1 c. MemWrite = 1 and MemRead = 0 d. MemWrite = 1 and MemRead = 1 For the beq instruction, branch taken is referred to the situation where the branch target address becomes the new PC when the condition is true. a. True b. False In the MIPS architecture for a branch instruction, the branch target address is given by . a. sum of the offset field of the instruction and the address of the instruction following the branch. b. the offset field of the instruction c. the address of the instruction following the branch Which of the following is correct for an load instruction referring to the right datapath? a. MemtoReg should be set to cause the read data from the data memory to be sent to the register file b. MemtoReg should be set to cause the ALUresult to be sent to the register file c. MemtoReg should be set to cause the Readdata2 from RF to be sent to the register file Which of the following is correct for an store instruction referring to the right datapath? a. ALUSrc should be set to cause the Readdata1 from the RF to be sent to the ALU as the second input b. ALUSrc should be set to cause the Readdata2 from the RF to be sent to the ALU as the second input c. ALUSrc should be set to cause the sign-extended 16-bit offset field from the instruction to be sent to the ALU as the second input d. We do not care about the setting of ALUSrc for loads The single-cycle datapath conceptually must have separate instruction and data memories due to the fact that . a. The formats of data and instructions are different in MIPS, and hence different memories are needed b. Having separate memories is less expensive c. The processor operates in one cycle and cannot use a single-ported memory for two different accessed within that cycle The MIPS ALU defines five different arithmetic and logic operations depending on four ALU control inputs. For the branch equal operation, the four ALUctl lines should be . a. 0000 b. 0010 c. 0110 d. 0111 The MIPS ALU defines five different arithmetic and logic operations depending on four ALU control inputs. For the store word instructions, the four ALUctl lines should be . a. 0000 b. 0010 c. 0110 d. 0111 The MIPS ALU defines five different arithmetic and logic operations depending on four ALU control inputs. For the slt word instructions, the four ALUctl lines should be . a. 0000 b. 0010 c. 0110 d. 0111 The MIPS ALU defines five different arithmetic and logic operations depending on four ALU control inputs. For the logic OR instructions, the 2-bit ALUOp control lines should be . a. 00 b. 01 c. 10 The MIPS ALU defines five different arithmetic and logic operations depending on four ALU control inputs. For the sw instructions, the 2-bit ALUOp control lines should be . [Show More]
Last updated: 8 months ago
Preview 4 out of 18 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

CECS 341 EXAM 1 & 2 BUNDLE
CECS 341 EXAM 1 & 2 BUNDLE
By Nurse Henny 8 months ago
$18
2
Reviews( 0 )
$16.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 01, 2025
Number of pages
18
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 01, 2025
Downloads
0
Views
16