Solution Manual For Managerial Economics, 9th Edition by William F. Samuelson, Stephen G. Marks, Jay L. Zagorsky-1. Managerial economics is the analysis of important management decisions using the
tools of economics. Mo
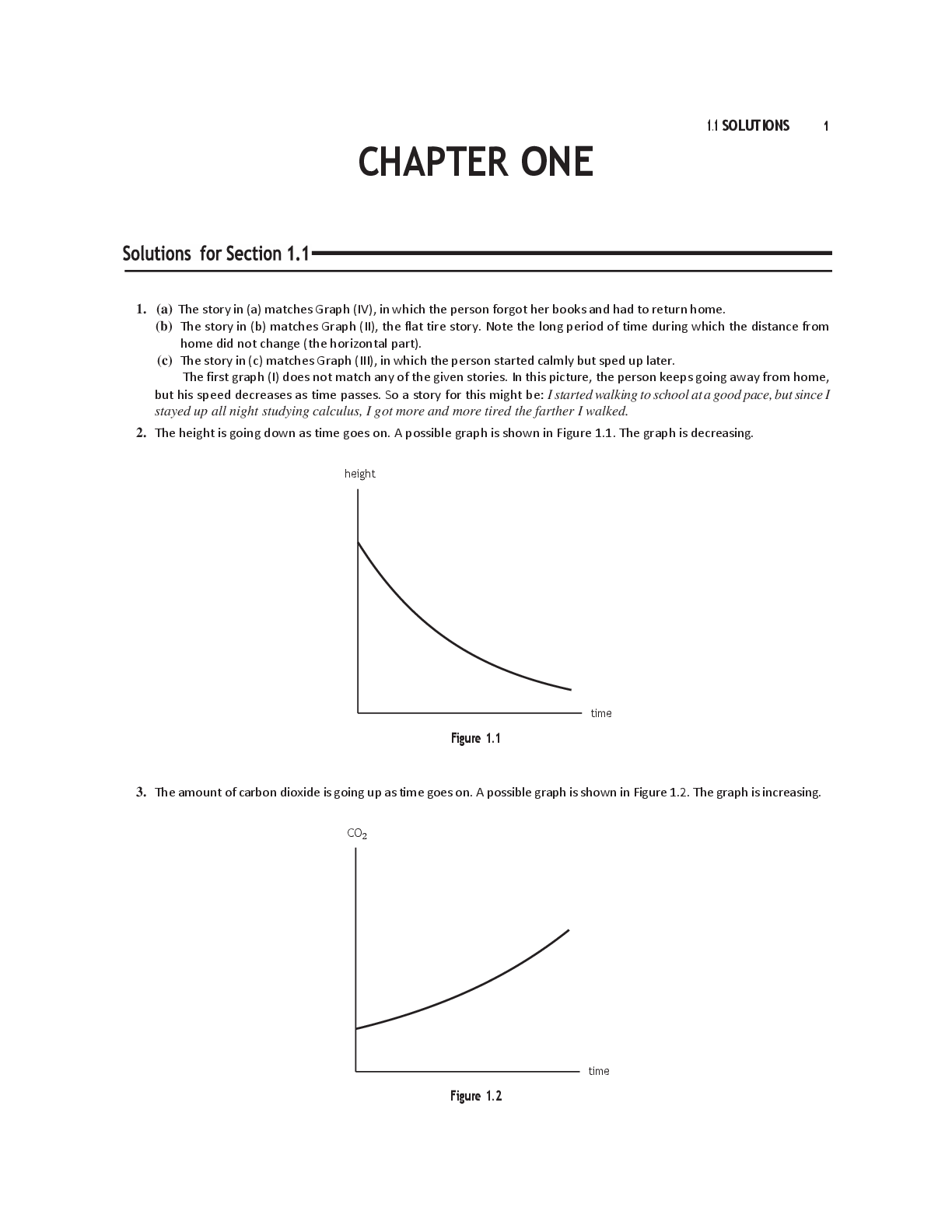
...
Solution Manual For Managerial Economics, 9th Edition by William F. Samuelson, Stephen G. Marks, Jay L. Zagorsky-1. Managerial economics is the analysis of important management decisions using the
tools of economics. Most business decisions are motivated by the goal of maximizing
the firm‟s profit. The tools of managerial economics provide a guide to profitmaximizing decisions.
2. i) Multinational Production and Pricing. The global automobile company needs
information on 1) demand (how many vehicles can be sold in each market at different
prices), 2) plant capacities and production costs, and 3) trade barriers and tariffs.
ii) Market Entry. Remember that Uber began as a ridesharing idea, before ultimately
becoming a market disruptor with respect to the long established taxicab industry.
Crucial necessary information and questions include: Would city regulators allow Uber
to operate at all? What market niche (how much demand) could it carve out of the taxi
and car service markets? At what prices relative to taxis? Would customers trust a
rideshare service? How many drivers could rideshare firms attract and at what costs?
iii) Building a New Bridge. The authority should estimate usage of the bridge over its
useful life, the likely cost of building and maintaining the bridge, and other important
side-effects, pro and con -- including positive effects on business activity and the
impacts on air pollution and traffic congestion.
iv) A Regulatory Problem. Before deciding whether to promote the oil-to-coal
conversion, government regulators need information on how much oil would be saved
(and the dollar value of savings) and the cost of the chain of side-effects -- not only the
direct cost of electricity provision but also pollution costs and environmental damage.
v) Boeing and the 737 Max. Boeing gathered extensive information on potential airline
demand for a new more fuel-efficient aircraft, yet considerable uncertainty remained
with respect to future orders. Would the new aircraft shift significant orders and sales
from Airbus, Boeing‟s longtime rival? Could Boeing achieve its aggressive R&D and
production plan on budget and on schedule? Could it address and solve myriad
reliability and safety problems, big and small? How severe would be ongoing regulatory
oversight and how high a bar would the FAA set for certification requirements? Five or
ten years from now, would the world economy continue to grow, fueling strong demand
for air travel and for the new and improved aircraft?
vi) An R&D Decision. The pharmaceutical company should quiz its scientists on the
chances of success (and the timetable for completion) for each R&D approach. The
company's marketing department would supply estimates of possible revenues from the
drug; its production department would estimate possible costs.
vii) David Letterman. Dave must carefully assess what he wants from a new contract (in
particular how much he values the earlier time slot). As the negotiations unfold, Dave
will glean valuable information as to the current competing offers of CBS and NBC. Of
course, Dave must also try to assess how far the two networks might be willing to go in
sweetening their offers.
[Show More]